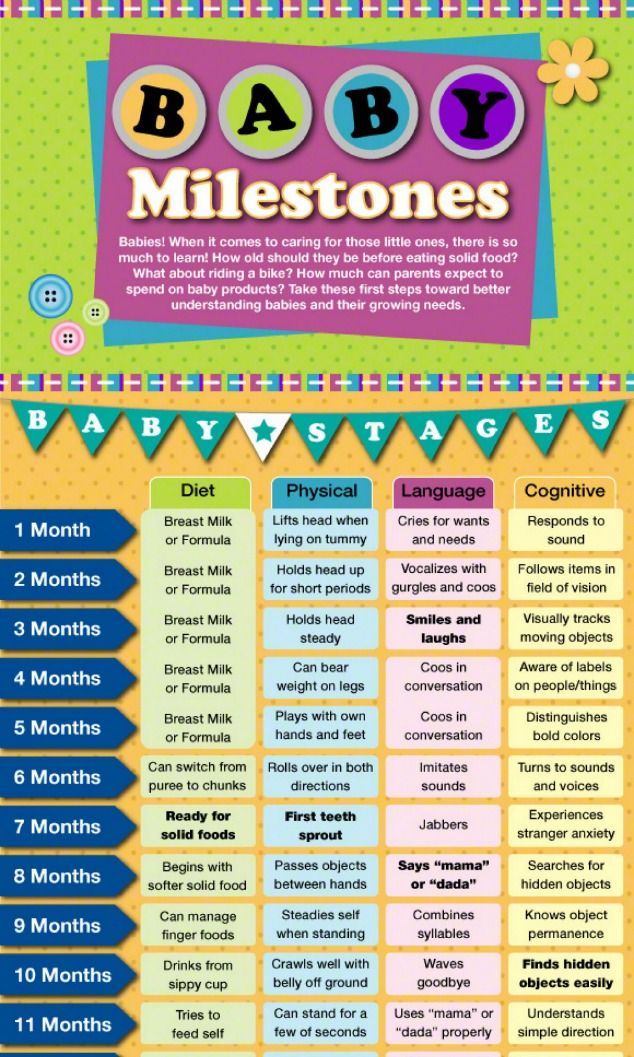
How many times newborn baby feed
Breastfeeding FAQs: How Much and How Often (for Parents)
Breastfeeding is a natural thing to do, but it still comes with its fair share of questions. Here's what you need to know about how often and how long to breastfeed your baby.
How Often Should I Breastfeed?
Newborn babies should breastfeed 8–12 times per day for about the first month. Breast milk is easily digested, so newborns are hungry often. Frequent feedings helps stimulate your milk production during the first few weeks.
By the time your baby is 1–2 months old, he or she probably will nurse 7–9 times a day.
In the first few weeks of life, breastfeeding should be "on demand" (when your baby is hungry), which is about every 1-1/2 to 3 hours. As newborns get older, they'll nurse less often, and may have a more predictable schedule. Some might feed every 90 minutes, whereas others might go 2–3 hours between feedings.
Newborns should not go more than about 4 hours without feeding, even overnight.
How Do I Count the Time Between Feedings?
Count the length of time between feedings from the time your baby begins to nurse (rather than at the end) to when your little one starts nursing again. In other words, when your doctor asks how often your baby is feeding, you can say "about every 2 hours" if your first feeding started at 6 a.m., the next feeding was around 8 a.m., then 10 a.m., and so on.
Especially at first, you might feel like you're nursing around the clock, which is normal. Soon enough, your baby will go longer between feedings.
How Long Does Nursing Take?
Newborns may nurse for up to 20 minutes or longer on one or both breasts. As babies get older and more skilled at breastfeeding, they may take about 5–10 minutes on each side.
How long it takes to breastfeed depends on you, your baby, and other things, such as whether:
- your milk supply has come in (this usually happens 2–5 days after birth)
- your let-down reflex (which causes milk to flow from the nipple) happens right away or after a few minutes into a feeding
- your milk flow is slow or fast
- the baby has a good latch, taking in as much as possible of your areola (the dark circle of skin around your nipple)
- your baby begins gulping right away or takes it slow
- your baby is sleepy or distracted
Call your doctor if you're worried that your baby's feedings seem too short or too long.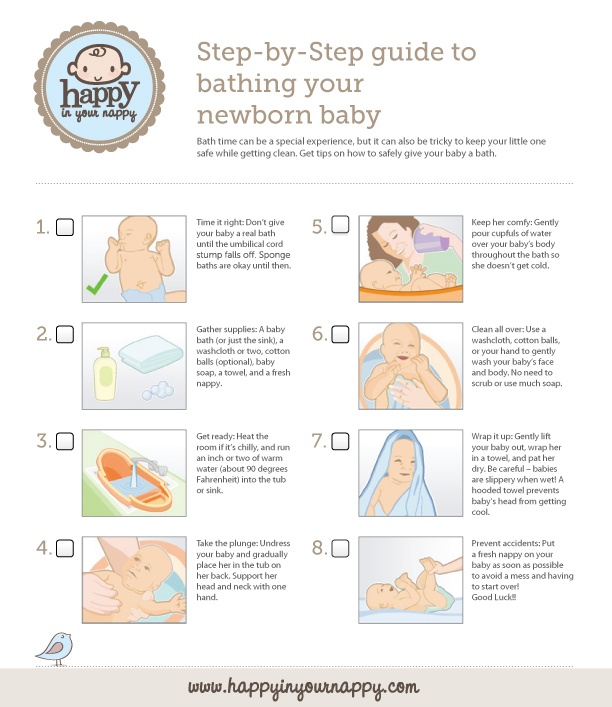
When Should I Alternate Breasts?
Alternate breasts and try to give each one the same amount of nursing time throughout the day. This helps to keep up your milk supply in both breasts and prevents painful engorgement (when your breasts overfill with milk).
You may switch breasts in the middle of each feeding and then alternate which breast you offer first for each feeding. Can't remember where your baby last nursed? It can help to attach a reminder — like a safety pin or small ribbon — to your bra strap so you'll know which breast your baby last nursed on. Then, start with that breast at the next feeding. Or, keep a notebook handy or use a breastfeeding app to keep track of how your baby feeds.
Your baby may like switching breasts at each feeding or prefer to nurse just on one side. If so, then offer the other breast at the next feeding. Do whatever works best and is the most comfortable for you and your baby.
How Often Should I Burp My Baby During Feedings?
After your baby finishes on one side, try burping before switching breasts. Sometimes, the movement alone can be enough to cause a baby to burp.
Sometimes, the movement alone can be enough to cause a baby to burp.
Some infants need more burping, others less, and it can vary from feeding to feeding.
If your baby spits up a lot, try burping more often. While it's normal for infants to "spit up" a small amount after eating or during burping, a baby should not vomit after feeding. If your baby throws up all or most of a feeding, there could be a problem that needs medical care. If you're worried that your baby is spitting up too much, call your doctor.
Why Is My Baby Hungrier Than Usual?
When babies go through a period of rapid growth (called a growth spurt), they want to eat more than usual. These can happen at any time. But in the early months, growth spurts often happen when a baby is:
- 7–14 days old
- 2 months old
- 4 months old
- 6 months old
During these times and whenever your baby seems extra hungry, follow your little one's hunger cues. You may need to breastfeed more often for a while.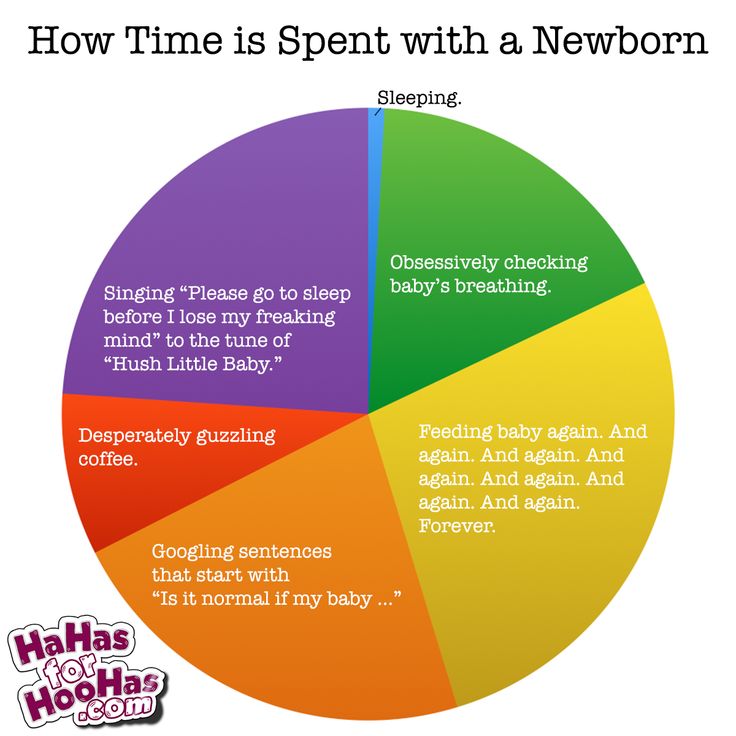
How Long Should I Breastfeed My Baby?
That's a personal choice. Experts recommend that babies be breastfed exclusively (without formula, water, juice, non–breast milk, or food) for the first 6 months. Then, breastfeeding can continue until 12 months (and beyond) if it's working for you and your baby.
Breastfeeding has many benefits for mom and baby both. Studies show that breastfeeding can lessen a baby's chances of diarrhea, ear infections, and bacterial meningitis, or make symptoms less severe. Breastfeeding also may protect children from sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), diabetes, obesity, and asthma.
For moms, breastfeeding burns calories and helps shrink the uterus. In fact, breastfeeding moms might return to their pre–pregnancy shape and weight quicker. Breastfeeding also helps lower a woman's risk of diseases like:
- breast cancer
- high blood pressure
- diabetes
- heart disease
It also might help protect moms from uterine cancer and ovarian cancer.
Breastfeeding FAQs: Sleep - Yours and Your Baby's (for Parents)
Breastfeeding is a natural thing to do, but it still comes with its fair share of questions. Here's what you need to know about making nights easier for you and your baby.
Where Should My Baby Sleep?
It’s a good idea to put your baby to sleep in your room without sharing a bed. That’s because bed-sharing puts babies at risk of suffocation, strangulation, and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
Experts recommend room-sharing for at least the first 6 months of life, especially if you’re breastfeeding. Here are some ideas:
- Put a bassinet, play yard, or crib next to your bed. This lets you keep that desired closeness that makes it easier to breastfeed at night. It also lowers your baby’s risk of SIDS.
- Buy a bassinet or play yard with one side that is lower, which attaches to your bed. This allows you to be next to your baby without the chance of rolling over onto your infant.

Don’t let your baby sleep in the same room as someone who is smoking.
Also:
- Don’t let your baby fall asleep on a product that isn’t specifically designed for sleeping babies, such as a sitting device (like a car seat), a feeding pillow (like the Boppy pillow), or an infant lounger (like the Dock-a-Tot, Podster, and Bummzie).
- Don’t use products or devices that claim to lower the risk of SIDS, such as sleep positioners (like wedges or incliners) or monitors that can detect a baby’s heart rate and breathing pattern. No known products can actually do this.
- Don’t use products that are weighted, such as a weighted blanket, sleeper, or swaddle.
- Don’t use products that have not been approved by the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) as meeting federal safety standards for infant sleep products
How Should My Baby Sleep?
Always place your baby on the back to sleep, not on their stomach or side, to help lower the chance of SIDS. When babies can roll over easily from front to back and back to front, it's fine for them to stay in the sleep position they choose.
When babies can roll over easily from front to back and back to front, it's fine for them to stay in the sleep position they choose.
When picking out bedding for your baby, keep these tips in mind:
- Use a firm sleep surface. Cover the mattress with a sheet that fits snugly. Make sure your crib, bassinet, or play yard meets current safety standards.
- Do not put anything else in the crib or bassinet. Keep plush toys, pillows, blankets, unfitted sheets, quilts, comforters, sheepskins, and bumper pads out of your baby's sleep area. Make sure there are no items within reach that could pose a hazard to your baby, such as cords, ties, or ribbons.
- Dress your baby for the room temperature, and don't overbundle. Watch for signs of overheating, such as sweating or feeling hot to the touch.
How Can I Make Nighttime Feedings Easier?
To make nursing in bed more comfortable, keep a donut-shaped nursing pillow on or near your bed or use a "husband" back pillow with arms on each side.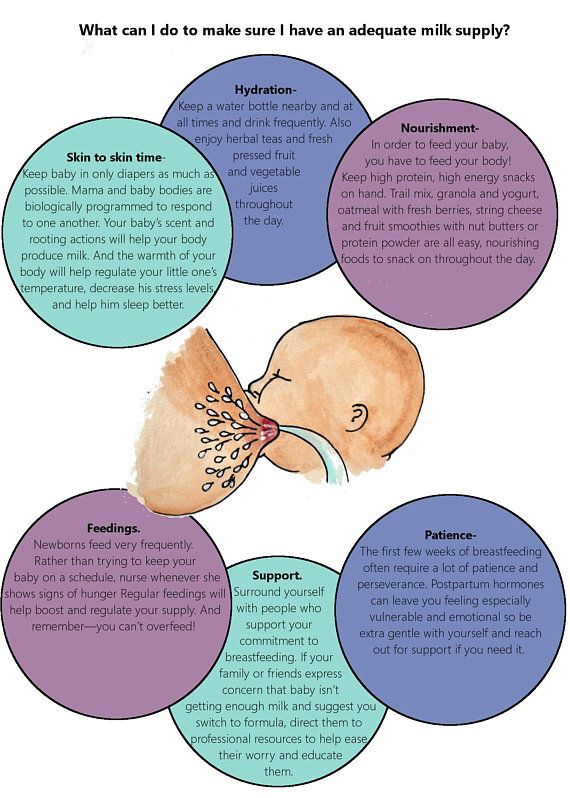
Keep the room dimly lit and any noises (talking, singing, etc.) to a minimum. This will help your baby realize that nighttime is for sleeping — not playing — and can help your baby fall back to sleep sooner.
My Baby Falls Asleep While Nursing. What Can I Do?
Newborns often fall asleep at the breast, especially after feeling satisfied from a feeding. (You'll know if your baby isn't nursing if you don't hear swallowing sounds, like little clicks, or see the jawbones moving.)
If you think your baby is asleep and hasn't finished nursing, here are some tips to try:
- Undress your baby and rub their back.
- Tickle your baby’s feet.
- Burp your baby.
- Change your baby's diaper or switch to the other breast.
- Gently compress (squeeze) or massage your breast at the end of feeding to encourage your baby to drink more.
Babies who latch on wrong may fall asleep at the breast. If this happens, break the suction and reposition your baby onto your breast to include both your nipple and areola.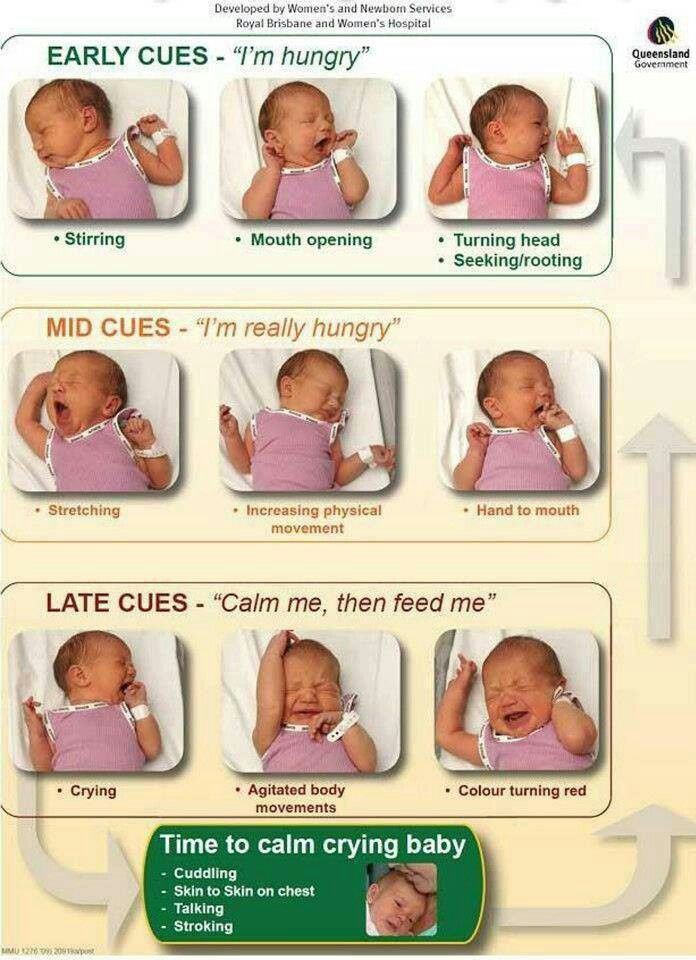 You can break the suction by slipping your finger in the side of your baby's mouth (between the gums) and then turning your finger a quarter turn.
You can break the suction by slipping your finger in the side of your baby's mouth (between the gums) and then turning your finger a quarter turn.
After you've broken the suction, try to burp your baby and switch to the other breast.
Is it OK to Nurse My Baby to Sleep?
In the first few months of life, it's practically impossible to keep a nursing baby awake who is satisfied with a full belly. But as babies grow, encourage them to sleep on their own. To do this:
- Put your baby down for naps and bed slightly awake. This teaches babies to get used to falling asleep on their own.
- Create a familiar and relaxing bedtime routine. Bathing, reading, and singing is soothing and signals an end to the day.
- Be consistent with the bedtime routine. Eventually, babies associate these steps with sleeping.
- Offer a pacifier. Experts recommend giving a pacifier at naptime and bedtime to babies under 1 year old to reduce the risk of SIDS. Only give a pacifier after breastfeeding is established, so no sooner than 3 weeks of age.
 If your little one doesn't want a pacifier, don't push it.
If your little one doesn't want a pacifier, don't push it.
When Will My Baby Sleep Through the Night?
Breastfed newborns' longest sleep periods are generally 2–3 hours — this is about how long their small bellies can go between feedings. If newborns do sleep for a while, they'll probably be extra-hungry during the day and may want to nurse more often.
And just when you think that sleeping through the night seems like a far-off dream, things start to get a little easier. At 3 months, a baby averages a total of 5 hours of sleep during daytime naps and 10 hours at night, usually with an interruption or two. Most babies this age sleep "through the night," meaning a 5-6 hour stretch. But every baby is different, so don't be surprised if your baby sleeps more or less than others.
Will it Hurt My Milk Supply to Let My Baby Sleep?
Letting your baby sleep for longer periods (usually at around 3 months of age) isn't going to hurt your breastfeeding efforts. Your body readjusts your milk supply based on when you nurse and how much your baby needs. Some babies will sleep through the night early but will make up for it during the day, so your breasts will accommodate that.
Your body readjusts your milk supply based on when you nurse and how much your baby needs. Some babies will sleep through the night early but will make up for it during the day, so your breasts will accommodate that.
As your baby matures and starts taking solid foods, the need for breast milk will decrease and your body will adjust for that too.
Reviewed by: Jamila H. Richardson, BSN, RN, IBCLC
Date reviewed: January 2021
Breastfeeding a newborn | What to Expect in the First Week
The first week of a baby's life is a wonderful but hectic time, especially if you haven't breastfed before. Our breastfeeding tips will help you settle in as quickly as possible
Share this information
The first time after childbirth, mothers are often confused. The body is still recovering, and you are already starting to get to know your newborn baby. The emotional state during this period can be unstable, especially between the second and fifth day, when many women have milk 1 and at the same time postpartum depression begins 2 . In addition, people around often expect (and demand) that a woman come to her senses as soon as possible and become a “super mom”. But the best thing to do this first week is just to be with your baby and get breastfeeding going.
In addition, people around often expect (and demand) that a woman come to her senses as soon as possible and become a “super mom”. But the best thing to do this first week is just to be with your baby and get breastfeeding going.
When should I start breastfeeding my newborn?
Try to breastfeed your baby within the first hour after birth. When the baby latch onto the breast and begins sucking rhythmically, it stimulates the mammary gland cells and starts milk production. nine0009 1 It is not for nothing that this time is called the “magic hour”!
“Ideally, the baby should be placed on the mother's stomach immediately after birth so that it can immediately attach to the breast. He won't necessarily eat, but he should be able to,” explains Cathy Garbin, an internationally recognized expert on breastfeeding.
“Hold your baby and let him find the breast on his own and put the nipple in his mouth. This is called the breast-seeking reflex. On the Internet you can watch videos that show what this process looks like. If the baby does not latch onto the nipple on its own, the midwife will help to properly attach it to the breast. But for starters, it’s good to give the baby the opportunity to do it on their own. In this case, the optimal position for the mother is reclining. ” nine0003
If the baby does not latch onto the nipple on its own, the midwife will help to properly attach it to the breast. But for starters, it’s good to give the baby the opportunity to do it on their own. In this case, the optimal position for the mother is reclining. ” nine0003
Don't spend that special first hour of your baby's life weighing and swaddling—or at least wait until he's suckling for the first time. Enjoy hugs and close skin-to-skin contact. This promotes the production of oxytocin, the hormone of love, in you and your baby, and oxytocin plays a key role in the supply of the first breast milk - colostrum. 3
“As soon as the obstetricians were convinced that our son was healthy, the three of us — me, my husband and our baby — were left to give us the opportunity to get to know each other. It was a very special hour - an hour of awkwardness, turbulent emotions and bliss. During this time, I breastfed my son twice, ”recalls Ellie, a mother of two from the UK. nine0003
nine0003
Did you know that breastfeeding helps to recover after childbirth? This is because oxytocin stimulates uterine contractions. In the first hours after childbirth, this contributes to the natural release of the placenta and reduces blood loss. 4
What if the birth did not go according to plan?
If you had a cesarean section or other complications during childbirth,
You can still make skin-to-skin contact with your baby and breastfeed him in the first hours after birth. nine0003
“If you can't hold your baby, have your partner do it for you and make skin-to-skin contact with the baby. This will give the baby a sense of security, care and warmth so that he can hold on until you recover, ”Katie advises.
If the baby is unable to breastfeed, it is advisable to start expressing milk as early as possible and do so as often as possible until the baby is able to feed on its own. “While breastfeeding in the first hours after birth lays an excellent foundation for the future, it is not so important,” Cathy reassures. “It is much more important to start lactation so that in the future, if necessary, you can start breastfeeding.” nine0003
“It is much more important to start lactation so that in the future, if necessary, you can start breastfeeding.” nine0003
To start milk production, you can express milk manually or use a breast pump that can be given to you at the hospital. 5 And with expressed precious colostrum, it will be possible to feed the child. This is especially important if the baby was born premature or weak, since breast milk is extremely healthy.
If a baby was born prematurely or has a medical condition and cannot be breastfed immediately, this is no reason not to continue breastfeeding. “I have worked with many new mothers who were unable to breastfeed their baby for the first six weeks due to preterm labor or other reasons. Nevertheless, all of them later successfully switched to breastfeeding,” says Kathy. nine0003
Does the baby latch on correctly?
Correct breastfeeding is essential for successful breastfeeding 6 , as it determines how effectively the baby will suckle milk and hence grow and develop.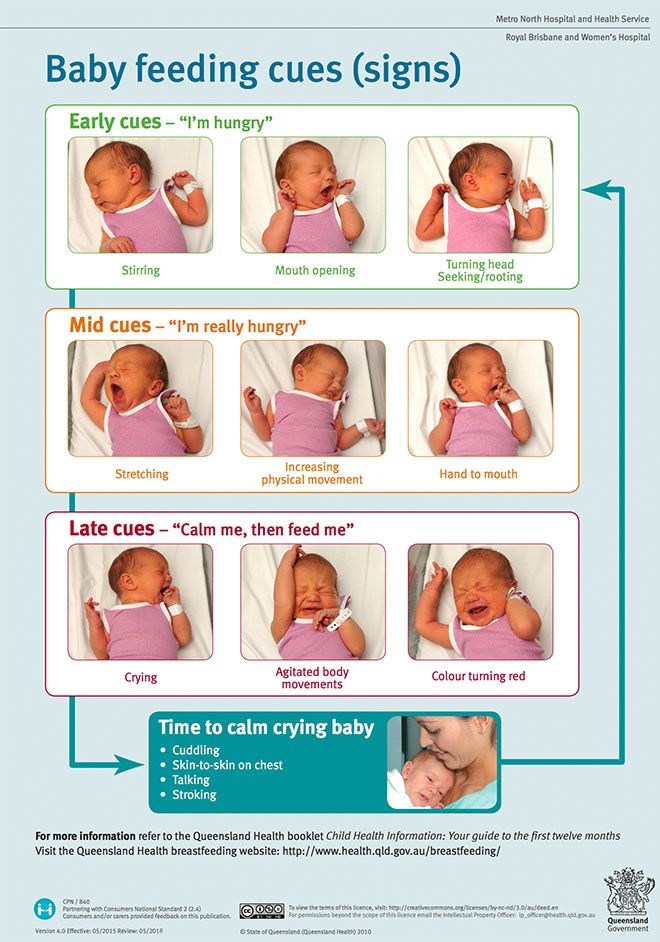 Latching on the breast incorrectly can cause sore or damaged nipples, so don't hesitate to ask your doctor to check that your baby is properly attached to the breast, even if you are told that everything is fine and you do not see obvious problems - especially while you are in the hospital. nine0003
Latching on the breast incorrectly can cause sore or damaged nipples, so don't hesitate to ask your doctor to check that your baby is properly attached to the breast, even if you are told that everything is fine and you do not see obvious problems - especially while you are in the hospital. nine0003
“While I was in the hospital, I called the doctor at every feed and asked me to check if I was breastfeeding correctly,” says Emma, mother of two from Australia. - There were several cases when it seemed to me that everything seemed to be right, but it was painful to feed, and the doctor helped me take the baby off the breast and attach it correctly. By the time I was discharged, I had already learned to do it confidently.”
When applying to the breast, point the nipple towards the palate. This will allow the baby to take the nipple and part of the areola under it into their mouth. It will be easier for him to suck if he has both the nipple and part of the areola around in his mouth. nine0009 6
nine0009 6
“When a baby latch on properly, it doesn't cause discomfort and it causes a pulling sensation, not pain,” Cathy explains. - The baby's mouth is wide open, the lower lip may be slightly turned outward, and the upper one lies comfortably on the chest. The body language of the child indicates that he is comfortable. There isn't much milk at this early stage, so you probably won't notice your baby swallowing, but he will suckle a lot and nurse frequently."
How often should a newborn be fed? nine0015
The frequency and duration of breastfeeding in the first week can vary greatly. “The first 24 hours of life are completely different for different children. Someone sleeps a lot (after all, childbirth is tiring!), And someone often eats, says Katie. - Such a variety greatly confuses young mothers. Everyone gives different advice, so it's important to remember that every mother and child is different."
“Colostrum is thicker than mature breast milk and is produced in smaller amounts, but has many benefits. When the baby eats colostrum, he learns to suck, swallow and breathe until milk begins to flow in more volume, ”explains Cathy. nine0003
When the baby eats colostrum, he learns to suck, swallow and breathe until milk begins to flow in more volume, ”explains Cathy. nine0003
Milk usually arrives on the second or fourth day after delivery. Until this time, the baby is applied to the breast 8-12 times a day (and sometimes more often!), including at night. 7 Feeding may last 10-15 minutes at this stage, or 45 minutes or even an hour, as the baby is just beginning to develop the muscles and coordination needed to suckle effectively.
“At first, the intensity of feeding is very high, often higher than many people realize, and this is shocking to most new mothers,” says Cathy. - Sometimes mom has no time to go to the toilet, take a shower and have a snack. It usually comes as a surprise." nine0003
Camille, a mother from Australia, experienced this. “The first week, Frankie ate every two hours, day and night, and each time it took half an hour to an hour to feed,” she recalls. “My husband and I were completely exhausted!”
Do I need to feed my newborn on a schedule?
The good news is that frequent feeding promotes lactation and stimulates milk production.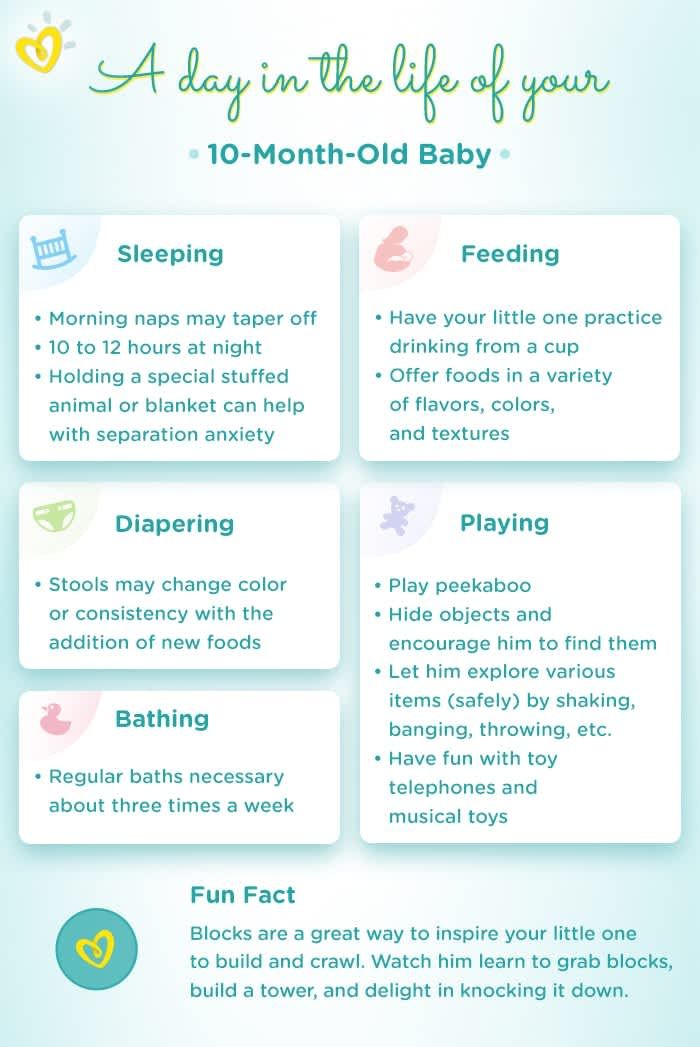 7 The more your baby eats, the more milk you will have. Therefore, forget about feeding your newborn on a schedule - this way he will have less chance of feeding. Try to feed your baby when he signals that he is hungry 8 :
7 The more your baby eats, the more milk you will have. Therefore, forget about feeding your newborn on a schedule - this way he will have less chance of feeding. Try to feed your baby when he signals that he is hungry 8 :
- tossing and turning in her sleep;
- opens eyes;
- turns his head if he feels a touch on his cheek;
- sticks out tongue;
- groans;
- licks lips;
- sucks fingers;
- is naughty;
- whimpers;
- is crying.
Crying is the last sign of hunger, so when in doubt, just offer your baby the breast. If he bursts into tears, it will be more difficult to feed him, especially at first, when both of you are just learning how to do it. As your baby grows, he will likely eat less frequently and take less time to feed, so breastfeeding will seem more predictable. nine0003
Does breastfeeding hurt?
You may have heard that breastfeeding is not painful at all, but in fact, in the first days, many new mothers experience discomfort. And this is not at all surprising, given that the nipples are not used to such frequent and strong sucking.
And this is not at all surprising, given that the nipples are not used to such frequent and strong sucking.
“Breastfeeding can be uncomfortable for the first couple of days – your body and your baby are just getting used to it. If a baby eats for too long and does not latch well, the sensations are almost the same as from unworn new shoes, Cathy compares. Just as tight shoes can rub your feet, improper suckling can damage your nipples. Prevention is always better than cure, so if the pain persists after a few days of feeding, contact a lactation consultant or healthcare professional.” nine0003
Maria, a mother from Canada, agrees: “Although my son seemed to latch onto the breast well, he damaged his nipples while feeding, and I was in pain. As it turned out, the reason was a shortened frenulum of the tongue. The breastfeeding specialists at our city clinic have been of great help in diagnosis and treatment.”
In addition, you may experience period cramps during the first few days after breastfeeding, especially if this is not your first baby. This is the so-called postpartum pain. The fact is that oxytocin, which is released during breastfeeding, contributes to further contraction of the uterus to restore its normal size. nine0009 4
This is the so-called postpartum pain. The fact is that oxytocin, which is released during breastfeeding, contributes to further contraction of the uterus to restore its normal size. nine0009 4
When milk arrives, the breasts usually become fuller, firmer and larger than before delivery. In some women, the breasts swell, harden and become very sensitive - swelling of the mammary glands occurs. 10 Frequent breastfeeding relieves these symptoms. For more breast care tips, read our article What is Breast Swelling?
How often does the newborn urinate and defecate?
What goes into the body must go back out. Colostrum
has a laxative effect, helping to eliminate meconium - the original feces. It looks a little scary - black and sticky, like tar. 11 But don't worry, it won't always be like this. Breastfed babies usually have a slightly sweet smell of stool.
How many times a day you will need to change diapers and how the contents should look like, see below.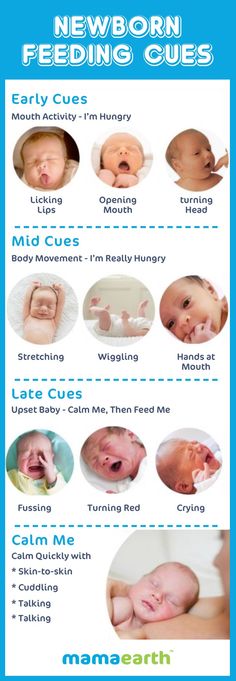
Day one
- Frequency: once or more.
- Colour: greenish black. nine0087
- Texture: sticky like tar.
Day two
- Frequency: twice or more.
- Colour: dark greenish brown.
- Texture: less sticky.
Day three
- Frequency: twice or more.
- Colour: greenish brown to brownish yellow.
- Texture: non-sticky.
Fourth day and then the entire first month
- Frequency: twice or more.
- Color: yellow (feces should turn yellow no later than by the end of the fourth day).
- Texture: grainy (like mustard with grains interspersed). Leaky and watery.
The baby's urine should be light yellow. On average, babies urinate once a day for the first two days. Starting around the third day, the number of wet diapers increases to three, and from the fifth day onwards, diapers have to be changed five times a day or more often. In addition, during the first few days, the weight of wet diapers increases. nine0009 11
In addition, during the first few days, the weight of wet diapers increases. nine0009 11
Is the baby getting enough breast milk?
Since very little milk is produced at first,
You may feel that this is not enough for your baby. But if you feed your baby on demand, you will produce exactly as much milk as he needs. If you want to keep the process under control, be guided by the frequency of diaper changes above. If your baby soils less diapers, check with your doctor.
“For the first three or four weeks, most babies just eat and sleep. If the child is worried and constantly asks for a breast, you should consult with your doctor, ”Katie recommends. nine0003
Sometimes the baby may vomit after feeding. If the vomit is the color of milk, this is not a cause for concern. But if there are orange, red, green, brown or black blotches in it, or the child vomits with a "fountain", consult a doctor. You should also consult a doctor if the baby has a high temperature, the fontanel (soft spot on the head) has sunk, blood is found in the stool, and also if the weight recorded at birth has not recovered within two weeks. 11
11
But if there are no frightening symptoms and the baby is growing at a normal pace, it means that he has enough milk. Soon you will both get used to breastfeeding and establish a more stable routine.
For the next step in breastfeeding, see Breastfeeding in the First Month: What to Expect.
Literature
1 Pang WW, Hartmann PE. Initiation of human lactation: secretory differentiation and secretory activation. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2007;12(4):211-221. - Pang, W.W., Hartmann, P.I., "Lactation initiation in the lactating mother: secretory differentiation and secretory activation." G Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2007;12(4):211-221.
2 Shashi R et al. Postpartum psychiatric disorders: Early diagnosis and management. Indian J Psychiatry . 2015; 57( Suppl 2): S 216– S 221. - Shashi R. et al., Postnatal mental disorders: early diagnosis and treatment. Indian J Saikiatri. 2015; 57(App 2):S216-S221.
2015; 57( Suppl 2): S 216– S 221. - Shashi R. et al., Postnatal mental disorders: early diagnosis and treatment. Indian J Saikiatri. 2015; 57(App 2):S216-S221.
3 Moberg KU, Prime DK. Oxytocin effects in mothers and infants during breastfeeding. Infant . 2013;9(6):201-206. - Moberg K, Prime DK, "The effects of oxytocin on mother and child during breastfeeding." nine0201 Infant. 2013;9(6):201-206.
4 Sobhy SI, Mohame NA. The effect of early initiation of breast feeding on the amount of vaginal blood loss during the fourth stage of labor. J Egypt Public Health Assoc . 2004;79(1-2):1-12. - Sobhi SI, Moham NA, "Early initiation of breastfeeding and its effect on vaginal bleeding in the fourth stage of labor." nine0201 G Egypt Public Health Assoc. 2004;79(1-2):1-2.
2004;79(1-2):1-2.
5 Meier PP et al. Which breast pump for which mother: an evidence-based approach to individualizing breast pump technology. J Perinatol . 2016;36(7):493. - Meyer P.P. et al., Breastpump Selection: A Scientific Approach to Customizing Pumping Technology. J Perinatol (Journal of Perinatology). 2016;36(7):493-499.
6 Cadwell K. Latching - On and Suckling of the Healthy Term Neonate: Breastfeeding Assessment. J Midwifery & Women ’ s 2007;52(6):638-642. — Cadwell, K., "Latching and sucking in healthy newborns: evaluation of breastfeeding." W Midwifery Women Health. 2007;52(6):638-642.
7 Kent JC et al. Principles for maintaining or increasing breast milk production. 2012;41(1):114-121. - Kent J.S. et al. , "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". J Obstet Ginecol Neoneutal Nurs. 2012;41(1):114-121.
, "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". J Obstet Ginecol Neoneutal Nurs. 2012;41(1):114-121.
8 Australian Breastfeeding Association [ Internet ]. Feeding cues ; 2017 Sep [ cited 2018 Feb ]. - Australian Breastfeeding Association [Internet], Feed Ready Signals; September 2017 [cited February 2018]
9 Jacobs A et al. S3-guidelines for the treatment of inflammatory breast disease during the lactation period. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd . 2013;73(12):1202-1208. - Jacobs A. et al., "Guidelines S -3 for the management of inflammatory breast disease during breastfeeding." Geburtskhilfe und Frauenheilkünde. 2013;73(12):1202-1208.
10 Lawrence RA, Lawrence RM. Breastfeeding: A guide for the medical profession. 7th ed. Maryland Heights MO, USA: Elsevier Mosby; 2010. 1128 p . - Lawrence R.A., Lawrence R.M., "Breastfeeding: A guide for healthcare professionals." Seventh edition. Publisher Maryland Heights , Missouri, USA: Elsevier Mosby; 2010. P. 1128.
Breastfeeding: A guide for the medical profession. 7th ed. Maryland Heights MO, USA: Elsevier Mosby; 2010. 1128 p . - Lawrence R.A., Lawrence R.M., "Breastfeeding: A guide for healthcare professionals." Seventh edition. Publisher Maryland Heights , Missouri, USA: Elsevier Mosby; 2010. P. 1128.
How Much Should a Newborn Baby Eat
Search Support IconSearch Keywords
Home ›› How Much Milk Should a Newborn Baby Drink?
Home ›› How much milk should a newborn baby drink? nine0136
↑ Top
Like every new mom, you're probably wondering, "How often should a newborn eat?" and “How many milliliters does a newborn baby drink at a time?”. A mother's body is designed to provide her baby with all the nutrients she needs, but every mom needs practical advice and confidence when it comes to how much milk a newborn should drink.
Whether you are breastfeeding, bottle feeding or a combination of the two, here you will find all the information you need to know about how much food your baby needs to grow and develop properly.
Signs indicating that the child is hungry
Every mother has a wonderful maternal instinct, but we cannot guess the child's desires from the first time. Over time, you will learn your child's unique gestures and body movements, as well as signs that he is hungry. In the meantime, here are some of the most common signs that a child is hungry:
- turns head towards your breast or bottle;
- clenches;
- puts pens in mouth;
- pouts, smacks or licks lips.
If your child is showing any of these signs, they are probably trying to tell you it's time to eat. Ideally, your baby should be fed on demand when he is hungry. If you're breastfeeding, on-demand feeding is a good way to keep your milk supply going as your body will naturally respond to your baby's needs and continue to produce the required amount of milk. Bottle-feeding on demand can also be beneficial for your baby, as it allows him to self-regulate his feeding needs. nine0003
nine0003
How much breast milk should a newborn drink?
So, how much should a newborn baby eat? A remarkable feature of each child is its uniqueness, so it would be wrong to feed the baby strictly according to the instructions. Don't panic if the recommendations below don't fit your own feeding schedule, but please contact your healthcare provider or pediatrician if you have any questions.
Although every baby is different, newborns typically eat every two to three hours, for a total of 8 to 12 meals a day. nine0003
How many milliliters does a newborn baby drink? At the very beginning, your body will only produce a small amount of yellowish and thick breast milk called colostrum. This milk is an ideal source of nutrients that your newborn needs, in addition, it has many immunological components. 1
How much milk does a newborn baby drink? Infants drink 30-60 ml per feeding, while this volume increases to 60-90 ml by two weeks of age. So don't worry if you don't feel like your body is producing much milk in those first few days after your baby is born! Feeding times will also vary, ranging from 10 to 30 minutes at the very beginning and then gradually increasing as your baby grows.
So don't worry if you don't feel like your body is producing much milk in those first few days after your baby is born! Feeding times will also vary, ranging from 10 to 30 minutes at the very beginning and then gradually increasing as your baby grows.
How much breastmilk the baby eats if bottle fed
If you decide to bottle feed your baby from time to time, do so at the same intervals and for the same period of time as if you were breastfeeding. Pumping is a great option for breastfeeding your baby. It will allow you to separate from the baby if necessary and at the same time retain all the benefits of breastfeeding. nine0037
It's also important to get a bottle that helps make bottle feeding more natural for both you and your baby. For example, take a look at this Philips Natural bottle. Its wide, physiologically shaped nipple promotes a natural latch that is identical to that of a mother's breast, making it easier to alternate between bottle and breastfeeding.