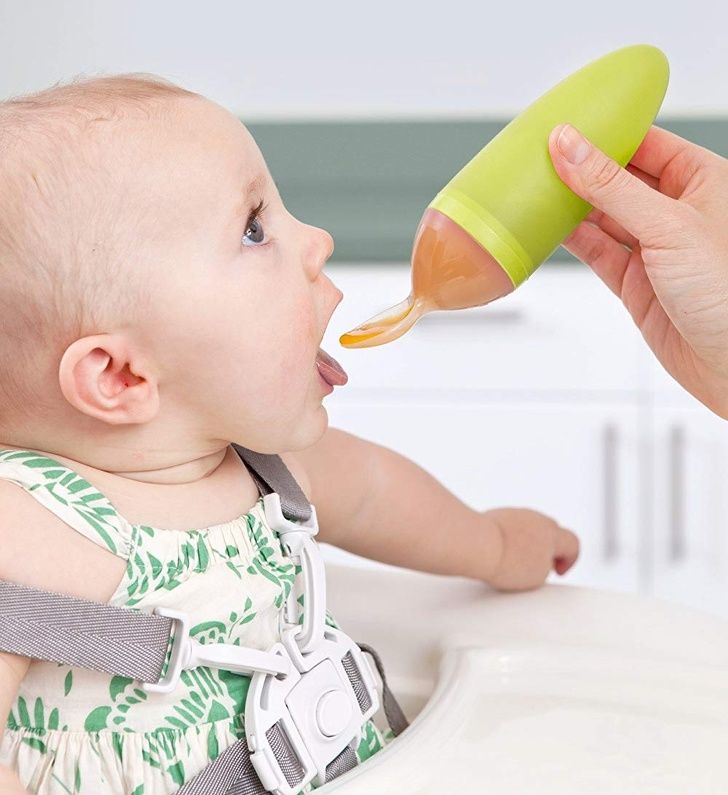
Baby hates food
What to Do When Baby Won't Eat Solids: 7 Simple Steps
When your baby won’t eat solids, it can be stressful. Learn why your baby is refusing food and how to get them to eat solid foods with 7 simple steps!
The spoon hits the floor.
Your baby makes a nasty face.
They might even shudder or gag.
All from a bite, or an attempt to feed your baby solid foods. It’s totally unexpected when babies respond with such disdain for baby food or table food. As parents, we’re often excited about this new milestone and it’s shocking when your baby won’t eat solids.
In real life though, it’s quite common for babies to gag on solids, seem uninterested, and outright refuse food.
While knowing it’s “normal” for babies to not seem interested in solid foods, even though everyone else’s baby seems to be gulping it down by the jar full, it still leaves the question, “How do you get a baby to eat solids?”
Well, I happen to know a thing or two about that. First, because I’ve personally helped a lot of families get their babies eating solids as a pediatric occupational therapist with over a decade of experience, but also because I’ve been there with my own son…
Going through it as a mom was a whole different ball game.
Of course, I knew that it was normal for babies to refuse baby food when it was first introduced, and I also knew that some babies didn’t much prefer baby food, but my Momma heart was worried. The worrying got worse when I watched my son act like he could’ve cared less about the delicious homemade sweet potatoes that I whipped up, as he turned his face away and threw the spoon across the room.
Meal after meal.
Day after day.
And, week after week.
With each passing day that he refused to eat solids, I got more worried, and more frustrated as I’d watch the food I’d prepared literally go down the drain. There came a point when I knew I needed to do more, to put some of my OT skills to use in my home, and that’s what I’m going to share with you here, because I know how stressful it is when your sweet adorable little baby won’t eat solids.
By the end of this guide, you’ll know :
-
- Why your baby is refusing solids
- Why they used to eat solids, but don’t anymore
- How to get them to eat solids and table foods
- Ways to get them more help (if you need it)
*Keep a look out for the free printable at the end too, if your baby is struggling with table foods!
Affiliate links used below. See our full disclosure.
Why Your Baby Won’t Eat Solids
There are a lot of factors that can actually play a role in any baby’s refusal to eat solid food. We’re going to walk through each of them below, but know that the reason your baby isn’t eating solids could be any one or combination of them. With a little detective work, you’ll figure it out!
Also, age has a little do with it, and will help you hone in on what’s going on.
6 or 7 Month Olds That Refuse Solids:
-
- Baby isn’t ready yet – 6 months of age is the perfect time to introduce baby to solid foods, but sometimes the baby isn’t ready.
 Actually, this is really common when the baby is closer to 4 and 5 months old if you’re starting a little earlier, but is still totally normal at 6 months of age.
Actually, this is really common when the baby is closer to 4 and 5 months old if you’re starting a little earlier, but is still totally normal at 6 months of age.
- Baby isn’t ready yet – 6 months of age is the perfect time to introduce baby to solid foods, but sometimes the baby isn’t ready.
Babies are still learning how to move their tongue and bring toys to their mouth, which helps them get used to having foreign objects in there. Each baby is unique and yours may just need some practice if they are in this age range.
They also may still be developing good trunk and head control, without it, eating is difficult!
Check out the American Academy of Pediatrics recommendations for introducing food and make sure your baby is ready for solids. You can also find my guide to Introducing Solids with more details on milestones to look for when 6 months old.
-
- A strong tongue thrust reflex – Most babies usually lose this reflex that helps them not choke if something accidentally gets into their mouth around 4-6 months, but it may linger for some.
If you notice that your baby still thrusts their tongue out every time you touch the spoon to their lips, they may need a little more time. It’s really hard for them to eat when they keep shoving their tongue out of their mouth!
It’s really hard for them to eat when they keep shoving their tongue out of their mouth!
-
- Doesn’t like the way food feels – Solid food is something so new and unfamiliar to babies, it can take a while for them to get used to the new texture in their mouth. Many babies do in fact get used to the feeling of solids, but some don’t.
Read more about that below under sensory.
8, 9, or 10 Month Olds That Refuse Solids:
-
- Sensory – By 8 months of age, most babies are ready from a developmental standpoint, and at this age, it’s definitely time to get the ball rolling, but some babies (like my son) still refuse. One of the most common reasons why older babies still won’t eat solids is because they don’t like the texture.
This boils down to the way their brains are thinking about (or processing) the sensory input they feel (aka the food in their mouth).
This isn’t a bad thing and doesn’t necessarily mean they have any kind of diagnosis, but it does mean we need to take some extra steps to help them tolerate the texture of food better.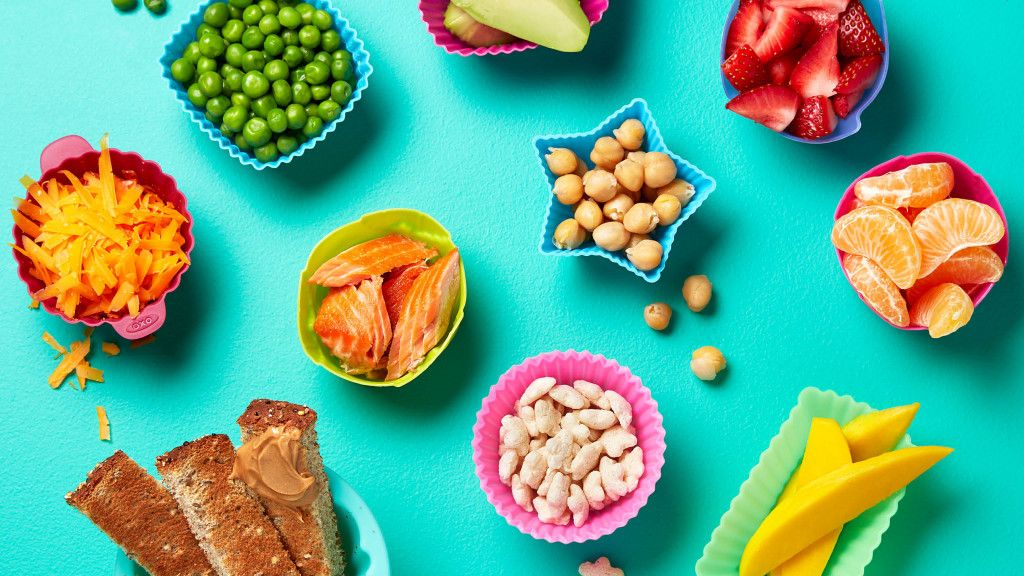 You can head to sensory issues with food to learn more.
You can head to sensory issues with food to learn more.
Babies that are sensitive to different textures usually gag immediately at the sight, touch, or taste of food.
-
- Coordination – Eating actually requires a lot of muscle coordination from opening the mouth, pulling food off of a spoon, closing the mouth, and effectively swallowing.
We take this for granted and don’t even think about it, but for some babies, it just isn’t coming natural.
Babies that are having difficulty with coordination, or oral motor skills (find exercises with that link,) usually gag when trying to swallow or after getting the food into their mouth.
Or, the food may fall out frequently, and babies won’t eat solids because they just don’t know how. When they don’t know how to eat, it isn’t that fun, and there isn’t a lot of interest.
If gagging is something you’re concerned about or is happening often, read more in guide on baby gagging.
-
- Food allergies – Believe it or not, sometimes babies will avoid certain types of foods because they’ve associated an upset tummy with the yogurt or cheese for example. It doesn’t happen all the time, but it’s something to consider, especially when it’s very specific allergenic food.
The most common types of food allergens are dairy, egg, soy, wheat, tree nut, peanut, fish, and shellfish. Severe eczema is another indicator that food allergies might be present.
Sometimes, signs become more obvious when cow’s milk is introduced.
-
- Not into baby food – While this is probably the least likely reason your baby is refusing solids, it is possible.
If you’ve consistently offered baby food or infant cereal with no interest from your baby and you don’t see any of the sensory or coordination signs we talked about above, then you might just might want to move on to table and finger foods.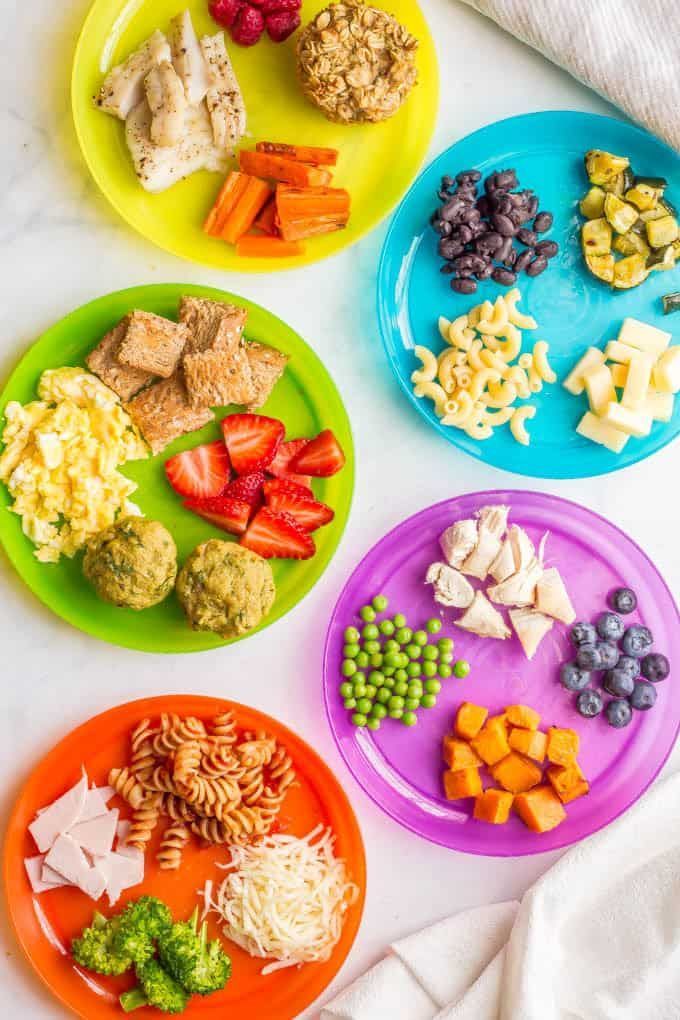
One way to do that is using a Baby Led Weaning approach, before you do that though read my BLW pros and cons.
*Get a seat in my free workshop and learn 5 big feeding mistakes that might be stopping your child from learning to eat. We’ll send you a free workbook too!
Why Baby Won’t Eat Solids Anymore (They Used to?)
-
- Some teething babies won’t eat – While it’s not as common, some babies start off eating baby food and then suddenly stop. A frequent cause of this is teething, and some babies teethe for a very. long. time. If your baby’s teeth are swollen, red, and seem to hurt, then this is likely the cause.
Try putting some teething gel on their gums 15-20 minutes before a meal. If you see an improvement, this is likely the culprit. Here’s a natural teething gel I like, but check with your doctor first.
-
- Going through a phase – Babies may get a little bug or slight cold that we aren’t even aware of or have some negative experience with food that seemed too minor to us as the parent, but makes them leery of eating.

- Going through a phase – Babies may get a little bug or slight cold that we aren’t even aware of or have some negative experience with food that seemed too minor to us as the parent, but makes them leery of eating.
If it’s the latter, some sensory sensitivities can develop if a baby goes for a while without eating any food. If this is the case for your baby, you’ll want to follow the steps below and focus on not pressuring your baby to eat. It’s really important that mealtimes are a positive experience.
-
- They’ve outgrown baby food – If your baby is later in their 7th month or older, they may just be sick of solid baby food and ready for the real deal table and finger foods. That may mean it’s time to change up baby’s diet!
I know that seems scary and makes some parents nervous. Don’t worry though, if you think this is why your baby suddenly won’t eat solids anymore, then head to how to transition to table foods.
How to Get Your Baby to Eat Solids
1. The absolute first thing I do with a baby not eating solids is to put a scoop of baby food or some other pureed food like yogurt onto the tray of their high chair.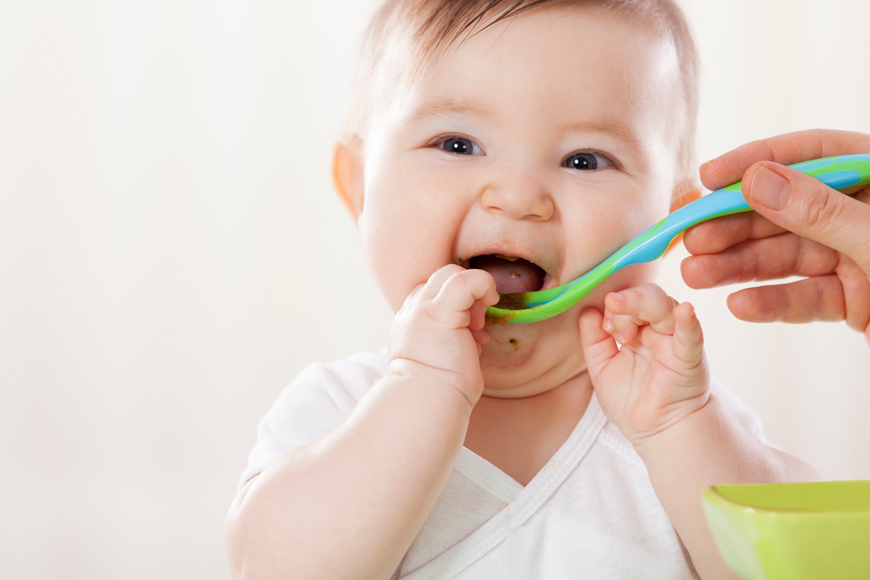
I know, the mess. It’s soooo important for babies to get messy though! If you’re skeptical, you’ve got to read: Why Babies Should Get Messy Eating. It will totally change your perspective and give you the inspiration to embrace the mess.
2. Encourage your baby to touch the food, but don’t force. Be silly and keep it light. Demonstrate.
If they refuse, try and try again. In fact, at every single meal, put a dollop of that food on their tray or even in a bowl that they can play with and touch. If they won’t touch after a few attempts, offer a spoon for them to stick into the food too.
This is one of my favorite beginner spoons that makes it really easy for baby to get some food onto it.
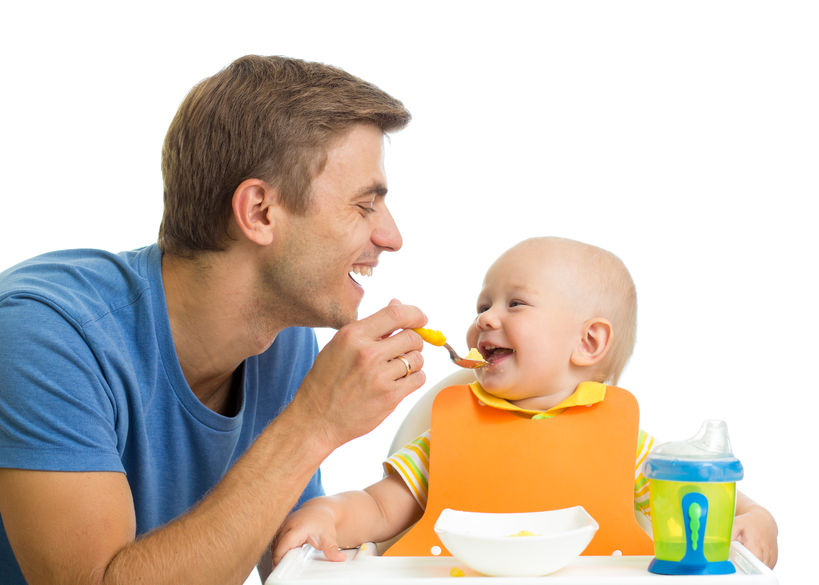
3. Once your child touches the solid food, you’re on your way! Allow them to touch, spread, and put it all over the tray and themselves. This is wonderful for their sensory processing and will make a huge difference in helping them get used to the texture of solids.
If they get upset once they’ve touched the food, or that they are now all messy, be very calm and reassuring.
Have a wet washcloth ready and quickly wipe them down. And, if this is how they respond, it’s a sign that you need to practice playing with these foods a lot! The more they touch and interact with the food, the closer they’ll be to eating it.
4. When baby has the food on their hand and they’re at least tolerating it, show them how to take their hand to their mouth, so they can taste it. You may need to demonstrate if baby won’t let you guide their hand.
Repeat this several times. After they eat from their hands several times, offer them some solid foods from a spoon.
5. You can also give them a large whole raw carrot or celery stalk at meals. I mean the whole darn thing. The point isn’t for them eat it (and if they can get pieces of it off, take it away), but for them to put it into their mouth.
When they do this, it helps desensitize their gag reflex and they get to practice biting, chewing, and moving their tongue around. It’s amazingly powerful and can make a big impact in a baby accepting solid foods. Make sure you demonstrate and keep offering at every meal.
It’s amazingly powerful and can make a big impact in a baby accepting solid foods. Make sure you demonstrate and keep offering at every meal.
6. Be consistent and patient. I can’t stress this enough, even though it’s often easier said than done! Have regular meals and follow the above steps 1-3 times a day for every meal. You can find sample schedules for babies ages 6 – 7 months, 8 – 10 months, and 11 -14 months if you’d like a guideline to follow.
7. Focus on meals being positive experiences for the baby, even if they aren’t eating anything. As parents, we can bring a lot of stress with us to meals, which can be hard to hide. But, this is definitely a “fake it til you make it” kind of situation.
Take a deep breath, put on a happy face, and work on the above steps. Going into the meal with no expectations of them eating anything will also help keep your frustration level down.
To learn MORE, grab a seat in my free online workshop.
In it, you’ll learn 5 big feeding mistakes that are stopping your baby or toddler from learning to eat table foods! It’s an eye opener and will help you take steps to give them the best start with eating table foods well (even if it already isn’t going well):
Strategies to Use Outside of Meals for Baby’s Refusing Solids
There are a few really powerful strategies you can use away from the highchair that will directly impact your baby eating solids during meals. Might seem strange, but if you suspect your baby is refusing because of sensory or coordination difficulties, doing these activities can be total game changers:
Might seem strange, but if you suspect your baby is refusing because of sensory or coordination difficulties, doing these activities can be total game changers:
-
- Brush their teeth – If you haven’t started yet, brush their teeth, and when you do, make sure you’re getting all over their gums and the sides, as well as the top of their tongue.
It only takes a few seconds, but it helps to both desensitize their mouth and improve coordination because the tongue gets practice moving in different directions. If your baby doesn’t like it, take it slow, and try often.
The more often you brush, the bigger the effect. Try for one to three times a day, and consider a vibrating toothbrush (yes, even for babies) for more powerful input in their mouth.
-
- Play in sensory bins – That may be a new term to you or you might be wondering what the heck that has to do with eating, but playing in different textures is super powerful and helps the sensory system understand different textures better.

- Play in sensory bins – That may be a new term to you or you might be wondering what the heck that has to do with eating, but playing in different textures is super powerful and helps the sensory system understand different textures better.
This correlates directly to eating. I can’t tell you how many times I’ve seen a kiddo that plays in sensory bins frequently, suddenly start eating more foods (my son included). Head to Sensory Bin Ideas to learn how to set one up.
-
- Chew on toys – So many babies that won’t eat solids never put toys or teethers in their mouth, which is really easy to overlook. If this is your baby, pull out a bunch of different teethers and have them around the house.
Demonstrate. Dip them in food or juice. Play with them in the bath. The more often they get teethers and toys into their mouths, the more it will help improve the coordination their mouth muscles need to eat and desensitize their gag reflex and sensory system.
I really love this teether because it gets in the back of the mouth and this one vibrates (all my friends get it from me at their baby shower).
Help for the Baby Not Eating Food
I’m not just talking about solid baby food or purees. You may have a baby that won’t eat any type of food, like puffs, cut up fruit, or toast. They’re getting older and older. You’re getting worried.
You may have a baby that won’t eat any type of food, like puffs, cut up fruit, or toast. They’re getting older and older. You’re getting worried.
Following the above steps will be incredibly important for your babies too, especially the strategies for outside of a meal. But, you’ll also want to use the steps I outline in getting your baby to eat table foods.
That’s a whole different animal all within itself, and there are some targeting tips that can make all the difference in your baby eating food.
You’ll want to focus on small pieces, and by 9 months of life be attempting table or finger foods.
While I don’t want you to worry, I know it’s tempting to keep waiting it out, and unfortunately, some doctors advise this quite often. This often does not help your baby to learn to eat wide variety of foods.
Babies instinctively learn to chew between roughly 8 and 11 months of age, when they move past that, it can be much harder for them to accept foods. It’s not impossible, and the same steps apply for older children, but it’s much better to be proactive then taking a “wait and see” approach.
It’s not impossible, and the same steps apply for older children, but it’s much better to be proactive then taking a “wait and see” approach.
Puffs, lil cheese curls, and baby mum mum’s are all great for baby’s first foods.
When to Get More Help for a Baby Not Eating Solids
If your baby doesn’t like solid baby food and won’t accept any table foods of finger foods by 9 months old, it’s a good idea to get an evaluation either from the free early intervention program in your state or from a feeding therapist.
You can also read more about typical feeding milestones for babies just to have a reference point. As I said earlier, all babies develop at a different pace and needing a little more help is very common.
Get My Free Printable: Learn to Eat Table Foods Cheat Sheet
There seem to be more questions than answers when you’re under the daily stress of your baby or toddler not eating table foods. Not to mention all of the well-intentioned bad advice that’s often given. Let’s clear that up.
Let’s clear that up.
I’ve created a free 5 page guide that clearly lists the steps to teach your baby or toddler to eat table or finger foods, plus a FAQ guide for parents to ease their worries when their babies won’t eat!
Get your free Learn to Eat Table Food Cheat Sheet printable here!
More on My Baby Won’t Eat Solids
How to Teach Your Baby to Self-Feed
Mega List of Table Food Ideas
How to Teach Your Baby to Drink from a Straw
The Best Mealtime Utensils and Tools for Babies
Click here to Pin This! (You’ll have as a quick reference)
Alisha Grogan is a licensed occupational therapist and founder of Your Kid’s Table. She has over 17 years experience with expertise in sensory processing and feeding development in babies, toddlers, and children. Alisha also has 3 boys of her own at home. Learn more about her here.
What You Need to Know About Baby Gagging (+ Expert Tips)
Your baby gagging can be terrifying. Learn about the gag reflex in babies and what to do when babies have a sensitive reflex and gag on food or their bottle.
Learn about the gag reflex in babies and what to do when babies have a sensitive reflex and gag on food or their bottle.
It’s a terrifying moment as a parent.
You know the one, because we’ve all been there, if only fleetingly.
It often happens as your baby is learning to eat.
They’ve taken a piece of food into their mouth, and we sit watching with big (sometimes fake) smiles on our face as if to offer encouragement. We watch closely, wondering if our little babe can pull off swallowing safely, and suddenly there’s a split second of silence. Their eyes pop out of their heads, they lunge forward, and they gag.
In that same split second, your heart is thumping so hard in your chest it feels like it’s going to bust through. You also leap forward, unsure of what you should even be doing. Your baby gags again and again. Something must be done, so you try to get that overcooked little piece of carrot out of their mouth. You succeed, collapsing into the chair, and pull the food away from your baby because, well, you need a second.
As you sit there, arms still twitching, as the adrenaline slowly dissipates, you wonder, “Is that normal?”
Or, as is the case for some babies, the baby gagging has become all too frequent, and you just don’t know how to stop it from happening.
That is just one of many instances that can play out in our homes with baby gagging. And, to be perfectly honest, sometimes it’s completely normal for a baby to gag as they’re learning to eat or on the nipple of their bottle.
And, sometimes it’s not.
To ease your fragile parent heart (I’ve got one too), we’re going to cover what the baby gag reflex is, when you need to worry about baby gagging, how to decrease baby gagging, and more! You’ll also find more tips in My Baby Won’t Eat Solids and How to Transition to Table Foods.
The Baby Gag Reflex
Believe it or not, babies are designed to gag on objects entering their mouth from the moment they come out of the womb. It’s a real reflex that’s there to protect them from actually choking on something, because as new infants, they have no skills to get an unexpected item out of their mouth.
This baby gag reflex is a very good thing.
When babies are first born, and for the first few months of life, this gag reflex is very sensitive and is triggered very easily. Meaning, something doesn’t have to get very far into a baby’s mouth to prompt the gag reflex and cause them to gag. (Find a total guide on Feeding Milestones.)
As they grow, get bigger, and start to put random objects into their mouth, their gag reflex moves further back in their mouth. The baby gag reflex becomes less sensitive, harder to elicit.
This is also a very good thing because it’s around the time babies learn to start eating real food. It would be very hard to eat if that gag reflex was still sensitive, which of course is the case some of the time…
A Sensitive Gag Reflex in Babies
Some babies seem to have a hyper-sensitive gag reflex, and this may be apparent very early on as bottles are introduced. You may be reading this right now because your baby consistently gags on a bottle.
This is even more likely for babies that are exclusively breastfed because they aren’t used to the feeling and texture of a bottle. The nipple may be bigger or go into their mouth further and trigger the baby gag reflex. Read tips here for getting a baby to take a bottle.
Other babies do just fine with bottles and nursing, but as in the example I started with, they frequently gag when trying to eat foods. Sometimes making it impossible for them to eat. This often occurs because the gag reflex is still too far forward in their mouth.
When Does Baby Gagging Occur
As I mentioned earlier, it is normal for all babies to gag sometimes. That gag reflex is present, and even if it isn’t that sensitive, you’re likely to see it happen on occasion. Let’s take a closer look at the times that will most likely be:
Baby Gags on Bottle
Some, not all, babies will gag when a bottle is put into their mouth because it goes a little too far back or the texture of the nipple feels a little different to them.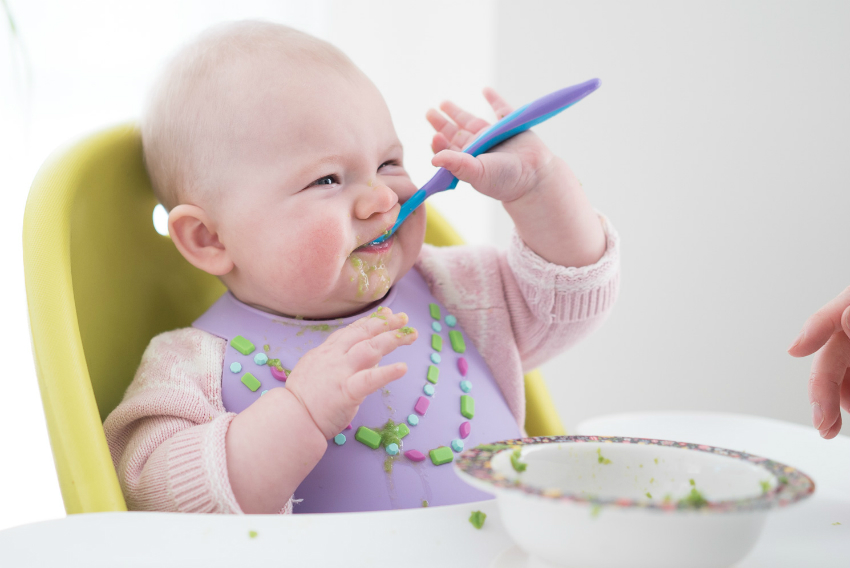 Although it can be disconcerting, it’s typical behavior from an infant if it doesn’t happen all that often.
Although it can be disconcerting, it’s typical behavior from an infant if it doesn’t happen all that often.
Baby Gags When Mouthing Toys
It’s even more common to see your baby gag when they are beginning to put teethers, various toys, and the keys they dug out of your purse into their mouth. They are literally desensitizing and moving that baby gag reflex further back into their mouth. Your baby is priming the pump for food usually weeks or months before they ever take a bite of food. (Read more about how to start feeding baby.)
Babies that chew on a lot of toys typically don’t have a sensitive gag reflex.
Baby Gagging on Food
Nearly all babies gag on food at some point. Eating is a highly coordinated event that we take for granted because it’s old hat.
Most babies will gag on foods because they are either too thick, as in the case with pureed baby food, and they have difficulty moving it back to swallow properly.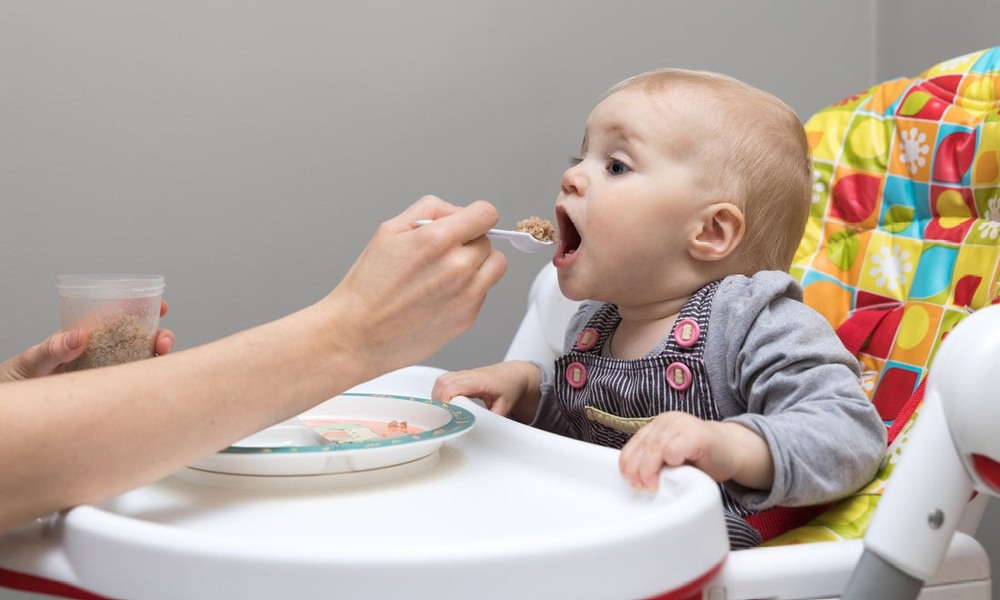 Or, if they’re eating table foods, they may lose track of the food and it hits their gag reflex before they can get it in place to swallow correctly.
Or, if they’re eating table foods, they may lose track of the food and it hits their gag reflex before they can get it in place to swallow correctly.
Again, this is a good thing, because if a piece of food haphazardly hits the back of the tongue and slides down their throat, there is a much higher likelihood that they could choke or aspirate on it (that’s when food goes into the lungs instead of the stomach, not a good thing). The gag helps project the food they lost track of out of their mouth, keeping them safe.
When baby gagging is excessive, there is likely one of two causes:
1.A baby’s ability to move their tongue and jaws around together to eat efficiently are called their oral motor skills. When their oral motor skills aren’t coordinated or the muscles like their tongue are weak, it’s very difficult to chew and swallow. If your baby gags AFTER trying to eat food, this is likely the cause. (Read more in oral motor exercises)
2. If a baby gags instantly after food touches their tongue, or perhaps just from looking at food, it’s a very good indicator that they are sensitive to the texture of the food. This is related to their sensory system and how their brain is understanding what the texture will feel like. (Read more in sensory issues with food)
This is related to their sensory system and how their brain is understanding what the texture will feel like. (Read more in sensory issues with food)
Lastly, there is one factor that DOES NOT affect baby gagging on food, and that’s if your baby has teeth or not. It’s a popular misconception that babies need teeth to eat. They do not.
The first and only teeth that most babies typically have for months are their front teeth, which are not used for chewing. The front teeth are used to bite off pieces of larger foods, and most babies are eating small pieces of food.
But, even if your baby is taking bites off of food, their gums are strong enough to do the job.
Some babies won’t get any teeth until after their first birthday, waiting until then could lead to a whole host of feeding problems. The moral of this story is not to worry about your baby eating or gagging on food if they don’t have teeth yet.
If you’re concerned about when to give what foods, that’s a valid question and there are some guidelines to follow, which help decrease gagging. Check out When can babies eat cheerios to find the top foods that parents have questions about!
Check out When can babies eat cheerios to find the top foods that parents have questions about!
Grab a seat to learn about other feeding mistakes that parents are often told in my free online workshop. You’ll learn what to avoid so that your baby gets over gagging and on to eating table foods. I’ll send the link right to your inbox:
Click here to get a seat in 5 Big Feeding Mistakes that are Stopping Your Baby/Toddler from Learning to Eat
How to Respond to a Baby Gagging
It’s very easy to respond to your baby gagging with hysterics or even concern, because it’s scary. But, our response, even just once, can really leave an impression on a baby. At these early ages, our babies watch our reactions constantly and may learn from them. They can pick up on how we’re feeling and the last thing we want them to do is link the danger feeling they’re sensing as related to eating.
It can become ingrained in them quite quickly that eating is a bad thing, even though they aren’t able to articulate that.
When your baby does gag, appear calm and reassuring. Even act like its not a big deal. If you have to fake it, goodness knows I have many times, even slapping a smile on my face as I say, “You’re okay, would you like a drink?”
If your baby continues to gag on food in their mouth, then gently lean them forward. This will either help the food fall out of their mouth or bring the food to the front of their mouth, so they can swallow it safely.
If they still continue to gag, make a hook with your pinky finger and put in to one side of their mouth and sweep it to the other side, sweeping any food out. You may have to do this a few times.
I realize that I’ve probably just petrified you! If you’re feeling very nervous about your baby choking, it would be helpful to take an infant CPR class. You can also read more here.
Affiliate links used below. See our full disclosure.
How to Decrease Baby Gagging
Yes, there are actually some steps you can take to help decrease baby gagging!
For Baby Gagging on a Bottle:
You’ll want to try small nipples and experiment with different flows.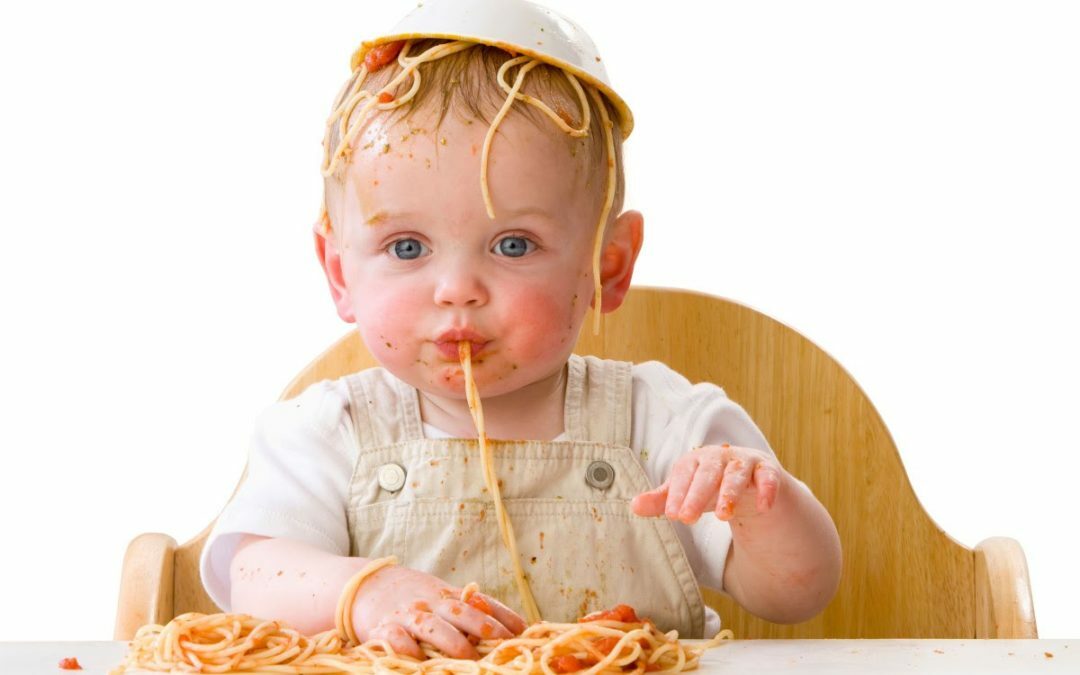 Some babies may gag because the milk is taking too long to come out and others because it’s way too fast for them to manage.
Some babies may gag because the milk is taking too long to come out and others because it’s way too fast for them to manage.
Also, make sure baby is in a semi upright position and that their head isn’t tipped too far back. Put the nipple to their lips first and let them feel it for a second. Then, slowly put it into their mouth.
If the gagging still continues, use a pacifier or your pinky finger to rub on their gums and the sides of their tongue three to four times a day to help desensitize the sensitive gag reflex.
For Babies Gagging on Food:
Make sure they have tons of opportunities to chew on teethers, safe toys, and even large pieces of whole foods they can’t get pieces off of. Think about a whole raw carrot or stalk of celery (if they can get pieces of it off, most can’t, then don’t use it). If they don’t seem interested, demonstrate and show them. This two pronged teether is one of my favorites because it reaches just far enough into their mouth and really works at desensitizing.
I also love vibrating teethers, because they vibrate and give lots of sensory input when they bite down. I used this one with all my kids.
You can also brush your child’s teeth, or rather their gums, and the sides of their tongue. Allow them to hold and bite on the toothbrush. This is a perfect little toothbrush for babies. The teeth/gum brushing also works to desensitize the gag reflex, improve oral motor skills, and improve sensory processing!
Read more here on how to teach your baby to eat finger foods. These steps will also be helpful to decrease gagging.
When Do You Need to Worry About Baby Gagging
First of all, it’s very important to know that baby gagging is different than a baby choking. Choking means something is already in their throat and they can’t get it out. Gagging is something in their mouth, or even nothing in their mouth, if they are just put off by a texture of food.
Many of us gag when we smell something absolutely putrid, some babies and children do that with foods they aren’t familiar with or don’t prefer.
If your baby is gagging so much, it’s difficult to feed them and your legitimately concerned about their growth because they aren’t eating or drinking enough, I’d recommend getting a feeding evaluation. If you live in the states, you can get that free through early intervention, or you can seek out feeding therapy from other sources.
And, if you want to make the most out of mealtimes in your home as your baby grows, download the 9 Steps to Improve Eating, I’ll send it right to your inbox! These are my top tips for raising a child that has a healthy relationship for food. Get this free printable here!
Before I end, I wanted to give a big shout out to the folks at Feedspot for naming Your Kid’s Table one of the best kids food blogs on the web! You can check out the whole list here.
More on Baby Gagging
How to Transition to Table Foods
What to Do When Baby Won’t Eat Solids: 7 Simple Steps
Mega List of Table Foods for Your Baby or Toddler
Feeding Red Flags for Babies and Toddlers
Did you pin this?
Use the button below or scroll to any picture in this post, tap it, and you’ll see the pin it button appear! You can stick in your favorite board for safe keeping!
Alisha Grogan is a licensed occupational therapist and founder of Your Kid’s Table. She has over 14 years experience with expertise in sensory processing and feeding development in babies, toddlers, and children. Alisha also has 3 boys of her own at home. Learn more about her here.
She has over 14 years experience with expertise in sensory processing and feeding development in babies, toddlers, and children. Alisha also has 3 boys of her own at home. Learn more about her here.
Nine reasons why a child does not want to eat
Komsomolskaya Pravda
House. FamilyMom and babyMom and baby: HealthHealth: parental advice
Anna GERASIMENKO
October 18, 2013 19:10
Small-minded or capricious? Are you afraid or just don't like it? Protests or never been hungry? We are sorting out with a psychologist why children may not have an appetite
- I will not eat your porridge until you buy me a hundred thousand Barbie dolls!0004
“A spoon for mom, a spoon for dad… Eat porridge, otherwise you won’t grow up… If you don’t eat, we won’t let you watch a cartoon…” With persuasion, threats, cunning, with songs and dances, parents try to feed their kids. Studies show that 20 to 60 percent of preschool and school-age children have nutritional problems. More than half of 4-5-year-olds are considered small-toddlers, and among nine-year-olds, 48 percent of children do not eat well.
More than half of 4-5-year-olds are considered small-toddlers, and among nine-year-olds, 48 percent of children do not eat well.
Feeding problems in childhood can lead to growth failure, eating disorders, and learning difficulties in the future. Why don't they eat? Someone doesn’t need much, someone is bored or anxious at the table, someone plays on mom’s nerves like that, and someone can’t do without the help of a neurologist. Together with psychologist Natalia Petrovna GRISHAEVA let's try to figure out what problems can deprive a child of appetite?
REASON 1 Classic little baby. He is thin, all in the parents. And he doesn't need a lot of food. WHAT TO DO: Watch your weight, consult your pediatrician and try to “invest” all the necessary vitamins into that small amount of food.
REASON 2 Protest. The most common reason. Even adults express their protest by hunger strike. The subtext is simple - I will die if you do not do what I want. Children have similar blackmail - pay attention to me! But the reasons for the protest may already be different: - The child attracts attention. Perhaps the situation in the family is not easy - mom and dad are arguing, or divorce, or parents are always at work and devote too little time to the child. "I'll stop eating and they'll notice me." - The child in the family is adored and pampered. He is capricious, selfish and used to being able to behave as badly as he likes, they will forgive him anyway. But children have a sense of inner justice. And in the soul, the child wants to be paid attention to his leprosy, so that everything is “like with people” - he was guilty - punished. He knows what disobedience, like refusing to eat, parents will not be able to forgive. - In the family, the heir is treated too strictly or even cruelly. Everything is forbidden to him, he is scolded for everything. How can a child punish a parent? In their own ways - do not sleep, "walk" in your pants or not eat.
Children have similar blackmail - pay attention to me! But the reasons for the protest may already be different: - The child attracts attention. Perhaps the situation in the family is not easy - mom and dad are arguing, or divorce, or parents are always at work and devote too little time to the child. "I'll stop eating and they'll notice me." - The child in the family is adored and pampered. He is capricious, selfish and used to being able to behave as badly as he likes, they will forgive him anyway. But children have a sense of inner justice. And in the soul, the child wants to be paid attention to his leprosy, so that everything is “like with people” - he was guilty - punished. He knows what disobedience, like refusing to eat, parents will not be able to forgive. - In the family, the heir is treated too strictly or even cruelly. Everything is forbidden to him, he is scolded for everything. How can a child punish a parent? In their own ways - do not sleep, "walk" in your pants or not eat.
WHAT TO DO: Don't be scared, don't beg, don't do everything he asks, don't threaten, but figure out why the child is protesting? What's wrong?
REASON 3 The child is not comfortable at the table Maybe he is forced to eat with a knife and fork, or he is constantly scolded for eating ugly or carelessly. Maybe someone at the table is chomping, and it’s just unpleasant for the baby to watch - the appetite disappears. Maybe at the table, mom and dad usually start to sort things out.
WHAT TO DO: Take care of yourself and postpone all quarrels, do not scold the baby when he squishes, but praise him when he holds the fork beautifully. If the baby is uncomfortable eating with someone who is squishing, feed him separately, it's okay. And do not scold the little one if it gets wet or dirty - it’s better to put an apron on the eater in advance, cover your knees with a napkin - let him enjoy the taste of food without worrying about the rules of etiquette yet.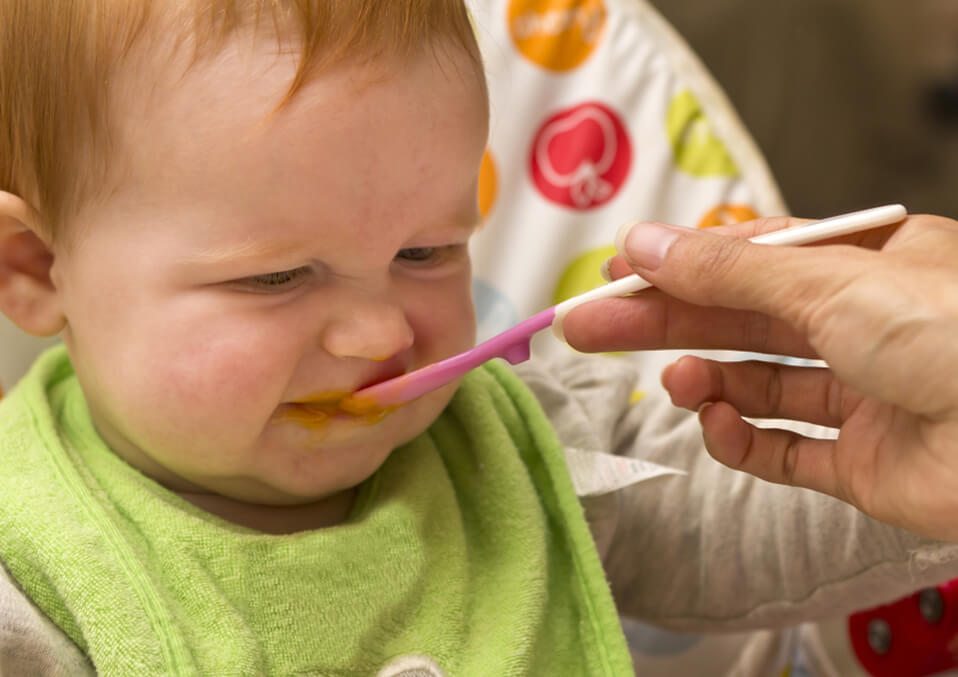
REASON 4 Used to eating with entertainment While the child is picking pasta in the plate, dramas and comedies are played out at the table by mom-dad, grandparents. Songs, dances, puppet theater, cutlets are drawn on the board and crossed out with each bitten piece. The child gets used to being entertained, and simply eating is no longer interesting for him. The same with cartoons. Of course, it is easier for parents when a child, having looked at the TV, crushes everything without looking. For children, the process of eating may seem boring - you have to sit, you have to try to wield spoons and forks, it seems to them that they are just wasting time, and it is much more fun to “spend” it with cartoons.
WHAT TO DO: Do not distract from food and do not eat in front of the TV. It is better to chat during lunch or dinner, come up with a ritual, for example, you tell each other about your best moments of the day at the table, or give each other advice. Doctors are sure that it is important not to be distracted from food so that it is properly digested, and you get all the energy you need.
Doctors are sure that it is important not to be distracted from food so that it is properly digested, and you get all the energy you need.
CAUSE 5 Fear As a rule, these are neurotic reactions caused by some events that frightened the child while eating. For example, a fish bone is stuck in the throat or the baby vomited when he ate something, etc. The child may not remember what exactly scared him, but the “sediment” remained. WHAT TO DO: Do not force, do not shame, do not scold. Understand, look for the cause. And then, it is desirable to get rid of fear together with a psychoneurologist.
REASON 6 Not tasty Such children are called capricious, but perhaps they eat only the usual food - pasta and sausages or potatoes and chicken... Arriving at a hotel or visiting someone, the baby does not find his own food and can refuse any other. WHAT TO DO: Try to regularly introduce your baby to new products from childhood. Do not bring sausages with you to visit, look for a compromise. Patient and playful. Invite your child to look in the refrigerator and choose their own food. He doesn’t like vegetables - make soup puree, try to cut out figures from cucumbers and carrots, fruits can be turned into cocktails, come up with funny names for everything, involve even the smallest gourmet in cooking. Very often, children agree to try a new unfamiliar dish at a party, when everyone else eats it with appetite.
Do not bring sausages with you to visit, look for a compromise. Patient and playful. Invite your child to look in the refrigerator and choose their own food. He doesn’t like vegetables - make soup puree, try to cut out figures from cucumbers and carrots, fruits can be turned into cocktails, come up with funny names for everything, involve even the smallest gourmet in cooking. Very often, children agree to try a new unfamiliar dish at a party, when everyone else eats it with appetite.
REASON 7 Doesn't eat to please mother. For example, it’s time for mom to go to work, but she doesn’t want to, and she says this: “I can’t send Petya to kindergarten, he DOES NOT EAT ANYTHING, I will have to sit at home with him.” And Petya shakes his mustache and does not eat, as his mother “programmed”. Or another option - the mother wants to show everyone that her child is special. WHAT TO DO: Parents to deal with their own fears and complexes.
REASON 8 The cult of food in the family Meals in your house are given too much importance. Mom cooks dinner, and this is an event. Did the child not eat? Catastrophe! Ate? Happiness! The kid quickly realizes that since food is so important, he can control his parents with the help of ate or did not eat. WHAT TO DO: Do not pay so much attention to whether the child is full or not, do not turn lunches and dinners into events. Snack on the road, sometimes skip meals, like all normal people.
Mom cooks dinner, and this is an event. Did the child not eat? Catastrophe! Ate? Happiness! The kid quickly realizes that since food is so important, he can control his parents with the help of ate or did not eat. WHAT TO DO: Do not pay so much attention to whether the child is full or not, do not turn lunches and dinners into events. Snack on the road, sometimes skip meals, like all normal people.
REASON 9 Never been hungry The child does not understand that food can bring joy, he was never hungry, did not wait for dinner, did not dream of soup, because his parents constantly push food into him before he gets hungry. WHAT TO DO : Try not to feed your baby. Accept his food refusals. Wait until he asks for food. Or create an unexpected situation - an empty refrigerator, there is nothing to cook for dinner. There is only, for example, potatoes. The child will want to eat and learn to appreciate the simplest dishes.
Age category of the site 18+
The online publication (website) is registered by Roskomnadzor, certificate El No. FS77-80505 dated March 15, 2021.
FS77-80505 dated March 15, 2021.
I.O. EDITOR-IN-CHIEF OF THE SITE - KANSKY VICTOR FYODOROVICH.
THE AUTHOR OF THE MODERN VERSION OF THE EDITION IS SUNGORKIN VLADIMIR NIKOLAEVICH.
Messages and comments from site readers are posted without preliminary editing. The editors reserve the right to remove them from the site or edit them if the specified messages and comments are an abuse of freedom mass media or violation of other requirements of the law.
JSC "Publishing House "Komsomolskaya Pravda". TIN: 7714037217 PSRN: 1027739295781 127015, Moscow, Novodmitrovskaya d. 2B, Tel. +7 (495) 777-02-82.
Exclusive rights to materials posted on the website www.kp.ru, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation for the Protection of the Results of Intellectual Activity belong to JSC Publishing House Komsomolskaya Pravda, and do not be used by others in any way form without the written permission of the copyright holder.
Acquisition of copyright and contact with the editors: [email protected]
The child does not eat much and generally does not like to sit at the table: what to do
Why does the child not eat anything? Is it worth it to force him and how to feed him in general? The teacher-psychologist of the highest category Ekaterina Matrenina answers.
Question. The child is 4 years old. He does not sit at the table, runs away, eats very little - literally two spoons. He doesn’t listen to any persuasion, maybe he doesn’t eat at all all day. In the garden, they complain about him that he himself does not eat and prevents children from eating. He loves sweets, but if he doesn't get them, he still doesn't eat anything. Active and even too touchy, persistent, does not want to talk and stubbornly stands his ground. It becomes more and more difficult to contact him. It can only be stopped by shouting or coercion. What to do?
Answer. Child nutrition is based on rituals - they are especially important for children of early and preschool age. By the age of four, the child has already formed all the skills associated with eating. He eats with a spoon and fork on his own, drinks from a mug, cleans up the dishes himself. Children at this age can accurately recognize the feeling of hunger and ask for food.
By the age of four, the child has already formed all the skills associated with eating. He eats with a spoon and fork on his own, drinks from a mug, cleans up the dishes himself. Children at this age can accurately recognize the feeling of hunger and ask for food.
To understand why a child refuses to eat, you need to pay attention to how meals are organized in the family. Here are typical situations due to which a child does not want to sit down at the table and eat:
- Many parents feed their children in front of the TV or on the go. At the same time, the child does not understand what kind of food and in what quantities he ate. Such feeding methods very quickly become a habit - as a result, the child cannot eat at the table without the cartoon turned on.
- Out of fear of leaving the child hungry, parents give him various snacks between meals: for example, cookies, bread, sweets.
- Parents force-feed their child. This approach to eating leads not only to behavioral problems, but also to various diseases (for example, obesity).

- It is not accepted in the family to eat all together at the table at the allotted time. Each family member eats at a time convenient for him, in a place convenient for him, because of which the child does not form any norms and eating habits. At 4 years old, a child is quite capable of adapting to the diet of adults. However, if the parents do not have such a regime, then the child will also have problems.
How to help your child improve their eating habits
The first thing parents need to do is to overcome their fear of “leaving their child hungry”. If he really feels hungry, he will not be silent. Give your child a chance to get hungry. Then offer to sit down at the table, having previously given a choice. Ask him what he would like to eat? Use the "choice without choice" technique - offer options that are available, for example: soup or buckwheat porridge.
Parents need to understand that their greatest help to a child is to lead by example.