Baby feeding breast milk
Breastfeeding vs. Formula Feeding (for Parents)
Choosing whether to breastfeed or formula feed their baby is one of the biggest decisions expectant and new parents will make.
Healt experts believe breast milk is the best nutritional choice for infants. But breastfeeding may not be possible for all women. For many, the decision to breastfeed or formula feed is based on their comfort level, lifestyle, and specific medical situations.
For moms who can't breastfeed or who decide not to, infant formula is a healthy alternative. Formula provides babies with the nutrients they need to grow and thrive.
Some mothers worry that if they don't breastfeed, they won't bond with their baby. But the truth is, loving mothers will always create a special bond with their children. And feeding — no matter how — is a great time to strengthen that bond.
The decision to breastfeed or formula feed your baby is a personal one. Weighing the pros and cons of each method can help you decide what is best for you and your baby.
All About Breastfeeding
Nursing can be a wonderful experience for both mother and baby. It provides ideal nourishment and a special bonding experience that many mothers cherish.
A number of health organizations — including the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), the American Medical Association (AMA), and the World Health Organization (WHO) — recommend breastfeeding as the best choice for babies. Breastfeeding helps defend against infections, prevent allergies, and protect against a number of chronic conditions.
The AAP recommends that babies be breastfed exclusively for the first 6 months. Beyond that, breastfeeding is encouraged until at least 12 months, and longer if both the mother and baby are willing.
Here are some of the many benefits of breastfeeding:
Fighting infections and other conditions. Breastfed babies have fewer infections and hospitalizations than formula-fed infants. During breastfeeding, antibodies and other germ-fighting factors pass from a mother to her baby and strengthen the immune system. This helps lower a baby's chances of getting many infections, including:
This helps lower a baby's chances of getting many infections, including:
- ear infections
- diarrhea
- respiratory infections
- meningitis
Breastfeeding also may protect babies against:
- allergies
- asthma
- diabetes
- obesity
- sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS)
Breastfeeding is particularly beneficial for premature babies.
Nutrition and ease of digestion. Often called the "perfect food" for a human baby's digestive system, breast milk's components — lactose, protein (whey and casein), and fat — are easily digested by a newborn.
As a group, breastfed infants have less difficulty with digestion than do formula-fed infants. Breast milk tends to be more easily digested so that breastfed babies have fewer bouts of diarrhea or constipation.
Breast milk also naturally contains many of the vitamins and minerals that a newborn requires. One exception is vitamin D — the AAP recommends that all breastfed babies begin receiving vitamin D supplements during the first 2 months and continuing until a baby consumes enough vitamin D-fortified formula or milk (after 1 year of age).
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates formula companies to ensure they provide all the necessary nutrients (including vitamin D) in their formulas. Still, commercial formulas can't completely match breast milk's exact composition. Why? Because milk is a living substance made by each mother for her individual infant, a process that can't be duplicated in a factory.
Free. Breast milk doesn't cost a cent, while the cost of formula quickly adds up. And unless you're pumping breast milk and giving it to your baby, there's no need for bottles, nipples, and other supplies that can be costly. Since breastfed babies are less likely to be sick, that may mean they make fewer trips to the doctor's office, so fewer co-pays and less money are paid for prescriptions and over-the-counter medicines.
Different tastes. Nursing mothers usually need 300 to 500 extra calories per day, which should come from a wide variety of well-balanced foods. This introduces breastfed babies to different tastes through their mothers' breast milk, which has different flavors depending on what their mothers have eaten. By tasting the foods of their "culture," breastfed infants more easily accept solid foods.
This introduces breastfed babies to different tastes through their mothers' breast milk, which has different flavors depending on what their mothers have eaten. By tasting the foods of their "culture," breastfed infants more easily accept solid foods.
Convenience. With no last-minute runs to the store for more formula, breast milk is always fresh and available whether you're home or out and about. And when women breastfeed, there's no need to wash bottles and nipples or warm up bottles in the middle of the night.
Smarter babies. Some studies suggest that children who were exclusively breastfed have slightly higher IQs than children who were formula fed.
"Skin-to-skin" contact. Many nursing mothers really enjoy the experience of bonding so closely with their babies. And the skin-to-skin contact can enhance the emotional connection between mother and infant.
Beneficial for mom, too. The ability to totally nourish a baby can help a new mother feel confident in her ability to care for her baby. Breastfeeding also burns calories and helps shrink the uterus, so nursing moms may be able to return to their pre-pregnancy shape and weight quicker. Also, studies show that breastfeeding helps lower the risk of breast cancer, high blood pressure, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease, and also may help decrease the risk of uterine and ovarian cancer.
Breastfeeding also burns calories and helps shrink the uterus, so nursing moms may be able to return to their pre-pregnancy shape and weight quicker. Also, studies show that breastfeeding helps lower the risk of breast cancer, high blood pressure, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease, and also may help decrease the risk of uterine and ovarian cancer.
p
Breastfeeding Challenges
Breastfeeding can be easy from the get-go for some mothers, but take a while to get used to for others. Moms and babies need plenty of patience to get used to the routine of breastfeeding.
Common concerns of new moms, especially during the first few weeks and months, may include:
Personal comfort. Initially, many moms feel uncomfortable with breastfeeding. But with proper education, support, and practice, most moms overcome this.
Latch-on pain is normal for the first week to 10 days, and should last less than a minute with each feeding. But if breastfeeding hurts throughout feedings, or if their nipples and/or breasts are sore, it's a good idea for breastfeeding mothers to get help from a lactation consultant or their doctor.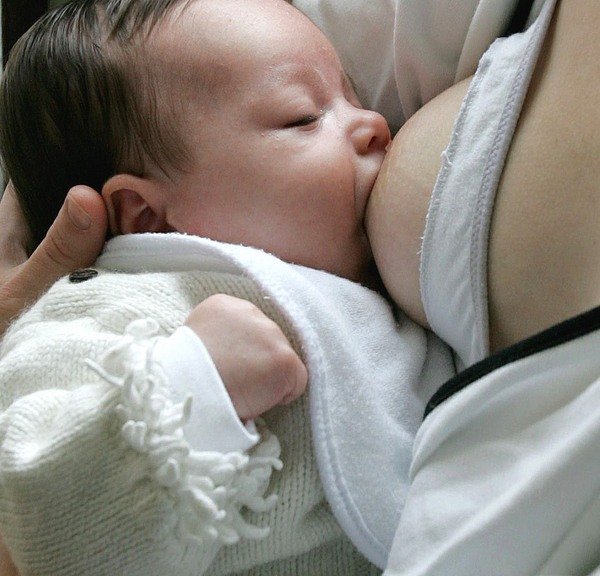 Many times, it's just a matter of using the proper technique, but sometimes pain can mean that something else is going on, like an infection.
Many times, it's just a matter of using the proper technique, but sometimes pain can mean that something else is going on, like an infection.
Time and frequency of feedings. Breastfeeding requires a big time commitment from mothers, especially in the beginning, when babies feed often. A breastfeeding schedule or the need to pump breast milk during the day can make it harder for some moms to work, run errands, or travel.
And breastfed babies do need to eat more often than babies who take formula, because breast milk digests faster than formula. This means mom may find herself in demand every 2 or 3 hours (maybe more, maybe less) in the first few weeks.
Diet. Women who are breastfeeding need to be aware of what they eat and drink, since these can be passed to the baby through the breast milk. Just like during pregnancy, breastfeeding women should not eat fish that are high in mercury and should limit consumption of lower mercury fish.
If a mom drinks alcohol, a small amount can pass to the baby through breast milk. She should wait at least 2 hours after a single alcoholic drink to breastfeed to avoid passing any alcohol to the baby. Caffeine intake should be kept to no more than 300 milligrams (about one to three cups of regular coffee) or less per day because it can cause problems like restlessness and irritability in some babies.
She should wait at least 2 hours after a single alcoholic drink to breastfeed to avoid passing any alcohol to the baby. Caffeine intake should be kept to no more than 300 milligrams (about one to three cups of regular coffee) or less per day because it can cause problems like restlessness and irritability in some babies.
Maternal medical conditions, medicines, and breast surgery. Medical conditions such as HIV or AIDS or those that involve chemotherapy or treatment with certain medicines can make breastfeeding unsafe. A woman should check with her doctor or a lactation consultant if she's unsure if she should breastfeed with a specific condition. Women should always check with the doctor about the safety of taking medicines while breastfeeding, including over-the-counter and herbal medicines.
Mothers who've had breast surgery, such as a reduction, may have difficulty with their milk supply if their milk ducts have been severed. In this situation, a woman should to talk to her doctor about her concerns and work with a lactation specialist.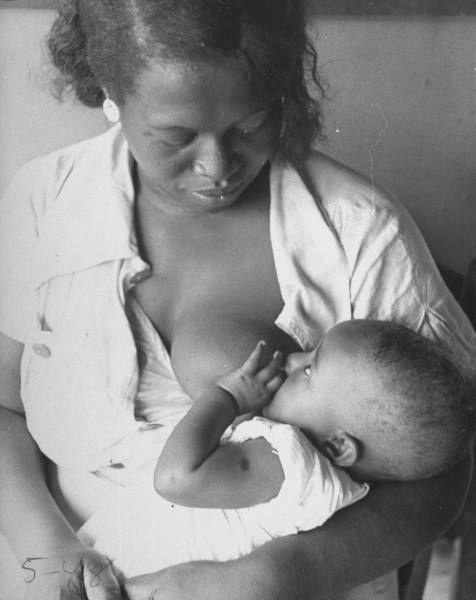
p
All About Formula Feeding
Commercially prepared infant formulas are a nutritious alternative to breast milk, and even contain some vitamins and nutrients that breastfed babies need to get from supplements.
Manufactured under sterile conditions, commercial formulas attempt to duplicate mother's milk using a complex combination of proteins, sugars, fats, and vitamins that aren't possible to create at home. So if you don't breastfeed your baby, it's important to use only commercially prepared formula and not try to make your own.
Besides medical concerns that may prevent breastfeeding, for some women, breastfeeding may be too difficult or stressful. Here are other reasons women may choose to formula feed:
Convenience. Either parent (or another caregiver) can feed the baby a bottle at any time (although this is also true for women who pump their breast milk). This allows mom to share the feeding duties and helps her partner to feel more involved in the crucial feeding process and the bonding that often comes with it.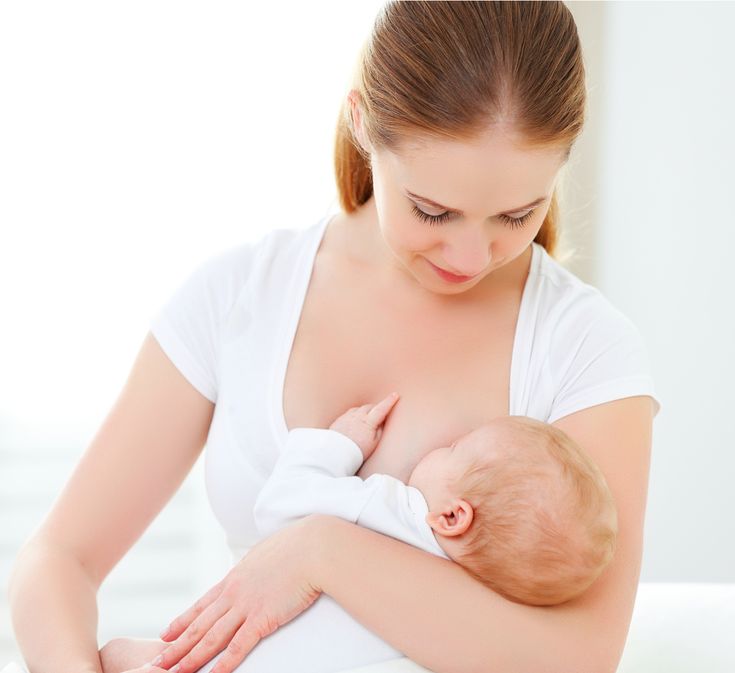
Flexibility. Once the bottles are made, a formula-feeding mother can leave her baby with a partner or caregiver and know that her little one's feedings are taken care of. There's no need to pump or to schedule work or other obligations and activities around the baby's feeding schedule. And formula-feeding moms don't need to find a private place to nurse in public.
Time and frequency of feedings. Because formula is less digestible than breast milk, formula-fed babies usually need to eat less often than breastfed babies.
Diet. Women who opt to formula feed don't have to worry about the things they eat or drink that could affect their babies.
page 7
Formula Feeding Challenges
As with breastfeeding, there are some challenges to consider when deciding whether to formula feed.
Lack of antibodies. None of the antibodies found in breast milk are in manufactured formula. So formula can't provide a baby with the added protection against infection and illness that breast milk does.
Can't match the complexity of breast milk. Manufactured formulas have yet to duplicate the complexity of breast milk, which changes as the baby's needs change.
Planning and organization. Unlike breast milk — which is always available, unlimited, and served at the right temperature — formula feeding your baby requires planning and organization to make sure that you have what you need when you need it. Parents must buy formula and make sure it's always on hand to avoid late-night runs to the store.
And it's important to always have the necessary supplies (like bottles and nipples) clean, easily accessible, and ready to go — otherwise, you will have a very hungry, very fussy baby to answer to. With 8-10 feedings in a 24-hour period, parents can quickly get overwhelmed if they're not prepared and organized.
Expense. Formula can be costly. Powdered formula is the least expensive, followed by concentrated, with ready-to-feed being the most expensive. And specialty formulas (such as soy and hypoallergenic) cost more — sometimes far more — than the basic formulas. During the first year of life, the cost of basic formula can run about $1,500.
And specialty formulas (such as soy and hypoallergenic) cost more — sometimes far more — than the basic formulas. During the first year of life, the cost of basic formula can run about $1,500.
Possibility of producing gas and constipation. Formula-fed babies may have more gas and firmer bowel movements than breastfed babies.
Making a Choice
Deciding how you will feed your baby can be a hard decision. You'll really only know the right choice for your family when your baby comes.
Many women decide on one method before the birth and then change their minds after their baby is born. And many women decide to breastfeed and supplement with formula because they find that is the best choice for their family and their lifestyle.
While you're weighing the pros and cons, talk to your doctor or lactation consultant. These health care providers can give you more information about your options and help you make the best decision for your family.
Breastfeeding FAQs: How Much and How Often (for Parents)
Breastfeeding is a natural thing to do, but it still comes with its fair share of questions. Here's what you need to know about how often and how long to breastfeed your baby.
Here's what you need to know about how often and how long to breastfeed your baby.
How Often Should I Breastfeed?
Newborn babies should breastfeed 8–12 times per day for about the first month. Breast milk is easily digested, so newborns are hungry often. Frequent feedings helps stimulate your milk production during the first few weeks.
By the time your baby is 1–2 months old, he or she probably will nurse 7–9 times a day.
In the first few weeks of life, breastfeeding should be "on demand" (when your baby is hungry), which is about every 1-1/2 to 3 hours. As newborns get older, they'll nurse less often, and may have a more predictable schedule. Some might feed every 90 minutes, whereas others might go 2–3 hours between feedings.
Newborns should not go more than about 4 hours without feeding, even overnight.
How Do I Count the Time Between Feedings?
Count the length of time between feedings from the time your baby begins to nurse (rather than at the end) to when your little one starts nursing again. In other words, when your doctor asks how often your baby is feeding, you can say "about every 2 hours" if your first feeding started at 6 a.m., the next feeding was around 8 a.m., then 10 a.m., and so on.
In other words, when your doctor asks how often your baby is feeding, you can say "about every 2 hours" if your first feeding started at 6 a.m., the next feeding was around 8 a.m., then 10 a.m., and so on.
Especially at first, you might feel like you're nursing around the clock, which is normal. Soon enough, your baby will go longer between feedings.
How Long Does Nursing Take?
Newborns may nurse for up to 20 minutes or longer on one or both breasts. As babies get older and more skilled at breastfeeding, they may take about 5–10 minutes on each side.
How long it takes to breastfeed depends on you, your baby, and other things, such as whether:
- your milk supply has come in (this usually happens 2–5 days after birth)
- your let-down reflex (which causes milk to flow from the nipple) happens right away or after a few minutes into a feeding
- your milk flow is slow or fast
- the baby has a good latch, taking in as much as possible of your areola (the dark circle of skin around your nipple)
- your baby begins gulping right away or takes it slow
- your baby is sleepy or distracted
Call your doctor if you're worried that your baby's feedings seem too short or too long.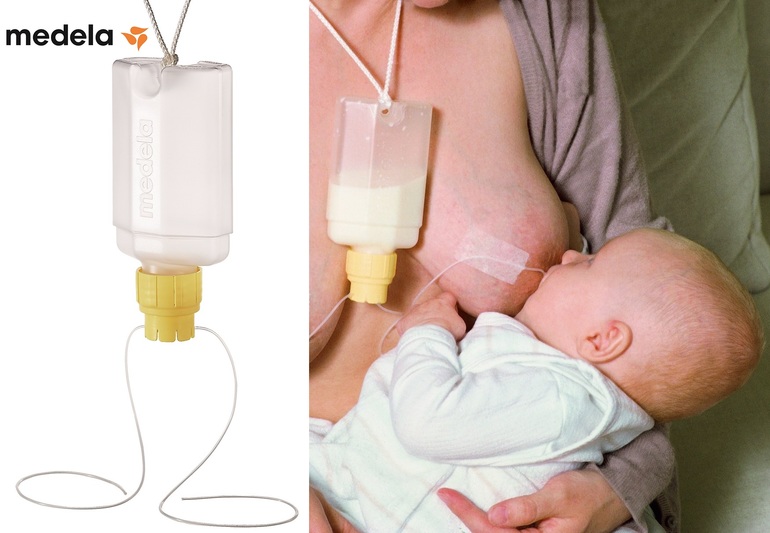
When Should I Alternate Breasts?
Alternate breasts and try to give each one the same amount of nursing time throughout the day. This helps to keep up your milk supply in both breasts and prevents painful engorgement (when your breasts overfill with milk).
You may switch breasts in the middle of each feeding and then alternate which breast you offer first for each feeding. Can't remember where your baby last nursed? It can help to attach a reminder — like a safety pin or small ribbon — to your bra strap so you'll know which breast your baby last nursed on. Then, start with that breast at the next feeding. Or, keep a notebook handy or use a breastfeeding app to keep track of how your baby feeds.
Your baby may like switching breasts at each feeding or prefer to nurse just on one side. If so, then offer the other breast at the next feeding. Do whatever works best and is the most comfortable for you and your baby.
How Often Should I Burp My Baby During Feedings?
After your baby finishes on one side, try burping before switching breasts. Sometimes, the movement alone can be enough to cause a baby to burp.
Sometimes, the movement alone can be enough to cause a baby to burp.
Some infants need more burping, others less, and it can vary from feeding to feeding.
If your baby spits up a lot, try burping more often. While it's normal for infants to "spit up" a small amount after eating or during burping, a baby should not vomit after feeding. If your baby throws up all or most of a feeding, there could be a problem that needs medical care. If you're worried that your baby is spitting up too much, call your doctor.
Why Is My Baby Hungrier Than Usual?
When babies go through a period of rapid growth (called a growth spurt), they want to eat more than usual. These can happen at any time. But in the early months, growth spurts often happen when a baby is:
- 7–14 days old
- 2 months old
- 4 months old
- 6 months old
During these times and whenever your baby seems extra hungry, follow your little one's hunger cues. You may need to breastfeed more often for a while.![]()
How Long Should I Breastfeed My Baby?
That's a personal choice. Experts recommend that babies be breastfed exclusively (without formula, water, juice, non–breast milk, or food) for the first 6 months. Then, breastfeeding can continue until 12 months (and beyond) if it's working for you and your baby.
Breastfeeding has many benefits for mom and baby both. Studies show that breastfeeding can lessen a baby's chances of diarrhea, ear infections, and bacterial meningitis, or make symptoms less severe. Breastfeeding also may protect children from sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), diabetes, obesity, and asthma.
For moms, breastfeeding burns calories and helps shrink the uterus. In fact, breastfeeding moms might return to their pre–pregnancy shape and weight quicker. Breastfeeding also helps lower a woman's risk of diseases like:
- breast cancer
- high blood pressure
- diabetes
- heart disease
It also might help protect moms from uterine cancer and ovarian cancer.
Breastfeeding your baby with special needs
If your baby has special needs and has difficulty latch-on, there are many other ways to breastfeed
Share this information
Breastfeeding is a serious stress for a baby. This process involves 40 muscles in the lips, tongue, jaw and cheeks, as well as six cranial nerves 1 for coordinating sucking, swallowing and breathing.
If a baby has a congenital disorder or disease that affects these muscles or nerves, the baby may not be physically fit to breastfeed or may not be able to get enough milk while nursing. But this does not mean that your baby should be deprived of extremely healthy breast milk. Moreover, the protective properties of milk and useful substances in its composition are even more necessary for children with special needs. nine0003
“Breast milk contains many living cells and growth factors that help boost immunity and prevent inflammation,” explains Dr. Katsumi Mitsuno, Professor of Internal Medicine in Pediatrics, Koto Toyosu Hospital at Showa University, “It is important for infants with special needs to give breast milk to prevent infectious diseases and ensure optimal nutrition.”
Katsumi Mitsuno, Professor of Internal Medicine in Pediatrics, Koto Toyosu Hospital at Showa University, “It is important for infants with special needs to give breast milk to prevent infectious diseases and ensure optimal nutrition.”
“Children with congenital and neurological pathologies are more susceptible to respiratory 2.3 and ear 4 infections and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract 5 , and are also more likely to require surgical intervention. Breast milk helps to protect the baby's body from infections and promotes recovery 6 ,” adds Dr. Mitsuno.
Reasons your baby may have difficulty breastfeeding
Cleft lip and/or palate
breastfeeding or supervising physician can show several helpful tricks. Newborns with cleft palate are often unable to breastfeed with sufficient force. nine0009 7
Prematurity
If the baby was born prematurely, he may be too weak and not have enough coordination to suckle effectively.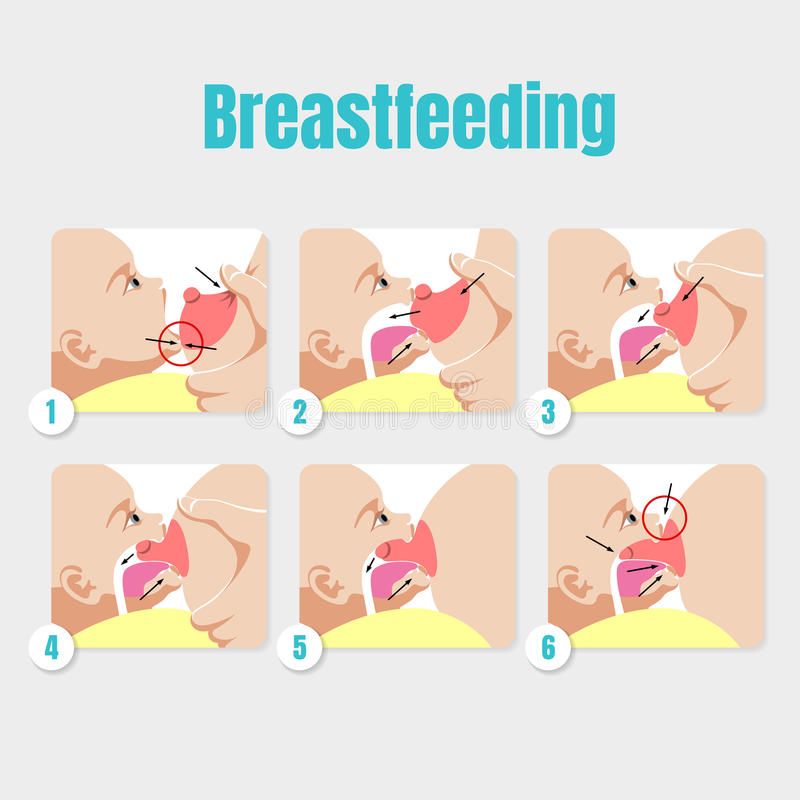 Read more about this in the article on breastfeeding premature babies.
Read more about this in the article on breastfeeding premature babies.
Down's syndrome and other chromosomal disorders
Babies with Down's syndrome typically have problems with muscle tone and mouth-tongue coordination that prevents effective breastfeeding. nine0009 8 Other chromosomal disorders, such as Edwards syndrome or Patau syndrome, also make breastfeeding difficult.
Neurological disorders
Neurological disorders (disorders of the brain, spine or nerves) often cause hypotonia, the medical term for low muscle tone. Cerebral palsy, 9 hydrocephalus, birth asphyxia, spina bifida, cerebral hemorrhage during childbirth, cerebral malformations and hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy can cause difficulties in breastfeeding. nine0003
Pierre Robin's syndrome
With Pierre Robin's syndrome, the baby's lower jaw is much smaller than normal. Often this is combined with a cleft palate and retraction of the tongue, making breastfeeding nearly impossible. 10
10
Maxillofacial Surgery
If your baby has had oral, tongue or jaw surgery, it may be painful or uncomfortable to suckle for a while.
Expressing milk for children with special needs
Regardless of whether the baby can breastfeed, the first step is to start milk production in order to get enough milk. If the baby is unable to feed directly from the breast, it is important to ensure frequent pumping to collect as much milk as possible. It is necessary to start and stimulate the production of milk as early as possible so that the baby has enough of it now and in the future.
Double pumping is recommended about eight times a day as this is the best way to stimulate a steady supply of milk. nine0009 11 Ask your healthcare provider or lactation consultant for help.
“For the first few months my life revolved around pumping. I set an alarm and woke up every three hours at night to express milk,” recalls Katherine, a mother of two from New Zealand, “Michael had a cleft palate, so he couldn’t suckle, and we had to use a special squeeze bottle. When he ate, I did not take my eyes off him - as soon as I turned away, he could choke, or I did not notice how milk began to flow from his nose, which he did not like very much. nine0003
When he ate, I did not take my eyes off him - as soon as I turned away, he could choke, or I did not notice how milk began to flow from his nose, which he did not like very much. nine0003
Participating in online support groups for mothers who only feed their babies with expressed milk has helped me a lot. I was able to express milk for my son for seven whole months - it was a real work in the name of love!”
Ways to breastfeed your baby
In some cases, your baby needs to be fed in a special way before he can breastfeed or bottle feed. For example, a feeding tube can be used to deliver milk directly into the baby's stomach. The tube is inserted by the attending physician, usually through the nose or mouth. As soon as the baby can eat in the usual way, the tube will be removed. nine0003
If the baby can swallow but is unable to breastfeed, alternative ways of feeding may be recommended. “For infants suffering from neurological disorders, you can use a drinking tube with a feeding tube or a special silicone nozzle on the finger, which an adult presses a finger against the palate. Some babies find it more convenient to eat with a special cup*, says Dr. Mitsuno. It all depends on the characteristics of the baby. Some people prefer drinking cups.” nine0003
Some babies find it more convenient to eat with a special cup*, says Dr. Mitsuno. It all depends on the characteristics of the baby. Some people prefer drinking cups.” nine0003
“Cup cup feeding* is one of the most popular and safest ways to feed a baby who cannot breastfeed,” Dr. Mitsuno continues. you will be able to breastfeed your baby longer. Cup feeding usually spills quite a lot of milk, 12 and the amount spilled must be measured and accounted for if a specific amount of milk is recommended for an infant.” nine0003
Sarah, a UK mother of three, recalls: “Our eldest daughter is a child with special needs. In particular, she has cerebral palsy. At first she suckled well at the breast, but on the third day her condition worsened, and until the age of two months she was fed expressed breast milk through a nasogastric tube. While she was in the hospital, I pumped milk every three hours.”
Sarah's story ended well: “At about eight weeks, my daughter's condition stabilized, and with the help of a specialist, we resumed breastfeeding.![]() She switched to breastfeeding very easily. By the time she was 12 weeks old and we took her home, she was exclusively breastfed. nine0003
She switched to breastfeeding very easily. By the time she was 12 weeks old and we took her home, she was exclusively breastfed. nine0003
Although many people cared for our baby, pumping made me feel important, my special role. It helped me get through that incredibly difficult period.”
If your baby can latch on
If your baby has special needs but is physiologically able to latch on, offer the breast regularly along with other feeding methods. Even if he can't suckle milk from his breast, this "soothing" suckling will help him feel safe, warm, and cared for. It will also help your baby practice suckling skills, making it easier for him to transition to breastfeeding later on. nine0003
If your baby can breastfeed but is not getting enough milk, talk to your doctor about how much pumped milk you need to supplement and how best to give it. You can give your baby expressed milk while breastfeeding with a supplemental feeding system* or use one of the devices mentioned above.
If your baby is recovering from maxillofacial surgery (eg for a cleft lip or palate), breastfeeding may be uncomfortable. However, offer your baby the breast along with other ways of feeding, according to some studies, sedative sucking can relieve pain. nine0009 13
“Everyone told me that because of the cleft lip, my son would not be able to breastfeed. But in fact, he was good at it, even though he injured my nipples while doing it,” recalls Nicola, a mother of three children from the UK, “After the operation, he was in pain at first, but soon everything returned to normal. He began to latch on very differently so it took us both some time to adjust, but pretty soon he was able to breastfeed normally and I breastfed him for up to a year.” nine0003
Literature
1 Walker M. Breastfeeding management for the clinician. 4th edition. Burlington, MA, USA: Jones & Bartlett Publishers; 2016. 738 p. — Walker, M., Breastfeeding Considerations for Practitioners, 4th edition.![]() Burlington, Massachusetts, USA: Jones & Bartlett Publishers; 2016. P. 738.
Burlington, Massachusetts, USA: Jones & Bartlett Publishers; 2016. P. 738.
2 Seddon PC, Khan Y. Respiratory problems in children with neurological impairment. nine0080 Arch DisChild. 2003;88(1):75-78. - Seddon PS, Khan Y, "Respiratory problems in children with neurological deficits." Arch Dis Child. 2003;88(1):75-78.
3 Proesmans M. Respiratory illness in children with disability: a serious problem?. Breathe. 2016;12(4): e 97. - Proesmans M., "Respiratory diseases in children with disabilities: a serious problem?" nine0120 Breeze (Breath). 2016;12(4):e97.
4 Zeisel SA, Roberts JE. Otitis media in young children with disabilities. Infants Young Child. 2003;16(2):106-119. - Zeisel SA, Roberts JI, "Otitis media in young disabled children". Infants Young Children. 2003;16(2):106-119.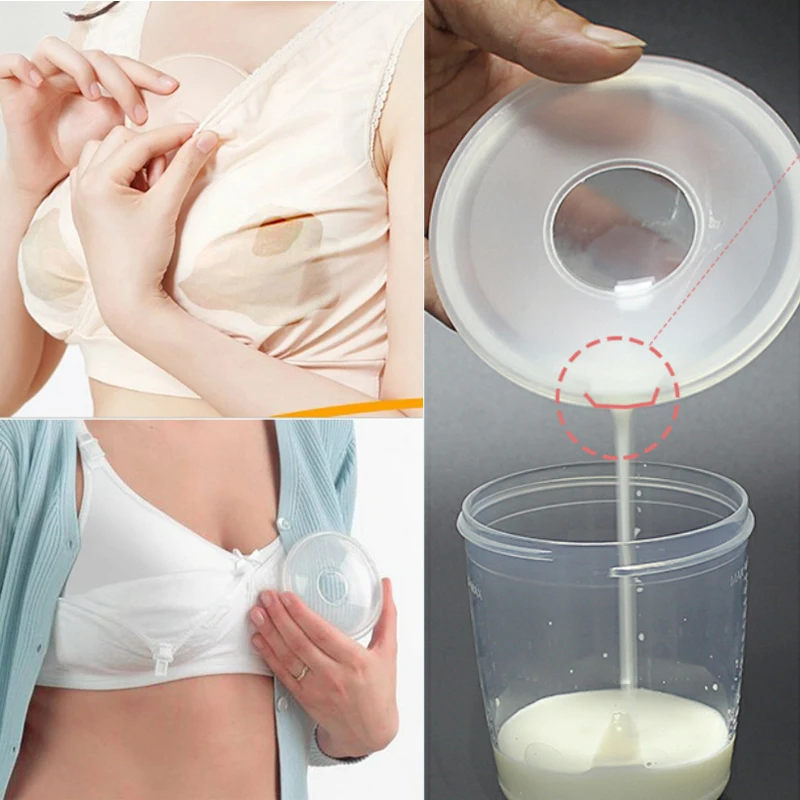
5 González DJ et al. Gastrointestinal disorders in children with cerebral palsy and neurodevelopmental disabilities. nine0080 An Pediatr (Barc). 2010;73(6):361. - Gonzalez D.J. et al., Gastrointestinal Disorders in Children with Cerebral Palsy and Neurological Diseases. An Pediatrician (Bark). 2010;73(6):361.
6 Salvatori G et al. Human milk and breastfeeding in surgical infants. Breastfeed Med . 2014;9(10):491-493. - Salvatori J. et al., Breast milk and breastfeeding in children undergoing surgery. nine0120 Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2014;9(10):491-493.
7 Reilly S et al. ABM Clinical Protocol# 17: Guidelines for breastfeeding infants with cleft lip, cleft palate, or cleft lip and palate, Revised 2013. Breastfeed Med . 2013;8(4):349-353. - Reilly S. et al., AVM Clinical Protocol #17: Guidelines for breastfeeding children with cleft lip, cleft palate, or cleft lip and palate, 2013 edition. Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2013;8(4):349-353. Thomas J et al . ABM Clinical Protocol #16: Breastfeeding the Hypotonic Infant, Revision 2016. Breastfeed Med 2016;11(6). - Thomas J. et al., "AVM Clinical Protocol #16: Breastfeeding a Baby with Reduced Muscle Tone, Revision 2016." Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2016;11(6).
et al., AVM Clinical Protocol #17: Guidelines for breastfeeding children with cleft lip, cleft palate, or cleft lip and palate, 2013 edition. Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2013;8(4):349-353. Thomas J et al . ABM Clinical Protocol #16: Breastfeeding the Hypotonic Infant, Revision 2016. Breastfeed Med 2016;11(6). - Thomas J. et al., "AVM Clinical Protocol #16: Breastfeeding a Baby with Reduced Muscle Tone, Revision 2016." Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2016;11(6).
9 Wilson EM, Hustad KC. Early feeding abilities in children with cerebral palsy: a parental report study. J Med Speech Lang Pathol. 2009: nihpa 57357. - Wilson I.M., Khustad K.S., "Early independent feeding ability in children with cerebral palsy: a study of parent reports". J Med Speech Lang Patol. 2009: nihpa 9 E et a. Feeding-facilitating techniques for the nursing infant with Robin sequence. Cleft Palate Craniofac 2006;43(1):55-60. — Nassar, I. et al., Feeding Ease Techniques for Babies with Robin Syndrome. Kleft Palet Kraniofak J. 2006;43(1):55-60. nine0120
2009: nihpa 9 E et a. Feeding-facilitating techniques for the nursing infant with Robin sequence. Cleft Palate Craniofac 2006;43(1):55-60. — Nassar, I. et al., Feeding Ease Techniques for Babies with Robin Syndrome. Kleft Palet Kraniofak J. 2006;43(1):55-60. nine0120
11 Kent JC Principles for maintaining or increasing breast milk production. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal 2012;41(1):114-121. - Kent J.S. et al., "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". nine0120 F Obstet Ginecol Neoneutal Nurs. 2012;41(1):114-121.
12 Dowling DA et al. Cup-feeding for preterm infants: mechanics and safety. J Hum Lact 2002;18(1):13-20. - Dowling D.A. et al., "Cup feeding preterm infants: technique and safety issues". F Hum Lakt. 2002;18(1):13-20.
J Hum Lact 2002;18(1):13-20. - Dowling D.A. et al., "Cup feeding preterm infants: technique and safety issues". F Hum Lakt. 2002;18(1):13-20.
13 Harrison D et al. nine0120 Breastfeeding for procedural pain in infants beyond the neonatal period. Cochrane Database of 2014;10: CD 11248 - Harrison D. et al., "Breastfeeding for Pain Relief from Medical Intervention in the Neonatal Period." Cochrane Database of System Rev. 2014;10: CD 11248
Read instructions before use. Consult with a specialist about possible contraindications.
* RU No. ФСЗ 2010/07353 of 07/19/2010
Breastfeeding after 1 month: what to expect
Do you know when breast milk production stabilizes? And how does the frequency and duration of feedings change as the baby grows? You will find answers to these questions in our recommendations for breastfeeding after the first month. nine0003
nine0003
Share this information
Congratulations: You made it through the first month of breastfeeding. Your breast milk has reached full maturity 1 , its production is stabilizing and there is little or no leakage from the breast. Don't worry, it's not getting less milk, it's just that your breasts are better able to produce and store it now. 2 At the age of six weeks, your baby will begin to please you with his charming toothless smiles, and by two months you will already have 500-600 feedings behind you. With a favorable development of events, problems with latch on by this point will already be resolved, and you can simply enjoy the convenience and benefits of breastfeeding. nine0003
When does breastfeeding decrease?
"Normal" feeding frequency for babies aged one to six months varies considerably, with some needing four times a day, others needing to breastfeed 13 times a day. 3
“From the age of one month, the amount of milk a baby consumes per feed increases, so that he can go without food for longer,” explains Cathy Garbin, a recognized international expert on breastfeeding, “A baby’s stomach grows, so he eat more at one time.![]() In addition, mature milk allows him to stay full longer.” nine0003
In addition, mature milk allows him to stay full longer.” nine0003
Feeding can last from 12 minutes to one hour -
the habits of babies vary so much! 3 But if the child is gaining weight and falls within this range, there is no cause for concern.
What is most surprising, no matter how often the baby eats, he consumes approximately the same amount of milk per day - both at one month and at six, when it is time to start complementary foods with solid food. 4
“However, sometimes the baby eats more and sometimes less, especially when he is unwell. It’s better to just listen to his needs,” Katie explains. nine0003
Is breast milk sufficient for the first six months?
Yes. Breast milk contains everything a baby needs for the first 90,449 six months of life—exclusively breastfed babies don't even need to drink more water! 5 Until about six months of age, a child's digestive system is simply not adapted to the digestion of solid food, and he will be able to drink cow's milk only after a year.
In addition, breastfeeding during this period prepares the child for further development. It strengthens the muscles of the mouth, develops the jaw and helps straighten the teeth 6.7 . All this will come in handy when the baby begins to eat and talk. And because what you eat and drink affects how your breast milk tastes, your baby discovers new tastes even before he starts eating solid foods. 8
In addition, when your baby is sick, your body produces breast milk that is
loaded with antibodies that help fight infection. 9 In other words, milk continues to protect the baby for many months as he grows and becomes more active. nine0003
Breastfeeding is also very comfortable once you get used to it. Claudia, a mother of two from the UK, notes: “No need to sterilize a mountain of bottles, prepare formula, carry it all with you, warm it up - in general, breastfeeding turned out to be very convenient, especially when my babies grew up and we began to leave the house more often. ".
".
At what age does a breastfed baby start sleeping through the night?
Waking up at night is normal for babies. Most babies between the ages of one and six months consume a fifth of their daily milk requirement at night, so nighttime feedings should not be neglected if you want your baby to get the required amount of calories. nine0009 3
"It really depends on what you mean by 'sleep through the night'," says Cathy. "And it's better than waking up every two hours anyway! I have met infants who, starting at six weeks old, fell asleep at 19:00 and woke up at 7:00, but most continue to wake up frequently at night after this age. All children are different."
In Wales, a study of more than 700 infants showed that almost 80% of children aged 6 to 12 months wake up at least once a night, and 25% of them wake up three times or more. And it did not depend on what type of feeding the child is on - breastfeeding or artificial. nine0009 10
And if nighttime awakenings are unavoidable anyway, breastfeeding is at least comfortable! Maina, a mother of two from Australia, agrees: “You can even take a nap while feeding in the middle of the night - both the body and the baby do their job on autopilot. No need to plan, measure, sterilize anything - ready-made food at the right temperature is right in your chest. I think it's ideal."
No need to plan, measure, sterilize anything - ready-made food at the right temperature is right in your chest. I think it's ideal."
My child wakes up more often. Perhaps he is hungry?
At about four months of age, a baby's sleep pattern changes as he, like an adult, has phases of deep and light sleep. Because of this, he may wake up more often at night. “At four months, sleep is more of a problem than feeding,” Cathy admits. “It can be exhausting, but try to adapt and be patient.” nine0003
Some call this " a four-month sleep regression ", but "progress" is more appropriate here. From the outside it may look like a step back, but in fact the child is approaching an important stage of development. He learns quickly, begins to become aware of the world around him, his perception is sharpened and, perhaps, there is anxiety about being separated from his mother. Crying when waking up and being able to eat milk cuddled up to mommy’s chest is a way for a baby to calm down. nine0009 11–13
nine0009 11–13
Resist the urge to “supplement” your baby with formula or start solid foods early
in an attempt to improve his sleep. Breast milk contains
hormones that make you sleepy and help you both relax
. Studies show that breastfeeding mothers actually sleep longer at night than formula- or formula-fed mothers
. 14
How does teething affect breastfeeding?
Teething usually begins around four months of age. When a baby has gum pain, he becomes restless, throws his chest and cries. All this, of course, is unpleasant.
However, breastfeeding can be an excellent sedative.
Studies have shown that babies who are breastfed
during the vaccination period cry less and forget pain more quickly. 15 Breastfeeding during teething can have the same calming effect. nine0003
An unpleasant side effect may be the child's attempts to try out his new teeth on the mother's breast. “Sometimes children flirt and bite their mother’s nipples. This can be felt in advance by how the behavior of the child changes when feeding: before biting, he removes his tongue, explains Cathy, “Usually this is not a problem and only happens a couple of times. It is enough to stop feeding, affectionately say that biting is not good, and the baby will soon leave this fun.
This can be felt in advance by how the behavior of the child changes when feeding: before biting, he removes his tongue, explains Cathy, “Usually this is not a problem and only happens a couple of times. It is enough to stop feeding, affectionately say that biting is not good, and the baby will soon leave this fun.
How to continue feeding if you have to be separated from the baby? nine0027
It happens that during the first six months, when the baby is still fully breastfed, the mother needs to be away for several hours - or even longer if she has to go to work or go away on business for a couple of days.
But this does not mean that you should stop breastfeeding. You can still feed your baby healthy breast milk - just express it and have someone give it to your baby when you're away. Here's Kathy's advice:
“Start expressing milk a couple of days in advance, in small batches, 40-60 ml at a time. So you will have the necessary supply for the time of your absence, but at the same time the amount of milk produced will remain the same.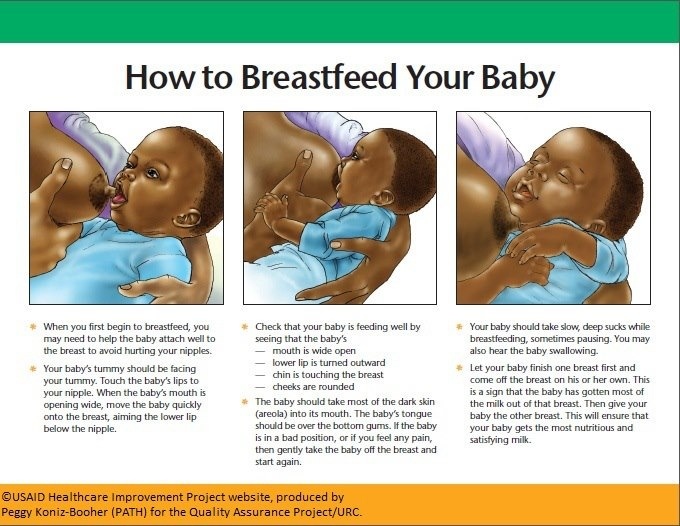 nine0003
nine0003
If you have to return to work, check with your employer about your daily schedule. Many mothers breastfeed their babies in the morning, evening and night, and pump milk at lunchtime to relieve discomfort and create a reserve for the next day.
This usually turns out to be much easier than one might think, and today many companies are well placed to do this, notes Cathy. “Breast pumps make it easy to solve this problem.”
Natalie, mother from the USA, shares her experience: “I feed Dylan as soon as he wakes up, and sometimes again before leaving for work, in order to maintain milk production and not lose contact with the child. At work, I pump twice the next day (in my absence, he eats two bottles of breast milk), and after work I rush home for the evening feed. I don't pump on the weekends - we resume regular breastfeeding." nine0003
Is it possible to continue breastfeeding after the introduction of solid foods?
When your baby begins to show interest in food and can sit up on his own - usually around six months of age - it's time to start solid foods. However, it is not necessary to stop breastfeeding, Cathy explains: “A baby’s iron stores during pregnancy are depleted by six months, so he needs additional sources of this element.
However, it is not necessary to stop breastfeeding, Cathy explains: “A baby’s iron stores during pregnancy are depleted by six months, so he needs additional sources of this element.
Start complementary foods with solid foods, but remember that breast milk remains a more important source of calories and nutrients until the baby is eight to nine months old. By this time, he will be eating much more solid food, but he will still need to breastfeed four to five times a day. By 12 months, the frequency of feeding may be two to six times a day. All babies are different, and many of them at this age are still getting half their daily calorie intake from breast milk.” nine0003
Don't forget that breast milk can be added to solid foods, such as cereals and purees, so that the baby can taste the familiar taste. If possible, use milk expressed just before feeding (not thawed) and add just before serving to keep bacteria and nutrients alive. 16
You may be pressured by others to stop breastfeeding when your baby is six months old, but the longer you breastfeed or pump milk, the better for you and your baby.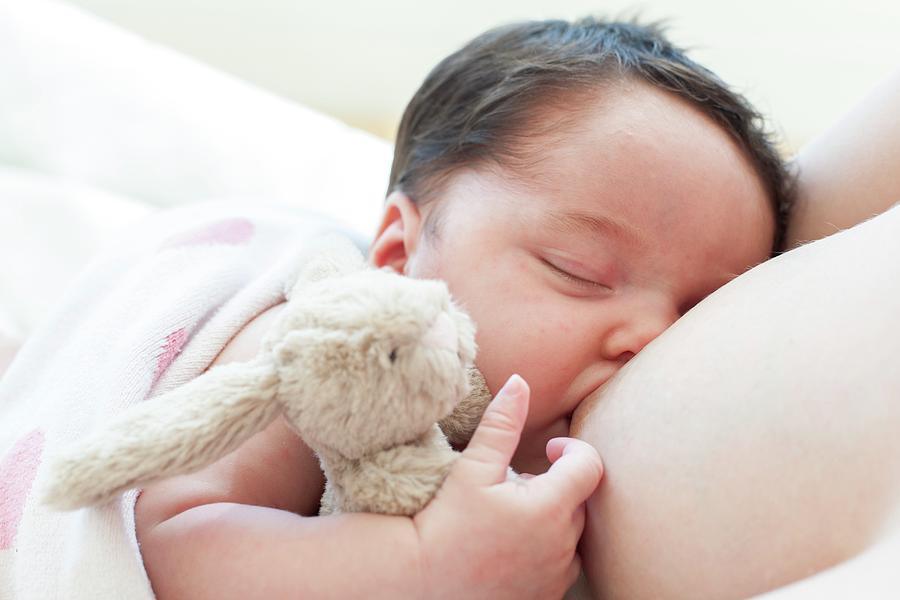 nine0003
nine0003
How long can I continue breastfeeding?
“The World Health Organization recommends breastfeeding along with solid foods until at least two years of age because it plays an important role in supporting immunity,” says Cathy. feels bad".
At eight months, the baby sometimes breastfeeds four times a day, but by one year old, the frequency of feedings can be reduced to two times a day. You yourself will understand which feeding regimen is more suitable for you and your baby. For example, Jane, a mother of two from the US, breastfed until the age of two: “I breastfed when I was at home - in the evenings and on weekends, when the children wanted to be close to me,” says Jane, “It helped a lot when they were sick . Breastfeeding has become my favorite form of comfort." nine0003
“When my son got a little older and bolder, he still often asked me to breastfeed him - as if to calm down and gain strength,” recalls Amy, a mother of two children from Canada, “When he happened to hit or skin his knee , breastfeeding was a wonderful way to comfort him.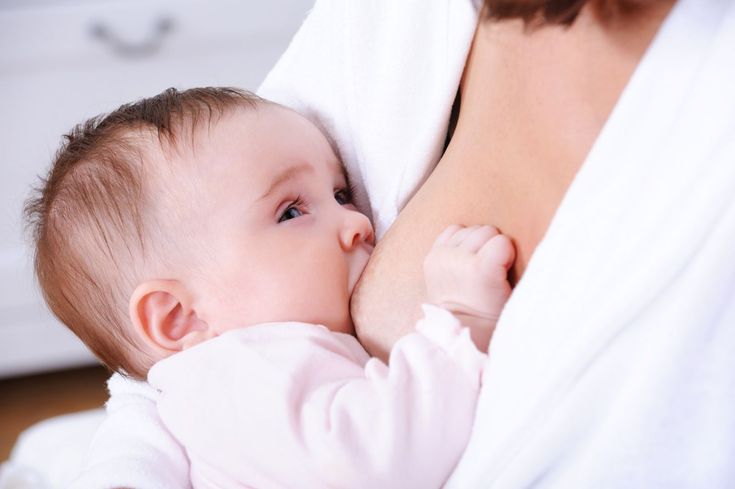 ”
”
If your baby is over a year old and you are still breastfeeding, people around you will probably tell you that this way he will never wean. But if children are not pressured, they usually refuse to breastfeed themselves between the ages of two and four. nine0009 17
“I didn’t intend to breastfeed for so long, but as a result, I still breastfeed my four-year-old daughter and 22-month-old son,” says Suzanne, mother of two from the UK, “I breastfeed my youngest before and after work, and in I express milk on business trips. The eldest daughter likes to breastfeed a little before bed or when she is upset - this is a great way to make contact. When I get tired of it, I remind myself what great benefit and comfort it brings them. I now plan to pursue a baby-initiated end breastfeeding strategy — let them decide when to stop.” nine0003
For more information on what to expect and lots of tips and tricks, see our guide Breastfeeding Problems After the First Month.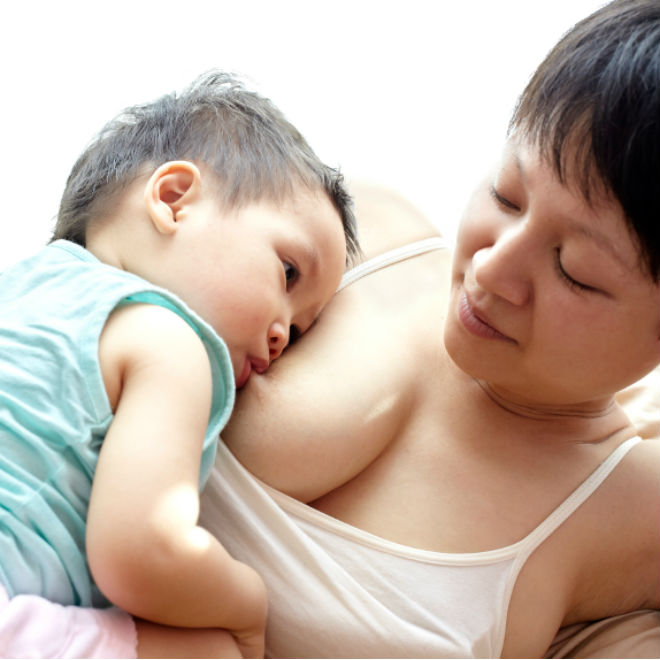
Literature
1 Ballard O, Morrow AL. Human milk composition: nutrients and bioactive factors. Pediatr Clin North Am . 2013;60(1):49-74. - Ballard O., Morrow A.L., "Composition of breast milk: nutrients and biologically active factors." nine0120 Pediatrician Clean North Am. 2013;60(1):49-74.
2 Kent JC et al. Principles for maintaining or increasing breast milk production. J Obstet , Gynecol , & Neonatal Nurs . 2012;41(1):114-21. - Kent J.S. et al., "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". J Obstet Ginecol and Neonatal Nurse. 2012;41(1):114-121. nine0120
3 Kent JC Volume and frequency of breastfeedings and fat content of breast milk throughout the day. Pediatrics. 2006;117(3): e 387-395. - Kent J.S. et al., "Amount and frequency of breastfeeding and fat content of breast milk during the day." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2006;117(3):e387-95.
- Kent J.S. et al., "Amount and frequency of breastfeeding and fat content of breast milk during the day." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2006;117(3):e387-95.
4 Kent JC et al. Longitudinal changes in breastfeeding patterns from 1 to 6 months of lactation. Breast Med . 2013;8(4):401-407. - Kent J.S. et al., Longitudinal changes in breastfeeding patterns from 1 to 6 months of lactation. Brest Med. 2013;8(4):401-407.
5 Almroth S, Bidinger PD. No need for water supplementation for exclusively breast-fed infants under hot and arid conditions. Trans R Soc Trop Med 1990;84(4):602-604. - Elmroth C, Bidinger PD, "No need for supplementation of exclusively breastfed infants in hot, dry conditions." Trans R Sots Trop Med Hyg. 1990;84(4):602-604.
6 Victora CG et al . Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet. 2016;387(10017):475-490. - Victor S.J. et al., Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms and long-term effects. Lancet 2016;387(10017):475-490.
Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet. 2016;387(10017):475-490. - Victor S.J. et al., Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms and long-term effects. Lancet 2016;387(10017):475-490.
7 Peres KG et al. Effect of breastfeeding on malocclusions: a systematic review and meta - analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2015;104( S 467):54-61. - Perez C.G. et al., "The impact of breastfeeding on malocclusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Akta Pediatr. 2015;104(S467):54-61.
8 Mennella JA, Beauchamp GK. Maternal diet alters the sensory qualities of human milk and the nursling's behavior. Pediatrics. 1991;88(4):737-744. - Mennella, JA, Beauchamp, GK, "Maternal nutrition affects the organoleptic properties of breast milk and infant behavior." nine0120 Pediatrix (Pediatrics).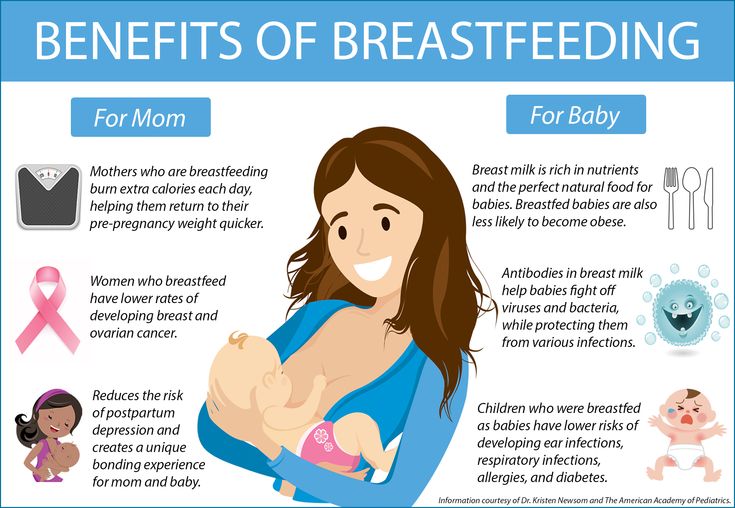 1991;88(4):737-744.
1991;88(4):737-744.
9 Hassiotou F et al. Maternal and infant infections stimulate a rapid leukocyte response in breastmilk. Clin Transl immunology. 2013;2(4). - Hassiot F. et al., "Infectious diseases of the mother and child stimulate a rapid leukocyte reaction in breast milk." Clean Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4).
10 Brown A, Harries V. Infant sleep and night feeding patterns during later infancy: Association with breastfeeding frequency, daytime complementary food intake, and infant weight. Breast Med . 2015;10(5):246-252. - Brown A., Harris W., "Night feedings and infant sleep in the first year of life and their association with feeding frequency, daytime supplementation, and infant weight." Brest Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2015;10(5):246-252.
11 Infant sleep information source. [Internet]. Normal Infant Sleep Development; December 2017 [cited 2018 Feb] - All about baby sleep. [Internet] "The development of normal sleep in a child", December 2017 [cited February 2018]. nine0120
[Internet] "The development of normal sleep in a child", December 2017 [cited February 2018]. nine0120
12 Baby sleep science. [Internet]. The-Four-Month-Sleep-Regression-What-is-it-and-What-can-be-Done-About-it. March 2014 [ cited 2018 Feb ] - The science of baby sleep. [Internet], "Four-month sleep regression: what it is and what to do about it." March 2014 [cited February 2018].
13 The Myth Of Baby Sleep Regressions – What’s Really Happening To Your Baby’s Sleep? [Internet]. Pinky Mckay ; December 2017 [ cited 2018 Feb ] - "The Myth of Baby Sleep Regression - What's Really Happening to Your Baby?" [Internet]. Pinky McKay, December 2017 [cited February 2018].
14 Kendall - Tackett
0 ET 9017 Al 9 9 .