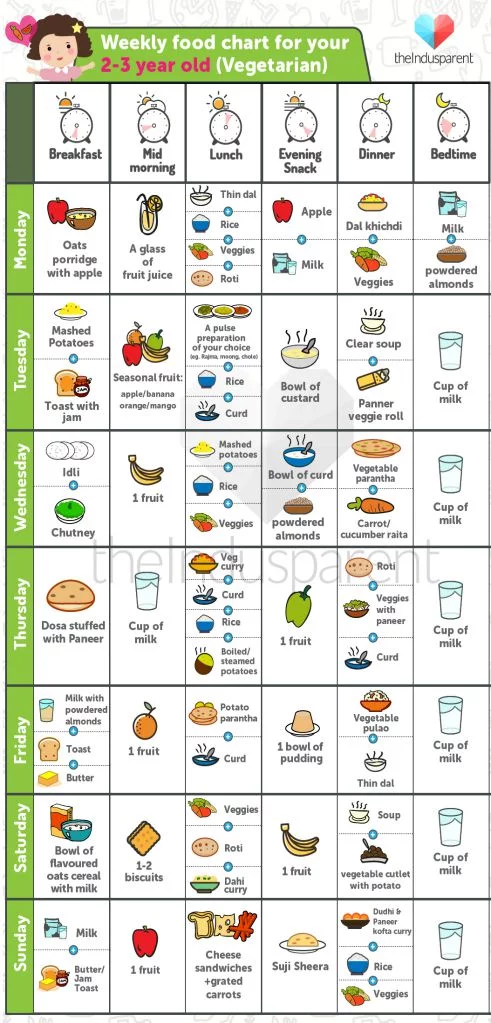
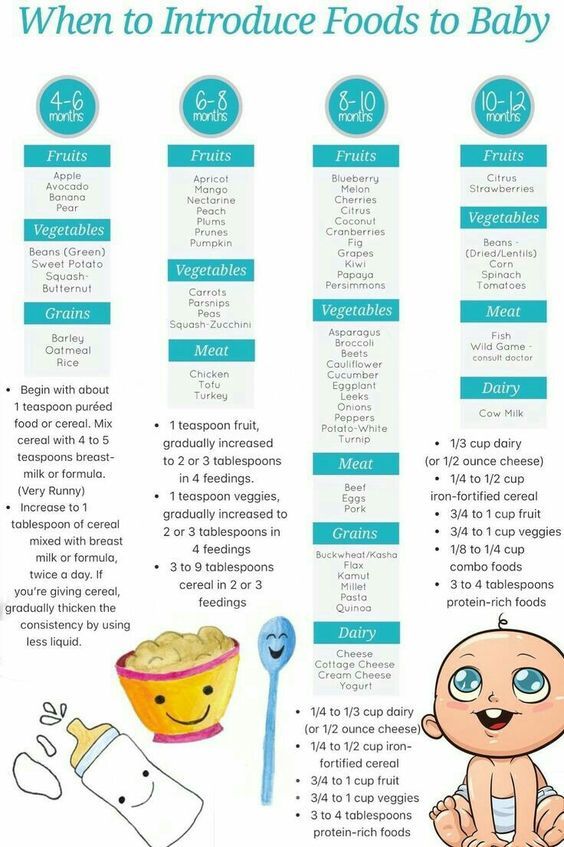
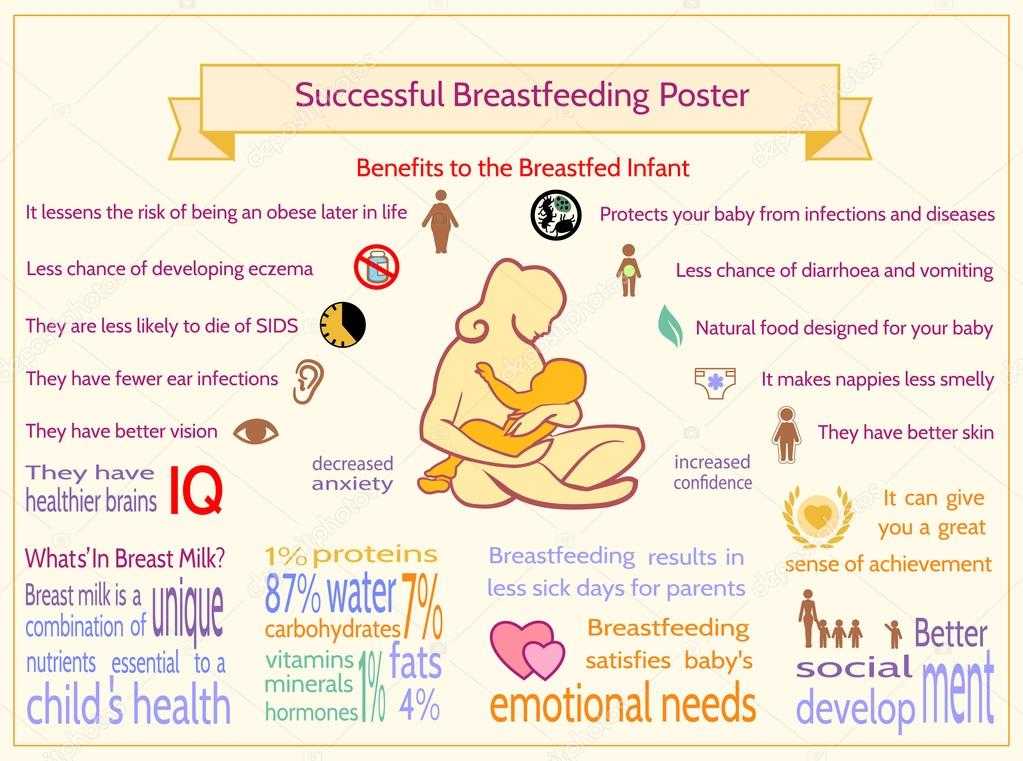
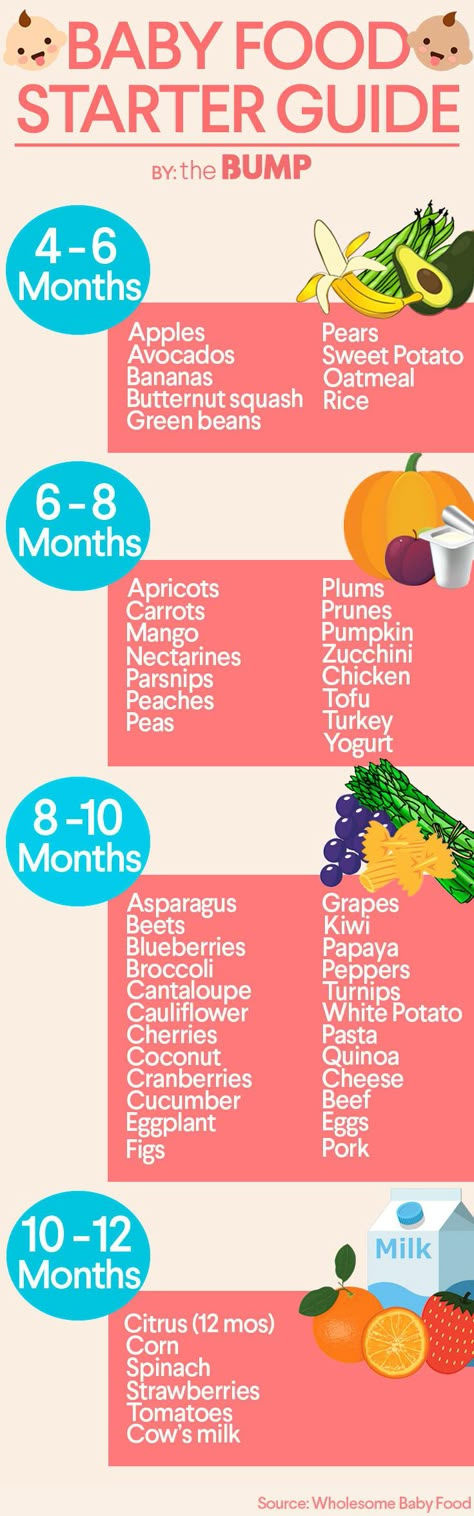
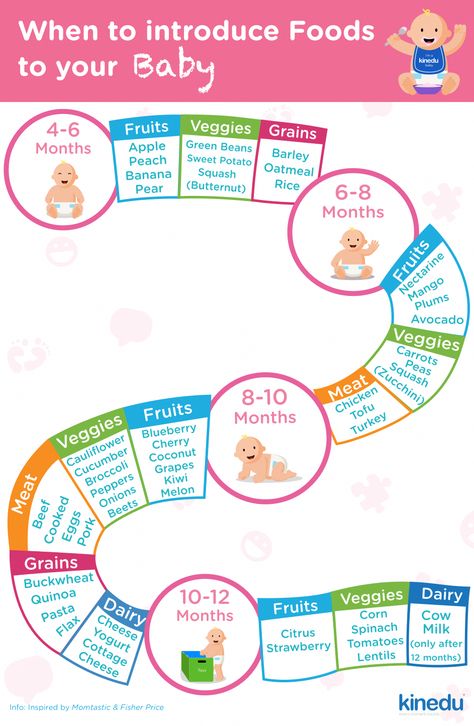
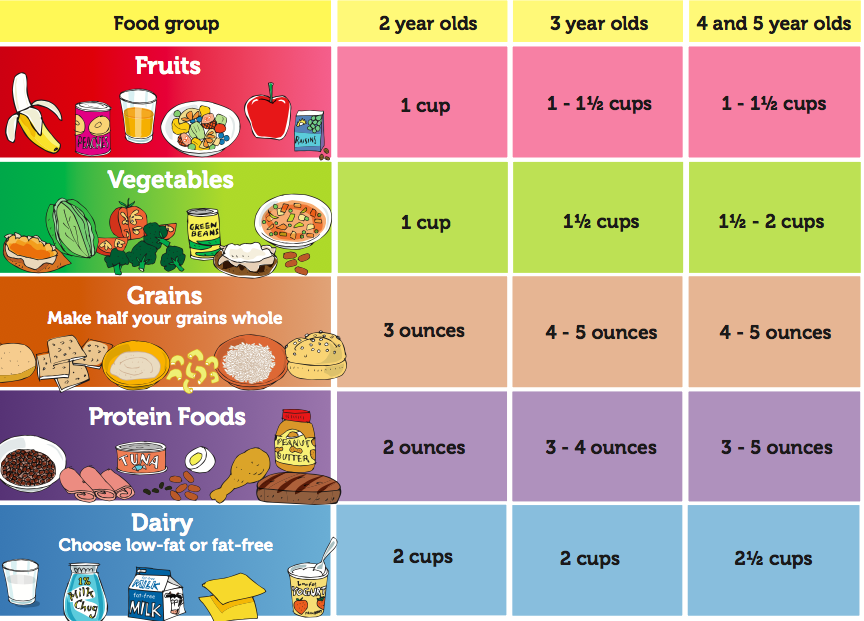
Year supply of baby food
Information for Families During the Formula Shortage
Read this page in:
- Spanish / Español
- Vietnamese / Tiếng Việt
- Creole / Kreyòl
- Navajo
There’s nothing as important to families as the health and safety of their babies, and the formula shortage has left many people feeling anxious about how they’ll feed them. Some young children, teens, and adults with medical needs also rely on formula for their nutrition. They may be impacted by the shortage, too.
We know it’s not easy to change your baby’s diet. However, if you can’t find formula in stock, here are some tips for finding safe substitutes.
Find Safe Substitutes
Information provided reflects input from physicians and other experts at the Department of Health and Human Services, American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), and the North American Society For Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition (NASPGHAN).
Image
Try a New Brand of Formula
One-Page Flier
- English
- Spanish
Note: Children younger than 6 months old should only drink breast milk or infant formula. Talk with your pediatrcian or other health care provider if you are having difficulty breastfeeding or finding infant formula.
Most babies will do just fine with different brands of formula, including store brands, as long as they're the same type, like cow's milk-based, soy, hypoallergenic (extensively hydrolyzed), or elemental (amino acid-based). Keep in mind that your baby may seem to not like the taste, or may have a hard time tolerating a different formula, initially. If this happens:
- Try slowly introducing small amounts of the new formula by mixing it with your regular formula. Slowly increase the amount of the new formula over time.
- Be patient, since it may take some time for your baby to get used to it.
- If your baby is vomiting, has gas pains, is crying or can't be calmed down during feedings, is losing weight, has diarrhea, has blood or mucus in their poop, or is straining to poop, they may not be tolerating the new formula.
 Call your pediatrician or other health care provider if you have questions.
Call your pediatrician or other health care provider if you have questions.
If you need help figuring out which formulas you may be able to substitute:
- Your pediatrician or other health care provider is always the best resource because they know your baby and their health history.
- You can also check this list of comparable formulas developed by an organization of pediatric gastroenterologists called NASPGHAN. Keep in mind that this list focuses on substitutes for formulas that were part of the February 2022 recall, so you might not see your baby's formula listed here. Any substitution should only be done under the recommendation and supervision of your pediatrician or other healthcare provider.
- Learn more about formula preparation and storage.
Image
Try Formula That’s Made in Another Country
You can also consider buying formula that's made outside of the United States in U.S. stores. Stores will start carrying or may already have these options. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has allowed these formula companies to market certain products in the United States, and may allow more infant formula products that meet its criteria to be sold in the U.S. When preparing formula made in other countries:
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has allowed these formula companies to market certain products in the United States, and may allow more infant formula products that meet its criteria to be sold in the U.S. When preparing formula made in other countries:
- Read the mixing instructions carefully for preparing powdered formulas. They may require different amounts of powder or water than formulas made in the U.S.
- Use the FDA's conversion chart to convert milliliters to fluid ounces and common conversions from Celsius (°C) to Fahrenheit (°F).
Consumers should be cautious when buying formula that’s made outside of the U.S. from online marketplaces, as it has the potential to be counterfeit. Learn more about how to spot counterfeit infant formula: What are counterfeit infant formulas? How can I avoid buying such products?
Image
Talk to Your Pediatrician or Other Health Care Provider About Substitutes for Hypoallergenic or Specialty Formula.

If you need hypoallergenic or medical specialty formula, it may be harder to find a substitute. Talk to your pediatrician or other health care provider about acceptable substitutes. Depending on which formula your baby needs, your doctor may be able to submit an urgent request for specialized formula to Abbott Nutrition, which is releasing some specialty and low-iron formulas on a case-by-case basis.
Feed Your Baby Safely
If you can't find enough formula, there may be some short-term options that can help in an urgent situation. You should also know about serious safety concerns related to certain alternative preparations for feeding your baby. Always talk to your pediatrician or other health care provider first if you don't have enough formula to feed your baby.
Image
Talk to Your Pediatrician or Other Health Care Provider About Short-Term Options
Image
Explore Resources for Breast Milk or Breastfeeding
Talk with your pediatrician or other health care provider about using human milk from a human milk bank.
- If possible, consider a local milk bank that is accredited through the Human Milk Banking Association of North America (HMBANA). Keep in mind that most of the milk from milk banks is given to hospitalized babies, and they may not have enough to serve healthy babies at all times.
- Never purchase human milk on the internet. Human milk bought through the internet could be diluted with other substances or contaminated with germs and might not be collected, stored, or transported safely. You also cannot be sure if the donor was medically screened for infectious diseases or drug use.
- Informal human milk sharing in the community also has risks. If you are considering feeding your baby with human milk from a source other than the baby’s mother, talk to your pediatrician or other healthcare provider about the potential risks.
For families who are using both breast milk and formula, consider shifting more of your baby’s diet to breast milk.
- This could mean you need to increase your breast milk supply. You can do this by breastfeeding your baby more frequently or by adding pumping sessions between breastfeedings. Pumped milk can be kept in a refrigerator and stored frozen for later use.
- The CDC provides more information about breastfeeding, travel, and pumping and local support for mothers who are breastfeeding.
Image
Avoid Unsafe Formula Practices and Buying More Than You Need
Don't try to make formula at home. There are serious health and safety concerns with homemade formula. Your baby's nutritional needs are very specific, especially in the first year of life. Homemade formula may contain too little or too much of certain vitamins and minerals, like iron. Homemade formula also increases the risk of contamination, which could make your baby sick or lead to infection.
Don't water down formula. Adding more water means your baby does not get enough of the nutrients they need and can lead to serious health problems, like seizures.
Don't use formula past the "best by" or "use by" date. The formula may not be safe and may have lost some of its nutrients.
Don't buy more formula than you need. The shortage is affecting families who are already navigating the stress of parenting during a pandemic. It can be tempting to buy as much formula as possible right now, but the AAP suggests buying no more than a 10-14 day supply to help improve shortages.
Get Help From WIC
If you need help buying formula, you’re not alone. About 43 percent of all babies in the U.S. receive help from the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC). WIC provides formula and food for your family, and can connect you to trained professionals who provide health screenings, breastfeeding support, and nutrition advice. You can also participate in WIC while you’re pregnant. Contact your local WIC clinic to see if you or your family is eligible.
Check your eligibility
Check out our Infant Formula Resources multilingual social media toolkit.
Get Help Finding Formula
Organizations in your community and formula companies may be able to help you find formula or safe substitutes.
Image
Community Resources
- Locate your nearest Community Action Agency (CAA): Your local CAA may be able to give you formula or connect you with local agencies that have formula.
- Call 211: United Way’s 2-1-1 can connect you to a community resource specialist who may be able to help you find local food pantries and other sources of formula.
- Find an accredited milk bank: The Human Milk Banking Association of North America (HMBANA) gives donated breast milk to families in need. You may need a prescription from your pediatrician or other health care provider to get donated breast milk from HMBANA.
Image
Formula Company Phone Numbers
Formula companies may be able to help you find formula or safe substitutes. Because a lot of people are looking for formula, you may experience long wait times. Most types of formula may also be out of stock.
Most types of formula may also be out of stock.
- MyGerber Baby Expert: Reach a certified nutrition or lactation consultant by phone, text, Facebook Messenger, web chat, or video call to help you find a similar formula that may be more readily available.
- Similac (Abbott’s) urgent product request line: Ask your gynecologist (OB/GYN) or your baby’s pediatrician or other health care provider to submit an urgent product request for metabolic or low-iron formula by downloading and completing the form.
- Enfamil (Reckitt’s) customer service line: Call 1-800-222-9123 (BABY-123) for help finding formula.
Learn About How the Shortage Started
Supply chain issues from the pandemic contributed to the current formula shortage. It worsened when Abbott Nutrition, one of the country’s largest formula producers, voluntarily recalled formula and closed one of its production facilities in Sturgis, Michigan. The President, agencies across the U.S. government, retailers, and the formula industry are working around the clock to address this shortage and get formula back on shelves. To date, production has ramped up 30-50%.
To date, production has ramped up 30-50%.
Learn About Actions the U.S. Government is Taking
- The President invoked the Defense Production Act. This law puts U.S. formula manufacturers first in line to receive the resources they need to increase formula production. The President is also working with other countries to airlift formula to the U.S. through Operation Fly Formula.
- The FDA and the U.S. Department of Justice negotiated a consent decree with Abbott Nutrition, under which Abbott Nutrition agreed to take specified corrective actions in order to start producing formula again at their Michigan facility. Abbott Nutrition has stated that it will focus on specialty formulas for people with metabolic and other needs first. FDA has also been meeting regularly with other major formula manufacturers who are working to produce more formula to meet the demand. Read more about FDA’s actions.
- The U.S. Department of Agriculture is working with states, tribal nations, and territories across the country to ensure that families who participate in WIC can use their benefits to purchase additional types of formula.

Read more about the additional steps that President Biden is taking to address the formula shortage.
What Should I Feed My Baby if I Can’t Find Baby Formula in Stores? (for Parents)
Reviewed by: Elana Pearl Ben-Joseph, MD
en español ¿Qué debo hacer si no puedo encontrar fórmula para bebés en las tiendas?
I’ve noticed that my supermarket is running out of baby formula, and I’ve heard that there is a nationwide shortage. My baby is too young to start solids. What should I do if I can’t find formula?
– Stella
There is indeed a national shortage of baby formula in the United States. The COVID-19 pandemic created supply chain and staffing issues, and a recent recall of baby formula due to contaminated products from a key factory added to the problem.
Here are some tips on how to deal with the baby formula shortage:
- Talk to your baby’s doctor. They might have sample cans of formula available and also can ask the manufacturer for specific types of formula.
 You can also call a local hospital, office of WIC (the federal Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children), or an established breast milk bank. Women’s shelters, food banks, and faith-based organizations also might be able to help. Avoid using breast milk from friends, community members, or online sources. These donations may not have been properly stored or pasteurized and can contain germs or other harmful substances.
You can also call a local hospital, office of WIC (the federal Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children), or an established breast milk bank. Women’s shelters, food banks, and faith-based organizations also might be able to help. Avoid using breast milk from friends, community members, or online sources. These donations may not have been properly stored or pasteurized and can contain germs or other harmful substances. - Shop around. Try other stores that you may not have gone to in the past, especially smaller independent grocery stores, pharmacies, or baby supply stores. They might not run out of formula as quickly as bigger stores.
- Order online if you can. Make sure that the websites are well-recognized companies and not auction sites or online marketplaces that can’t guarantee safe products.
- Switch to any available formula. This should be OK for most babies unless they are on a specific type of formula for medical reasons.
 Store-brand formulas are less expensive. Check with your baby’s doctor if you are not sure about making a switch.
Store-brand formulas are less expensive. Check with your baby’s doctor if you are not sure about making a switch. - Connect with other parents (in person or on social media groups). They might have extra formula or ideas about where to get some.
- Do not give your baby:
- homemade formula. This can be dangerous and has even led to infant deaths.
- watered-down formula to make it last longer. This is dangerous, as it reduces the amount of nutrients in each bottle. Always follow instructions on the package or recommendations from your baby’s doctor.
- goat milk or plant-based milks (like almond, rice, coconut, or oat milks) if your baby is younger than 1 year old. These milks lack the nutrients your baby needs for growth and development.
NOTE: Cow’s milk usually is only recommended for babies after their first birthday. In an emergency, though, babies 6 months of age and older who do not get a specific type of formula for medical reasons can drink cow's milk, but for no longer than a week and not more than 24 ounces per day.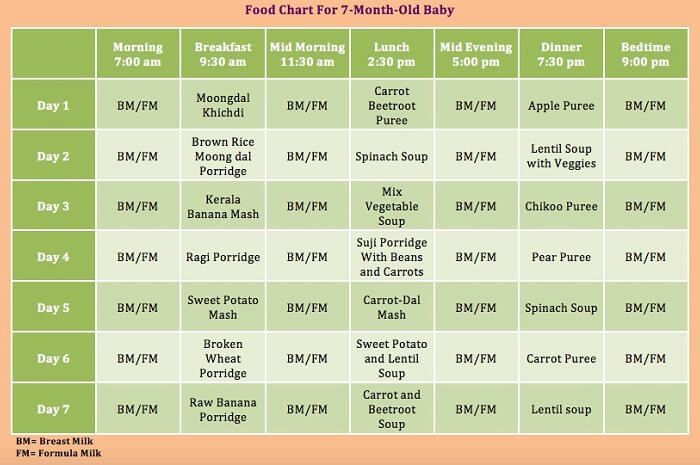 Cow’s milk does not contain enough iron for a growing baby. So, if you give your baby cow’s milk, also offer iron-containing solid foods or iron supplements. Soy milk also may be OK for a few days for babies who are close to 1 year old, as long as it is fortified with protein and calcium.
Cow’s milk does not contain enough iron for a growing baby. So, if you give your baby cow’s milk, also offer iron-containing solid foods or iron supplements. Soy milk also may be OK for a few days for babies who are close to 1 year old, as long as it is fortified with protein and calcium. - formula you bought overseas. Foreign products are not regulated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and may not be safe. For this reason, goat milk formula is not an option for babies younger than 1 year old because infant-appropriate goat milk formulas are all made overseas.
- toddler formula. If your baby is nearing their first birthday, though, toddler formula can be OK for a few days.
If you run out of formula and can’t find any, in a pinch you can give oral rehydration solution (such as Pedialyte, Enfalyte, or a store brand) for a couple of days. Babies older than 4 to 6 months can also get puréed (finely ground) foods. And remember that babies older than 1 year do not need to drink formula at all — most of their foods can be eaten as solids and they can drink milk or water.
More information is available online at:
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services
Reviewed by: Elana Pearl Ben-Joseph, MD
Date reviewed: May 2022
90,000 truth about what's in the ingredients.- Ekaterina Borisovna, there is a lot of debate about the benefits of baby food from a jar. Let's try to confirm or dispel the myths and tell parents the whole truth about children's canned products.
Myth #1. Baby food in jars is made from vegetables and fruits that are not suitable for sale in their natural form. Raw materials of poor quality underlie it.
- Not true. The production of canned baby food is a complex technological process consisting of several mandatory steps, including a careful selection of raw materials. The quality and safety of baby food initially depends on this.
When sorting , all vegetables and fruits with any defects are utilized, and a batch of raw materials of uniform quality is formed.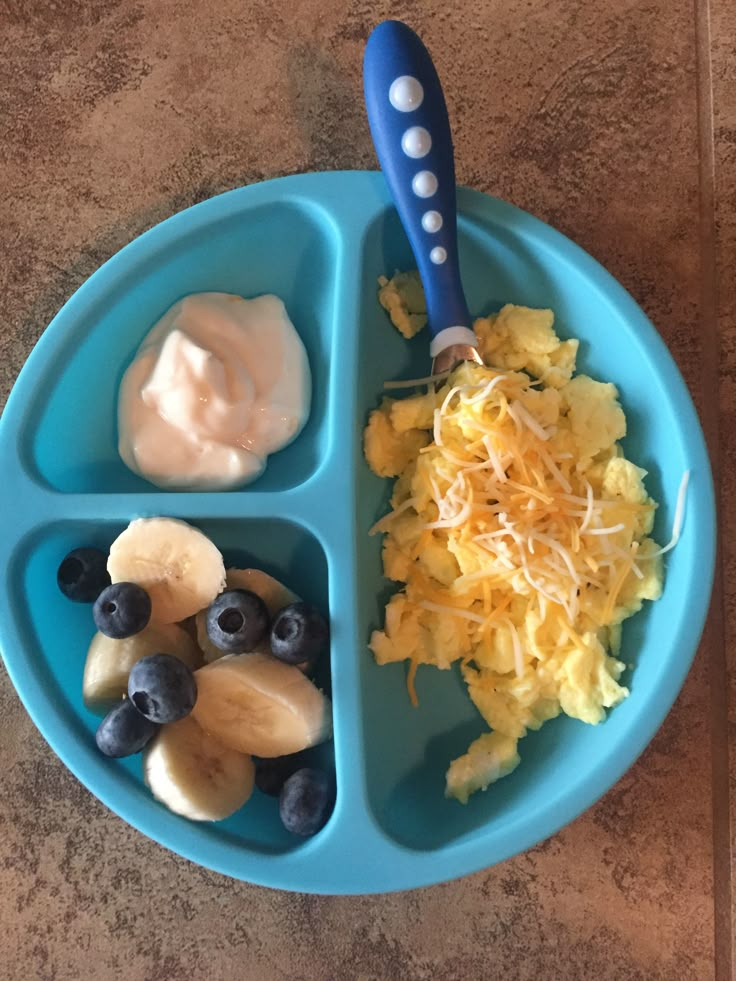
Sorting includes:
- visual assessment of raw materials;
- removal of non-standard, unripe, moldy and broken fruits. Grouping by size and weight is not carried out: these indicators do not affect the quality of finished baby food.
When cleaning raw materials , all inedible and low-nutrient parts are removed from fruits and vegetables - the skin, seeds, stalks, the core is removed from apples and pears. Parents can be sure that their baby will receive only the most useful and nutritious.
Myth No. 2: The quality of baby food in jars is doubtful - it contains a lot of preservatives that are dangerous for babies.
- The inclusion of preservatives in baby food is prohibited by law , at least in our country. But the use of vitamin D or ascorbic acid is allowed. They do not harm babies, but significantly increase the benefits of the product.
- Ekaterina Borisovna, however, it is known that without preservatives, the shelf life of products is reduced.
— A long shelf life of baby food without preservatives is ensured by aseptic production technology, product sterilization and vacuum packaging, which protects it from harmful microorganisms. The cotton that we hear when opening the jar is an indicator of the correct packaging and safety of the product.
Myth #3. There are other unnatural ingredients in canned food without preservatives that can be harmful to a child's health.
- The complete composition of baby food must be clearly stated on the packaging by the manufacturer. Corn starch or rice flour can be added as safe thickeners to give the desired consistency. But the range of children's canned food allows you to choose products without these additives. The presence of spices is not forbidden, but their list is limited and strictly regulated.
technological substances to impart aroma and enhance color and taste.
Myth #4.
 Flavor enhancers are added to canned food, otherwise children refuse to eat it.
Flavor enhancers are added to canned food, otherwise children refuse to eat it. - Production technologies allow extracting the maximum of useful elements from raw materials and at the same time preserving its taste. For example, , in order not to destroy biologically active substances, raw materials for baby puree are not boiled , but in order to obtain a delicate texture and not spoil the taste, it is wiped in special mashing machines in an atmosphere of steam or inert gases. Such subtleties of production explain the unique taste of canned puree, which you cannot get at home on your own.
Read also
- how to introduce puree into complementary foods
Myth #5. Canned baby food is expensive and costs parents more than homemade purees.
- Seasonal harvest is inexpensive, making mashed potatoes seems like an elementary task. But there are few fruits of our own in our country. Harvesting a year in advance is a difficult and costly business (you will need a capacious freezer). Preserving vegetables is even more difficult, you need at least a basement. In addition, the amount of vitamins with this method of harvesting decreases in proportion to the storage time (autumn apples lose most of their useful properties by spring).
Harvesting a year in advance is a difficult and costly business (you will need a capacious freezer). Preserving vegetables is even more difficult, you need at least a basement. In addition, the amount of vitamins with this method of harvesting decreases in proportion to the storage time (autumn apples lose most of their useful properties by spring).
— Fruit and vegetable sections are filled in stores all year round.
Yes, but children need variety in their diet. Today an apple, tomorrow a pear, the day after tomorrow an apricot. For example, to prepare 100 g of apricot puree, you will need at least 300 g of apricots without peel and stone. For the price, this is comparable to the price of a jar, but you still need time to buy and cook.
And the most important thing is safety. At the plant, raw materials for baby food are thoroughly tested for the content of toxic substances. The standards for the content of pesticides, nitrates and other chemical additives for sale in the store are different, and no one guarantees that the zucchini bought from the grandmother on the market did not grow in the zone of increased radiation or was not fed with nitrogenous fertilizers. Therefore industrial canned puree is safer than , and at a price that's about what it comes out to be.
Therefore industrial canned puree is safer than , and at a price that's about what it comes out to be.
Myth #6. There are few vitamins and nutrients in a jar of complementary foods, as they are destroyed during the conservation process.
- Vegetables and fruits are full of healthy nutrients during the harvest season. But during long-term storage, they lose almost everything except fiber and starch. In addition to this, the fruits are irrevocably destroyed during heat treatment at home - for example, during cooking, up to 20% of vitamin B and more than 50% of ascorbic acid are lost.
The picture is quite different in the factory production of complementary foods, when the useful properties of the raw materials are preserved to the maximum. In addition, complementary foods can be additionally saturated with vitamins and trace elements. Food packaging always indicates their presence and the percentage of the daily dose.
Myth #7.
 Food from a jar provokes the development of allergies.
Food from a jar provokes the development of allergies. - The risk of developing an allergic reaction to food in a jar is no higher than to food prepared by oneself. If a child is allergic to pumpkin, then boiled, steamed and canned, there will be a reaction to it. Another question is that an auxiliary component of canned puree (for example, starch or ascorbic acid) can cause allergies. In this case, it is safer to choose products without such additives.
Often confused with allergies food intolerance . The symptoms are similar, but the reasons for the latter lie in non-compliance with the rules of complementary foods (for example, they gave a new product ahead of schedule or immediately in large quantities). Without knowing it, mothers expose the child's body to excessive stress when the baby's enzyme system is not yet ready to process the edible "gift". For this reason, the child's body becomes covered with a rash, problems with the tummy, regurgitation and other delights appear.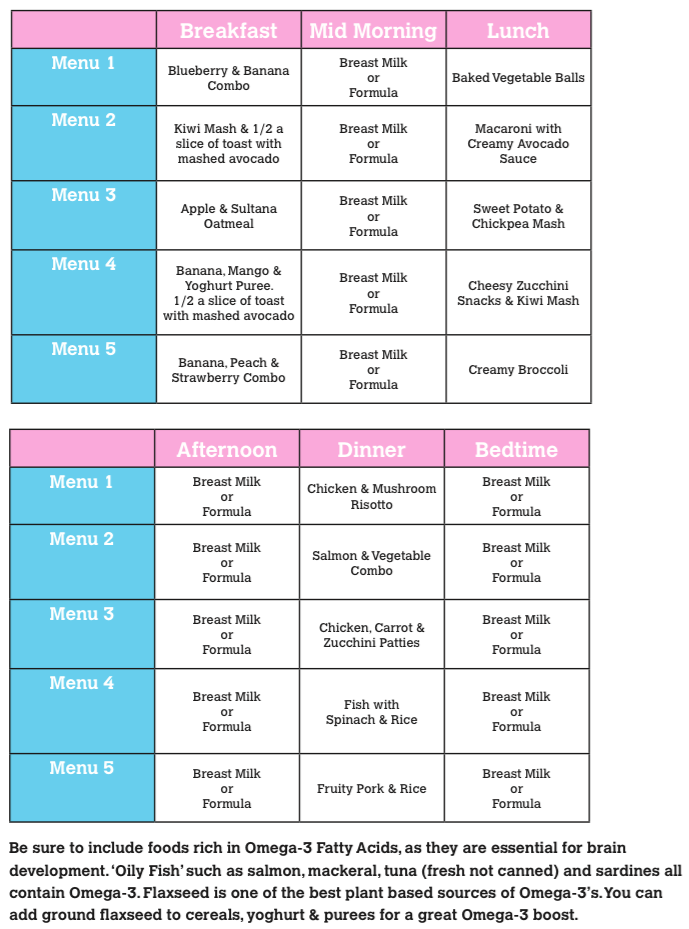
Complementary foods: what you need to know
- It is worth trying a new product in small quantities.
- The daily dose is increased gradually.
- Red cheeks, rashes on the arms and under the knees - a reason to exclude the product from the child's diet and consult a doctor.
Myth #8. There are many counterfeits of baby food on the market, and products of well-known brands are more often counterfeited. Parents in the store will not be able to distinguish a fake from the original.
— Control over the quality of nutrition for children is multifaceted and is carried out at all stages - from the procurement of raw materials to the sale in the store. Compliance with safety standards during production and storage, the usefulness of the product in terms of protein, carbohydrate and fat components, the concentration of vitamin elements and other components declared on the package are monitored. Organoleptic testing determines the quality of products by taste, aroma, appearance, consistency.
Organoleptic testing determines the quality of products by taste, aroma, appearance, consistency.
Unfortunately, despite the fairly strict control, information about reviews from the sale of low-quality baby food periodically pops up. Probably, this cannot be avoided, as well as the falsification of medicines and other goods. But you can protect yourself as much as possible from acquiring fakes.
How to choose quality baby food in jars
- It is better to buy food in large specialized stores, pharmacies.
- Consider value for money. If the price is significantly lower than usual, do not rush to buy an annual supply, study the composition and the certificate of conformity for the product.
- Carefully inspect the package. Do not take a damaged package with traces of worn paint, smeared or blurry letters, a swollen or crumpled jar.
- Always try a new product before giving it to a child. You can easily distinguish changes in taste, smell, texture.

Myth #9. Manufacturers add starch to thickening canned food, but they do not always report this on the packaging. This is true? And will the iodine test show the presence of starch?
- In stores, a fairly wide range of baby purees with and without the addition of starch. A significant component of starch is glucose , the main source of our vital energy. Starch is often a natural product. In nature, there are many plants and products from which starch can be extracted: potato, corn, rice and wheat are widely known.
The debate about the dangers or benefits of starch can go on forever. Children are able to absorb starch from birth, it's all about its volume. A small amount of thickener in baby food will be absorbed by the child. Harmful daily proportion of starch - from 30 g.
Starch is included in 90% of the food that a person consumes in everyday life. You should not be afraid of it, but you need to be careful, because starch:
- in case of excessive use and individual tendency causes constipation;
- is capable of provoking an allergic reaction;
- increases the calorie content of food and promotes weight gain;
- contains a lot of carbohydrates, but is useless as a source of vitamins.

Therefore, if a child has a tendency to allergic reactions, overweight or constipation, you should not use food with the addition of starch. Children with underweight or unstable stools may well try it.
Reaction with iodine - a qualitative reaction to starch with the formation of a dark blue spot. This is a really affordable method of checking baby food. But before using it, you should study which products contain starch. It is possible that a positive reaction will not be on an artificially added component, but on natural starch. A lot of natural starch in potatoes, corn, legumes, carrots, zucchini, pumpkin, banana and unripe apples. And it is natural that the reaction with iodine in the puree of these products will be positive. But in the composition of mashed broccoli or white cabbage, starch should not be, unless the manufacturer specifically added it.
Myth #10. The child gets used to eating from a jar and for a long time refuses the "adult" table.

- Opposite. Children in infancy and under 18 months are not allowed to give sugar, salt, seasonings and spices. Therefore, until the mother has included these “adult” supplements in her child’s diet, purchased food will remain his favorite food. But having tried salty or sweet once, the baby begins to demand a new product and refuse fresh canned food.
Children and adults have different perceptions of tastes. Therefore, you can not give the baby a dish that you like to taste, sweeten and add salt to food. When the time comes and the child is ready to receive products close to the common table, he himself will gladly refuse fresh jars, trying more and more new tastes.
— Ekaterina Borisovna, can canned baby food completely replace homemade baby food?
- Of course, and quite successfully. Regardless of the season, it is possible to provide the baby with a complete and varied diet only with the help of canned food. Yes, and it is impossible to repeat the taste of factory food on your own due to the special manufacturing technology. In addition, despite the fact that the assortment of fruits and vegetables in the store is quite large even in winter, their taste and useful properties, and most importantly, safety, are very doubtful. Of course, it is worth remembering about the time that a mother can devote to a baby, instead of puzzling over the variety of menus and cooking.
In addition, despite the fact that the assortment of fruits and vegetables in the store is quite large even in winter, their taste and useful properties, and most importantly, safety, are very doubtful. Of course, it is worth remembering about the time that a mother can devote to a baby, instead of puzzling over the variety of menus and cooking.
— Why are MAMAKO ® baby purees good for children? What are their advantages?
— Very often, kids get bored with the taste of monocomponent puree, and not everyone eats cottage cheese willingly either. Puree MAMAKO ® consists of fruits and tender goat curd without thickeners, preservatives or other artificial additives. Such a puree with a delicate creamy taste can be introduced into the diet from 6 months, it is more nutritious and serves as an additional source of calcium, which is necessary during the period of intensive growth. Therefore, along with monocomponent purees, I always recommend including such interesting, and most importantly - without sugar and thickeners, healthy products in the child's diet.
I would like to once again appeal to young parents - be above prejudice. Canned food is simple, convenient, useful and safe. We all use the achievements of progress for our comfort: cellular communications, microwave ovens, all kinds of gadgets have firmly entered our lives. So industrial baby food was created for the convenience of young parents. It is developed taking into account the physiological needs of the baby, meets all safety requirements and contains more useful nutrients due to gentle heat treatment than puree cooked at home from untested vegetables and fruits.
Storage of baby food: terms and requirements for the storage of baby food
Glinskikh Elena
Published: 01/15/2023
Reading time:
224
All parents want to see their baby cheerful, active and healthy. The harmonious development of the child largely depends on the correct and high-quality diet. The market for special baby food is striking in its diversity, and everyone strives to choose the best for the child. But for the safety of the baby and its full development, it is not enough to buy high-quality products. You also need to know how to properly store baby food.
The market for special baby food is striking in its diversity, and everyone strives to choose the best for the child. But for the safety of the baby and its full development, it is not enough to buy high-quality products. You also need to know how to properly store baby food.
The importance of proper storage of baby food
All children need warmth, care and attention. But the child is gradually growing, while he needs to eat varied. And here the question arises: is it possible to save the cooked product until the next feeding? Here it is important to pay attention to the fact that the child's immune system is not yet strong enough, so the storage of baby food should be given special attention. The well-being and health of the baby often depends on the conditions in which and how long they are kept.
About the safety of baby food
In the Russian Federation there is a whole regulation on the safety of food for children - that's what it is called. This document sets out requirements for manufacturers and sellers of children's products related to the protection of children from toxic and chemical substances. This applies not only to baby food produced in our country, but also imported from abroad. That is why when buying infant formula, porridge, puree or other product, you can be sure of its quality and safety. The regulation requires not only the correct production, but also the packaging, storage and disposal of baby food:
This document sets out requirements for manufacturers and sellers of children's products related to the protection of children from toxic and chemical substances. This applies not only to baby food produced in our country, but also imported from abroad. That is why when buying infant formula, porridge, puree or other product, you can be sure of its quality and safety. The regulation requires not only the correct production, but also the packaging, storage and disposal of baby food:
- Children's products are sold only through special stores or dedicated departments of supermarkets (therefore, it is better to buy them there or, in extreme cases, in a pharmacy).
- Expiration dates are set by the manufacturer, who is fully responsible for the quality of his product.
- Transportation of baby food is carried out in accordance with the requirements of the technical regulations for the transportation of any products.
At the same time, a number of conditions must be observed in the production of baby food:
- Do not use highly acidic curd products.

- Do not add soy flour or grains contaminated with impurities.
- Offal is prohibited except for tongue, liver, heart and blood.
- Do not include in baby food beef with a fat content of more than 12%, pork - 32%, lamb - 9%.
- Do not use salted butter or products with a fat content below 82%*.
For a complete list of products prohibited in the production of baby food, you can follow the link attached to the article.
Rules for storing different types of food
Undoubtedly, breast milk is the most valuable and beneficial for a child. But there are situations when a mother needs to leave the house and she expresses milk in order to feed the baby on time. In addition, the child grows, over time he needs complementary foods. Expressed breast milk, formula-fed infant formula and complementary foods require a special approach, and it is very important to know the conditions and shelf life of baby food.
How long can open packages of infant formula and cereals be kept?
Opened jars (packages) of fruit, vegetable and meat puree should only be stored in the refrigerator. And after opening the package, you can eat only within 12 hours **. After the expiration date or 12 hours after opening the package, the product must be disposed of, since it can no longer be eaten. Yes, not only for children, but also for adults.
Many people are also wondering how long homemade baby food, such as freshly prepared vegetable or fruit purees and juices, can be stored. There are two main options to use immediately after preparation (the best) or freeze. Such a product will also be suitable for eating for 12 hours, after which it will begin to deteriorate. Frozen fruits and vegetables can be stored in the freezer for up to six months, depending on the culture. However, even frozen products have expiration dates, after which it would be wiser to throw them away than eat them.
General storage rules
A huge variety and affordable cost of products make it much easier to prepare complementary foods for children. But along with this, many parents face another problem: where to store baby food? So that the products do not lose their qualities from the influence of external factors, the following basic rules must be observed.
- Hygiene. Be sure to wash your hands thoroughly before preparing food and feeding your baby. The child's dishes should always be clean and stored separately in sterile conditions.
- Storage location. Dry cereals and mixtures should be stored in a ventilated cupboard out of the reach of children. In caring for a baby, mothers are loaded with various problems and worries. It is difficult for them to remember everything, so it is recommended to stick a label on each product with the date of its opening. This will help you meet the deadlines.
- When feeding a child with vegetable and fruit juices, puree or sour-milk products in jars, remember that after breaking the integrity of the package, the use of its contents is allowed on average up to 12 - 24 hours.
 Different manufacturers may have different terms, read carefully what is written on the label! Be sure to ensure that the integrity of the packaging has not been violated even in the store. Most manufacturers on the jars have a special protection against opening. Fresh puree in jars emits a characteristic “pop” when opened, juices must have either a protective foil film or a special opening mechanism. Unopened jars of juices and purees can be stored in the cupboard, while dairy products should only be kept in the refrigerator.
Different manufacturers may have different terms, read carefully what is written on the label! Be sure to ensure that the integrity of the packaging has not been violated even in the store. Most manufacturers on the jars have a special protection against opening. Fresh puree in jars emits a characteristic “pop” when opened, juices must have either a protective foil film or a special opening mechanism. Unopened jars of juices and purees can be stored in the cupboard, while dairy products should only be kept in the refrigerator. - Vessels for storing baby food can be glass or plastic, but must be labeled accordingly, indicating the absence of toxic impurities in the composition of the material.
Food for a child is a source of energy and a guarantee of full growth and development. Therefore, it is very important not only to buy quality products, but also to learn how to properly store them. The health and well-being of the baby, the resistance of his body to the adverse effects of the external environment often depend on this.