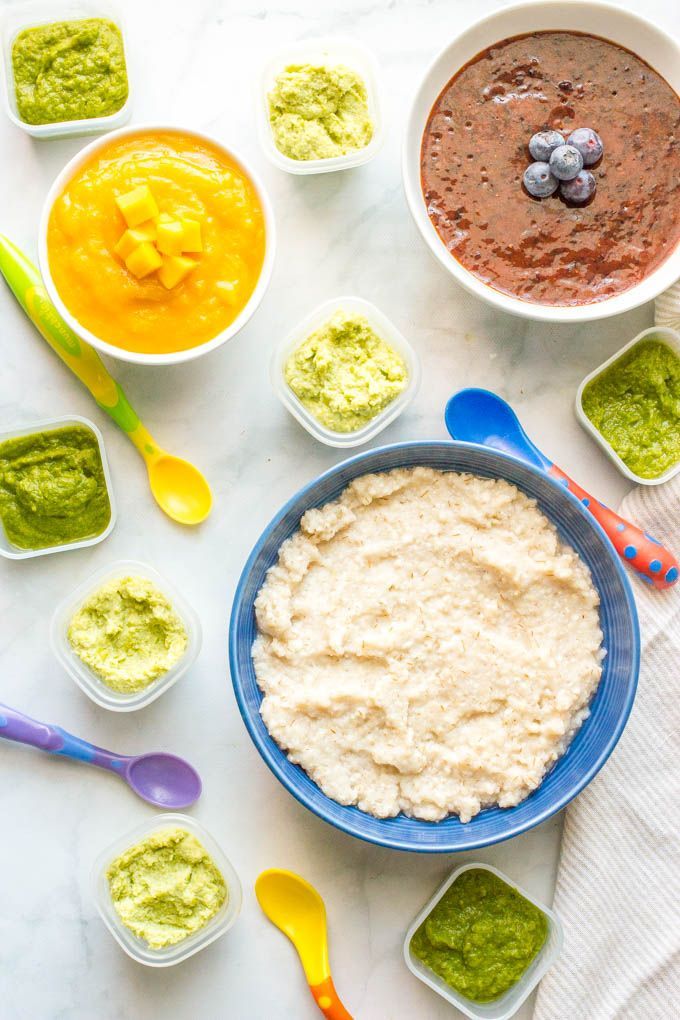
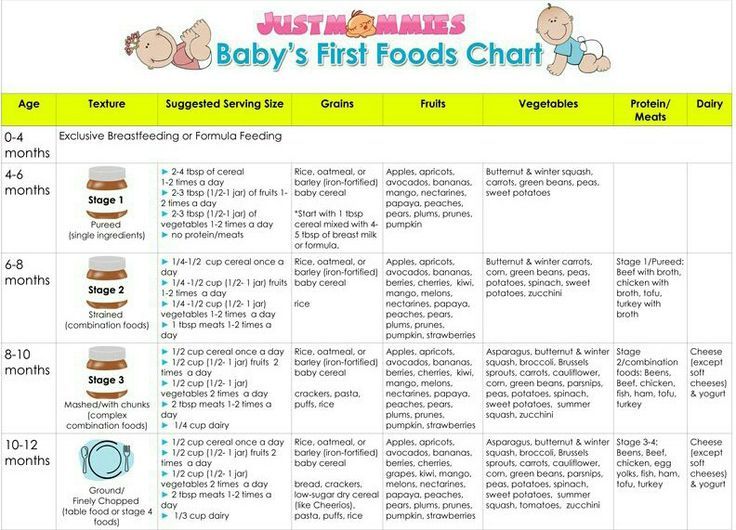
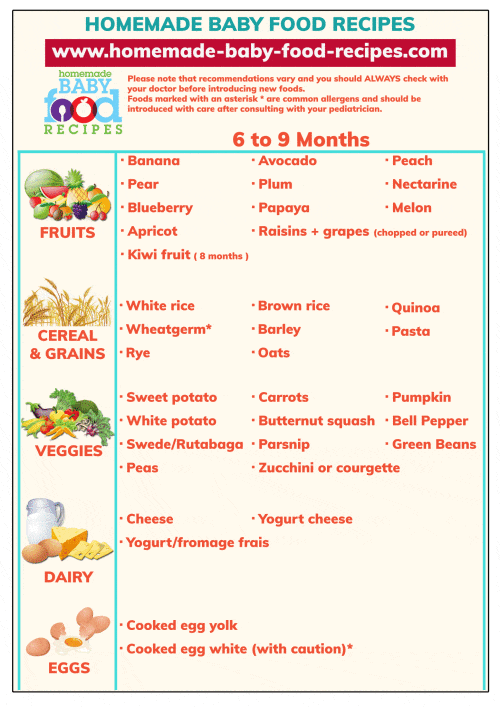
Food to eat while trying for a baby
Trying to Conceive - Diet Tips & What to Eat
A healthy start
The role of diet in conception
From eating a nutrient-rich diet to taking key nutrients in the form of supplements, what you eat can play an important role in increasing your potential to conceive. Discover the benefits of a balanced diet for both you and your partner, and which foods to include to give yourself the best chance of a successful pregnancy.
Expert advice
Get the support you need, the moment you need it
Join now for FREE
Eating your way to pregnancy
Before you start trying to conceive, it's important for both you and your partner to maintain a healthy diet. Eating well, avoiding alcohol, and being within the right weight range for your height will improve your chances of conceiving and will set the conditions for the optimum development of your baby during pregnancy1
The nutritional status of a woman before and during pregnancy influences the growth and development of her baby, forming the foundations for their future health².
What mum eats matters
Paying attention to your diet is important when you're trying for a baby. If you have low nutrient stores prior to pregnancy, you'll have less to maintain your baby’s growth and development during pregnancy, while a lack of vitamins and minerals may impact your health and well-being too3.
Getting in shape
What you weigh can be as important as what you eat. Maintaining a healthy weight prior to conception can help safeguard your baby’s future health and development. Having a BMI of between 20 and 25, can help reduce the risk of having a low birth weight baby, and pregnancy complications such as high blood pressure and diabetes3.
Use the NHS Choices' tool to calculate your BMI to see if you are a healthy weight for pregnancy.
Being underweight
Your weight also plays a part in your fertility. If you are underweight (with a BMI under 20) you're less likely to conceive.
Women who have a low BMI (under 20) are less likely to conceive⁴.
However research has shown that women who are well below the average or ideal weight can still conceive3, so try not to worry if you fall into this category. Increasing your calorie intake, sensibly, by increasing your portion sizes at mealtimes and including nutritious snacks throughout the day is a good way to gain any necessary weight.
Being overweight
If you have a BMI above 25, your ovulation cycle and response to fertility treatment may be affected. Some women choose to lose weight before trying to conceive, as dieting is not recommended during pregnancy.
Being overweight does not prevent all women from conceiving⁵.
Whilst many overweight mums can conceive naturally, a prospective study of women who were not ovulating has shown that a simple weight loss and physical activity programme can result in natural ovulation, conception and successful pregnancy6. Being overweight during pregnancy may also increase your risk of certain complications, such as higher caesarean section rates and lower breastfeeding rates after delivery17.
What dad eats matters too
While it is not yet fully understood, there are a number of factors, including diet, thought to influence male fertility7. For this reason, it is advisable for prospective dads to pay attention to their diet too. It's also a good idea for dad to keep his weight in check too as overweight parents have been linked to increased obesity risk in their children18.
Low intake of fruit and vegetables has been associated with low sperm count.⁷
Zinc (found in meat, shellfish and milk), selenium (brazil nuts, fish and meat) and vitamin C (oranges, red/green peppers and potatoes) may be of particular importance for sperm production8.
Your ‘what to eat’ checklist when trying to conceive
Ensuring you eat the right foods in the right quantities will help you achieve a balanced diet and may increase your chances of conceiving. This means eating from all of the food groups below, every day:
- Bread, rice, potatoes and other starchy foods. Base your meals on these and choose wholegrain varieties for their fibre content. You'll also get calcium, iron and B vitamins9.
- Fruit and vegetables. Fresh, frozen or canned (avoid those with added salt). Five (x 80g) portions per day are recommended. Variety is key to ensuring a range of nutrients10.

Smoothies only count as 1 of your 5-a-day if the skins and pulp of the fruit are included.
- Milk and dairy foods. Two-three portions of milk, yogurt or cheese are a good source of calcium. Choose lower-fat versions and avoid unpasteurised milk or cheeses11.
- Meat, fish, eggs, beans and nuts. Aim for two portions a day, except for fish, which should be eaten twice a week (with one serving being oily fish). Eating fish is good for your health and the development of your baby. However, there are some types of fish to avoid in pregnancy due to their high levels of mercury12.
Tinned tuna doesn’t count as oily fish, so you can eat this in addition to your maximum of 2 portions a week but do not eat more than four medium sized tins of tuna per week when you are planning a pregnancy or are pregnant.
¹³
- Fluids. To avoid dehydration, drink 1.5–2 litres (or six–eight 200ml glasses) of water, milk, soup, squash or fruit juices. After exercising or in hot weather, you will need more. It's recommended that you limit your intake of caffeine to 200mg per day to avoid risks or complications during pregnancy14.
- Fat and sugar. Unsaturated fats, like oily fish, nuts and seeds, avocados and olive oil, can help to lower cholesterol and provide essential fatty acids. Saturated fats should be kept to a minimum – 20g a day for women and 30g for men15. And sugar should make up no more than 10% of your daily diet – about 50g or ten teaspoons per day for women16.
Omega 3, found in oily fish, contributes to normal brain and eye development, so is an important nutrient to eat before and during pregnancy.¹²
In addition to these foods, folic acid and vitamin D supplements are an important part of your conception diet. Find out more about these prenatal supplements.
Find out more about these prenatal supplements.
Next steps
Ways to enhance your conception diet:
- Take a folic acid supplement (400mcg) daily for at least three months before conception and for the first trimester of pregnancy
- A 10 mcg vitamin D supplement is recommended every day throughout your pregnancy so it may be a good idea to start taking it if you are trying to conceive
- Swap white bread and pasta for wholemeal varieties
- Eat two portions of oily fish a week – try salmon, mackerel, trout or herring
- Eat five portions of fruit and vegetables a day – one portion = one apple, or two satsumas, or one heaped tbsp of raisins, or three heaped tbsp of cooked carrots
- Drink 1.5–2 litres of fluids a day (preferably water)
View references
1. NHS UK. Protect your fertility [Online]. Available at: www.nhs.uk/Livewell/Fertility/Pages/Protectyourfertility.aspx[Accessed May 2014]
2. Gluckman PD et al. The developmental origins of adult disease. Matern Child Nutr 2005;1:130–141.
Gluckman PD et al. The developmental origins of adult disease. Matern Child Nutr 2005;1:130–141.
3. NHS UK. Have a healthy diet in pregnancy [Online]. Available at: www.nhs.uk/conditions/pregnancy-and-baby/pages/healthy-pregnancy-diet.aspx [Accessed May 2014]
4. Zaadstra et al. Fat and female fecundity:prospective study of the effect of body fat distribution on conception rates. Br Med J 1993;306:484-487.
5. The Centre for Pregnancy Nutrition, University of Sheffield, 2005.
6. Clark et al. Weight loss in infertile women results in improvement in reproductive outcome for all forms of infertility treatment. Hum Reprod 1998;13:1502-1505.
7. Wong et al. New evidence of the influence of exogenous factors on sperm count in man. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2003;110:49-54.
8. Tas et al. Occupational hazards for the male reproductive system. Crit Rev Toxicol 1996;26:261-307.
9. NHS UK. Starchy foods [Online]. Available at: www.nhs.uk/Livewell/Goodfood/Pages/starchy-foods. aspx[Accessed May 2014]
aspx[Accessed May 2014]
10. NHS UK. 5 a day [Online]. Available at: www.nhs.uk/LiveWell/5ADAY/Pages/5ADAYhome.aspx [Accessed May 2014]
11. NHS UK. Milk and dairy foods [Online]. Available at: www.nhs.uk/Livewell/Goodfood/Pages/milk-dairy-foods.aspx[Accessed May 2014]
12. NHS UK. Fish and shellfish [Online]. Available at: www.nhs.uk/Livewell/Goodfood/Pages/fish-shellfish.aspx[Accessed May 2014]
13. Patient UK. Diet and lifestyle during Pregnancy [Online]. Available at: http://patient.info/health/diet-and-lifestyle-during-pregnancy [Accessed May 2014]
14. NHS UK. Water and drinks [Online]. Available at: www.nhs.uk/livewell/goodfood/pages/water-drinks.aspx [Accessed May 2014]
15. NHS UK. Eat less saturated fat [Online]. Available at: www.nhs.uk/livewell/goodfood/pages/Eat-less-saturated-fat.aspx[Accessed May 2014]
16. NHS UK. How much sugar is good for me? [Online]. Available at: www.nhs.uk/chq/pages/1139.aspx [Accessed May 2014]
17. Abdelmaboud et al (2012) Increase in moderate and extreme obesity in pregnancy. IMJ Vol 105; 5
IMJ Vol 105; 5
18. Kelly et al (2011) A comparison of maternal and paternal BMI in early pregnancy Aust NZ Journal Obs Gyn Apr 51(2):147-150
Last reviewed: 4th July 2016
Foods That Make You Fertile - Pregnancy Center
There’s no shortage of old wives’ tales (and Internet legends) touting the fertility benefits of certain foods — and the baby-busting potential of others. And if you’re thinking about starting a baby making campaign (or you’re already waging one), you’re probably wondering which are fertility fact…and which, fertility fiction. The truth is, you can get pregnant no matter what you eat — and no matter what you don’t eat. But there is some fascinating, if preliminary, research showing that your fertility may be what you eat — and that filling your belly with certain foods (and avoiding others) may just help you fill your belly with a baby faster. The scientific jury’s still debating the food-fertility connection (or is there one?), but in the meantime it’s definitely interesting food for thought. And speaking of food, take the following list with a grain of salt (and a prenatal vitamin — which is a proven preconception must). Fill up on those foods that have fertility promise (they’re all healthy anyway), and avoid as best you can foods researchers have speculated may decrease your chances of conceiving. Bottom line (and you don’t need a scientist to tell you this): eat a nutritious, balanced prepregnancy diet, and you’re likely fueling your fertility. Make a diet of junk food and fast food, and you’re probably not doing your fertility a favor.
And speaking of food, take the following list with a grain of salt (and a prenatal vitamin — which is a proven preconception must). Fill up on those foods that have fertility promise (they’re all healthy anyway), and avoid as best you can foods researchers have speculated may decrease your chances of conceiving. Bottom line (and you don’t need a scientist to tell you this): eat a nutritious, balanced prepregnancy diet, and you’re likely fueling your fertility. Make a diet of junk food and fast food, and you’re probably not doing your fertility a favor.
Fertility-Friendly Foods
- Dairy. It pays to bone up on dairy (milk, yogurt, and cheese) when you’re trying to conceive. Adding dairy to your preconception diet is good not only for bone health but also — potentially — for your reproductive health. So drink that milk, spoon up that yogurt, sip that smoothie, nibble on that cheese. Sticking to low-fat or fat-free dairy products makes sense most of the time, especially if you’re trying to lower your bottom line preconception (after all, extra weight can weigh on fertility).
 But there is some early research showing that women who have problems with ovulation may benefit from splurging on a serving a day of full-fat dairy. Before you dip too far into the Ben & Jerry’s, though, remember that overdoing the full-fat will defeat the purpose if it packs on the pounds.
But there is some early research showing that women who have problems with ovulation may benefit from splurging on a serving a day of full-fat dairy. Before you dip too far into the Ben & Jerry’s, though, remember that overdoing the full-fat will defeat the purpose if it packs on the pounds. - Lean animal protein. Let’s talk (lean) turkey…and lean chicken and lean beef. All these protein sources are chock-full of iron — an important nutrient that helps beef up fertility. In fact, studies show that women who pump up their iron intake during the preconception period have a higher fertility rate than women who are iron-deficient. A couple caveats: Steer clear of high-fat cuts of meat (bring home the pork tenderloin, but not the bacon), and don’t overdo any kind of animal protein (stick to no more than 3 servings). That’s because research shows that too much protein (even lean protein) can decrease fertility. Consider swapping out one serving of animal protein for a serving of plant protein (think beans, tofu, or quinoa).
 If you’re a vegan, be sure your prenatal vitamin has iron in it, and ask your practitioner if you might need any extra supplementations.
If you’re a vegan, be sure your prenatal vitamin has iron in it, and ask your practitioner if you might need any extra supplementations. - Fatty fish. Salmon (choose wild if you can), sardines, herring, and other types of fatty fish are swimming in fertility-boosting benefits, thanks to the high levels of omega-3 fatty acids they boast. Loading up your diet with those fabulous fats allows for increased blood flow to reproductive organs and may help to regulate reproductive hormones. Not a fan of fish? Hook your omega-3 fatty acids from flaxseed (you’ll find it in some breads), almonds, walnuts, pumpkin seeds, and enriched eggs (you’ll see them marketed as “omega” or “DHA” eggs).
- Complex carbs. Never came across a carb you didn’t like (and what estrogen producer has)? It’s time to get a tad more discriminating. When you can, consume carbs of the complex kind (whole grains, beans, vegetables, and fruits) as opposed to the refined varieties (white bread, white rice, refined cereal, sugary treats of all types).
 That’s because there may be a link between your carb choices and your fertility. Here’s why: Digesting refined carbs causes an increase in blood sugar and insulin in the body — and increased insulin levels can disrupt reproductive hormones and mess with the menstrual cycle (not a good scenario when you’re trying to conceive). Complex carbs, on the other hand, take longer to digest and don’t cause spikes in insulin levels — they may also promote regular ovulation. Holy whole wheat, batmom!
That’s because there may be a link between your carb choices and your fertility. Here’s why: Digesting refined carbs causes an increase in blood sugar and insulin in the body — and increased insulin levels can disrupt reproductive hormones and mess with the menstrual cycle (not a good scenario when you’re trying to conceive). Complex carbs, on the other hand, take longer to digest and don’t cause spikes in insulin levels — they may also promote regular ovulation. Holy whole wheat, batmom! - Oysters. You’ve heard that oysters can heat things up between the sheets, but did you know they can also boost your fertility? The oyster — famous for being Nature’s answer to Viagra — is the food chain’s most concentrated source of zinc, a nutrient that’s crucial for conception. Zinc deficiency can disrupt the menstrual cycle and slow the production of good-quality eggs — neither of which is good for fertility. Not a fan of oysters in any form? Slurping those bivalves is not the only way to get your share of zinc.
 Find zinc in smaller amounts in other fertility-friendly foods, incuding beef, poultry, dairy, nuts, eggs, whole grains, and legumes.
Find zinc in smaller amounts in other fertility-friendly foods, incuding beef, poultry, dairy, nuts, eggs, whole grains, and legumes. - Yams. If you’re hoping for a bun in your oven, think about cooking up some yams for dinner. Some researchers have suggested that this Thanksgiving staple may contain an ovulation-stimulating substance, offering as evidence the fact that wild yam eating populations have a higher rate of twins. Whether or not this theory pans out (after all, the yams we eat are raised, not wild), it’s worth tossing a few in the pan tonight anyway. After all, they’re super-rich in fertility-friendly vitamins (their deep color is a giveaway).
- Berries. Thinking pink or blue? Think raspberries and blueberries. Packed with antioxidants, these members of the berry family protect your body from cell damage and cell aging — and this includes cells in your reproductive system (aka your eggs). Wondering whether you should be picking other berries, too (like strawberries and blackberries?) Definitely do.
 All berries are berry, berry good for your fertility…it’s just that raspberries and blueberries are the berry, berry best. Out of season? Buy them frozen.
All berries are berry, berry good for your fertility…it’s just that raspberries and blueberries are the berry, berry best. Out of season? Buy them frozen.
Fertility Busters
- High-mercury fish. You’ve probably heard that high mercury fish is a pregnancy no-no. But did you know that too much mercury can affect fertility, too? That’s right — research has shown a connection between infertility and high levels of mercury. What’s more worrisome: mercury is stored in the body — so even if you’re careful to follow the guidelines for fish consumption while you’re pregnant, your baby-to-be could still be harmed by the mercury you ingested preconception. So avoid eating high-mercury fish when you’re trying to conceive, including swordfish, king mackerel, tilefish, fresh tuna (limit canned, too; light has less mercury than white), and shark. Are you a sushi fan? Get your fill now (you won’t be able to indulge once you’re officially expecting), but do stick to low-mercury fish.

- Trans fats. Trans fats are nobody’s friends, which is why these unhealthiest of unhealthy fats are being pulled from more and more products. But here’s a reason why you might want to consider pulling all trans fats from your preconception diet: some research shows that the more trans fats in a woman’s diet, the higher her chances of developing ovulatory infertility. Trans fats (also called hydrogenated or partially hydrogenated oils) are found in processed and fried foods. Read nutrition labels carefully to check for trans fats so you can be sure to avoid them. While you’re at it, mostly stay away from saturated fats of all kinds. Get your fats the healthy way (canola oil, olive oil, flaxseed oil, nuts, avocados, and so on).
- Caffeine. A heavy caffeine habit can be a big-time fertility buster. Studies have linked downing too much caffeine with lowered fertility and an increased risk of miscarriage. But you doesn’t mean you have to give up your old pal, Joe.
 Up to 200 mg a day (that would buy you about two shots of espresso or 12 ounces of brewed coffee) is considered safe — now and when you’re expecting.
Up to 200 mg a day (that would buy you about two shots of espresso or 12 ounces of brewed coffee) is considered safe — now and when you’re expecting.
What Is Implantation Bleeding?
Bleeding early in pregnancy doesn’t always mean trouble. Read on to learn about the kind that can occur naturally when the fertilized egg implants in ...
By Meryl Davids Landau
Abortion Controversy Heats Up
The Supreme Court has set a date to hear a Roe v. Wade challenge, Texas has tightened its abortion laws, and abortion rights advocates point out a grim...
By Cheryl Alkon
The Best Pregnancy Test in 2022
Looking for the best pregnancy test in 2022? Here are the top pregnancy tests when it comes to accuracy, reliability, and usability from brands like Clearblue. ..
..
By Sara Lindberg
Healthy nutrition for children: what you need to know
Alexandra Sitnova
pediatric nutritionist
Author profile
Ekaterina Kushnir
learned how to feed children
Author profile
want to make the food perfect.
But often this desire only leads to additional problems. We talked with children's nutritionist and author of books Alexandra Sitnova about when it's not worth worrying about a child's nutrition, how to help him diversify his diet, and much more.
What to talk about
- What to do if the child eats almost nothing
- How to make sure that the child eats enough
- Should you persuade the child to eat
- Are there foods that should not be given to children at all
- What should be present in the child's menu
- At what age can sweets be given to children
- What to do if a child prefers sweets to healthy food
- How to make a child eat more vegetables and fruits
- How to make a teenager's diet healthier
- What processed foods can be included in the diet
- Do's and don'ts to tell your child about food
- How to suspect an eating disorder in a child RPP
- What problems should I contact a pediatric nutritionist
What should I do if my child eats almost nothing?
When I hear that children do not eat anything, I immediately want to look at them and their food diary. Often they eat normally, they just don't want to eat what their parents, grandmothers, or the local doctor think they should.
Often they eat normally, they just don't want to eat what their parents, grandmothers, or the local doctor think they should.
Recently, during a consultation, I had just such a case - a child who, according to his parents, did not eat anything. But in fact, his daily diet included three chicken drumsticks, a lot of dairy products, and various fruits. He just refused soup, so his parents were worried.
/list/dietology/
12 important questions for nutritionist Elena Motova
Another case - complaints that the child does not eat anything, drinks only milk. We look at the food diary, and every day he eats 30 different foods. Yes, he loves milk and asks for it at every meal, but he also eats enough other food.
When it seems that a child eats almost nothing, you need to look at what he actually eats. When children do refuse to eat, they tend to have health problems, such children often end up in the hospital with signs of malnutrition. These are rare situations that are usually associated with some kind of disease.
These are rare situations that are usually associated with some kind of disease.
How can you make sure your child is eating enough? Are there food standards?
All children should eat according to their appetite. The appetite of each child will be different, it depends on a huge number of factors - for example, weight, height, physical activity and temperature around.
You cannot compare two children even of the same age in terms of appetite and assign them the same food ration. The amount of food eaten by children of the same age and gender can vary by 50%. Here you can’t focus on grams or calories, only on the child’s appetite and his physical development.
/stat-oh-my-weight/
How many Russians suffer from obesity
If a child develops well, he is active, alert, not sleepy, his weight and height do not differ much from age norms, then he eats enough.
If the child does not have confirmed vitamin and mineral deficiencies with clinical symptoms, then he also eats enough. It is important to say that blood tests for vitamins and minerals are often taken without indications, and then deviations in these tests are treated. You should not do this if the child does not have any symptoms.
It is important to say that blood tests for vitamins and minerals are often taken without indications, and then deviations in these tests are treated. You should not do this if the child does not have any symptoms.
Understanding if a child is eating normally - NHS
To understand if a child is eating too much, you also need to look at his development. Some children may have weight and height above the norm and not be obese, that is, they have a normal body mass index, for example, they are more active than their peers.
WHO Childhood Obesity Calculator
How to Raise Your Kids Without Going Broke
The best resources on coping with parenthood and getting the most out of the government are in your inbox every Tuesday. Free
Is it worth persuading a child to eat?
You can try to persuade the child to eat. But this is usually a bad strategy, because children, like adults, know how to feel hunger and satiety.
It is enough to remember yourself in childhood. Almost everyone had an adult who tried to persuade them to eat: look, what a delicious salad, what potatoes I stewed, why don’t you eat cake, I tried so hard.
Almost everyone had an adult who tried to persuade them to eat: look, what a delicious salad, what potatoes I stewed, why don’t you eat cake, I tried so hard.
/healthy-food/
How much does healthy food cost for a family of four
It is easy to remember what emotions arose: rejection, shame, discomfort, awkwardness. We were uncomfortable with what we had to eat. Our children experience the same thing, so persuasion tactics are not effective. It may work a couple of times, but in the long run, persuasion only reduces the child's desire to eat.
The best thing to do is to give the child food and not participate in his meal unless he asks for help.
Are there foods that should not be given to children at all?
Alcohol is perhaps the only absolutely harmful product that should not be given to children under any circumstances.
For other foods, there may be an age before they should be given.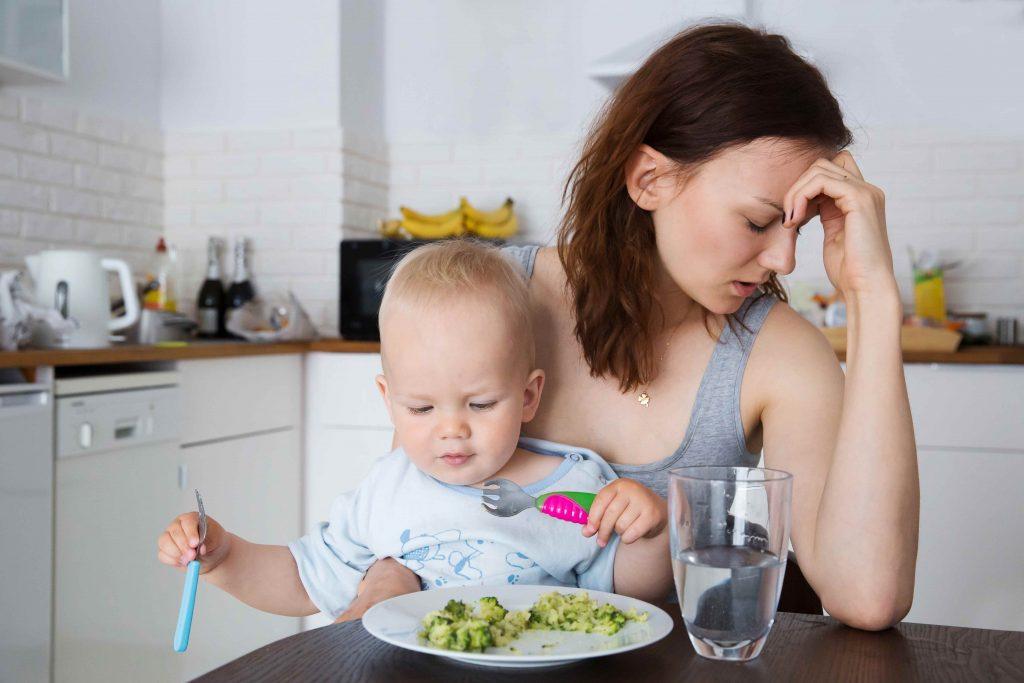 For example, honey is not allowed for children under one year old, because there is a risk of botulism. For older children and adults, there is no such danger - the spores of the bacterium that causes botulism cannot survive in the acidic environment of the stomach.
For example, honey is not allowed for children under one year old, because there is a risk of botulism. For older children and adults, there is no such danger - the spores of the bacterium that causes botulism cannot survive in the acidic environment of the stomach.
/guide/prikorm-detyam/
How to introduce complementary foods to children
Thermally unprocessed meat, eggs, fish are not given to children under five years of age, as the risk of intestinal infections is high. The same goes for unpasteurized milk and moldy cheeses.
Foods not to be given to young children - NHS
Whole nuts are not given to children under four due to the risk of suffocation.
All this applies to many other products that are not given to children under a certain age, because there are health risks. Most food restrictions end when a child reaches four or five years of age.
What should be on the child's menu?
The optimal menu for a child includes:
- Five to six servings of vegetables and fruits.

- Five or six servings of cereals - this is cereal, and bread, and crispbread, and cereal, and pastries.
- Two to three servings of animal or vegetable protein.
- Two or three portions of dairy products: milk, cottage cheese, yogurt, kefir.
Children's Healthy Plate - Harvard Public Health School
One serving is one baby's fist. The larger it is, the larger the serving. It is more convenient to measure with cams than grams or spoons.
With this diet, the child will receive enough nutrients, fiber, vitamins and minerals. Of course, there may be deviations from the diet; one cannot always strive for a reference menu.
6 Nutrition Myths You Should Stop Believing
For example, a child might eat seven servings of grains during their growth period, or two servings of dairy but four servings of protein, or vice versa. It is also normal if the child eats a little less or more than the recommended servings - this may be his individual feature.
The child may even, for example, not eat dairy products at all - this is acceptable. At the same time, his diet will be complete if you add calcium-containing plant foods and additional protein to it.
Another example: a child may choose not to eat meat, fish, eggs, but to eat vegetable protein and dairy products. This is also a valid and healthy food option.
Such a pyramid can be oriented according to the child's age Such a pyramid can be oriented according to the child's ageAt what age can sweets be given to children?
Sweet is recommended not to include in the diet of children until at least two years old.
Of course, if a baby under two years old accidentally tries some sweetness, for example, bites off a piece of his mother's bun, nothing bad will happen, but sweets should not be part of the daily diet.
After two years, sugar may be present in the child's diet, but we do not talk about its regular consumption until four or five years.
How much sugar to eat - Harvard Public School of Health
Early and regular sugar intake is associated with an increased risk of tooth decay, obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease in children. It cannot be said that if a child eats cookies, then he will 100% have caries and be overweight, but the probability is higher.
It is usually easy to avoid sweets until the age of two, since children at this age are in the family, not yet attending kindergarten.
It is important to note that we are talking not only about sweets, but also about any sugar - granulated sugar added to cereals and curds, sweeteners like juice concentrate, honey, maple syrup, and the like. All this should not be introduced into the child's diet too early. This does not apply to fruits - they do not apply to added sugars.
/sweet-evil-2/
“It’s almost like quitting smoking”: 9 more tips to help you eat less sweets
How much sugar can be in a child’s diet
| Age | Sugar norm | How much is | For comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Up to 2-4 years | Withhold sugar until at least 2 years, avoid regular use until 4 years | No sweetened products | - |
| 4-6 years | No more than 19 grams of sugar per day | Approximately 3 full teaspoons or 5 sugar cubes | Approximate amount of sugar in 2 90 ml Rastishka bottles |
| 7-10 years | No more than 24 grams of sugar per day | Approximately 4 full teaspoons or 6 sugar cubes | Approximately the amount of sugar in 50 grams of dark chocolate |
| Over 10 years old and adults | Not more than 30 grams of sugar per day | Approximately 5 full teaspoons or 7 sugar cubes | One can of Coca-Cola contains 35 grams of sugar: that's more than the daily allowance |
to 2-4 years old
Sugar rate
Do not give sugar up to 2 years, avoid regular use up to 4 years
How much
,no sweetened products
-
-
4-6 years
Sugar requirement
No more than 19 grams of sugar per day
How much is
Approximately 3 full teaspoons or 5 sugar cubes
For comparison
About so much sugar in 2 bottles of Znishki, 90 ml
7-10 years
Sugar rate
NOT more
For comparison
About the amount of sugar in 50 grams of dark chocolate
Over 10 years old and adults
Sugar norm
No more than 30 grams of sugar per day 90 3 03
Approximately 5 full teaspoons or 7 sugar cubes
For comparison
One can of Coca-Cola contains 35 grams of sugar: more than the daily allowance
What if a child prefers sweets to healthy food?
The first question is what we consider sweet. Fruits are often referred to as sweets, but this is not true. Fruit is a healthy, healthy and important product for children. If a child loves fruits and chooses them from a large number of foods, this is normal.
Fruits are often referred to as sweets, but this is not true. Fruit is a healthy, healthy and important product for children. If a child loves fruits and chooses them from a large number of foods, this is normal.
Another thing is if the child eats only cookies, sweets, sweetened yoghurts, curds and the like. This, of course, is not the norm.
/sweet-evil/
“Only the first few weeks are difficult”: 8 tips to help you eat less sweets
Often, an excess of sweets in the diet is associated with the fact that they try to feed the child with all their might. For example, a baby does not like cottage cheese, so sugar is added to it so that he eats at least a little. Or the child does not like soup, but then they promise him cookies, so the wrong habit is formed.
If children prefer sweets, you need to look at how it appeared in their lives and what role it plays. For example, sweets are often a motivation for a child to eat other foods. There are several ways to gradually reduce the amount of sweets in your diet.
There are several ways to gradually reduce the amount of sweets in your diet.
Stop motivating with sweets. Sweets should be given along with the main meal, limiting their portion. That is, the child does not need to put a plate of borscht and a whole cake, but you can put a small candy. As soon as parents stop being afraid to do this, and the child understands that he can eat sweets just like that, the motivational component disappears. Children stop demanding sweets.
Gradually reduce sweets in the diet. For example, give not five cookies, but four, add not three spoons of sugar to porridge, but two. Then continue to reduce portions gradually, a little bit once a week. So little by little you can come to a safe amount of sweets for the child.
Plan your sweets. For example, the family agrees that they buy a cake on Saturdays or ice cream on Sundays. That is, they buy sweets not when the child made a scandal at the checkout of the store, but when the parents planned it, they talked with the child.
Then children know that they can eat sweets, they don't forbid them, they don't need to overeat them somewhere, they will always be there on a certain day. As a result, they start eating less sweets.
Do not be intimidated by sweets. Children should not be told that if they eat a piece of cake, their teeth will fall out tomorrow or their stomach will ache. This will not happen, but they will see and remember that parents cannot always be trusted.
/fruits-and-vegetables/
How I started eating more fresh fruits and vegetables
How can I get my child to eat more fruits and vegetables?
It is unlikely that my answer will be unexpected - you need to eat them yourself. Most families do not eat enough vegetables and fruits. There are objective reasons for this - for example, it is expensive, and subjective - adults do not like vegetables, do not know how to cook them, are afraid of store-bought fruits, and so on.
Only one in ten adults in the world eat enough fruits and vegetables. In Russia, approximately 50% of families eat vegetables and fruits irregularly.
There is no magic here: if we ourselves started eating vegetables and fruits today, then the child will not start eating them tomorrow. This is a long process. Many children take three to six months to change their diet.
Basic advice: eat vegetables and fruits ourselves, put them on the table, don’t make an unpleasant mess out of them, cut them into nice pieces on a plate, offer them with every meal, don’t insist, don’t force. We don’t try to hide zucchini in cutlets or spinach in juices, but we learn to eat with pleasure. Then the children will start repeating after us.
/400g/
How many fresh vegetables and fruits do Russians eat
How can a teenager eat healthier?
Teenagers who only eat chips and drink cola are isolated cases of serious nutritional problems. Such children will be in a state of nutritional deficiency.
Such children will be in a state of nutritional deficiency.
Of course, as children enter adolescence and receive pocket money, at some point they spend it on food. Usually this is the food that is limited or not available at home. This is normal, this is the stage of growing up.
If a child after school went to the store and bought chips, it is important to overcome the desire to scold, scold, deprive of pocket money, punish, intimidate. It is worth accepting this as the decision of the child and his choice. Then, just as in the case of younger children, the teenager will understand that food is allowed, he is not scolded. This means that he will not have the desire to stock up on such food and hide from his parents with it.
He will understand that if he wants chips or cola, he can go and buy them. As a result, he will switch to something else, start making decisions not in favor of fast food or sweets.
/food-label/
How to read food labels
It is the forbidden that becomes desirable. When we try to severely limit ourselves in any products, we go on diets, we have breakdowns. When there are no prohibitions, then there are no breakdowns.
When we try to severely limit ourselves in any products, we go on diets, we have breakdowns. When there are no prohibitions, then there are no breakdowns.
An important point: before becoming a teenager, a child must understand that all these products are not something terrible, dangerous and forbidden, but something that he can try at a certain age.
You can talk to him that sometimes we buy hamburgers and cola when we go to a cafe, or we get popcorn at the cinema, or sometimes we eat chips at home. Parents are often afraid that the child will get into an environment where fast food is available and begin to overeat. But if there is no ban, this is unlikely to happen.
Should you always cook homemade food? What semi-finished products can be added to the diet?
It is not necessary to cook homemade meals all the time. Of course, it is associated with healthier eating habits, allowing you to eat more vegetables and fruits, a variety of grains, and get more fiber. But sometimes it’s okay to eat in a restaurant, order food with delivery, buy ready-made products in a store.
But sometimes it’s okay to eat in a restaurant, order food with delivery, buy ready-made products in a store.
Speaking of semi-finished products, you need to understand that they are different. So, a frozen vegetable mixture is also a semi-finished product, but it is a healthy healthy product. A mixture for soup made from dry grains and dried vegetables is also a semi-finished product, but it is useful and allows you to diversify your diet.
/recept-for-kids/
How much does it cost to cook at home for children and with them
However, convenience foods are also, for example, sausages. They often contain too much salt and saturated fat and are highly processed foods. Such products, of course, should be limited in the diet of children over five years old and avoided in the menu of children under five years of age.
That is, you can eat any food, but it is important to choose foods that provide the greatest variety, allow you to eat more vegetables and fruits, and limit those that are high in sugar, salt, saturated fat.
What can and cannot be said to a child about food?
What we tell a child about food affects his habits to a lesser extent than what we show and how we ourselves relate to food. But if parents speak negatively about the weight or appearance of the child, comment on his food, this increases the risk of nutritional problems in the future.
Also, do not intimidate with food - for example, telling that cola will make a hole in the stomach. The child will see that no hole has formed in himself or his friends, and his level of trust in adults will decrease.
/eat-gluten/
“You have to eat homemade food or you die”: 10 burning questions about healthy eating run, jump high and so on. Also, food helps us grow and be strong, enables our organs to work properly.
It is necessary to tell about the fact that food is different. So, some food gives only energy, pleasant taste sensations, a sense of celebration. For example, cake and other sweets. But it does not fill the body with vitamins and minerals, does not help to grow and develop. Such food can be eaten, but if we make it the basis of nutrition, it will be harder to play and learn.
But it does not fill the body with vitamins and minerals, does not help to grow and develop. Such food can be eaten, but if we make it the basis of nutrition, it will be harder to play and learn.
This knowledge is enough for a child to understand how food works, why it is needed, not to avoid certain foods, to learn to love food.
How to suspect an eating disorder in a child?
Eating disorders, ED, are often overdiagnosed in children. Often, even the minimum selectivity of a child in nutrition is recorded here.
Eating Disorders in Children - American Academy of Pediatrics
This happens not only in Russia, but also in many other countries. But abroad, this is usually done by the parents themselves, and the doctor stops them, can determine from the list of criteria whether there really are violations or not.
In Russia, on the other hand, doctors often give parents the impression that their child has an eating disorder. It happens that such a diagnosis is made if the child does not eat one product, he does not like the smell or texture of some food. Many adults behave the same way, say, they cannot eat boiled onions or drink frothy milk, but no one diagnoses them because of this.
Many adults behave the same way, say, they cannot eat boiled onions or drink frothy milk, but no one diagnoses them because of this.
An eating disorder should be suspected if:
- The child is critically short of height or weight.
- His physical development is impaired.
- There is regular weakness, drowsiness, the child is constantly cold and cannot get warm.
- He does not show interest in active activities, that is, we see that there is a lack of energy.
It is also possible for a child to have an eating disorder if they do not eat many food groups. For example, 80-90% of the diet is dairy products, and he does not want the rest. Or when a child eats only one product - for example, only one brand or in a certain form. For example, he drinks only kefir of one brand from a bottle. There will be no other kefir, and if this one is poured into a cup, it will also refuse.
/eating-disorders/
How to cure eating disorders
You can also suspect an eating disorder in a child if he has severe anemia, severe deficiency of calcium, B vitamins, protein.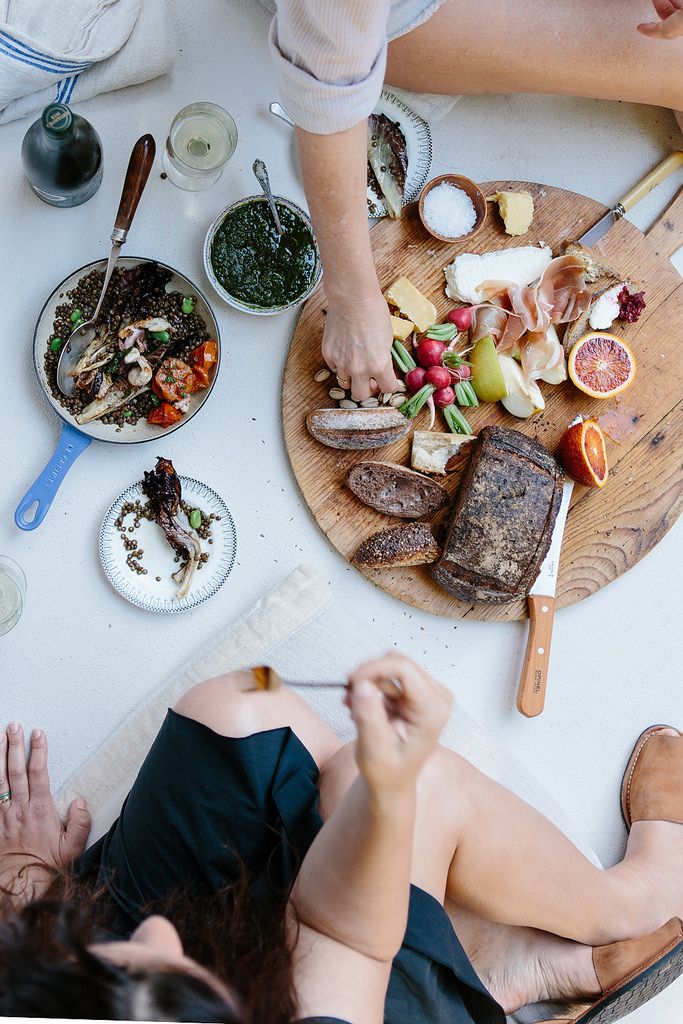
If parents think their child has an eating disorder, they should see a doctor.
In most cases, all of the above signs are absent in a child. He may have a weight at the lower limit of the norm, he may give preference to the same dairy products, but they do not take up 90, but 50%, he may have anemia, but not critical, but one that is eliminated by taking iron supplements. In these cases, we are not talking about RPP, but about a selective diet, which is adjusted by training and changing feeding tactics.
True eating disorders are very rare in children. And in most cases, if it is, then there are some concomitant diseases.
Which doctor should I go to if parents suspect a child has an ED?
The history is taken by the pediatrician. It evaluates whether the child has physical manifestations of selective nutrition: his weight, height, development, nutritional deficiencies, and so on.
If the child's nutrition has not been corrected, and his selectivity prevents him from developing, it is worth going to a psychiatrist. Only a psychiatrist can make such a diagnosis as RPP, not the parents themselves and not the pediatrician.
Only a psychiatrist can make such a diagnosis as RPP, not the parents themselves and not the pediatrician.
/list/psihiatr/
12 important questions for psychiatrist Kirill Sychev
This is important, because when a child does not have eating disorders, we can teach him. He does not need psychotherapy, nutritional support and so on.
If there is an eating disorder, then a team should work: a psychiatrist, a psychotherapist, a nutritionist prescribing additional food, planning the sequence in which new foods are introduced into the diet.
Sometimes psychologists take over the correction of the nutrition of such children, but they cannot properly expand the child's diet when each new product is worth its weight in gold. You can’t introduce zucchini or cookies as a third product if the child eats only two: this will not give the right amount of energy and nutrients.
In my practice I have seen two children with an eating disorder where it was confirmed by a psychiatrist. Such cases cannot be confused with anything, they are significantly different from "does not eat any vegetables" or "refuses meat and fish." These are not the children who can be forced or persuaded to eat, feed under a cartoon.
Such cases cannot be confused with anything, they are significantly different from "does not eat any vegetables" or "refuses meat and fish." These are not the children who can be forced or persuaded to eat, feed under a cartoon.
What problems should I contact a pediatric nutritionist and how to choose such a specialist?
Nutriciology, unfortunately, is largely discredited by specialists who prescribe dietary supplements for everyone. Many people think that a nutritionist is someone who will give you a promo code to buy a huge list of vitamins, put you on a strict diet with no dairy products, gluten, fruits, or anything else.
In fact, nutrition is the science of healthy and varied nutrition, and a nutritionist is the person who will help plan the menu.
/list/dont-be-bad-bad/
6 dietary supplements from Instagram* that you are unlikely to need
children were interested in them, read food labels, diversify the family menu.
A nutritionist works only with healthy people. He cannot treat obesity, anemia, other conditions or diseases, prescribe tests and read them. Its mission is to help healthy people plan healthy diets.
When choosing a nutritionist, it is important to look at the reviews of the people with whom he has worked, as well as what the specialist says and writes about. If he prescribes supplements, tries to exclude products or entire product groups from the menu, you should refuse his services. This is not about healthy eating and not about healthy eating habits.
Your own feelings are also important - is there trust in a specialist, is it comfortable to work with him. But education, course certificates, and so on are not always an indicator of professionalism, because there are few educational programs that train good nutritionists.
Remember
- It is extremely rare for children to actually eat nothing. More often, parents' complaints are related to the fact that the child does not eat what, in their opinion, he should.

- Every child should eat according to his appetite, there are no nutritional norms.
- Coaxing children to eat is ineffective in the long run and only reduces their interest in food.
- Alcohol is perhaps the only absolutely harmful product that under no circumstances should be given to children. For other products, there may be an age until which they should not be given.
- It is good if the child eats enough vegetables and fruits, grains, dairy products and protein. Deviations from the optimal menu are acceptable, since almost any diet can be adjusted so that it contains all the necessary nutrients.
- Sweet is recommended not to include in the diet of children until at least two years old.
- Sweet should not be a motivation to eat other foods. If the child is already used to eating a lot of sweets, gradually reducing their amount in the diet can help.
- For children to eat more fruits and vegetables, adults need to eat them themselves.

- The ban on fast food and other food that adults consider harmful, on the contrary, makes it more desirable for a teenager.
- You can eat any food, including fast food, but strive for a varied and healthy diet.
- Eating disorders are often overdiagnosed. Such children are rare.
- In case of suspicion of eating disorders, you should first visit a pediatrician, and then contact a psychiatrist.
- The child should be told why food is needed and what it is, but not intimidate, do not comment on his appearance and taste preferences.
- A nutritionist works only with healthy people, he cannot prescribe tests or treat anything. Also, a good specialist does not prescribe a huge amount of dietary supplements.
Materials that will help parents save their budget and sanity are in our telegram channel @t_dety.
How to write an article about your parenting experience, we tell in our manual: read it and become our author.
How to eat cheap and healthy
I got into a difficult life situation and decided to cut my food expenses a lot. I had never saved on fruits before, I bought red fish, good meat, nuts, and so on. Now the budget is such that you need to meet the living wage. At the same time, I understand how important it is to eat right, otherwise there is a risk that this saving will result in spending on medical services.
What do you recommend?
Vika Vishnyakova
nutritionist
Author Profile
A healthy diet doesn't have to be about expensive fresh or farm produce. Eating with health benefits is possible with any budget and any preferences and habits, if you know the basic principles of diet planning and be able to choose products.
I will tell you how to go to the supermarket if you have little money and cook healthy food out of what you buy.
What is a healthy diet
According to international health organizations, a healthy diet is a balanced diet that includes various food groups and diversity within them.
Healthy Eating - WHO
Healthy Eating Plate - Harvard School of Public Health
Recommendations to Citizens: Healthy Eating - Rospotrebnadzor
Food groups are a conditional division of all foods according to their predominant role in human nutrition: vegetables and fruits, grains, sources protein, fats and oils.
Dairy products are sometimes classified as a separate group, as the UK Department of Health does. Then a balanced diet consists of five food groups The Australian Department of Health also adheres to this scheme. And some countries, such as Canada and the United States, combine dairy products with protein sourcesHealthy eating, as defined by the World Health Organization, includes fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and whole grains. Everything else is optional. Salt, sugar and saturated fats are recommended to be consumed in limited quantities.
No matter what scientifically based recommendation we look at, vegetables and fruits will always be the basis of the diet: they are advised to eat from 400 grams per day in all forms. And the rest of the plate or volume of consumption will be divided equally between cereals and protein sources.
And the rest of the plate or volume of consumption will be divided equally between cereals and protein sources.
/list/healthy-eating-myths/
No sugar or carbohydrates: 6 myths about healthy eating
There are no special foods, supplements or orthodox approaches like raw or paleo diets in healthy eating. All recommendations come down to variety and the choice of minimally processed foods.
Minimally processed foods are those that no one has tried to cook before us, such as a whole apple or frozen green beans. If flavor enhancers — salt, sugar, fats, and oils — are added to minimally processed foods, these are already processed foods: for example, cheese, bread, pineapple syrup, or chocolate milk.
If part of the nutritional value is removed from the product, for example, the shell of the grain, which contains fiber or unsaturated fats, and then many actions are performed with the raw materials - dried, ground, pressed, etc. - and at the same time many flavor enhancers are added, then the product becomes ultra-processed. These are, for example, chips, chocolate, donuts, ham.
- and at the same time many flavor enhancers are added, then the product becomes ultra-processed. These are, for example, chips, chocolate, donuts, ham.
/eda-uchebnik/
How to eat tasty and healthy
How to save on food
The best way to eat cheap is to cook at home and buy minimally processed ingredients. The two main commandments of a healthy diet sound exactly the same. Therefore, you should not worry that saving on food will undermine your health.
Here's how to choose the most nutritious food and not overpay.
Compare prices. They say that for the cheapest products you should go to the market - maybe this is so. But the difference in price will be noticeable only if you buy in bulk, and this is not always convenient in terms of delivery and subsequent storage. In addition, this greatly reduces the diversity of the diet: 5 kilograms of a tomato is worse for health than one kilogram of tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers and 2 kilograms of apples each.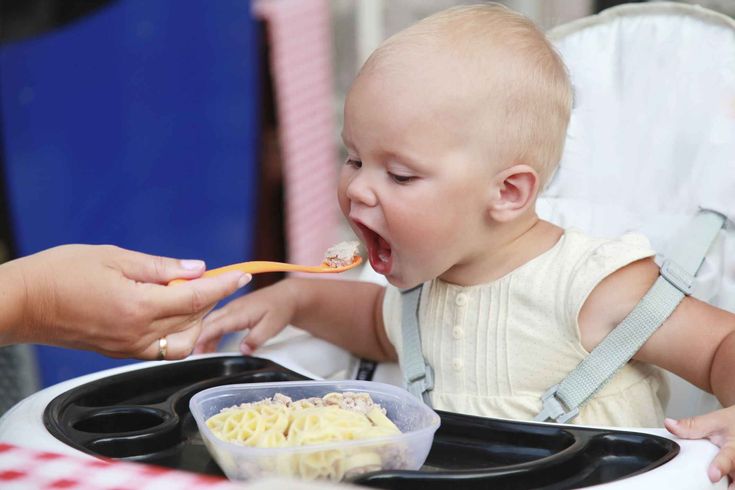 Therefore, I would not advise buying exclusively in the markets.
Therefore, I would not advise buying exclusively in the markets.
/dostavka-produktov/
How do I save on grocery delivery
Thanks to online stores, which often offer free delivery, it is much more convenient in a relaxed atmosphere to compare the offers of several large supermarkets and choose the cheapest products there.
For example, you can compare prices for different products in Sbermarket. It is enough to select a category of goods and a supermarket. For example, in "Auchan" 1 kilogram of bananas costs 69.49 R. Source: "Sbermarket" And in "Lenta" - 94.79 R. Source: Sbermarket Follow the discounts. In the store - offline or online - pay attention to what vegetables and fruits are now on sale at a discount. Take them first, and then complete the basket with fruits of other colors. The American Heart Association suggests collecting rainbows on a plate, that is, eating vegetables, fruits and berries of different colors.
There is no most useful vegetable or fruit, so if a certain fruit - for example, mango or pineapple - seems expensive, you can safely exclude it from the diet without damage to health. Remember: variety is an important part of a healthy diet, so chasing exotics or farm products is pointless in terms of health care. Discounts and promotions will not always be for only one product, so if you can’t eat, for example, oranges this week, then you will probably succeed next.
/vegetarianism/
They say being a vegetarian is healthy. Truth?
This rule also applies to other food groups. But we need to eat more vegetables and fruits every day than products from other groups. Therefore, it is important to first resolve the issue with a minimum of vegetables and fruits in the diet, and then move on to choosing other products.
Bulgur is a variant of wheat in the diet. It is no healthier than buckwheat or barley, but often more expensive. And if there is a discount on bulgur, then you can use this version of wheat for a change. Source: Sbermarket
And if there is a discount on bulgur, then you can use this version of wheat for a change. Source: Sbermarket Shop affordable. Always a low price for products familiar to central Russia: beets, carrots, cabbage, apples, onions. So don't ignore them.
Also pay attention to seasonally cheap goods. For example, in autumn for pumpkin and zucchini, and in summer for nectarines and cherries.
Frozen vegetables, fruits, berries and even greens will help maintain variety out of season.
Community 04/27/21
Is it true that vitamins are found only in fresh herbs?
Canned food is also a good option, because it is convenient: no need to cut, wash, boil. Canned food saves time, effort and often money. For example, 500 grams of ready-made vegetables can cost around 100 R.
The loss of vitamins during preservation is no more than with another method of heat treatment, and fiber generally remains in the same amount. Therefore, it is not necessary to classify canned vegetables and fruits as useless or harmful products. Yes, they contain salt, sugar and vegetable oil, but if this is not the only food in your diet, then you are unlikely to go over the norm for these ingredients.
Therefore, it is not necessary to classify canned vegetables and fruits as useless or harmful products. Yes, they contain salt, sugar and vegetable oil, but if this is not the only food in your diet, then you are unlikely to go over the norm for these ingredients.
Do not build a diet around meat. Usually, the lion's share of the food budget is made up of animal products, especially meat and seafood. There is a special love for meat in Russia: often in food diaries I meet meat in various forms three times a day, and vegetables only a few times a week.
When planning a diet, many people first decide how to cook meat, then choose a side dish for it, and vegetables - according to the leftover principle. This approach has nothing to do with a healthy diet.
Fortunately for a small budget, a plant-based diet is considered healthier by the scientific community. This does not mean that you need to completely exclude meat and become a vegan, it is enough to assign animal products a moderate role in the diet, for example, no more than three servings per week. The rest of the protein can be obtained from fish and vegetable sources - legumes and nuts.
/fish/
Is it true that fish is an essential part of a healthy diet?
You don't have to buy fresh fish - canned fish will do. I often come across the opinion that there is nothing useful left in canned fish, but this is not at all true: studies have shown that there are more omega-3s in it than in raw fish. Also, canned fish contains more calcium due to soft bones that can be eaten.
Legumes are a rather unpopular product in the diet of the average Russian, and meanwhile Rospotrebnadzor and the UK Ministry of Health recommend consuming at least one serving of legumes a day. And in this case, budget cuts play into the hands: including beans, soybeans, chickpeas, lentils or peas in the diet is more beneficial than meat. At the same time, you will get not only protein, but also fiber, vitamins, minerals, and less saturated fat than in meat.
/beans/
Are beans and legumes really hard to digest?
Another alternative to meat in the diet, in addition to fish and legumes, are organ meats and poultry. They contain enough iron to be a healthier and cheaper substitute for mammalian meat.
Don't be afraid of cheap products. Often the cheapest products have the simplest composition and more nutritional value than their expensive counterparts.
For example, the cheapest gray bread is the most healthy: it contains more fiber, vitamins and minerals due to second grade flour than its expensive counterpart, which is more similar in composition to pastries. And minimally processed cereals, that is, containing also a grain shell, are often cheaper than refined options.
And minimally processed cereals, that is, containing also a grain shell, are often cheaper than refined options.
/healthy-food/
How much does a healthy meal cost for a family of four
How to save 30,000 R per month on food and cheap analogues. Prices are current at the time of publication.
In total, you can save 30,387 R per month and, it seems, survive on a living wage.
Two daily diets
| Food group and serving size | Luxury version | Cost | Economy version | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetables and fruits, 400 g | Mango, 1 pc. | 189.9 R | Vegetable mix, frozen, 200 g, 0.5 pack | 30 Р |
| Fresh blueberries, 80 g | 126 Р | Raisins, 40 g | 11 R | |
| Avocado, 1 pc. | 85 P | Banana, 80 g, 1 pc. | 7 P | |
Cucumber, 1 pc. | 44 R | Fresh carrots, 80 g, 1 pc. | 3.4 P | |
| Tomato, 1 pc. | 43 R | |||
| Protein sources, 2 servings | Beef, steak, 160 g | 405 P 9019four | Canned chickpeas, 120 g, without liquid | 32 R |
| Pike perch fillet, 140 g | 124 Р | Canned fish, 125 g, 0.5 can | 26.5 P | |
| Milk, 2.5 servings | Hard cheese, 40 g | 51 P | Ryazhenka, 225 ml | 27.5 P |
| Farm milk, 250 ml | 30 Р | Hard cheese, 30 g | 25.3 R | |
| Curd cheese, 30 g | 16.5 R | |||
| Cereals, 3 dry servings | Quinoa 65g | 48 P | Barley grits, 80 g | 13 R |
| Couscous, 90 g | 40 P | Brown rice, 65 g | 10.4 P | |
| Hercules bread, 80 g | 16 R | Darnitsky bread, 80 g | 3. 5 P 5 P | |
| Fats and oils, 2-3 tsp. | Clarified butter ghee, 10 g | 23.6 P | Olive oil, 10 ml | 6.5 P |
| Total per daily ration | 1225.5 P | 212.6 P |
Luxurious daily
Vegetables and fruits, 400 g
Mango, 1 pc.
189.9 Р
Fresh blueberry, 80 g
126 Р
Avocado, 1 pc.
85 P
Cucumber, 1 pc.
44 P
Tomato, 1 pc.
43 p
Springs of protein, 2 servings
beef, steak, 160 g
405 °
Sudak fillet, 140 g
124 R
POWNITION 9000 9000 9000 9000 hard , 40 g
51 R
Farm milk, 250 ml
30 R
Grain, 3 servings in dry form
Films, 65 g
48 48
Kuskus, 90 g
9000 ° CBread Hercumles Gerkules , 80 g
16 R
Fats and oils, 2-3 tsp.
Clarified butter ghee, 10 g
R 23.6
Total per daily ration
1225.5 R
Daily ration option
Vegetables and fruits, 400 g
Frozen mixture, 200 g, 0.5 packs
30 R
raisins, 40 g
11 P
banana, 80 g, 1 pc.
7 Р
Fresh carrots, 80 g, 1 pc.
3.4 p
Springs of protein, 2 servings
Nut canned, 120 g, without liquid
32 r
canned fish, 0.5 banks
26.5 p
Milk, 2.5 servings
Buzhenka, 225 ml
27.5 r
hard cheese, 30 g
25.3 Р
Curd cheese, 30 g
16.5 p
Grain, 3 servings in dry form
Barley cereals, 80 g
13 r
Brush rice, 65 g
10.4 R
Darnitsky bread, 80 g
3.5 p
fats and oil, 2-3 hours. .
Olive oil, 10 ml
6.