How long feed baby breast milk
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) | Breastfeeding
What are the benefits of breastfeeding?
Breastfeeding is good for both infants and mothers. Breast milk is the best source of nutrition for most infants. As an infant grows, breast milk changes to meet the infant’s nutritional needs. Breastfeeding can also help protect the infant and mother against certain illnesses and diseases:
Benefits to Infants
Infants who are breastfed have a lower risk of:
- Asthma.
- Obesity.
- Type 1 diabetes.
- Severe lower respiratory disease.
- Acute otitis media (ear infections).
- Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
- Gastrointestinal infections (diarrhea/vomiting).
- Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) for preterm infants.
Benefit to Mothers
Mothers who breastfeed their infants have a lower risk of:
- Breast cancer.
- Ovarian cancer.
- Type 2 diabetes.
- High blood pressure.
Families can visit CDC’s Infant and Toddler Nutrition website to learn more about what to expect while breastfeeding.
When should a mother avoid breastfeeding (contraindications)?
Breast milk provides the best nutrition for most infants, including premature and sick newborns. However, there are rare exceptions when breast milk or breastfeeding is not recommended. Learn more about contraindications to breastfeeding.
Only a few medications are contraindicated (not recommended) while breastfeeding. Although many medications do pass into breast milk, most have little or no effect on milk supply or on an infant’s well-being. However, health care providers should always weigh the risks and benefits when prescribing medications to breastfeeding mothers.
Learn more about safe prescription medication use while breastfeeding.
Top of Page
How is growth assessed for breastfed infants?
In the United States, the World Health Organization (WHO) Growth Standard Charts are recommended for use with both breastfed and formula-fed infants and children, from birth to 2 years of age, to monitor growth. The WHO growth charts reflect growth patterns among children who were predominantly breastfed for at least 4 months and were still breastfeeding at 12 months. The WHO growth charts establish the growth of the breastfed infant as the norm for growth and are the standards for how children should grow when provided optimal conditions. Clinicians should be aware that healthy breastfed infants typically gain weight faster than formula-fed infants in the first few months of life but then gain weight more slowly for the remainder of infancy, even after complementary foods are introduced.
The WHO growth charts reflect growth patterns among children who were predominantly breastfed for at least 4 months and were still breastfeeding at 12 months. The WHO growth charts establish the growth of the breastfed infant as the norm for growth and are the standards for how children should grow when provided optimal conditions. Clinicians should be aware that healthy breastfed infants typically gain weight faster than formula-fed infants in the first few months of life but then gain weight more slowly for the remainder of infancy, even after complementary foods are introduced.
For children older than 2 years (2 to 19 years of age) CDC and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend that health care providers use the CDC Growth Reference Charts.
Visit the Growth Chart Training website for a set of self-directed, interactive training courses.
Source: Grummer-Strawn LM, Reinold C, Krebs NF. Use of the World Health Organization and CDC growth charts for children aged 0 to 59 months in the United States.![]() MMWR Recomm Rep. 2010;59(RR-9):1–15.
MMWR Recomm Rep. 2010;59(RR-9):1–15.
Top of Page
How long should a mother breastfeed?
The U.S. Dietary Guidelines for Americans [PDF-30.6MB] recommend that infants be exclusively breastfed for about the first 6 months, and then continuing breastfeeding while introducing appropriate complementary foods until your child is 12 months old or older. The American Academy of Pediatrics and the World Health Organization also recommend exclusive breastfeeding for about the first 6 months, with continued breastfeeding along with introducing appropriate complementary foods for up to 2 years of age or longer.
Mothers should be encouraged to breastfeed their children for at least 1 year. The longer an infant is breastfed, the greater the protection from certain illnesses and long-term diseases. The more months or years a woman breastfeeds (combined breastfeeding of all her children), the greater the benefits to her health as well.
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. To learn more about infant and toddler feeding, visit CDC’s Infant and Toddler Nutrition website.
To learn more about infant and toddler feeding, visit CDC’s Infant and Toddler Nutrition website.
Top of Page
What can happen if someone else’s breast milk is given to another child?
Very few illnesses are transmitted via breast milk. Learn more about what to do if an infant or child is mistakenly fed another woman’s expressed breast milk.
Top of Page
Are special precautions needed for handling breast milk?
CDC does not list human breast milk as a body fluid to which universal precautions apply. Occupational exposure to human breast milk has not been shown to lead to transmission of HIV or Hepatitis B infection. However, because human breast milk has been implicated in transmitting HIV from mother to infant, gloves may be worn as a precaution by health care workers who are frequently exposed to breast milk (e.g., people working in human milk banks (defined below). For additional information regarding universal precautions as they apply to breast milk in the transmission of HIV and Hepatitis B infections, visit the following resources:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Perspectives in disease prevention and health promotion update: universal precautions for prevention of transmission of human immunodeficiency virus, Hepatitis B virus, and other bloodborne pathogens in health-care settings. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1988;37(24):377–388.
Perspectives in disease prevention and health promotion update: universal precautions for prevention of transmission of human immunodeficiency virus, Hepatitis B virus, and other bloodborne pathogens in health-care settings. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1988;37(24):377–388.
Top of Page
Where can mothers find more information about preparation and storage of breast milk?
CDC has guidelines for proper storage and preparation of breast milk to maintain the safety and quality of expressed breast milk for the health of the baby.
For more information about specific storage and preparation of breast milk questions, such as where to store breast milk at work, and what to do when the power goes out, visit CDC’s Storage and Preparation of Breast Milk Frequently Asked Questions.
Top of Page
What are human milk banks?
Human milk banks are a service established for the purpose of collecting milk from donors and processing, screening, storing, and distributing donated milk to meet the specific needs of individuals for whom human milk is prescribed by licensed health care providers. When possible, human milk banks also serve healthy infants who have been adopted or are not able to get their own mother’s milk.
When possible, human milk banks also serve healthy infants who have been adopted or are not able to get their own mother’s milk.
Milk banks accept donations directly at their deposit sites or they can arrange for safe, overnight transportation of human milk at no cost to the donor. Learn more about donating to a milk bank by visiting the Human Milk Banking Association of North America (HMBANA).
Top of Page
Is it safe for families to buy breast milk on the internet?
The American Academy of Pediatrics and the Food and Drug Administration recommend avoiding Internet-based milk sharing sites and instead recommend contacting milk banks. Research has demonstrated that some milk samples sold online have been contaminated with a range of bacteria.1
Nonprofit donor human milk banks, where processed human milk comes from screened donors, have a long safety record in North America. All member banks of the Human Milk Banking Association of North America (HMBANA) must operate under specific evidence-based guidelines that require extensive testing and processing procedures as well as self-reported health information and a health statement from both the donor’s health care provider and the infant’s health care provider. Because most of the milk from milk banks is given to hospitalized and fragile infants, milk banks may not have enough to serve healthy infants at all times. To find a human milk bank, contact HMBANA.
Because most of the milk from milk banks is given to hospitalized and fragile infants, milk banks may not have enough to serve healthy infants at all times. To find a human milk bank, contact HMBANA.
1Keim, SA, Hogan, JS, McNamara, KA, et al. Microbial contamination of human milk purchased via the internet. Pediatrics. 2013;132(5).
Top of Page
What legal rights do breastfeeding mothers have?
Breastfeeding Laws
- All 50 states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands have laws that specifically allow women to breastfeed in any public or private location. Visit the National Conference of State Legislatures to learn more about federal and state laws that protect and support breastfeeding.
Workplace Laws
- The “Break Time for Nursing Mothers Provision” of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) requires employers to support breastfeeding mothers to express breast milk for 1 year after each child’s birth by providing mothers with reasonable break time and a private, non-bathroom space to express their breast milk.
 Visit the United States Department of Labor to learn more.
Visit the United States Department of Labor to learn more.
Travel Laws
- Air travelers are permitted by the Transportation Security Administration (TSA) to bring breast milk, formula, and juice in excess of 3.4 ounces in their carry-on baggage and it does not need to fit within a quart size bag. Ice packs, freezer packs, and other accessories needed to keep the liquid cool are also allowed in carry-on bags. All liquids and partially frozen accessories are subject to being screened by X-ray. TSA is required by the Bottles and Breastfeeding Equipment Screening Act (BABES act) to provide ongoing training to ensure TSA staff receive consistent training related to traveling with breast milk, formula, and infant feeding equipment. Visit the TSA to learn more about traveling with breast milk, formula, and juice. For tips on travel and breastfeeding, visit Travel Recommendations for the Nursing Mother.
Visit the Federal Policies, Programs, & Initiatives website to learn more about laws related to breastfeeding protections.
Top of Page
How can a mother continue to provide breast milk to her infant after returning to work or school?
Being prepared for returning to work or school can help a mother ease the transition and continue to breastfeed after her maternity leave is over. The Office on Women’s Health has information for making this transition easier.
When a mother is away from her infant, she can pump or hand express her breast milk so that her infant can drink breast milk from a bottle. Mothers can visit CDC’s Infant and Toddler Nutrition website to learn more about pumping breast milk.
Mothers who are expressing their breast milk should visit the CDC’s Proper Storage and Preparation of Breast Milk website to learn how to prepare and store breast milk safely for her infant.
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) requires employers to support breastfeeding mothers to express breast milk for 1 year after each child’s birth by providing mothers with reasonable break time and a private, non-bathroom space to express their breast milk. For more information about the types of employees and employers to which the requirements apply, refer to the United States Department of Labor’s Frequently Asked Questions.
For more information about the types of employees and employers to which the requirements apply, refer to the United States Department of Labor’s Frequently Asked Questions.
Top of Page
Where can mothers find breastfeeding support and additional Information about breastfeeding?
Help mothers find lactation support through the following resources:
- International Lactation Consultant Association (IBCLCs)
- United States Lactation Consultant Association (IBCLCs)
- Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) clinics
- La Leche League
Help mothers find resources about breastfeeding by directing them to the following websites:
- CDC— Infant and Toddler Nutrition
- Office on Women’s Health—Breastfeeding
- American Academy of Pediatrics—Healthy Children
- United States Breastfeeding Committee—State Coalitions Directory
- US Department of Agriculture—WIC Breastfeeding Support
Top of Page
Does breastfeeding during a child’s vaccine injections help with pain management?
Parents who are breastfeeding should be encouraged to breastfeed children age 2 years or younger before, during, and after their child’s vaccination. Several aspects of breastfeeding are thought to decrease pain by multiple mechanisms: being held by the parent, feeling skin-to-skin contact, suckling, being distracted, and ingesting breast milk. Potential adverse events such as gagging or spitting up have not been reported. Alternatives to breastfeeding include bottle-feeding with expressed breast milk or formula throughout the child’s procedure, which simulates aspects of breastfeeding.
Several aspects of breastfeeding are thought to decrease pain by multiple mechanisms: being held by the parent, feeling skin-to-skin contact, suckling, being distracted, and ingesting breast milk. Potential adverse events such as gagging or spitting up have not been reported. Alternatives to breastfeeding include bottle-feeding with expressed breast milk or formula throughout the child’s procedure, which simulates aspects of breastfeeding.
Top of Page
Does breastfeeding after a child’s rotavirus vaccine impact the vaccine’s efficacy?
There is not sufficient evidence to suggest that breastfeeding can have a negative effect on rotavirus vaccine efficacy. A previous study found that human milk from women who live in areas with endemic rotavirus contains antibodies that can neutralize live rotavirus vaccine virus. However, in licensing trials, the effectiveness of rotavirus vaccine in breastfed infants was comparable to that in non-breastfed infants.
CDC does not recommend restricting or discontinuing breastfeeding before or after a child receives the rotavirus vaccine. Breastfed infants should be vaccinated according to the same schedule as non-breastfed infants.
Breastfed infants should be vaccinated according to the same schedule as non-breastfed infants.
Learn More about prevention of Rotavirus Gastroenteritis among infants and children.
Top of Page
Breastfeeding FAQs: How Much and How Often (for Parents)
Breastfeeding is a natural thing to do, but it still comes with its fair share of questions. Here's what you need to know about how often and how long to breastfeed your baby.
How Often Should I Breastfeed?
Newborn babies should breastfeed 8–12 times per day for about the first month. Breast milk is easily digested, so newborns are hungry often. Frequent feedings helps stimulate your milk production during the first few weeks.
By the time your baby is 1–2 months old, he or she probably will nurse 7–9 times a day.
In the first few weeks of life, breastfeeding should be "on demand" (when your baby is hungry), which is about every 1-1/2 to 3 hours. As newborns get older, they'll nurse less often, and may have a more predictable schedule. Some might feed every 90 minutes, whereas others might go 2–3 hours between feedings.
Some might feed every 90 minutes, whereas others might go 2–3 hours between feedings.
Newborns should not go more than about 4 hours without feeding, even overnight.
How Do I Count the Time Between Feedings?
Count the length of time between feedings from the time your baby begins to nurse (rather than at the end) to when your little one starts nursing again. In other words, when your doctor asks how often your baby is feeding, you can say "about every 2 hours" if your first feeding started at 6 a.m., the next feeding was around 8 a.m., then 10 a.m., and so on.
Especially at first, you might feel like you're nursing around the clock, which is normal. Soon enough, your baby will go longer between feedings.
How Long Does Nursing Take?
Newborns may nurse for up to 20 minutes or longer on one or both breasts. As babies get older and more skilled at breastfeeding, they may take about 5–10 minutes on each side.
How long it takes to breastfeed depends on you, your baby, and other things, such as whether:
- your milk supply has come in (this usually happens 2–5 days after birth)
- your let-down reflex (which causes milk to flow from the nipple) happens right away or after a few minutes into a feeding
- your milk flow is slow or fast
- the baby has a good latch, taking in as much as possible of your areola (the dark circle of skin around your nipple)
- your baby begins gulping right away or takes it slow
- your baby is sleepy or distracted
Call your doctor if you're worried that your baby's feedings seem too short or too long.
When Should I Alternate Breasts?
Alternate breasts and try to give each one the same amount of nursing time throughout the day. This helps to keep up your milk supply in both breasts and prevents painful engorgement (when your breasts overfill with milk).
You may switch breasts in the middle of each feeding and then alternate which breast you offer first for each feeding. Can't remember where your baby last nursed? It can help to attach a reminder — like a safety pin or small ribbon — to your bra strap so you'll know which breast your baby last nursed on. Then, start with that breast at the next feeding. Or, keep a notebook handy or use a breastfeeding app to keep track of how your baby feeds.
Your baby may like switching breasts at each feeding or prefer to nurse just on one side. If so, then offer the other breast at the next feeding. Do whatever works best and is the most comfortable for you and your baby.
How Often Should I Burp My Baby During Feedings?
After your baby finishes on one side, try burping before switching breasts. Sometimes, the movement alone can be enough to cause a baby to burp.
Sometimes, the movement alone can be enough to cause a baby to burp.
Some infants need more burping, others less, and it can vary from feeding to feeding.
If your baby spits up a lot, try burping more often. While it's normal for infants to "spit up" a small amount after eating or during burping, a baby should not vomit after feeding. If your baby throws up all or most of a feeding, there could be a problem that needs medical care. If you're worried that your baby is spitting up too much, call your doctor.
Why Is My Baby Hungrier Than Usual?
When babies go through a period of rapid growth (called a growth spurt), they want to eat more than usual. These can happen at any time. But in the early months, growth spurts often happen when a baby is:
- 7–14 days old
- 2 months old
- 4 months old
- 6 months old
During these times and whenever your baby seems extra hungry, follow your little one's hunger cues. You may need to breastfeed more often for a while.
How Long Should I Breastfeed My Baby?
That's a personal choice. Experts recommend that babies be breastfed exclusively (without formula, water, juice, non–breast milk, or food) for the first 6 months. Then, breastfeeding can continue until 12 months (and beyond) if it's working for you and your baby.
Breastfeeding has many benefits for mom and baby both. Studies show that breastfeeding can lessen a baby's chances of diarrhea, ear infections, and bacterial meningitis, or make symptoms less severe. Breastfeeding also may protect children from sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), diabetes, obesity, and asthma.
For moms, breastfeeding burns calories and helps shrink the uterus. In fact, breastfeeding moms might return to their pre–pregnancy shape and weight quicker. Breastfeeding also helps lower a woman's risk of diseases like:
- breast cancer
- high blood pressure
- diabetes
- heart disease
It also might help protect moms from uterine cancer and ovarian cancer.
Termination of breastfeeding | Stopping breastfeeding
When is it time to stop breastfeeding and what is the best way to do it? Read our article for useful practical tips on weaning.
Share this information
How long should breastfeeding continue? Three months? Six? Year? Or maybe a few years?
The World Health Organization (WHO) and other authorities recommend that infants be exclusively breastfed for the first six months and then continue to be breastfed along with other foods (complementary foods) for at least two years. 1
The fact is that breast milk is not just food. It is a natural sedative if the child is anxious or tired. In addition, milk contains immune-boosting components, the amount of which increases dramatically when the baby gets sick. 2
According to anthropologists, the natural age of a person to stop breastfeeding is even more than two years. Given factors such as tooth development, body weight, comparison with other primates, and historical evidence, some scientists believe that breastfeeding may last up to two to four years. A number of researchers even believe that our ancestors breastfed children up to six or seven years of age. 3
Given factors such as tooth development, body weight, comparison with other primates, and historical evidence, some scientists believe that breastfeeding may last up to two to four years. A number of researchers even believe that our ancestors breastfed children up to six or seven years of age. 3
Today, more than 60% of mothers in developed countries start giving their babies formula or complementary foods before six months of age, 4 although WHO does not recommend this.
When is it time to stop breastfeeding?
Weaning means that you gradually stop breastfeeding your baby. Ideally, the first step in this process is the gradual introduction of complementary foods, starting at about six months of age. In this case, breastfeeding continues. The weaning process continues until the mother's milk has been completely replaced by other foods and drinks.
“After six months, the baby needs higher doses of certain nutrients, such as iron, zinc, vitamins B and D, that he cannot get from breast milk or from his own reserves,” says Sarah Beeson, health visitor from Great Britain.
“But solid food should at first only supplement the main diet with breast milk and gradually replace it. Mother's milk remains the main source of nutrition for the baby for many months to come.”
On average, a seven-month-old baby gets 93% of its calories from breast milk. And even between the 11th and 16th months, milk provides him with about half of the daily calorie intake. 5
“Sometimes moms think that breastmilk isn't that important once a baby has started solid foods, but the truth is, no matter how many months old a baby is, there's nothing better than your milk,” continues Sarah.
In fact, the process of finishing breastfeeding can take as long as mother and baby want. “When to stop breastfeeding is up to you,” says Sarah. The only thing that matters is what you think is right for you and your child.”
How to wean
Whenever you decide to start weaning your baby, it's best to do it gradually. An abrupt cessation of breastfeeding can lead to lactostasis, blockage of the milk ducts and mastitis, and in a child such a sudden change can adversely affect the state of the digestive and immune systems. In addition, it will be difficult for both of you psychologically.
In addition, it will be difficult for both of you psychologically.
When should I stop breastfeeding?
Sometimes mothers mistakenly believe that it is time to stop breastfeeding, when in fact there is no reason to. If you're returning to work, breastfeeding can be a great way to stay close to your baby during this difficult time for both of you. You can express milk at work, and morning and evening feeding sessions will give you the opportunity to spend time alone with your baby. If you need to leave without your baby, you can also express milk and bring or send it home.
If you get sick, this is not always a reason to stop breastfeeding. Read our advice in the article on breastfeeding when sick and consult with your healthcare professional.
Weaning up to six months
If you cannot continue breastfeeding until six months and want to try weaning your baby, start by replacing one feeding a day with a bottle of formula.
“It's best to start with midday feedings. Babies are very alert and able to smell breast milk nearby, so ask your partner or relative to give your baby a bottle when you're in the other room,” Sarah advises.
Babies are very alert and able to smell breast milk nearby, so ask your partner or relative to give your baby a bottle when you're in the other room,” Sarah advises.
“Be hygienic when preparing meals. Be prepared for the fact that the baby will take fewer servings of expressed milk per day than if he was fed directly from the breast. Don't make him eat more milk than he wants."
You will probably feel that your breasts are fuller and more tender. This is due to the fact that your body is rebuilding to produce less milk. If this creates discomfort, try expressing some milk—just enough to relieve the discomfort without stimulating extra production.
When your body adjusts to the new volume - usually after a few days - replace with formula for one more meal a day. Continue this until you have changed all feedings and your baby is completely weaned.
“I had complications after my first birth, as a result I lost a lot of weight very quickly, and besides, I developed mastitis. Lactation was very weak, and at three months I was forced to stop breastfeeding,” recalls Jennifer, a mother of two from the UK, “I gradually replaced one feeding, so physically it was easy, but mentally it was hard for me.”
Lactation was very weak, and at three months I was forced to stop breastfeeding,” recalls Jennifer, a mother of two from the UK, “I gradually replaced one feeding, so physically it was easy, but mentally it was hard for me.”
If you want to maintain closeness with your baby and all the health benefits of breastfeeding, but still need to cut down on breastfeeding, try partial weaning, replacing only a few feeds a day with formula.
Weaning after six months
Once your baby starts eating solid foods (about six months old), you will notice that breastfeeding naturally occurs less and less. For a year, it can be reduced to just a couple of times a day, and feedings will be replaced by full meals and healthy snacks.
Anyway, if you intend to continue to reduce breastfeeding, do it gradually, replacing one feeding at a time. Use formula milk if your baby is under 12 months old. With cow's milk, you should wait at least up to a year.
“When I decided to wean my son, I breastfed him three times a day and gave him other foods three times plus light snacks. Gradually, I replaced all breastfeedings with formula. By 11 months, we only had one nighttime breastfeed left,” says Ruth, a UK mom.
Gradually, I replaced all breastfeedings with formula. By 11 months, we only had one nighttime breastfeed left,” says Ruth, a UK mom.
There are various ways to distract a child from changes in his diet. Some mothers suggest that instead of breastfeeding something to drink and eat together to maintain a sense of closeness. You can also change your daily routine, play your favorite game, or replace feeding with caresses - from you or from your partner. Some children take longer to get used to the new food, but in the end everything falls into place. If you are having difficulty weaning, ask your healthcare provider for advice.
Ending breastfeeding naturally
Ending breastfeeding can be guided by the baby's wishes. This is called baby-initiated weaning, or the natural termination of breastfeeding. Such a process is likely to be long and gradual. Month after month, feeding sessions will become shorter and less frequent, until one day the child completely loses interest in the breast.
“My daughter stopped breastfeeding on her own when she was four years old,” says Sarah, a mother from the UK. And once, when we were on vacation, she seemed to just forget about her breasts. Now, six months later, she sometimes still asks for breasts, but she already knows that there is no milk there.
You will have a huge amount of time for the body to adapt, so there should be no discomfort or swelling of the breast. However, you may find it difficult emotionally, so spend more time petting and bonding with your baby.
“Child-initiated termination of breastfeeding was right for me because I never gave my son formula or a bottle. I didn’t want to abruptly stop feeding and refuse him,” recalls Kelly, a mother from the UK, “He himself lost interest in breasts at the age of two and a half years. For us, it was the best scenario, although emotionally it was not very easy for me.”
What if you need to stop breastfeeding quickly?
It is best not to stop breastfeeding abruptly, but sometimes it is necessary for medical reasons or because you cannot be near the baby.
If you have been breastfeeding your baby up to this point, you will most likely have to express your milk to avoid breast swelling. Some mothers prefer to use a breast pump for this, others find it easier to express milk manually. You only need to pump a little, just to eliminate the discomfort, otherwise your body will take it as a signal to produce more milk.
At first, the breasts may swell and become tender, but this will pass. Breast milk contains a so-called feedback lactation inhibitor. When breastfeeding is stopped, this inhibitor tells your body to slow down milk production, but it can take days or even weeks for your breasts to rebuild.
Certain medications can relieve pain and should be discussed with your doctor. Always follow your pharmacist's instructions or directions, and consult your healthcare professional before taking any medication.
“I had to abruptly stop breastfeeding when my daughter was eight months old because she had to take strong painkillers,” says Peggy, a mother from Switzerland. “It was very difficult because the baby was constantly looking for a breast and crying. I held her tightly to me as I gave her a bottle. This calmed her, and after a month everything was all right.
“It was very difficult because the baby was constantly looking for a breast and crying. I held her tightly to me as I gave her a bottle. This calmed her, and after a month everything was all right.
Can I continue breastfeeding if I want to get pregnant again?
Breastfeeding is a natural contraceptive. However, this method is not the most reliable, especially after six months or if you are not exclusively breastfeeding. This means that you can get pregnant even while you are breastfeeding.
Pregnant and breastfeeding mothers sometimes receive conflicting advice about whether to stop breastfeeding. Consistent feeding of two children of different ages is of course possible, and with the advent of the second baby, your body will produce the kind of milk that both of them need.
It is not uncommon for an older child to refuse to breastfeed or skip feedings if the mother is pregnant. This may be due to changes in milk composition that occur during pregnancy. Milk can change the taste and become less sweet. 6 If your baby is under one year of age when he starts to stop breastfeeding, make sure he continues to gain weight.
Milk can change the taste and become less sweet. 6 If your baby is under one year of age when he starts to stop breastfeeding, make sure he continues to gain weight.
Talk to your doctor if you want to continue breastfeeding during pregnancy, but have had a preterm birth or miscarriage, or have any bleeding in the past.
If you need medical help to conceive, certain drugs and procedures may not be suitable while you are breastfeeding. Discuss all possible options before deciding to stop breastfeeding.
And finally...
Whenever you decide to end breastfeeding, and whatever method you choose to do so, be kind to yourself and your baby. This is a huge change for both of you physically, hormonally, and emotionally, so proceed thoughtfully and carefully.
“Although my body responded normally to stopping breastfeeding, it was psychologically difficult for me. The thing that united us for so long is over, - Jane, a mother of two children from the USA, shares her impressions, - I worked long hours, five days a week, and breastfeeding made me feel that I occupy a special place in the lives of children. But when it stopped, we soon found other ways to be together.”
But when it stopped, we soon found other ways to be together.”
Literature
1 World Health Organization. [Internet] Health Topics: Breastfeeding: 2018 [Accessed: 02/08/2018]. Available from : http://www.who.int/topics/breastfeeding/en - World Health Organization. "Health Issues: Breastfeeding" [Internet]. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 2018 [Visit 02/08/2018]. Article linked: http://www.who.int/topics/breastfeeding/e
2 Hassiotou et al. Maternal and infant infections stimulate a rapid leukocyte response in breastmilk. Clin Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4): e 3. - Hassiot F. et al., "Infectious diseases of the mother and child stimulate a rapid leukocyte reaction in breast milk." Clean Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4):e3.
3 Dettwyler KA. When to wean: biological versus cultural perspectives. Clin Obstet Gynecol . 2004; 47(3)712-723. - Dettwiler KA, "Time to wean: weaning from a biological and cultural point of view". Klin Obstet Ginekol (Clinical obstetrics and gynecology). 2004; 47(3):712-723.
2004; 47(3)712-723. - Dettwiler KA, "Time to wean: weaning from a biological and cultural point of view". Klin Obstet Ginekol (Clinical obstetrics and gynecology). 2004; 47(3):712-723.
4 Victora CG Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet. 2016;387(10017):475-490. - Victor S.J. et al., "Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms and long-term effects". Lancet 2016;387(10017):475-490.
5 Dewey KG et al. Breast milk volume and composition during late lactation (7-20 months). J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr . 1984;3(5):713-720. — Dewey C.G. et al., "Amount and composition of breast milk in late lactation (7-20 months)". F Pediatrician Gastroenterol Nutr. 1984;3(5):713-720.
6 Prosser CG et al. Mammary gland function during gradual weaning and early gestation in women. Aust J Exp Biol Med 9021 9029 Sci. 1984;62( Pt 2):215-228. - Prosser S.G. et al., "Breast Function During Gradual Weaning and Early Gestation." Aust J Exp Biol Med Sai. 1984;62( Pt 2):215-228.
Aust J Exp Biol Med 9021 9029 Sci. 1984;62( Pt 2):215-228. - Prosser S.G. et al., "Breast Function During Gradual Weaning and Early Gestation." Aust J Exp Biol Med Sai. 1984;62( Pt 2):215-228.
Breastfeeding after 1 month: what to expect
Do you know when breast milk production stabilizes? And how does the frequency and duration of feedings change as the baby grows? You will find answers to these questions in our recommendations for breastfeeding after the first month.
Share this information
Congratulations: You made it through the first month of breastfeeding. Your breast milk has reached full maturity 1 , its production stabilizes, and it leaks almost or not at all from the chest. Don't worry, it's not getting less milk, it's just that your breasts are better able to produce and store it now. 2 At the age of six weeks, your baby will begin to please you with his charming toothless smiles, and by two months you will already have 500-600 feedings behind you. With a favorable development of events, problems with latch on by this point will already be resolved, and you can simply enjoy the convenience and benefits of breastfeeding.
2 At the age of six weeks, your baby will begin to please you with his charming toothless smiles, and by two months you will already have 500-600 feedings behind you. With a favorable development of events, problems with latch on by this point will already be resolved, and you can simply enjoy the convenience and benefits of breastfeeding.
When does breastfeeding decrease?
"Normal" feeding frequency for babies aged one to six months varies considerably, with some needing four times a day, others needing to breastfeed 13 times a day. 3
“From the age of one month, the amount of milk a baby consumes per feed increases so that he can go without food for longer,” explains Cathy Garbin, a recognized international expert on breastfeeding, “A baby’s stomach grows, so he eat more at one time. In addition, mature milk allows him to stay full longer.”
Feeding can last from 12 minutes to one hour -
the habits of babies vary so much! 3 But if the child is gaining weight and falls within this range, there is no cause for concern.
What is most surprising, no matter how often the baby eats, he consumes approximately the same amount of milk per day - both at one month and at six, when it is time to start complementary foods with solid food. 4
“However, sometimes the baby eats more and sometimes less, especially when he is unwell. It’s better to just listen to his needs,” Katie explains.
Is breast milk sufficient for the first six months?
Yes. Breast milk contains everything a baby needs for the first
six months of life - exclusively breastfed babies don't even need to drink water! 5 Until about six months of age, a child's digestive system is simply not adapted to the digestion of solid food, and he will be able to drink cow's milk only after a year.
In addition, breastfeeding during this period prepares the child for further development. It strengthens the muscles of the mouth, develops the jaw and helps straighten the teeth 6.7 .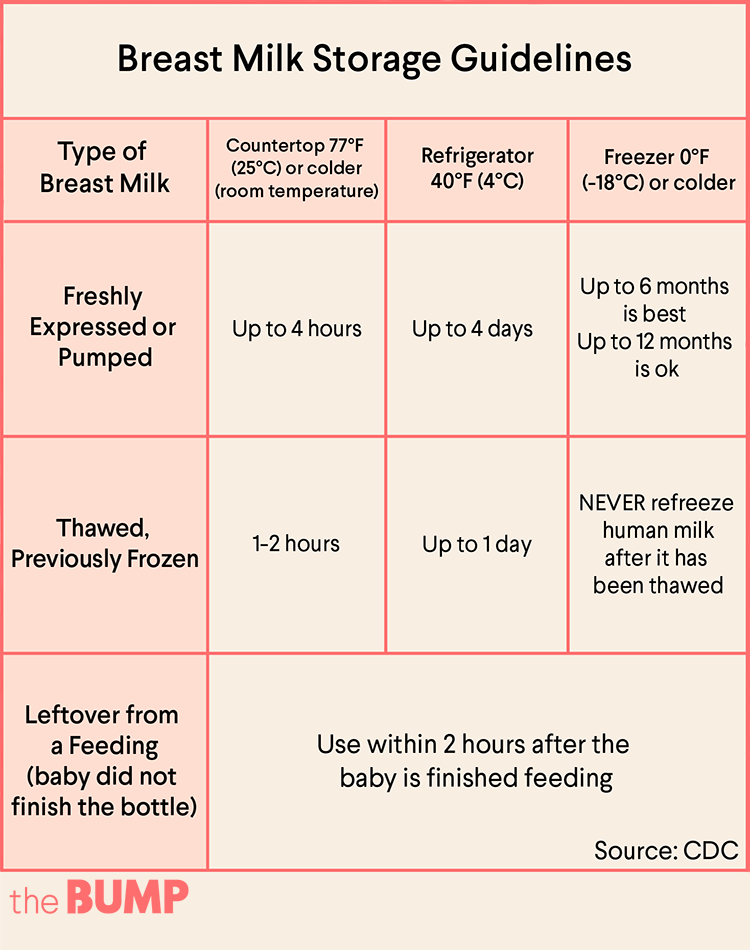 All this will come in handy when the baby begins to eat and talk. And because what you eat and drink affects how your breast milk tastes, your baby discovers new tastes even before he starts eating solid foods. 8
All this will come in handy when the baby begins to eat and talk. And because what you eat and drink affects how your breast milk tastes, your baby discovers new tastes even before he starts eating solid foods. 8
In addition, when your baby is sick, your body produces breast milk that is
rich in antibodies that help fight infection. 9 In other words, milk continues to protect the baby for many months as he grows and becomes more active.
Breastfeeding is also very comfortable once you get used to it. Claudia, a mother of two from the UK, notes: “No need to sterilize a mountain of bottles, prepare formula, carry it all with you, warm it up - in general, breastfeeding turned out to be very convenient, especially when my babies grew up and we began to leave the house more often. ".
At what age does a breastfed baby start sleeping through the night?
Waking up at night is normal for babies. Most babies between the ages of one and six months consume a fifth of their daily milk requirement at night, so nighttime feedings should not be neglected if you want your baby to get the required amount of calories. 3
3
"It really depends on what you mean by 'sleep through the night,'" says Cathy. "And it's better than waking up every two hours anyway! I have met infants who, starting at six weeks old, fell asleep at 19:00 and woke up at 7:00, but most continue to wake up frequently at night after this age. All children are different."
In Wales, a study of more than 700 infants showed that almost 80% of children aged 6 to 12 months wake up at least once a night, and 25% of them wake up three times or more. And it did not depend on what type of feeding the child is on - breastfeeding or artificial. 10
And if nighttime awakenings are unavoidable anyway, breastfeeding is at least comfortable! Maina, a mother of two from Australia, agrees: “You can even take a nap while feeding in the middle of the night - both the body and the baby do their job on autopilot. No need to plan, measure, sterilize anything - ready-made food at the right temperature is right in your chest. I think it's ideal."
I think it's ideal."
My child wakes up more often. Perhaps he is hungry?
At about four months of age, a baby's sleep pattern changes as he, like an adult, has phases of deep and light sleep. Because of this, he may wake up more often at night. “At four months, sleep is more of a problem than feeding,” Cathy admits. “It can be exhausting, but try to adapt and be patient.”
Some call this " a four-month sleep regression ", but "progress" is more appropriate here. From the outside it may look like a step back, but in fact the child is approaching an important stage of development. He learns quickly, begins to become aware of the world around him, his perception is sharpened and, perhaps, there is anxiety about being separated from his mother. Crying when waking up and being able to eat milk cuddled up to mommy’s chest is a way for a baby to calm down. 11–13
Resist the urge to “supplement” your baby with formula or start solid foods early
in an attempt to improve his sleep. Breast milk contains
Breast milk contains
hormones that make you sleepy and help you both relax
. Studies show that breastfeeding mothers actually sleep longer at night than formula- or formula-fed mothers
. 14
How does teething affect breastfeeding?
Teething usually begins around four months of age. When a baby has gum pain, he becomes restless, throws his chest and cries. All this, of course, is unpleasant.
However, breastfeeding can be an excellent sedative.
Studies have shown that babies who are breastfed
during the vaccination period cry less and forget pain more quickly. 15 Breastfeeding during teething can have the same calming effect.
An unpleasant side effect may be the child's attempts to try out his new teeth on the mother's breast. “Sometimes children flirt and bite their mother’s nipples. This can be felt in advance by how the behavior of the child changes when feeding: before biting, he removes his tongue, explains Cathy, “Usually this is not a problem and only happens a couple of times. It is enough to stop feeding, affectionately say that biting is not good, and the baby will soon leave this fun.
It is enough to stop feeding, affectionately say that biting is not good, and the baby will soon leave this fun.
How to continue feeding if you have to be separated from the baby?
It happens that during the first six months, when the baby is still fully breastfed, the mother needs to be away for several hours - or even longer if she has to go to work or go away on business for a couple of days.
But this does not mean that you should stop breastfeeding. You can still feed your baby healthy breast milk - just express it and have someone give it to your baby when you're away. Here's Katie's advice:
“Start expressing milk a couple of days in advance, in small batches, 40-60 ml at a time. So you will have the necessary supply for the time of your absence, but at the same time the amount of milk produced will remain the same.
If you have to return to work, check with your employer about your daily schedule. Many mothers breastfeed their babies in the morning, evening and night, and pump milk at lunchtime to relieve discomfort and create a reserve for the next day.
This usually turns out to be much easier than one might think, and today many companies are well placed to do this, notes Cathy. “Breast pumps make it easy to solve this problem.”
Natalie, mother from the USA, shares her experience: “I feed Dylan as soon as he wakes up, and sometimes again before leaving for work, in order to maintain milk production and not lose contact with the child. At work, I pump twice the next day (in my absence, he eats two bottles of breast milk), and after work I rush home for the evening feed. I don't pump on the weekends - we resume regular breastfeeding."
Is it possible to continue breastfeeding after the introduction of solid foods?
When your baby begins to show interest in food and can sit up on his own - usually around six months of age - it's time to start solid foods. However, it is not necessary to stop breastfeeding, Cathy explains: “A baby’s iron stores during pregnancy are depleted by six months, so he needs additional sources of this element.
Start complementary foods with solid foods, but remember that breast milk remains a more important source of calories and nutrients until the baby is eight to nine months old. By this time, he will be eating much more solid food, but he will still need to breastfeed four to five times a day. By 12 months, the frequency of feeding may be two to six times a day. All babies are different, and many of them at this age are still getting half their daily calorie intake from breast milk.”
Don't forget that breast milk can be added to solid foods, such as cereals and purees, so that the baby can taste the familiar taste. If possible, use milk expressed just before feeding (not thawed) and add just before serving to keep bacteria and nutrients alive. 16
You may be pressured by others to stop breastfeeding when your baby is six months old, but the longer you breastfeed or pump, the better for you and your baby.
How long can I continue breastfeeding?
“The World Health Organization recommends breastfeeding along with solid foods until at least two years of age because it plays an important role in supporting immunity,” says Cathy. feels bad".
feels bad".
At eight months, the baby sometimes breastfeeds four times a day, but by one year old, the frequency of feedings can be reduced to two times a day. You yourself will understand which feeding regimen is more suitable for you and your baby. For example, Jane, a mother of two from the US, breastfed until the age of two: “I breastfed when I was at home - in the evenings and on weekends, when the children wanted to be close to me,” says Jane, “It helped a lot when they were sick . Breastfeeding has become my favorite form of comfort."
“When my son got a little older and bolder, he still often asked me to breastfeed him - as if to calm down and gain strength,” recalls Amy, a mother of two children from Canada, “When he happened to hit or skin his knee , breastfeeding was a wonderful way to comfort him.”
If your baby is over a year old and you are still breastfeeding, people around you will probably tell you that this way he will never wean. But if children are not pressured, they usually refuse to breastfeed themselves between the ages of two and four. 17
17
“I didn’t intend to breastfeed for so long, but as a result, I still breastfeed my four-year-old daughter and 22-month-old son,” says Suzanne, mother of two from the UK, “I breastfeed my youngest before and after work, and in I express milk on business trips. The eldest daughter likes to breastfeed a little before bed or when she is upset - this is a great way to make contact. When I get tired of it, I remind myself what great benefit and comfort it brings them. I now plan to pursue a baby-initiated end breastfeeding strategy — let them decide when to stop.”
For more information on what to expect and lots of tips and tricks, see our guide Breastfeeding Problems After the First Month.
Literature
1 Ballard O, Morrow AL. Human milk composition: nutrients and bioactive factors. Pediatr Clin North Am . 2013;60(1):49-74. - Ballard O., Morrow A.L., "Composition of breast milk: nutrients and biologically active factors. " Pediatrician Clean North Am. 2013;60(1):49-74.
" Pediatrician Clean North Am. 2013;60(1):49-74.
2 Kent JC et al. Principles for maintaining or increasing breast milk production. J Obstet , Gynecol , & Neonatal Nurs . 2012;41(1):114-21. - Kent J.S. et al., "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". J Obstet Ginecol and Neonatal Nurse. 2012;41(1):114-121.
3 Kent JC Volume and frequency of breastfeedings and fat content of breast milk throughout the day. Pediatrics. 2006;117(3): e 387-395. - Kent J.S. et al., "Amount and frequency of breastfeeding and fat content of breast milk during the day." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2006;117(3):e387-95.
4 Kent JC et al. Longitudinal changes in breastfeeding patterns from 1 to 6 months of lactation. Breast Med . 2013;8(4):401-407. - Kent J.S. et al., Longitudinal changes in breastfeeding patterns from 1 to 6 months of lactation. Brest Med. 2013;8(4):401-407.
Breast Med . 2013;8(4):401-407. - Kent J.S. et al., Longitudinal changes in breastfeeding patterns from 1 to 6 months of lactation. Brest Med. 2013;8(4):401-407.
5 Almroth S, Bidinger PD. No need for water supplementation for exclusively breast-fed infants under hot and arid conditions. Trans R Soc 1990;84(4):602-604. - Elmroth S., Bidinger P.D., "No need for supplementation of exclusively breastfed infants in hot, dry conditions." Trans R Sots Trop Med Hyg. 1990;84(4):602-604.
6 Victora CG et al . Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet. 2016;387(10017):475-490. - Victor S.J. et al., "Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms and long-term effects". Lancet 2016;387(10017):475-490.
7 Peres KG et al. Effect of breastfeeding on malocclusions: a systematic review and meta - analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2015;104( S 467):54-61. - Perez K.G. et al., "The impact of breastfeeding on malocclusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Akta Pediatr. 2015;104(S467):54-61.
8 Mennella JA, Beauchamp GK. Maternal diet alters the sensory qualities of human milk and the nursling's behavior. Pediatrics. 1991;88(4):737-744. - Mennella, JA, Beauchamp, GK, "Maternal nutrition influences the organoleptic properties of breast milk and infant behavior." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 1991;88(4):737-744.
9 Hassiotou F et al. Maternal and infant infections stimulate a rapid leukocyte response in breastmilk. Clin Transl immunology. 2013;2(4). - Hassiot F. et al., "Infectious diseases of the mother and child stimulate a rapid leukocyte reaction in breast milk. " Clean Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4).
" Clean Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4).
10 Brown A, Harries V. Infant sleep and night feeding patterns during later infancy: Association with breastfeeding frequency, daytime complementary food intake, and infant weight. Breast Med . 2015;10(5):246-252. - Brown A., Harris W., "Night feedings and infant sleep in the first year of life and their association with feeding frequency, daytime supplementation, and infant weight." Brest Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2015;10(5):246-252.
11 Infant sleep information source. [Internet]. Normal Infant Sleep Development; December 2017 [cited 2018 Feb] - All about baby sleep. [Internet] "The development of normal sleep in a child", December 2017 [cited February 2018].
12 Baby sleep science. [Internet]. The-Four-Month-Sleep-Regression-What-is-it-and-What-can-be-Done-About-it. March 2014 [ cited 2018 Feb ] - The Science of Baby Sleep. [Internet], "Four-month sleep regression: what it is and what to do about it." March 2014 [cited February 2018].
[Internet], "Four-month sleep regression: what it is and what to do about it." March 2014 [cited February 2018].
13 The Myth Of Baby Sleep Regressions – What’s Really Happening To Your Baby’s Sleep? [Internet]. Pinky Mckay ; December 2017 [ cited 2018 Feb ] - "The Myth of Baby Sleep Regression - What's Really Happening to Your Baby?" [Internet]. Pinky McKay, December 2017 [cited February 2018].
14 Kendall - Tackett K ET . The effect of feeding method on sleep duration, maternal well-being, and postpartum depression. Clinical Lactation . 2011;2(2):22-26. - Kendall-Tuckett K. et al., "Influence of feeding pattern on sleep duration, maternal well-being and the development of postpartum depression.![]()
Learn more