Foods to increase weight of baby during pregnancy
Diet Tips To Increase Fetal Weight In Third Trimester – Pampers India
For 28 weeks, you’ve dealt with morning sickness, swollen legs, and uncomfortable nights. Over the next three months, your baby’s final developments will cause your bump to grow larger, and your body will get ready for childbirth. The third trimester of your pregnancy are most crucial for your baby’s health and well-being. To better understand what’s going on during this time, let’s take a look at the developments that will increase your baby’s weight week by week over the next 12 weeks with the help of this baby weight chart during pregnancy in grams:
| Week of pregnancy | Developments | Baby weight chart during pregnancy in grams | Baby height chart during pregnancy in centimetres |
|---|---|---|---|
| Week 28 | At this point, your baby can partially open its eyes and its central nervous system controls body temperature and rhythmic breathing. | 1,000 grams | 37.6 centimetres |
| Week 29 | You will start to feel your baby’s kicks and movements as your little one starts to make grasping motions. | 1,200 grams | 38.6 centimetres |
| Week 30 | Your baby’s hair has started to grow out now, and red blood cells will begin to form in the bone marrow. | 1,300 grams | 39.9 centimetres |
| Week 31 | At this point, your baby’s development is almost complete. The only thing left is for your little one to quickly put on the required weight. | 1,500 grams | 41.1 centimetres |
| Week 32 | Until now, a soft layer of hair, known as lanugo, was protecting your baby’s skin. This week, the hair will shed and you should be able to see your little one’s toenails. This week, the hair will shed and you should be able to see your little one’s toenails. | 1,700 grams | 42.4 centimetres |
| Week 33 | This week, for the first time ever, your baby’s pupils will respond to light stimuli. All their bones, except the skull, will start to harden. | 1,900 grams | 43.7 centimetres |
| Week 34 | This week, your baby’s fingernails will develop. | 2,100 grams | 45 centimetres |
| Week 35 | Your bundle of joy is growing nicely and their skin has started to turn smooth and rosy. | 2,400 grams | 46.2 centimetres |
| Week 36 | It’s starting to get a little cramped inside, with your baby taking up most of the amniotic sac. | 2,600 grams | 47.4 centimetres |
| Week 37 | Your baby has got a firm grasp now, and his or her head will start to descend to prepare for childbirth. | 2,900 grams | 48.6 centimetres |
| Week 38 | You’re almost there. Your baby’s head and body will have the same circumference by now. | 3,100 grams | 49.8 centimetres |
| Week 39 | It’s almost time for your baby to come out, and this week their body will start to accumulate fat to help them stay warm once they are born. | 3,300 grams | 50.7 centimetres |
| Week 40 | Your baby is fully developed and your due date is finally here. | 3,500 grams | 51.2 centimetres |
Of course, the way your baby develops and how tall or heavy your little one is will depend from pregnancy to pregnancy. This baby weight chart will give you a rough guide of what is happening each week and how your baby is gaining weight. Since the third trimester is crucial in preparing your baby for the outside world, it’s imperative that you track your pregnancy weight. If you haven’t quite put on the required amount of weight, your doctor may ask you to increase your calorie intake to help your baby grow.
If you’re wondering how to increase baby weight specifically, here’s a look at some nutritious foods that you should include in your diet:
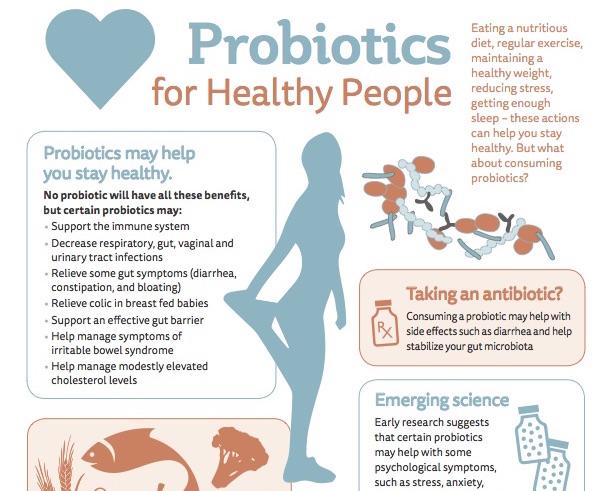
1. Eggs, Milk, Yogurt & Tofu
All of these foods have a high protein content, sufficient intake of protein in pregnancy is very crucial. The proteins you consume during this time will mostly be used to keep your baby’s growth on track while also maintaining your maternal tissues.
The proteins you consume during this time will mostly be used to keep your baby’s growth on track while also maintaining your maternal tissues.
2. Broccoli, Watercress & Cheese
These are some fabulous sources of calcium. You’ll need to incorporate this baby weight gain food to your diet to ensure that your baby’s teeth and bones grow and harden as required.
3. Fruits
Fresh fruits like kiwis, bananas, melons and strawberries can help you meet your daily vitamin C requirement. This vitamin is necessary to ensure that your baby’s placenta continues to function properly. Additionally, vitamin C helps your little one absorb the iron from the food you eat, which is required to maintain a healthy immune system.
4. Lentils
If you still feel like your 9 month baby pregnancy weight is below average, you should definitely load up on your lentils. Apart from adding protein to your diet, lentils are also rich in vitamin B1, known as thiamine, and fibres. You can consume lentils in the form of a dal, stew, or even porridge.
Apart from adding protein to your diet, lentils are also rich in vitamin B1, known as thiamine, and fibres. You can consume lentils in the form of a dal, stew, or even porridge.
5. Avocados
Avocados are a crucial baby weight gain food as they are rich in fibre and vitamins C and E. Plus, it’s a good source of healthy fats, which will help them stay warm after birth.
6. Salmon
As your baby’s brain completes its development, it’s essential that you consume a good amount of omega-3 fatty acids. Salmon will provide you with the omega-3 you require, along with giving you a healthy dose of Docosahexaenioc Acid or DHA.
7. Dark, Leafy Green Veggies
It’s time to stock up on your intake of spinach, kale and other leafy vegetables, nuts and whole grains. Rich in magnesium, these foods help the development of your baby’s bones, while also preventing your uterus from early contractions and cramps.
Rich in magnesium, these foods help the development of your baby’s bones, while also preventing your uterus from early contractions and cramps.
Even though you now know how to increase baby weight during your third trimester, it’s important that you don’t make any major changes to your third trimester diet plan without the approval of your doctor.It’s crucial to remember that your pregnancy journey is different from anybody else’s experience, so even if your friend’s or sister’s baby was a certain weight in the 38th week of pregnancy, its okay if your baby’s weight is different. As long as you continue to eat healthy and get the nutrients you and your baby require, you’ll enjoy a healthy and happy pregnancy.
How to Increase Baby Weight during Pregnancy
- Home
- Pregnancy
- Diet & Nutrition
- Prenatal Care How to Increase Fetal Weight While Pregnant
Once you find out that you are pregnant, it is important to pay heed to your diet, exercise, and lifestyle for the optimal growth and development of your unborn baby. Every mother wishes to have a healthy baby, and one of the parameters that help you know about your baby’s well-being is the foetal weight.
Every mother wishes to have a healthy baby, and one of the parameters that help you know about your baby’s well-being is the foetal weight.
Video : How to Increase Fetal Weight During Pregnancy
How is Foetus Weight Measurement Done?
Most pregnant women will have their first ultrasound scan in the first trimester. Your radiologist will take various measurements to understand the foetal growth and development. Following are some measurements that your radiologist will make:
- FL or Femur length
- HC or Head circumference
- AC or Abdominal circumference
- OFD or Occipitofrontal diameter
- BPD or Biparietal diameter
- HL or Humerus length
With the above-mentioned parameters, your radiologist will establish the foetal weight and gestational age. You will also be told about your EDD or estimated date of delivery. The measurements made by the doctor may not be exact, but it will help your doctor establish the overall well-being of the foetus.
You will also be told about your EDD or estimated date of delivery. The measurements made by the doctor may not be exact, but it will help your doctor establish the overall well-being of the foetus.
Also Read: Foetal Anaemia – Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
What is the Ideal Weight of a Foetus?
Every baby grows differently; therefore, the table below is only to give you an idea, and not the ideal baby weight gain, week by week during pregnancy.
| Pregnancy in Weeks | Foetal weight in Grams |
| 8 | 1 |
| 9 | 2 |
| 10 | 4 |
| 11 | 7 |
| 12 | 14 |
| 13 | 23 |
| 14 | 43 |
| 15 | 70 |
| 16 | 100 |
| 17 | 140 |
| 18 | 190 |
| 19 | 240 |
| 20 | 300 |
| 21 | 360 |
| 22 | 430 |
| 23 | 501 |
| 24 | 600 |
| 25 | 660 |
| 26 | 760 |
| 27 | 875 |
| 28 | 1005 |
| 29 | 1153 |
| 30 | 1319 |
| 31 | 1502 |
| 32 | 1702 |
| 33 | 1918 |
| 34 | 2146 |
| 35 | 2383 |
| 36 | 2622 |
| 37 | 2859 |
| 38 | 3083 |
| 39 | 3288 |
| 40 | 3462 |
| 41 | 3597 |
| 42 | 3685 |
Effective Tips to Increase Foetal Weight During Pregnancy
As a mommy-to-be you may wonder how to make your unborn baby gain weight, Follow some of these tips to increase foetal weight during pregnancy:
-
A Healthy and Balanced Diet
Diet plays the most important role in pregnancy.
 You should include fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, meat, and poultry in your diet if you wish to increase foetal weight.
You should include fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, meat, and poultry in your diet if you wish to increase foetal weight.
-
Include Nuts and Dry Fruits in Your Diet
A well-balanced diet also constitutes nuts and dry fruits. You may eat almonds, apricots, figs, walnuts, and other nuts and dry fruits. However, it is recommended not to go overboard with them.
-
Prenatal Vitamins
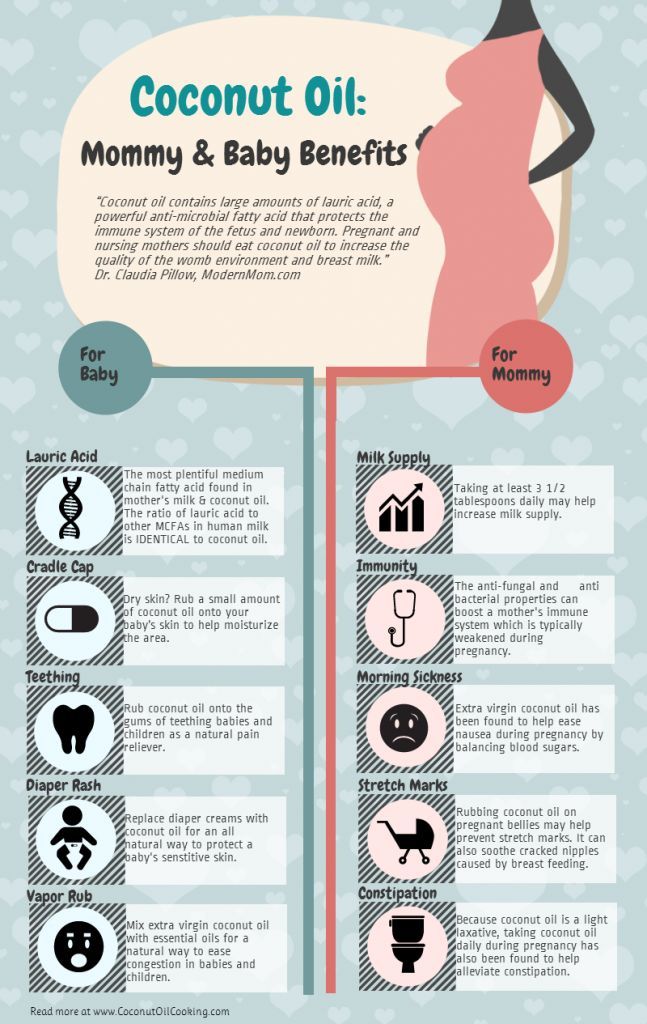
You will be given prenatal vitamins for your baby’s proper growth and development. These vitamins also help your baby gain weight. You should take these vitamins regularly for optimal foetal weight gain during pregnancy.
-
Stay Hydrated
Drink adequate amounts of fluids to avoid any kind of dehydration in pregnancy. Dehydration in pregnancy may lead to some serious medical complications. You may take fruit juices, vegetable juices, milk, buttermilk or water to keep your body well-hydrated.
-
Take Adequate Rest
It is very important for a pregnant woman to have plenty of rest. Over-exertion or unnecessary pressure may affect foetal development and growth. Try and get a minimum eight hours of uninterrupted sleep to keep your energy levels intact.
-
Stay Calm And Positive
It is not only important to take care of your physical health, but also mental wellbeing. Any kind of stress and anxiety can affect you as well as your unborn baby’s health. The resulting emotional outbursts may lead to over-eating, under-eating, or making wrong food choices, and all these may affect foetal health.
-
Medical Guidance
Your doctor will guide you in case your baby is not gaining a sufficient amount of weight. You may be told to take additional supplements or make dietary changes to increase foetal weight.
The above-mentioned tips may help your baby gain weight during pregnancy. However, it is recommended to take your doctor’s advice in this matter.
However, it is recommended to take your doctor’s advice in this matter.
What Can You Eat to Increase Baby Weight During Pregnancy?
You may include the following foods to help the foetus gain weight during pregnancy:
-
Sweet Potatoes
Sweet potatoes are loaded with fibre, potassium, Vitamin C, Vitamin B6, iron, copper, and beta-carotene. The presence of beta-carotene (an antioxidant) in sweet potatoes gets converted into Vitamin A by your body. Vitamin A, as we know, is essential for foetal skin, bones, and eyes. Sweet potatoes increase the iron levels in the body. You may eat them in mashed, baked, stewed, or shallow-fried form.
-
Lentils And Beans
Lentils and beans are jam-packed with iron and protein. You will also get enough fibre, folate and calcium by including beans and lentils in your diet. If you are a vegetarian, beans will provide you with minerals that you may otherwise get from a non-vegetarian diet (meat and poultry).
 Being rich in zinc, beans are great for reducing the risk of prolonged labour, low birth weight babies, or premature deliveries.
Being rich in zinc, beans are great for reducing the risk of prolonged labour, low birth weight babies, or premature deliveries.
-
Orange Juice
Start your day with a glass of fresh orange juice and spike up your Vitamin C, potassium and folate levels. Folate and folic acid are extremely important in pregnancy. By meeting your body’s daily requirements of these nutrients, you can reduce the baby’s chances of catching certain birth defects. Orange juice helps in keeping your overall health, metabolism, and muscle functions in place.
-
Yoghurt
Calcium, protein, Vitamin B, zinc and other bone-building nutrients are power-packed in yoghurt. As a mommy-to-be, your daily calcium requirement is 1000 mg, and you can meet this requirement with yoghurt. Apart from keeping your bone and teeth health in place, adequate amounts of calcium in the body reduce the chances of preterm labour or low birth weight babies.
-
Green Leafy Vegetables
Green vegetables such as spinach, kale, broccoli, and asparagus are loaded with essential nutrients and anti-oxidants.
 Green leafy vegetables work wonders for a pregnant woman and her developing foetus. You may get your daily dosage of calcium, potassium, Vitamin A, folate, and fibre by eating leafy vegetables. You may eat them in raw, cooked, baked, or stir-fried form for maximum benefits.
Green leafy vegetables work wonders for a pregnant woman and her developing foetus. You may get your daily dosage of calcium, potassium, Vitamin A, folate, and fibre by eating leafy vegetables. You may eat them in raw, cooked, baked, or stir-fried form for maximum benefits.
-
Salmon
Salmon is one of the best sources of omega-3 fatty acids and protein. Omega-3 fatty acids are very beneficial for a growing foetus as they help in brain and eye development, as well as supplying the required amount of protein to mothers. Salmon is considered safe for pregnant women, as it has very low levels of mercury in it.
-
Eggs
Egg are a powerhouse of protein, Vitamin A, and Vitamin D, all of which are incredible for the growth and development on the foetus. In fact, the protein profile of eggs is unmatched by any other food, making it beneficial to eat during pregnancy. Eggs are also rich in folic acids and iron, which work towards strengthening amniotic membranes and preventing birth defects and low birth weight in the foetus.
-
Milk
A daily intake of 200-500 ml of milk per day can help pregnant women increase foetal weight. Milk contains a high amount of protein and calcium, which are essential for the growth and development of the foetus. You can drink milk in plain form or come up with interesting porridge and smoothie recipes.
-
Chicken
Chicken is a great food that helps increase foetal weight. This lean meat is high in proteins that promote cell and muscle development in the body. Besides proteins, chicken also has a high amount of iron that reduces anaemia in the mother and fetus.
-
Soybean
Soybean is a rich source of protein for vegetarians and can be consumed in various forms. High in iron as well, soybean prevents anaemia due to its high iron content. You can consume soya in the form of soy milk, soya nuggets, tofu, etc.
Precautions to Take While Trying to Increase Your Baby’s Weight in the Womb
Some dietary choices may help you increase your baby’s weight in the womb. However, it is very important that you do so in a healthier manner. Overdoing anything may lead to complications. These are some precautions that you should take:
However, it is very important that you do so in a healthier manner. Overdoing anything may lead to complications. These are some precautions that you should take:
- Avoid Alcohol and Smoking: You should strictly avoid alcohol consumption and smoking in pregnancy. Both these habits can prove to be fatal for your developing baby and may also lead to serious medical complications.
- Reduce Caffeine Intake: Consuming high amounts of coffee, tea or aerated beverages can have a negative impact on foetal health.
- Avoid Fried, Sugary or Fatty Foods: Regular intake of such food items may make you prone to obesity, which in turn increase the chances of cholesterol and hypertension. It is recommended to go easy on oily, fatty, and sugary food items. Staying away from certain food categories will help you have a healthy pregnancy and also be beneficial for your unborn child.
Making healthy food choices during pregnancy is key to ensuring your baby’s growth and development is on track. We have made some suggestions in context to dietary changes that you can make during pregnancy to increase foetal weight. However, consult your doctor before making any changes or amends to your diet. With expert guidance and support, you will not only have a healthy pregnancy, but also a healthy baby.
We have made some suggestions in context to dietary changes that you can make during pregnancy to increase foetal weight. However, consult your doctor before making any changes or amends to your diet. With expert guidance and support, you will not only have a healthy pregnancy, but also a healthy baby.
References & Resources: Livestrong
Also Read:
Foetal Development: Growth in First, Second and Third Trimester
Baby Size — Week by Week Comparison with Fruits and Veggies
Previous article « Chikungunya in Children
Next article Vitamin D Deficiency in Babies »
- RELATED ARTICLES
Weight during pregnancy. What increase is considered optimal?
Why is excessive weight gain during pregnancy particularly harmful? What should be the calorie content of the diet? How to build your diet so that you can eat varied (and tasty), but at the same time not gain too much? Let's figure it out.
What makes up weight gain during pregnancy?
An increase in the subcutaneous fat layer during pregnancy is a normal and natural process.
While the baby is growing inside you, he needs energy and external protection. But during pregnancy, weight increases not only and not so much due to the adipose tissue of the mother: there is more fluid in the body, the uterus grows, the fetus and placenta develop, and the breasts increase in preparation for the feeding process.
Interestingly, weight loss during the period of toxicosis can later provoke its increase: the body will try to regain what was lost.
Expectant mothers especially actively gain weight in the second trimester and the beginning of the third, but closer to childbirth, a pregnant woman can even lose 1-2 kilograms.
As long as the weight increases more or less evenly and does not go beyond the upper limit of the norm, there is nothing to worry about. But if your weight is rapidly going up, you should be wary.
How to correctly calculate the weight, and what increase is considered optimal?
In Russian obstetric practice, it is generally accepted that the total gain should not exceed 12 kg. for the entire pregnancy. Of these 12 kg. 5-6 accounts for the fetus, placenta, amniotic fluid, another 1.5-2 - for an increase in the uterus and mammary glands, and only 3-3.5 - for the fat mass of a woman.
But this is a general indicator, a kind of "average temperature in the hospital." The optimal increase is calculated individually and depends on the initial weight of the pregnant woman, her age, the number of fetuses and the size of the child (children), physical activity.
WHO recommends that optimal weight gain be calculated based on Body Mass Index (BMI).
It is determined by the formula: body weight (kg) / height squared (m).
| BMI | Recommended weight gain |
|---|---|
19. 8-26 (normal body weight) 8-26 (normal body weight) | 12.5-15 kg |
| 26.1-29 (overweight) | 11.5 - 14 kg |
| over 29 (obese) | 7-9 kg |
How to calculate the optimal weight gain?
To do this, use the following chart:
- Calculate your BMI: divide your initial weight in kg. for height in meters squared.
For example, your "pre-pregnancy" weight was 60 kg with a height of 170 cm.
BMI = 60: (170 x 170) = 20.76.
- A BMI of less than 18.5 indicates underweight. Indicators from 18.5 to 25 are within the norm, from 25 to 30 are above the norm, and a figure greater than 30 indicates obesity.
- Now that you know your BMI, find the optimal weekly increase in the table and compare it with yours.
| Week of pregnancy | Underweight before pregnancy (BMI less than 18. 5) 5) | Normal pre-pregnancy weight (BMI 18.5 to 24.9) | Overweight before pregnancy (BMI over 30) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 0-0.9 kg | 0-0.7 kg | 0-0.5 kg |
| 6 | 0-1.4 kg | 0-1 kg | 0-0.6 kg |
| 8 | 0-1.6 kg | 0-1.2 kg | 0-0.7 kg |
| 10 | 0-1.8 kg | 0-1.3 kg | 0-0.8 kg |
| 12 | 0-2 kg | 0-1.5 kg | 0-1 kg |
| 14 | 0.5-2.7 kg | 0.5-2 kg | 0.5-1.2 kg |
| 16 | up to 3.6 kg | up to 3 kg | up to 1.4 kg |
| 18 | up to 4.6 kg | up to 4 kg | up to 2.3 kg |
| 20 | up to 6 kg | up to 5.9 kg | up to 2.9 kg |
| 22 | up to 7.2 kg | up to 7 kg | up to 3. 4 kg 4 kg |
| 24 | up to 8.6 kg | up to 8.5 kg | up to 3.9 kg |
| 26 | up to 10 kg | up to 10 kg | up to 5 kg |
| 28 | up to 13 kg | up to 11 kg | up to 5.4 kg |
| 30 | up to 14 kg | up to 12 kg | up to 5.9 kg |
| 32 | up to 15 kg | up to 13 kg | up to 6.4 kg |
| 34 | up to 16 kg | up to 14 kg | up to 7.3 kg |
| 36 | up to 17 kg | up to 15 kg | up to 7.9 kg |
| 38 | up to 18 kg | up to 16 kg | up to 8.6 kg |
| 40 | up to 18 kg | up to 16 kg | up to 9.1 kg |
Recently, doctors are increasingly talking about an individual approach and urge not to panic if the increase is slightly beyond the normal range. When assessing the state of health of a pregnant woman, the doctor focuses not only on weight, but also takes into account the results of tests and examinations and other important indicators.
When assessing the state of health of a pregnant woman, the doctor focuses not only on weight, but also takes into account the results of tests and examinations and other important indicators.
Why is excessive weight gain dangerous?
Gaining extra pounds can lead to gestational diabetes, hypertension, preeclampsia, or cause a caesarean section.
In addition, excessive weight gain during pregnancy may increase the risk of obesity and associated cardiovascular disease.
What can I do to keep my weight within normal limits during pregnancy?
First of all, consult a nutritionist. If there is no such doctor in the antenatal clinic, it makes sense to contact a specialist on a commercial basis. He will develop an individual diet, which will contain all the useful elements, and will offer to keep a food diary. It will also tell you how to eat right and weigh yourself.
To prevent excessive weight gain during pregnancy, it is enough to follow simple rules of a healthy diet:
- Eat often and in small portions;
- Always keep a “healthy snack” on hand: fresh apple wedges, unsweetened crackers, dried fruit, or sugar-free yogurt;
- Refuse soda, chips, sausages and sausages;
- Minimize sweets;
- Avoid fast food;
- Limit the use of condiments, especially salt, which retains water in the body;
- Choose steamed dishes;
- Eat more fiber-rich foods such as whole grain bread, bran, vegetables;
The diet of a pregnant woman should be varied. Include grains, vegetables, fruits, dairy products, meat and fish, legumes, or nuts.
Include grains, vegetables, fruits, dairy products, meat and fish, legumes, or nuts.
It must be remembered that expectant mothers should never starve and adhere to extreme diets.
How many calories per day do you need during pregnancy?
It is difficult to calculate the energy value per day on your own, and then strictly adhere to a certain number of calories, and it is not necessary, unless it is recommended by a nutritionist or endocrinologist. On average, you can aim for 2000-2500 calories per day, but it is important to understand that the need for calories depends on many factors: age, initial weight, health status and level of physical activity.
When should I be on the alert?
Strictly speaking, it is better for a pregnant woman not to worry and entrust her condition to a doctor who will control the development of pregnancy, analyzes and monitor weight. It is important to take tests to determine the level of fasting blood glucose once a trimester. The appearance of glucosuria, an increase in fasting blood glucose (more than 5.5 mmol / l) or an hour after a meal (more than 7.7 mmol / l) indicate the possible development of "diabetes in pregnancy", in connection with which the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment . In addition, a sharp increase in body weight can cause preeclampsia.
The appearance of glucosuria, an increase in fasting blood glucose (more than 5.5 mmol / l) or an hour after a meal (more than 7.7 mmol / l) indicate the possible development of "diabetes in pregnancy", in connection with which the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment . In addition, a sharp increase in body weight can cause preeclampsia.
These and other diseases can be dangerous, which is why you need to carefully monitor the body weight during the gestation period, but remember that pregnancy is not the time for strict diets.
When using any materials from the site nutriclub.ru, a link to the site is required.
© Nutriclub, 2020
You will also be interested
- Nutriclub - healthy nutrition and child development
- Pregnancy
- Mom's health and well-being
- weight during pregnancy.
 What increase is considered optimal? - Nutriclub
What increase is considered optimal? - Nutriclub
What foods make a baby gain weight in the womb
During fetal development, the fetus is completely dependent on the mother's lifestyle. A woman throughout her pregnancy is obliged to monitor her health, give up bad habits and carefully consider nutrition. The correct diet, filled with a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals, is switched at the planning stage. What and how much should a pregnant woman eat so that the child does not lack nutrients, and his body weight remains within the normal range?
Contents [ show ]
- How does the diet of a pregnant woman affect the weight gain of the fetus
- What foods affect the weight gain of the child in the womb
- What should be the menu of the mother
- Diet of the expectant mother by trimesters
- What to eat with a lack of mass body weight of the fetus
- Diet for overweight fetus
- Does a strong weight gain of a pregnant woman affect the fetus
- To sum up
How does the diet of a pregnant woman affect fetal weight gain
It is important to eat right at any stage of life. But pregnancy is a special period for a woman when the body needs a balanced menu. All foods that the expectant mother eats have a direct impact on the development of the fetus and an increase in its anthropometric indicators.
But pregnancy is a special period for a woman when the body needs a balanced menu. All foods that the expectant mother eats have a direct impact on the development of the fetus and an increase in its anthropometric indicators.
In general, a pregnant woman's diet is not much different from a normal healthy diet. It is recommended to increase the total calorie content by no more than 300 kcal and eat fractionally. Eating in small portions 5-6 times a day, the mother provides the fetus with a constant supply of useful trace elements.
If a woman eats poorly and restrictedly during pregnancy, a mechanism is “launched” in the child's body that is responsible for the maximum assimilation of micronutrients from a minimum amount of food. This is fraught with the threat of obesity in adulthood - in conditions of sufficient food, the body will consume substances in such a way that they are not enough.
Why does the weight of the baby in the womb depend on what and how much the mother eats? Child and maternal organisms are inextricably linked from the moment of the birth of a new life until childbirth. Whatever a woman eats, her child gets. With a lack of nutrients, the baby does not gain weight, its internal organs and systems do not develop according to the standards. If a pregnant woman abuses fatty, high-calorie foods or fast food, the fetus accumulates subcutaneous fat too quickly, which is fraught with serious complications during childbirth.
Whatever a woman eats, her child gets. With a lack of nutrients, the baby does not gain weight, its internal organs and systems do not develop according to the standards. If a pregnant woman abuses fatty, high-calorie foods or fast food, the fetus accumulates subcutaneous fat too quickly, which is fraught with serious complications during childbirth.
What foods affect the baby's weight gain in the womb
Many pregnant women only hear from their doctor about the need to adjust their diet when the scale shows a large increase or after detecting an increase in blood glucose levels. If a woman does not gain weight or her weight does not increase according to the standards with each week of pregnancy, gynecologists are in no hurry to sound the alarm. Note that both states are invalid. During the gestation period, a woman is obliged to monitor her diet in order to avoid health problems - both her own and the baby she is carrying.
To avoid excessive fetal weight gain, the expectant mother will have to give up a number of unhealthy and high-calorie foods. In the "black list":
In the "black list":
- fast food: french fries, hamburgers, pizza and other types of fast food;
- chips, croutons, snacks;
- smoked products;
- preserves and preserves;
- pastries, baked goods and sweets in large quantities;
- semi-finished products.
Avoid high salt intake during pregnancy. Salty food causes water retention, which leads to an increase in the load on the kidneys. This causes swelling, increased pressure and other health problems for the mother and child.
What should be the mother's menu
Expectant mother must be responsible for the preparation of the daily diet. If a woman does not receive enough nutrients from food, this is fraught with nutritional deficiencies for the fetus. Because of this, during the gestation period, the child is more susceptible to the development of autoimmune reactions, in the future he is threatened with metabolic problems. The task of the mother is to provide the fetus with all the conditions for stable weight gain and development. In addition, the weight gained by the mother and the fetus depends on how safely, quickly and easily the birth will take place.
In addition, the weight gained by the mother and the fetus depends on how safely, quickly and easily the birth will take place.
Nutritional deficiency is a protein-energy deficiency that negatively affects the development and functioning of all systems of the human body.
During pregnancy, a woman should eat for two. The menu is thought out so that daily food covers the daily need for valuable substances.
I trimester
Until the 13th week, the body adapts to the new state. A woman feels tired, her mood is constantly changing, her appetite disappears or increases. Under the influence of hormones, taste preferences change, an acute reaction to pungent odors appears. Often in the first trimester, a pregnant woman feels constant discomfort due to toxicosis.
It is extremely important in the first weeks of pregnancy to take care of a balanced diet. Within three months, the foundation for the health of the crumbs is laid. Mom needs to get enough vitamins, minerals and other trace elements that will help the baby grow in accordance with the norms and reduce the risks of developing intrauterine pathologies.
Mom needs to get enough vitamins, minerals and other trace elements that will help the baby grow in accordance with the norms and reduce the risks of developing intrauterine pathologies.
In the first trimester pregnant women are allowed to:
- chicken, white meat, turkey, beans - protein is a source of essential amino acids, it is the most important building material for muscle tissue;
- fish - alternate fatty and lean varieties, eg salmon with pollock or cod with salmon;
- hard fruits and raw vegetables - high in fiber, which is important to overcome possible intestinal problems, in particular constipation;
- seaweed, seafood, walnuts - sufficient iodine supplies are needed;
- buckwheat, pomegranate, cauliflower, liver - the mother's body consumes a lot of iron, so it is important to replenish its balance in a timely manner.
Daily calorie intake from weeks 1 to 13 is 2500–2700 kcal. B/F/U – 110/75/350 g.
The state of health is normalized, physical activity increases. In the fetus at this time, hair and nails begin to grow, bone tissue strengthens, muscles begin to contract, and bone mineralization occurs. In the second trimester, the mother's diet should be changed. The menu should be designed so that the number of calories almost does not increase, and the nutritional value increases.
The diet includes:
- cheese, cottage cheese, sesame seeds, milk - to provide mother and child with calcium;
- butter and vegetable oils, eggs, fatty fish, cod liver - to replenish vitamin D reserves;
- greens, cabbage, spinach, beets, pork and beef liver, buckwheat - for the prevention of iron deficiency.
The recommended amount of calories per day is 2800-3000 kcal. B/F/U – 120/85/100
III trimester
By the 27th week, almost all systems and organs of the child in the mother's womb are formed. From this time until childbirth, the baby is stored in subcutaneous fat.
It is important for mom to adjust the diet and monitor weight gain.
In the third trimester, the correct diet of a pregnant woman contains:
- vegetable oils - they contain polyunsaturated acids Omega 3 and Omega 6, which the human body does not synthesize, necessary for the absorption of minerals and vitamins;
- vegetables - both fresh and boiled or baked;
- fruits and berries are natural storehouses of vitamins.
The calorie content of food consumed per day should not exceed 2900-3100 kcal. B/F/U - 100/75/100 g.
What to eat when the fetus is underweight
A mother's diet during pregnancy determines how healthy the baby will be born. If the doctor has determined that the fetus weighs less than normal for a certain period, the expectant mother is advised to pay attention to eating habits. But this does not mean that you need to eat a lot of fatty, sweet, starchy foods.
In order for a child to avoid intrauterine malnutrition, it is necessary to include in the menu:
- more protein - beef, white meat, chicken eggs, dairy products;
- carbohydrates - cereals, vegetables and fruits;
- calcium - green leafy vegetables, flax and sesame seeds, cottage cheese, hard cheese;
- sweets - natural chocolate, homemade marshmallows, dried fruits.

A balanced diet will have a positive effect on the development of the baby in the womb, and will also improve the well-being of a pregnant woman.
Hypotrophy - insufficient increase in body weight in relation to its height and age.
Diet for excess body weight of the fetus
If the doctor sees on ultrasound that the child exceeds the weight parameters, the specialist recommends that the woman think about her diet. It is not worth counting calories or getting hung up on the problem - you just need to make some adjustments to the diet and menu:
- eat fractionally 5-6 times a day with an interval of 3-4 hours;
- refuse unhealthy snacks;
- process food in useful ways - boil, stew or bake;
- limit the amount of salt;
- Avoid sweets and fast carbohydrates.
A pregnant woman needs to monitor her fluid intake, drink at least 2 liters of purified, but not carbonated water daily.

.