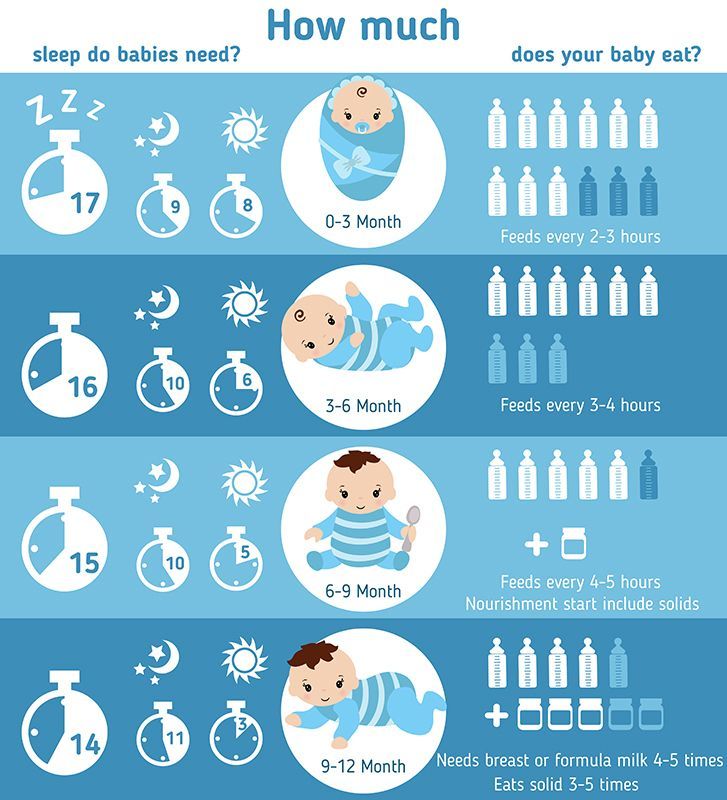
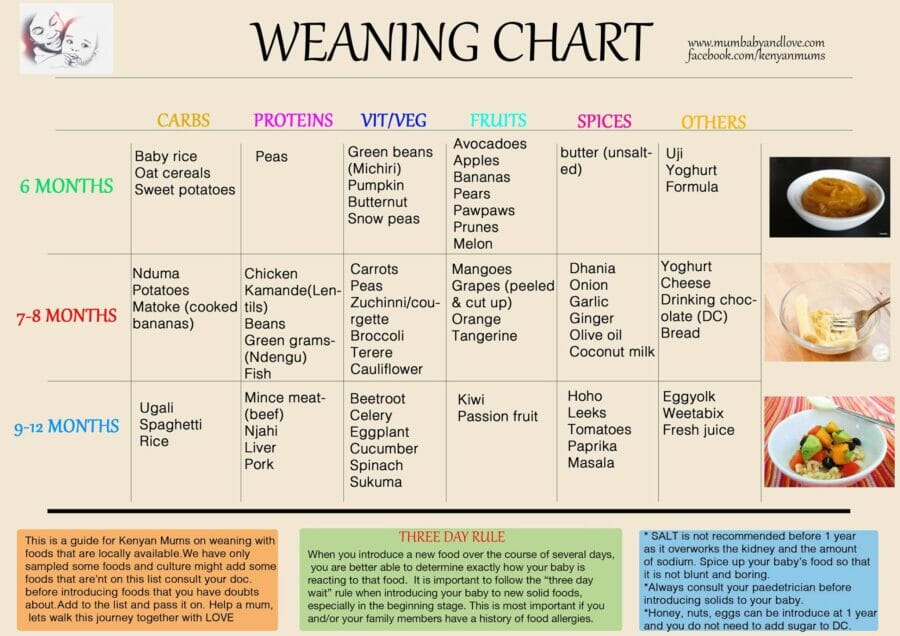
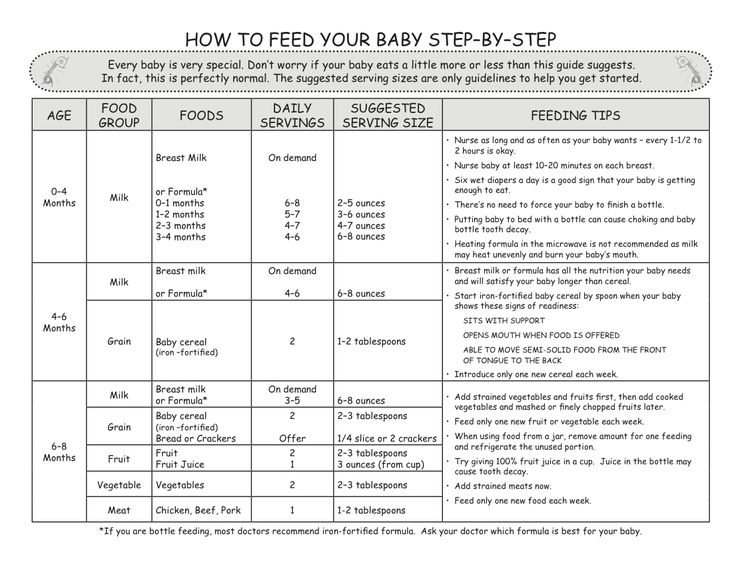
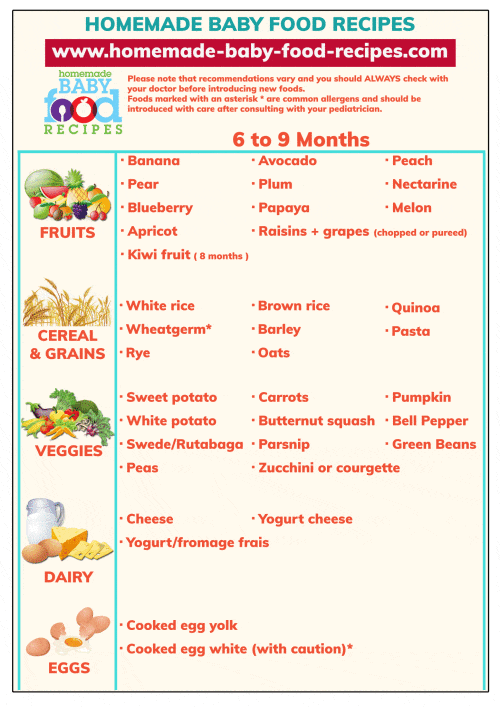
Feeding a baby with diarrhea
When your child has diarrhea Information | Mount Sinai
Drinking Fluids
It is easy for a child with diarrhea to lose too much fluid and become dehydrated. Lost fluids need to be replaced. For most children, drinking the kinds of fluids they normally have should be enough.
Some water is OK. But too much water alone, at any age, can be harmful.
Other products, such as Pedialyte and Infalyte, may help keep a child well-hydrated. These products can be bought at the supermarket or pharmacy.
Popsicles and Jell-O can be good sources of fluids, especially if your child is vomiting. You can slowly get large amounts of fluids into children with these products.
You may also give your child watered-down fruit juice or broth.
Do not use medicines to slow down your child's diarrhea without talking to a doctor first. Ask your child's health care provider if using sports drinks is OK.
Diet for Children With Diarrhea
In many cases, you can continue feeding your child as usual. The diarrhea will normally go away in time, without any changes or treatment. But while children have diarrhea, they should:
- Eat small meals throughout the day instead of 3 big meals.
- Eat some salty foods, such as pretzels and soup.
When necessary, changes in the diet may help. No specific diet is recommended. But children often do better with bland foods. Give your child foods such as:
- Baked or broiled beef, pork, chicken, fish, or turkey
- Cooked eggs
- Bananas and other fresh fruits
- Applesauce
- Bread products made from refined, white flour
- Pasta or white rice
- Cereals such as cream of wheat, farina, oatmeal, and cornflakes
- Pancakes and waffles made with white flour
- Cornbread, prepared or served with very little honey or syrup
- Cooked vegetables, such as carrots, green beans, mushrooms, beets, asparagus tips, acorn squash, and peeled zucchini
- Some desserts and snacks, such as Jell-O, popsicles, cakes, cookies, or sherbet
- Baked potatoes
In general, removing seeds and skins from these foods is best.
Use low-fat milk, cheese, or yogurt. If dairy products are making the diarrhea worse or causing gas and bloating, your child may need to stop eating or drinking dairy products for a few days.
Children should be allowed to take their time returning to their normal eating habits. For some children, a return to their regular diet can also bring a return of diarrhea. This is often due to mild problems the gut has while absorbing regular foods.
Things Your Child Should Avoid Eating or Drinking
Children should avoid certain kinds of foods when they have diarrhea, including fried foods, greasy foods, processed or fast foods, pastries, donuts, and sausage.
Avoid giving children apple juice and full-strength fruit juices, as they can loosen stool.
Have your child limit or cut out milk and other dairy products if they are making diarrhea worse or causing gas and bloating.
Your child should avoid fruits and vegetables that can cause gas, such as broccoli, peppers, beans, peas, berries, prunes, chickpeas, green leafy vegetables, and corn.
Your child should also avoid caffeine and carbonated drinks at this time.
When children are ready for regular foods again, try giving them:
- Bananas
- Crackers
- Chicken
- Pasta
- Rice cereal
When to Call the Doctor
Call your child's provider if your child has any of these symptoms:
- Much less activity than normal (not sitting up at all or not looking around)
- Sunken eyes
- Dry and sticky mouth
- No tears when crying
- Not urinated for 6 hours
- Blood or mucus in the stool
- Fever that does not go away
- Stomach pain
Easter JS. Pediatric gastrointestinal disorders and dehydration. In: Bakes KM, Buchanan JA, Moreira ME, Byyny R, Pons PT, eds. Emergency Medicine Secrets. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 65.
Pediatric gastrointestinal disorders and dehydration. In: Bakes KM, Buchanan JA, Moreira ME, Byyny R, Pons PT, eds. Emergency Medicine Secrets. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 65.
Kotloff KL. Acute gastroenteritis in children. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 366.
Schiller LR, Sellin JH. Diarrhea. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 16.
Last reviewed on: 12/10/2021
Reviewed by: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Diarrhea (0-12 Months)
Is this your child's symptom?
- Sudden increase in the number and looseness of stools
- Diarrhea means 3 or more watery or very loose stools.
 Reason: 1 or 2 loose stools can be normal with changes in diet.
Reason: 1 or 2 loose stools can be normal with changes in diet.
Causes of Acute Diarrhea
- Virus (such as Rotavirus). An infection of the intestines from a virus is the most common cause.
- Bacteria (such as Salmonella). Less common cause. Diarrhea often contains streaks of blood.
- Giardia (a parasite). More likely in child care center outbreaks.
- Antibiotic Diarrhea. Many antibiotics cause mild diarrhea. This is not an allergic reaction. Keep giving the antibiotic. Call your doctor if any serious symptoms occur.
- Serious Causes. Most bacterial diarrhea goes away on its own. A few can cause a severe large bowel infection (such as Shigella colitis). C. difficile is a serious cause that can occur after being on strong antibiotics.
- Serious Complication: Dehydration. This is the health problem where the body has lost too much fluid.
 (See below for more on this).
(See below for more on this).
Causes of Recurrent Diarrhea
- Cow's Milk Allergy. Can cause loose, slimy stools in babies. Can be blood-streaked. Starts within the first 2 months of life. Need to avoid cow's milk formulas.
- Lactose Intolerance. Lactose is the sugar in milk. Many people cannot absorb lactose. The gut bacteria convert the lactose to gas. The main symptoms are a lot of gas, loose stools and stomach bloating. Onset usually at age 4 or 5. This most often runs in the family (genetic).
Diarrhea Scale
- Mild: 3-5 watery stools per day
- Moderate: 6-9 watery stools per day
- Severe: 10 or more watery stools per day
- The main risk of diarrhea is dehydration.
- Loose or runny stools do not cause dehydration.
- Frequent, watery stools can cause dehydration.
Dehydration: How to Know
- Dehydration means that the body has lost too much fluid.
 This can happen with vomiting and/or diarrhea. A weight loss of more than 3% is needed. Mild diarrhea or mild vomiting does not cause this. Neither does a small decrease in fluid intake.
This can happen with vomiting and/or diarrhea. A weight loss of more than 3% is needed. Mild diarrhea or mild vomiting does not cause this. Neither does a small decrease in fluid intake. - Dehydration is the most important complication of diarrhea. Dehydration is a reason to see your doctor right away.
- These are signs of dehydration:
- Decreased urine (no urine in more than 8 hours) happens early in dehydration. So does a dark yellow color. If the urine is light straw colored, your child is not dehydrated.
- Dry tongue and inside of the mouth. Dry lips are not helpful.
- Dry eyes with decreased or absent tears
- In babies, a depressed or sunken soft spot
- Slow blood refill test: Longer than 2 seconds. First, press on the thumbnail and make it pale. Then let go. Count the seconds it takes for the nail to turn pink again. Ask your doctor to teach you how to do this test.
- Fussy, tired out or acting ill. If your child is alert, happy and playful, he or she is not dehydrated.

Diarrhea in Breastfed Babies: How to Tell
- Diarrhea in a breastfed baby is sometimes hard to tell.
- Normal breastfed stools are loose (often runny and seedy). Stools are yellow, but sometimes can be green. The green color is from bile. Runny stools can even be bordered by a water ring. These are all normal stools.
- Breastfed babies often pass more than 6 stools per day. Until 2 months of age, they may pass a stool after each feeding. But, if stools suddenly increase in number and looseness, suspect diarrhea. If it lasts for 3 or more stools, the baby has diarrhea.
- If the stools contain mucus, blood or smell bad, this points to diarrhea.
- Other clues to diarrhea are poor eating, acting sick, or a fever.
Diarrhea in Formula-Fed Infants: How to Tell
- Formula-fed babies pass 1 to 8 stools per day during the first week. Then it starts to slow down to 1 to 4 per day. This lasts until 2 months of age.
- The stools are yellow in color and thick like peanut butter.

- Suspect diarrhea if the stools suddenly increase in number or looseness. If it lasts for 3 or more stools, the baby has diarrhea.
- If the stools contain mucus, blood, or smells bad, this points to diarrhea.
- Other clues to diarrhea are poor eating, acting sick or a fever.
- After 2 months of age, most babies pass 1 or 2 stools per day. They can also pass 1 every other day. They no longer appear to have mild diarrhea.
When to Call for Diarrhea (0-12 Months)
Call 911 Now
- Not moving
- You think your child has a life-threatening emergency
Call Doctor or Seek Care Now
- Dehydration suspected. No urine in over 8 hours, dark urine, very dry mouth and no tears.
- Blood in the stool
- Constant stomach pain lasts more than 2 hours
- Vomits 3 or more times
- Age less than 1 month with 3 or more diarrhea stools in past 24 hours
- Severe diarrhea. 10 or more watery stools in the last 24 hours.

- Fever over 104° F (40° C)
- Fever in baby less than 12 weeks old. Caution: Do NOT give your baby any fever medicine before being seen.
- Weak immune system. Examples are sickle cell disease, HIV, cancer, organ transplant, taking oral steroids.
- Your child looks or acts very sick
- You think your child needs to be seen, and the problem is urgent
Contact Doctor Within 24 Hours
- Moderate diarrhea. 6 or more watery stools in the last 24 hours.
- Stomach pains that do not go away after each diarrhea stool
- Fever lasts more than 3 days
- Close contact with person or animal who has bacterial diarrhea
- Contact with reptile (snake, lizard, turtle) in past 14 days
- Travel to country at risk for diarrhea within past month
- You think your child needs to be seen, but the problem is not urgent
Contact Doctor During Office Hours
- Diarrhea lasts more than 2 weeks
- Loose stools are a frequent problem
- You have other questions or concerns
Self Care at Home
- Mild diarrhea (probably caused by a virus)
Seattle Children's Urgent Care Locations
If your child’s illness or injury is life-threatening, call 911.
- Bellevue
- Everett
- Federal Way
- Seattle
- Virtual Urgent Care
Care Advice for Diarrhea
- What You Should Know About Diarrhea:
- Most diarrhea is caused by a virus.
- Bacterial infections as a cause of diarrhea are not common.
- Diarrhea is the body's way of getting rid of the germs.

- The main risk of diarrhea is dehydration. Dehydration means the body has lost too much fluid.
- Most children with diarrhea don't need to see their doctor.
- Here are some tips on how to keep ahead of the fluid losses.
- Mild Diarrhea:
- Most kids with diarrhea can eat a normal diet.
- Drink more fluids to prevent dehydration. Formula or breastmilk are good choices for diarrhea.
- Do not use fruit juices. Reason: They can make diarrhea worse.
- Solid foods: If on solid foods, eat more starchy foods (such as cereal, crackers, rice, pasta). Reason: They are easy to digest.
- Formula-Fed Babies with Frequent, Watery Diarrhea:
- Keep giving formula but feed more often. Offer as much formula as your child will take.
- Mix formula the normal way. Reason: The formula contains plenty of water and doesn't need more.
- Solid foods: If on baby foods, continue them. Cereals are best.

- Breastfed Babies with Frequent, Watery Diarrhea:
- Give your baby breastmilk more often.
- Also, give extra fluid if breast milk isn't keeping up with the fluid losses. You can use formula or ORS (Pedialyte).
- Solid foods: If on baby foods, continue them. Cereals are best.
- Oral Rehydration Solutions (ORS), such as Pedialyte:
- ORS is a special fluid that can help your child stay hydrated. You can use Pedialyte or the store brand. It can be bought in food stores or drug stores.
- When to use: Start ORS for frequent, watery diarrhea if you think your child is getting dehydrated. That means passing less urine than normal. Increase fluids using ORS. Continue giving breastmilk, formula or regular milk.
- Amount: For babies, give 2-4 ounces (60-120 mL) of ORS after every large watery stool.
- Caution: Do not give ORS as the only fluid for more than 6 hours. Reason: Your child will need calories and cry in hunger.

- Fever Medicine:
- For fevers above 102° F (39° C), give an acetaminophen product (such as Tylenol).
- Another choice is an ibuprofen product (such as Advil). Caution: avoid ibuprofen until 6 months or older.
- Note: Fevers less than 102° F (39° C) are important for fighting infections.
- For all fevers: Keep your child well hydrated. Give lots of cold fluids.
- Diaper Rash - Prevention:
- Wash buttocks after each stool to prevent a bad diaper rash.
- To protect the skin, use an ointment (such as Vaseline or Desitin). Put it on the skin around the anus.
- Return to Child Care:
- Your child can go back to child care after stools are back to normal.
- The fever should also be gone.
- What to Expect:
- Viral diarrhea lasts 5-14 days.
- Severe diarrhea only occurs on the first 1 or 2 days. But, loose stools can last for 1 to 2 weeks.

- Call Your Doctor If:
- Blood in the diarrhea
- Dehydration suspected (no urine in over 8 hours, dark urine, very dry mouth, and no tears)
- Diarrhea lasts over 2 weeks
- You think your child needs to be seen
- Your child becomes worse
And remember, contact your doctor if your child develops any of the 'Call Your Doctor' symptoms.
Disclaimer: this health information is for educational purposes only. You, the reader, assume full responsibility for how you choose to use it.
Last Reviewed: 02/28/2023
Last Revised: 12/30/2022
Copyright 2000-2023 Schmitt Pediatric Guidelines LLC.
Diet for diarrhea in a 1-year-old child
When a child is sick, it is always a serious test for a family. Moreover, if the baby has vomiting, frequent loose stools, fever, he refuses to eat. In such cases, parents naturally face the question: what to do?
The first thing to do is to see a doctor. In most cases, this condition is associated with an acute intestinal infection and can lead to serious consequences for the baby. And timely treatment allows you to quickly deal with the problem.
In most cases, this condition is associated with an acute intestinal infection and can lead to serious consequences for the baby. And timely treatment allows you to quickly deal with the problem.
The second significant issue facing the parents of a sick child is the issue of proper nutrition. Unfortunately, you can still find recommendations to stop feeding a child during diarrhea, but this should not be done categorically.
Important!
It has been proven that "water-tea" breaks and starvation diets significantly weaken the protective functions of the child's body and lead to a delay in recovery processes in the intestines. Therefore, at present, most pediatricians insist on the mandatory continuation of the child's nutrition in case of acute intestinal infections, but with the obligatory consideration of the latest achievements in nutrition.
The main principles for managing the nutrition of a child with diarrhea should be:
| Phased | The development of the disease has a staging, each stage must correspond to certain approaches to diet therapy |
| Accounting for the age of the child | Each age should have its own products and its own schemes for their purpose |
| Accounting for the severity of the disease |
There are three main stages of diet therapy. The first stage corresponds to the acute period of the disease, when the maximum manifestations of the disease are noted (vomiting, loose stools, fever), and the child may refuse his usual diet. During this period, proper nutrition is an integral part of treatment. And the success of treatment largely depends on the correct organization of diet therapy in a child.
The first stage corresponds to the acute period of the disease, when the maximum manifestations of the disease are noted (vomiting, loose stools, fever), and the child may refuse his usual diet. During this period, proper nutrition is an integral part of treatment. And the success of treatment largely depends on the correct organization of diet therapy in a child.
The second stage is the recovery period. There are no longer those manifestations of the disease that were noted in the baby in the acute period, the child has an appetite, he becomes more active, but it must be remembered that any acute intestinal infection leads to significant changes in the child's body. This is a violation of the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract, and dysfunction of enzyme systems, bile secretion and other digestive processes. It takes time to restore the correct functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, which requires a sparing diet at this stage. Violation of the diet during this period can lead to the formation of a chronic pathology of the gastrointestinal tract.
The third stage of diet therapy is aimed at a gradual transition to the usual diet for this baby. Breastfed babies should continue to breastfeed. If the baby is bottle-fed, the doctor will prescribe a formula that matches the baby's condition. In children older than one year, it is necessary to exclude whole milk from the diet, they are also shown the appointment of fermented milk products as a diet therapy, the favorable properties of which are due to a number of positive qualities: the presence of lactic acid gives the product pronounced bactericidal properties and inhibits the growth of pathogenic microflora, the positive effect of these products on intestinal microbiocenosis, the secretory function of the digestive glands and intestinal motility, and they also have immunomodulatory properties.
One of the important components of diet therapy is the use of dairy-free cereals with pro- and synbiotics. Clinical studies have shown that the appointment of this diet therapy contributes to a more rapid relief of the main symptoms of intestinal dysfunction, as well as the restoration of intestinal microflora.
Choose foods for the diet
It is most correct to start with rice porridge, as it has pronounced sorption properties and helps to stop diarrhea. As the child recovers, oatmeal and buckwheat porridge can be included in the diet.
Vegetables and fruits are an important component in the first stage of diet therapy. Preference should be given to products that contain pectin (baked apple, boiled carrots), as they contribute to the sorption of pathogens and their toxins. At the first stage of diet therapy, the use of fresh vegetables and fruits, as well as juices, is not shown.
The second stage - the patient's condition improves, the child becomes active, appetite improves, and in some children it even becomes elevated, which is often perceived by parents as a signal for increased nutrition. It is absolutely impossible to do this, since the child's body has not yet recovered from the disease. During this period, it is necessary to continue eating sour-milk, lactose-free and low-lactose products. An obligatory component of diet therapy is the use of nutrition with probiotics.
An obligatory component of diet therapy is the use of nutrition with probiotics.
The third stage is the gradual expansion of the diet according to the age of the child. At this stage, the most justified is the widespread use of probiotic foods in order to restore and maintain the function of the gastrointestinal tract and its microbiocenosis.
What to feed a child with diarrhea at first?
- freshly cooked rice;
- bananas;
- natural apple juice;
- boiled potatoes;
- boiled chicken meat;
- crackers and stale bread;
- lean fish;
- weak tea.
What can you eat with diarrhea in a child and an adult | Diet for diarrhea
Co-author, editor and medical expert - Klimovich Elina Valerievna.
Number of views: 2 902 536
Date last updated:0003
What can you eat if you have diarrhea?
What to drink with diarrhea?
What should I avoid if I have diarrhea?
What is diarrhea and how to treat it
It is very important to adjust your diet and eating habits to help your body cope with the problem as effectively as possible.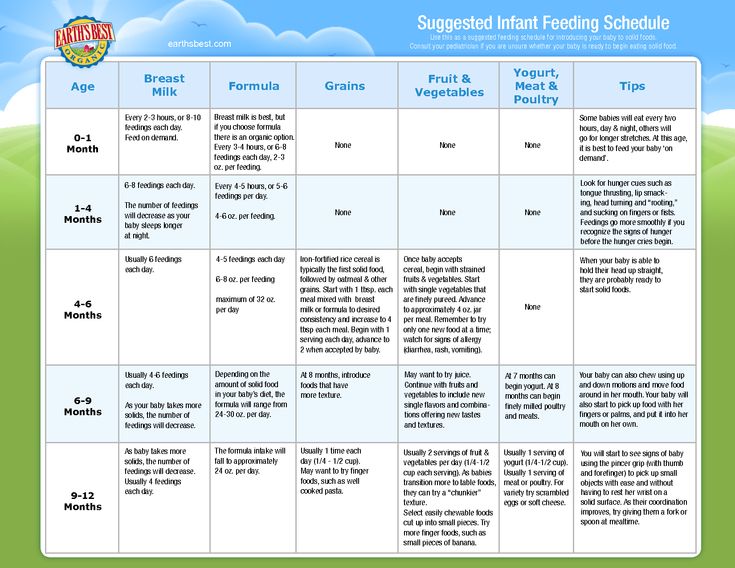 If you do not know what to eat with diarrhea, use our recommendations.
If you do not know what to eat with diarrhea, use our recommendations.
Top of page
What can you eat with diarrhea?
- Diet for diarrhea should include foods high in pectin: applesauce, bananas, yogurt. Pectin - water-soluble fiber - helps to cope with indigestion.
- Pay attention to foods rich in potassium - fruit juices, jacket potatoes, bananas. When the intestines are upset, the body actively loses potassium and its restoration is necessary.
- Don't forget to add salt to your meals. Meals should include salty soups, broths, crackers, etc., which will help retain water in the body and stay hydrated.
- Get enough protein. With an upset stomach, you can eat lightly fried beef, turkey, chicken, or hard-boiled eggs to avoid fatigue and fatigue.
- Eat hot processed vegetables and fruits. Some raw vegetables and fruits can make diarrhea worse. When dieting, try a simple soup with asparagus, carrots, beets, zucchini, mushrooms or celery, mashed potatoes or jacket potatoes.

Back to Contents
What to drink with diarrhea?
Drink at least a glass of fluid after each bout of diarrhea to prevent dehydration. In case of intestinal upset, drink water, weak tea, apple juice, low-fat broth. A liquid diarrhea diet does not burden the digestive tract with heavy work and helps prevent irritation.
Back to Contents
What Should I Avoid When I Have Diarrhea?
- Avoid caffeinated drinks and foods that are very hot or cold. It will irritate the gastrointestinal tract.
- Avoid fatty, fried and heavy foods during the diet. Such a diet will only exacerbate intestinal upset.
- Avoid foods that cause gas in the intestines - chewing gum, carbonated drinks. They irritate the digestive tract.
- Limit milk and dairy products. They can be hard to digest.
- Avoid nuts, raw fruits and vegetables, bran and whole grain bread in your diet. They irritate the digestive tract.