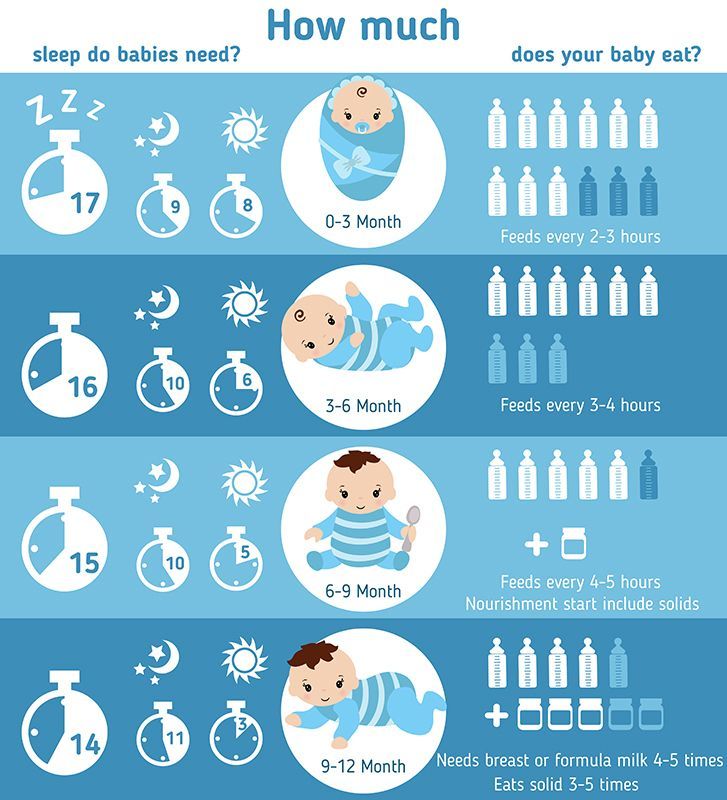
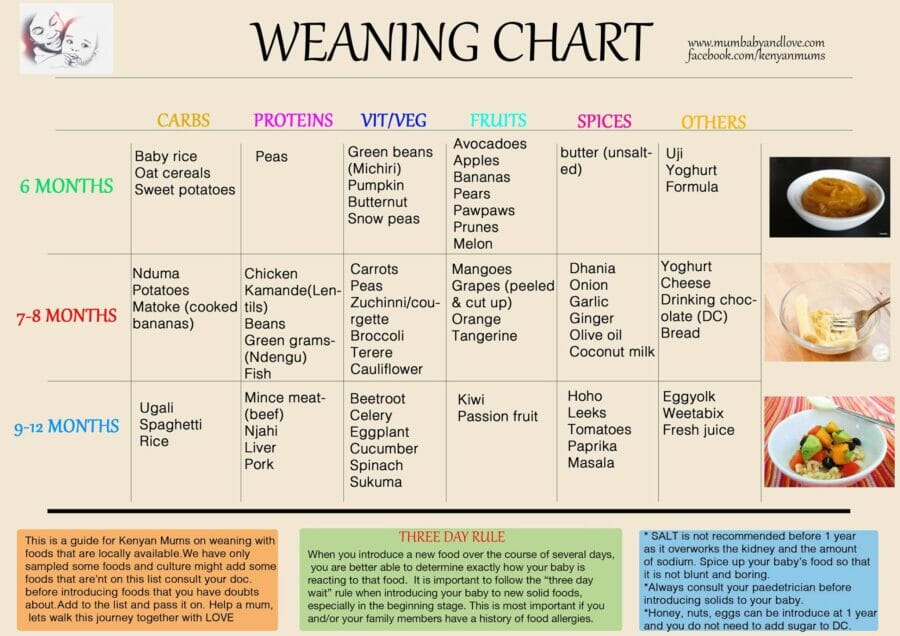
How to feed baby rabbits at home
Caring For Orphan Baby Rabbits
Wild Baby Bunnies – Orphaned or Not?
Wild baby bunnies are most often not orphaned! Many people mean well when they contact HRS after discovering an “abandoned” nest of wild rabbits. Often they wish to “rehabilitate” them with some advice from others. The reality is fewer than 10% of orphaned rabbits survive a week, and the care that people attempt to provide can be illegal, unnecessary, and potentially harmful.
The best thing you can do is put the bunny right back where you found him, in the general area, as the mom will only come back at night to call and find him. Leave the area. If injured, please contact a wildlife rehabber or rabbit vet immediately! You can search Google for your state/country and wildlife rehabber. Also search your state + wild rabbit rehabbers. You can call your Humane Society for referral and also check here: http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator If you find a baby with eyes open, and he appears healthy, leave him be.
I/My Dog/My Cat Found a Rabbit Nest! What Do I Do?
Rabbits hide their nests in plain view, often putting them in the open, sometimes in the middle of the lawn, as well as in brush piles and long grass. If you find a nest that has been disturbed, do all you can to restore and protect it. Do NOT bring it inside. If a dog has discovered the nest, keep your dog away from the area and reconstruct the nest with grasses. If need be, you can move the nest a few feet away where safer, even up to 5-6 feet away. A moved nest should always be covered with string in a tic tac toe pattern and monitored to be sure the mother found it and came back to the babies. She will scrabble away the surface area to feed her babies beneath her and then scrabble the earth, grass, leaves, back over the nest to hide it again so it’s pretty easy to see if the string has been disturbed and if the babies are warm.
Baby jackrabbits wait like this for momBabies should never be put back into a nest that has been flooded with water, has bugs/ants visibly crawling in and out, or if a baby has been killed and there is blood in the nest.
Use common sense. Baby bunnies who have fleas are compromised and should be immediately taken to a wildlife rehabber or humane society, rabbit vet.
Rabbit mothers nurse their babies for approximately 5 minutes a day. Both wild and domestic mothers will be in the nest early in the morning and then again in the evening. The milk is very rich and the babies “fill up” to capacity within minutes. Mother rabbits do not “sit” on the babies to keep them warm as do some mammals and birds. They build a nest with fur and grasses which helps to keep the babies warm in between feedings. For domestic/pet rabbits, do not force a mother rabbit to sit in the nest box. You can pick up the babies and see if they are feeding by checking the size of their stomachs (should not be sunken in), the pinkness of their skin and activity level (they should not be blue in color or sluggish in movement) and the amount of time that you hear them crying (baby bunnies should be quiet most of the day…. if they are crying constantly then they are not getting fed). If you come across a nest of wild bunnies, and the mother is nowhere to be seen, please DO NOT disturb them.
if they are crying constantly then they are not getting fed). If you come across a nest of wild bunnies, and the mother is nowhere to be seen, please DO NOT disturb them.
If your dog disturbs a nest, or you find a wild bunny with his eyes open, please put him back if not injured. Mom will be coming back at night to call and feed him only once in the middle of the night. Do not take the bunny inside or feed him! IT IS A MATTER OF HIS/HER SURVIVAL AND UP TO US AS HUMANS TO LEAVE NATURE BE AND LET THE MOM CARE FOR HER YOUNG. We often hear of mothers moving their babies and their nests, and have seen moms come back every night for up to a week to look for her missing baby. Do not take the baby from the mom or she will be frantic. Many call or write saying, “… but it is raining, etc., ” but remember, these are wild bunnies and belong out there.
I/My Dog/My Cat Destroyed a Wild Rabbit Nest! What Do I Do?
Remake the nest as best you can with grasses, hay, straw in the same place. Nests can be moved to a safer place up to 10′ away from the original site and can be reconstructed if necessary. To make a new nest, dig a shallow hole about 3″ deep and put into it as much of the original material as you can recover, including the mother’s fur. Add dried grass as needed, and put the young back. Mother rabbits return to the nest to nurse only at night, staying away as much as possible so as not to attract predators. To determine if the mother is returning, create a tic-tac-toe pattern over the nest with straw, grasses or tiny twigs. Wait 24 hours to see if the twigs have been disturbed. She may be able to feed them without moving the twigs much, so double check–If the babies look healthy, are warm, then the mother is coming back. If they are cold, dehydrated, get them to a professional; do not care for them yourself. Please contact a Wildlife Rehabber or rabbit vet or Humane Society immediately. Google your state and wildlife rehabbers.
Nests can be moved to a safer place up to 10′ away from the original site and can be reconstructed if necessary. To make a new nest, dig a shallow hole about 3″ deep and put into it as much of the original material as you can recover, including the mother’s fur. Add dried grass as needed, and put the young back. Mother rabbits return to the nest to nurse only at night, staying away as much as possible so as not to attract predators. To determine if the mother is returning, create a tic-tac-toe pattern over the nest with straw, grasses or tiny twigs. Wait 24 hours to see if the twigs have been disturbed. She may be able to feed them without moving the twigs much, so double check–If the babies look healthy, are warm, then the mother is coming back. If they are cold, dehydrated, get them to a professional; do not care for them yourself. Please contact a Wildlife Rehabber or rabbit vet or Humane Society immediately. Google your state and wildlife rehabbers. Also check http://www.humanesociety.org/animals/resources/tips/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator.html and http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator
Also check http://www.humanesociety.org/animals/resources/tips/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator.html and http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator
How Do I Know If the Wild Baby Bunnies Need Help?
Very young wild baby bunnies with eyes closed and ears back rarely survive in captivity, even given the most expert human care; and so it is very important to determine whether they really need help. Try to assess whether the infants seem warm and healthy or cold, thin, and dehydrated. One test for dehydration is to gently pinch the loose skin at the back of the neck. If it does not spring back in one second, or stays in a “tent,” the bunny is SEVERELY dehydrated and needs rehabilitation IMMEDIATELY by a professional rabbit vet or rehabber. Another test is to stroke the genital area to stimulate elimination if the eyes are closed. If the pee is brown and gritty, the mother rabbit has not been there to help the bunnies urinate. The brown, gritty urine is toxic, and the infant bunny must be cared for by a professional. Please contact a Wildlife Rehabber or rabbit vet immediately. Google your state and wildlife rehabber, call your Humane Society, and also check http://www.humanesociety.org/animals/resources/tips/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator.html and http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator.
The brown, gritty urine is toxic, and the infant bunny must be cared for by a professional. Please contact a Wildlife Rehabber or rabbit vet immediately. Google your state and wildlife rehabber, call your Humane Society, and also check http://www.humanesociety.org/animals/resources/tips/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator.html and http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator.
Older baby bunnies who are found outside of the nest may not be orphaned or in need of assistance. This is most often the case. Baby cottontails are born without fur but develop a full coat in a week. Their eyes open in 10 days, and in three to four weeks they are weaned. At this age, they may explore the world outside of the nest but return there to sleep. They are not ignored by the mother but stay with the family group until four or five weeks of age. To determine whether a bunny of this age needs assistance, first see if the bunny feels cold to the touch; perform the dehydration test. Also look for bleeding, convulsing, fly larvae, broken limbs; if any, get to a rabbit vet or emergency vet immediately. If he is just out and about, leave him be. He is discovering his world, waiting for mom to return at night when we humans are asleep. Don’t assume because he is letting you pick him up, he needs help. They are prey animals, taught to freeze when a predator (or human) approaches. Leave him be!
Also look for bleeding, convulsing, fly larvae, broken limbs; if any, get to a rabbit vet or emergency vet immediately. If he is just out and about, leave him be. He is discovering his world, waiting for mom to return at night when we humans are asleep. Don’t assume because he is letting you pick him up, he needs help. They are prey animals, taught to freeze when a predator (or human) approaches. Leave him be!
What if the Baby Bunny is Injured?
Either call or take him to your local rabbit vet, humane society or animal shelter/animal control. Call first as often they will come pick up the baby. If after hours, contact a local emergency rabbit vet or rabbit vets found here and also here. The best thing you can do for an injured wild baby bunny is to get in touch with a skilled Wildlife Rehabber by searching your state/country and wildlife rehabber, or calling your Humane Society, and or trying this link http://www.humanesociety.org/animals/resources/tips/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator. html and http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator
html and http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator
Is there anything I can do to avoid orphaning wild baby bunnies?
The harsh reality is that many of us who care about wild baby bunnies may be contributing to the suffering and death. House cats who roam outside will kill about every other time they go out. And unlike feral cats who hunt because they are hungry, and kill immediately, house cats maul and torment their prey, sometimes skinning baby bunnies alive. Cat owners need to provide managed outdoor habitats for their cats – such as window boxes or pens. Providing a bell on your cat will help warn the wildlife if you cannot keep him inside. Keep your dogs on a leash with you if you see a rabbit nest.
Lawn chemicals can produce convulsing death in baby rabbits. According to the Poison Control Center for Animals, lawn applications that contain herbicides are not directly toxic to small animals; but they may make toxic plants more palatable to them and may make the animals sick for a few days. Products which contain insecticides, such as Dursban or Diazinion, which are added to many lawn products to control fleas or grubs in the lawn, are toxic.
Products which contain insecticides, such as Dursban or Diazinion, which are added to many lawn products to control fleas or grubs in the lawn, are toxic.
The Bunny is
Wild and Really Orphaned – How do I care for it?Again, make sure you KNOW for sure the mom was killed and the bunnies are abandoned (not warm, etc.). You will not see the mom. The mom will only come back in the middle of the night to feed her babies. If the mom was killed, the best thing you can do for a wild orphaned baby bunny is to get in touch with a skilled rehabilitator. In the meantime, call your local humane society or animal control and one of these vets for a wildlife referral: Rabbit Vets and Pet Bunny Vets. Google your state and wildlife rehabbers, and also try http://www.humanesociety.org/animals/resources/tips/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator.html and http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator
How much formula should I feed a Wild Orphaned Bunny until I get him/her to a rehabber?
The following is a guideline for the daily amount to feed a TRULY orphaned wild bunny (mother was killed, etc. ) Remember with wild bunnies, the mom only comes back at night to call and feed him once or so for 5 mins; please put him back for her if just found and healthy. She leaves them alone between feedings. Don’t assume they are abandoned! Wild rabbits NEED a skilled wildlife rehabber. You should not feed at home or the chances of their surviving is extremely low! Most die from bloat, wrong feedings/stress. These feedings are NOT meant to take place of an actual rehabber, but for someone only who may live too far from a rehabber and is faced with a wild mother, killed, for example. All others need to call your humane society, local rabbit vet, or google your state and wildlife rehabber. You can also check here http://www.humanesociety.org/animals/resources/tips/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator.html and http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator
) Remember with wild bunnies, the mom only comes back at night to call and feed him once or so for 5 mins; please put him back for her if just found and healthy. She leaves them alone between feedings. Don’t assume they are abandoned! Wild rabbits NEED a skilled wildlife rehabber. You should not feed at home or the chances of their surviving is extremely low! Most die from bloat, wrong feedings/stress. These feedings are NOT meant to take place of an actual rehabber, but for someone only who may live too far from a rehabber and is faced with a wild mother, killed, for example. All others need to call your humane society, local rabbit vet, or google your state and wildlife rehabber. You can also check here http://www.humanesociety.org/animals/resources/tips/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator.html and http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator
Age + Amount (This WILL vary SO MUCH depending on type of rabbit. It is impossible over the Internet to see your particular rabbit, so this is only approximate.) Use KMR kitten or KMR kitten plus Goat milk, regular not low fat. Add a pinch of acidophilus (aka Probiotic) to the formula to promote healthy gut flora. Formulas vary depending on region. Avoid Esbilac and any puppy formulas! FEED TWICE A DAY ONLY for healthy babies, three times if low weight. It may be easiest to start with a 3 cc/ml syringe or an eyedropper. Feed only with the bunny sitting UPRIGHT, and point syringe down towards bottom or side of mouth, so if too much comes out, the baby does not aspirate. At first, they may only take a few drops at one feeding until they are not stressed and used to this.
It is impossible over the Internet to see your particular rabbit, so this is only approximate.) Use KMR kitten or KMR kitten plus Goat milk, regular not low fat. Add a pinch of acidophilus (aka Probiotic) to the formula to promote healthy gut flora. Formulas vary depending on region. Avoid Esbilac and any puppy formulas! FEED TWICE A DAY ONLY for healthy babies, three times if low weight. It may be easiest to start with a 3 cc/ml syringe or an eyedropper. Feed only with the bunny sitting UPRIGHT, and point syringe down towards bottom or side of mouth, so if too much comes out, the baby does not aspirate. At first, they may only take a few drops at one feeding until they are not stressed and used to this.
Newborn to One Week: 2- 2+1/2 cc/ml each feeding (two feedings per day).
1-2 weeks: 5-7 cc/ml each feeding (two feedings per day). (depending on bunny..may be much LESS if smaller rabbit!) Newborn babies (if eyes closed) all need to be stimulated to urinate and defecate prior to or following feeding until their eyes open.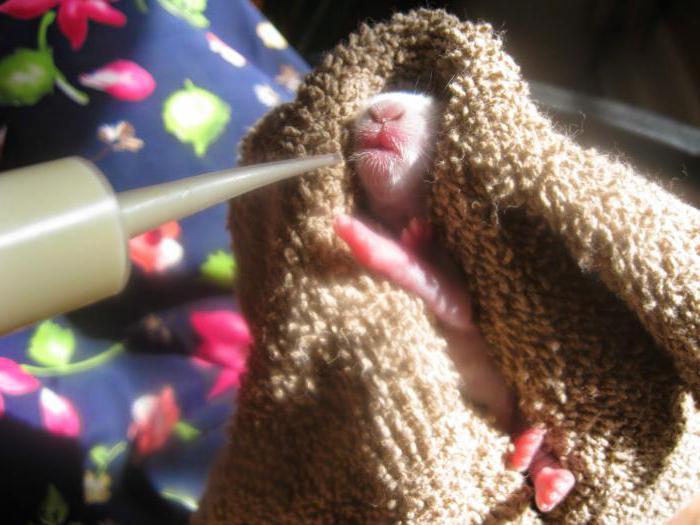 (Except Jackrabbits do not). *See how to below.
(Except Jackrabbits do not). *See how to below.
2-3 weeks: 7-13 cc/ml each feeding (two feedings). Domestic eyes open at about 10 days of age. Start introducing them to timothy and oat hay, pellets and water (always add fresh greens for wild ones).
3-6 weeks: 13-15 cc/ml each feeding (two feedings–again, may be LESS depending on size of rabbit! A cottontail/brush bunny will take so much less!! Half this at most.) Cottontails wean and release about 3-4 weeks and jackrabbits much later (9+ weeks), whereas domestic rabbits are 6 weeks.
6 weeks-9weeks for Jackrabbits only, continue up to 9 weeks with formula, gradually changing to a dish for the warm formula, replacing the formula after 9 weeks slowly, continue adding more of their natural greens and hay (dandelions, oat hay, timothy hay, Italian parsley, carrot tops, small carrots cut up) and a small water bowl. Most markets will sell these greens. They need a rehabber before release!
They need a rehabber before release!
Wild rabbits NEED a skilled wildlife rehabber. These feedings are NOT meant to take place of an actual rehabber, but for someone who may live too far from a rehabber and is faced with a wild mother, killed, for example. Please call your humane society for referrals to rehabbers, or your rabbit vets, or google your state or country and wildlife rehabbers. You can also try here: http://www.humanesociety.org/animals/resources/tips/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator.html and by state here: http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator or http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator
*After each feeding it is important to gently make the bunny defecate and or urinate (brush bunnies/cottontails only..if the eyes are not opened yet) to keep the intestinal and urinary system running smoothly (just UNTIL their eyes open). No need to do this for jackrabbits; they go on their own. Use a cotton ball moistened with warm water after eating, and gently stroke the anal area until the bunny starts producing stool and urine and keep stroking until the bunny stops.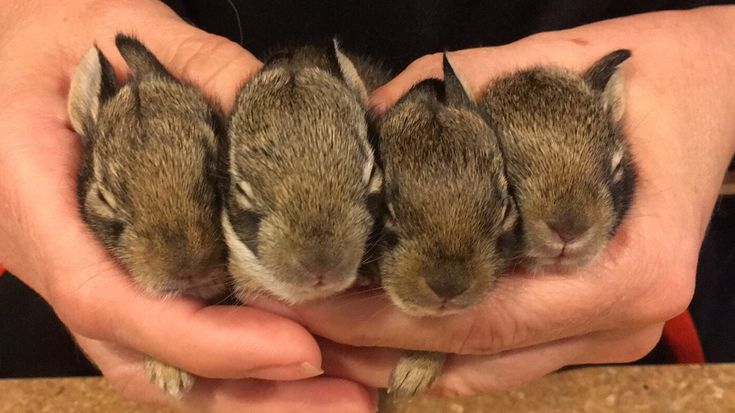 You are reproducing the behavior of the mother rabbit who would lick her young to stimulate them to go to the bathroom and to keep the nest clean. Again, ONLY if the eyes are still closed. Handle a wild rabbit only during feedings as excessive handling can be extremely stressful/potentially fatal. Wild rabbits don’t need heat if furred and healthy. Wild rabbits should not be fed at home, but get them to a professional rehabber as it IS CRITICAL for their survival and to be with their own kind. Most die from overfeeding and/or stress.
You are reproducing the behavior of the mother rabbit who would lick her young to stimulate them to go to the bathroom and to keep the nest clean. Again, ONLY if the eyes are still closed. Handle a wild rabbit only during feedings as excessive handling can be extremely stressful/potentially fatal. Wild rabbits don’t need heat if furred and healthy. Wild rabbits should not be fed at home, but get them to a professional rehabber as it IS CRITICAL for their survival and to be with their own kind. Most die from overfeeding and/or stress.
As soon as the wild bunnies’ eyes are open, you may introduce them to plain alfalfa pellets, hay, such as oat hay, timothy, alfalfa and veggies such as carrot tops, Italian parsley, dandelion greens. Dandelion greens and hay (timothy and oat hay) are extremely important for wild rabbits. You can add whole oats from a feed store, and some grated carrots. The greens must be fresh, rinsed, and replaced if not eaten in a few hours. You can place them in a cup of cold water with just the tops sticking out to keep them fresher. (For a domestic rabbit baby, see section under the Domestic heading). Wild cottontail and brush bunny rabbits should be released as soon as they are eating hay and greens and are approximately 5 inches in body length and run from you. This varies with the area, so size is not easy to say. They will be small, but the longer you keep them, the more agitated and difficult to handle they will become and the less likely their chances for survival in the wild. Release ONLY at dusk or dawn. Jackrabbits (hares) are not ready until 9+ weeks.Make sure they get exercise daily. Jackrabbits mature much slower than the brush/cottontails and need to develop strength. If they are ready, earlier, they will let you know.
(For a domestic rabbit baby, see section under the Domestic heading). Wild cottontail and brush bunny rabbits should be released as soon as they are eating hay and greens and are approximately 5 inches in body length and run from you. This varies with the area, so size is not easy to say. They will be small, but the longer you keep them, the more agitated and difficult to handle they will become and the less likely their chances for survival in the wild. Release ONLY at dusk or dawn. Jackrabbits (hares) are not ready until 9+ weeks.Make sure they get exercise daily. Jackrabbits mature much slower than the brush/cottontails and need to develop strength. If they are ready, earlier, they will let you know.
WARNING: Jackrabbits really NEED a skilled wildlife rehabber as they can run from you, throw themselves into walls to get away; many have died or severely injured themselves in captivity as they are so very wild. Please DO NOT raise them if you are not a skilled wildlife rehabber. This is vital. Noises and sounds easily frighten the jackrabbit and they are not able to be handled after 9 weeks. Often, sadly, we get reports of how a well-meaning person who tried to raise a wild rabbit, only to find it literally died of fright or got injured inside the cage. They are wild and belong with their own kind, out in the wild.
This is vital. Noises and sounds easily frighten the jackrabbit and they are not able to be handled after 9 weeks. Often, sadly, we get reports of how a well-meaning person who tried to raise a wild rabbit, only to find it literally died of fright or got injured inside the cage. They are wild and belong with their own kind, out in the wild.
Jackrabbits really enjoy being raised together, whereas cottontails/brush bunnies may fight and do fine alone. Give them a carrier as their place of privacy (line with thick towels) with plenty of fresh hay and greens described above and water bowl. Again, wild rabbits need a skilled wildlife rehabber; it is critical to their survival.
The Bunny is DOMESTIC (i.e., pet rabbit, NOT wild) and Really Orphaned – How do I care for a domestic baby?
Baby Domestic Agouti Bunny Baby Domestic/Pet Agouti rabbit babyRemember that both the domestic pet rabbit and wild bunny moms only feed their young usually once in the middle of the night. Don’t assume the mom is not caring for them if you don’t see her nurse them. Check their tummies to see if they are round and the babies are warm in the morning–this means she is caring for them. In the rare situation that you have an orphaned domestic bunny, such as when a domestic rabbit mom is sick or refuses to care for her young, you will need to feed the babies. Overfeeding is a leading cause of death in these youngsters which results in fatal intestinal disease.
Don’t assume the mom is not caring for them if you don’t see her nurse them. Check their tummies to see if they are round and the babies are warm in the morning–this means she is caring for them. In the rare situation that you have an orphaned domestic bunny, such as when a domestic rabbit mom is sick or refuses to care for her young, you will need to feed the babies. Overfeeding is a leading cause of death in these youngsters which results in fatal intestinal disease.
If truly orphaned, use KMR KITTEN powder formula (can also use Meyenberg Regular Goat milk found at Safeway in the milk section or Whole Foods until you can find the KMR KITTEN formula), and follow the directions on the can. It may be easiest to start with a 3 cc/ml syringe or an eyedropper. Some use pet nurser nipples on the end of a luer lock syringe, or a teat cannula on the end of a syringe. Feed only with the bunny sitting UPRIGHT, and point syringe down towards bottom or side of mouth, so if too much comes out, the baby does not aspirate! For those who are slow to learn nursing, SC fluids may be necessary to prevent electrolyte imbalance or dehydration (check with a vet on this only!!).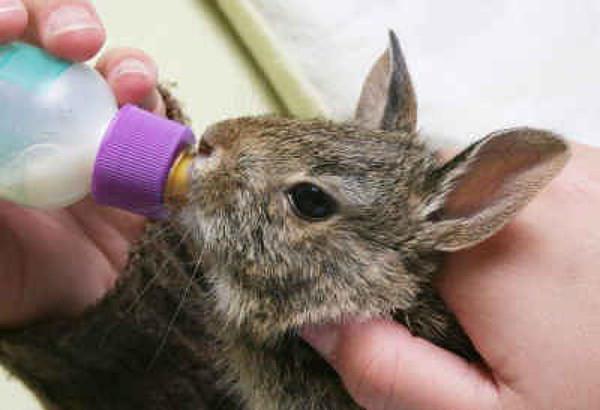 Domestic buns with closed eyes should be fed 2 x a day, and the number of feedings gradually decreased until they are weaned. If their eyes are still closed, you need to stimulate their bottoms with a warm moist towel after feedings to help them to pee. (Domestics are weaned about 6 weeks compared to wild bunnies who are weaned about 3-4 weeks for cottontails and 9+ weeks for jackrabbits). Bloat is commonly associated with too frequent feedings and too much at one time.
Domestic buns with closed eyes should be fed 2 x a day, and the number of feedings gradually decreased until they are weaned. If their eyes are still closed, you need to stimulate their bottoms with a warm moist towel after feedings to help them to pee. (Domestics are weaned about 6 weeks compared to wild bunnies who are weaned about 3-4 weeks for cottontails and 9+ weeks for jackrabbits). Bloat is commonly associated with too frequent feedings and too much at one time.
Feeding Amounts for DOMESTIC/PET Orphaned babies*: Feed twice a day up to these amounts: Newborn– 2.5 cc/ml each feeding. One week old: 6-7 cc/ml each feeding. Two weeks old: 12-13 cc/ml each feeding. Three weeks to six weeks: Up to 15 cc/ml each feeding (a.m. and p.m.). Note this is for DOMESTIC, NOT WILD bunnies. Each bunny varies. If this is a smaller rabbit, he will consume much less. Do NOT overfeed! Contact an HRS contact, rabbit vet, to be sure.
*After each feeding it is important to make the bunny defecate and urinate (if the eyes are not opened yet) to keep the intestinal tract and urinary system running smoothly (only UNTIL their eyes are open). Use a cotton ball moistened with warm water and gently stroke the anal area until the bunny starts producing stool and urine and keep stroking until the bunny stops. You are reproducing the behavior of the mother rabbit who would lick her young to stimulate them to go to the bathroom and to keep the nest clean.
Use a cotton ball moistened with warm water and gently stroke the anal area until the bunny starts producing stool and urine and keep stroking until the bunny stops. You are reproducing the behavior of the mother rabbit who would lick her young to stimulate them to go to the bathroom and to keep the nest clean.
Provide a soft nest area in a box with clean towels, and cover the babies so it is dark until their eyes are open. Do NOT provide extra heat if the room temperature is at least 65 to 70 degrees F because excessive heat can be fatal. If the room is cooler, then you may place a heating pad on a low setting under no more than HALF of the nest so the bunny can move to a cooler area if it gets too warm, and be sure there is no way the mother rabbit can get to or chew the electrical cord!
For domestic rabbits, if you have a healthy adult rabbit at home and you can collect cecotropes (the soft, chain-like droppings that the rabbit usually eats) then these can be mixed with the KMR to give the baby bunny normal bacteria for its intestinal tract. Only one cecotrope per day for 4-5 days is needed. This is particularly important for rabbits under one week of age. Also good is to sprinkle a pinch of acidophilus powder, also called “Probiotic” from human capsules in the milk a little each time for healthy flora for both wild and domestic bunnies.
Only one cecotrope per day for 4-5 days is needed. This is particularly important for rabbits under one week of age. Also good is to sprinkle a pinch of acidophilus powder, also called “Probiotic” from human capsules in the milk a little each time for healthy flora for both wild and domestic bunnies.
As soon as their eyes are open, you may introduce the bunnies to plain alfalfa pellets, hay, such as oat hay, timothy, alfalfa. Please refer to the handout Care of Rabbits for more information on diet for domestic, pet rabbits. You may reach [email protected] for domestic/pet rabbit questions. Below is the email for wild rabbit questions: [email protected] (wild) (If links above did not answer your question).
(See above for wild rabbits). For all rabbits, avoid ANY regular milk, puppy formulas, etc. Use KITTEN formulas like KMR. Avoid Esbilac. Feed only upright. Less is better than more! Overfeeding will cause bloat and pain and possible death. Please get to a rehabber.
Sources: Caring for Cricket – What Not To Do When You Find a Wild Baby Bunny by Julie Smith and Handout by Midwest Exotic Animal Hospital, and additional wild bunny info by M. Wilson (HRS educator and rehabber). For questions not answered about wild rabbits above, email: wildbunnyrehab at gmail.com
Below content was merged from: /caring-for-orphans/
Rabbit mothers nurse their babies for approximately 5 minutes a day. They will be in the nest or nest box early in the morning and then again in the evening. The milk is very rich and the babies “fill up” to capacity within minutes. Mother rabbits do not “sit” on the babies to keep them warm as do some mammals and birds. They build a nest with fur and grasses which helps to keep the babies warm in between feedings. Do not force a mother rabbit to sit in the nest box. You can pick up the babies and see if they are feeding by checking the size of their stomachs (should not be sunken in), the pinkness of their skin and activity level (they should not be blue in color or sluggish in movement) and the amount of time that you hear them crying (baby bunnies should be quiet most of the day…. if they are crying constantly then they are not getting fed). If they are warm, mom is most likely feeding them, but again, she only comes back in the middle of the night.
if they are crying constantly then they are not getting fed). If they are warm, mom is most likely feeding them, but again, she only comes back in the middle of the night.
If you come across a nest of bunnies in the wild and the mother is no where to be seen, please DO NOT disturb them…this is normal. By removing them from the nest you are greatly reducing their chances of survival.In the rare situation that you have an orphaned bunny, such as when a mother rabbit is killed by another animal or in the road, or when a domestic rabbit refuses to care for her young, you may try feeding with Kitten Milk Replacer (KMR) or Meyenberg Goat Milk (for wild rabbits, but they need a professional reahabber–do not feed at home). Remember though, that both wild/domestic bunny moms only feed in the middle of the night, so don’t assume she is not caring for them! For true orphans, remember to feed ONLY TWICE A DAY. Overfeeding is a leading cause of death in these youngsters which results in fatal intestinal disease. Provide a soft nest area in a box with clean towels, and cover the babies (if eyes are closed) so it is dark.
Provide a soft nest area in a box with clean towels, and cover the babies (if eyes are closed) so it is dark.
DO NOT provide extra heat if the room temperature is at least 65 to 70F because excessive heat can be fatal. If the room is much cooler, then you may place a heating pad on a low setting under no more than HALF of the nest so the bunny can move to a cooler area if it gets too warm.
For a wild bunny, you need to get him to a wildlife rehabilitator if he is TRULY orphaned (mom was killed). Remember with wild bunnies, the mom ONLY comes back at night to call and feed him; please put him back for her if just found and healthy. With domestics, the mom only feeds once or twice a day for only 5 minutes. Leave babies with the mom. For wild orphans, first google your state and wildlife rehabber, and call your humane society, also try http://www.humanesociety.org/animals/resources/tips/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator.html and http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitatoror as it is illegal in most states to keep a wild animal, and they really need a professional as this is critical.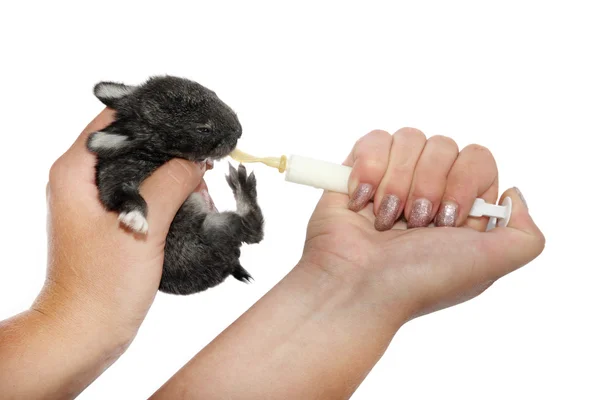 Local rabbit veterinarians or humane societies may also know of a rehab facility.
Local rabbit veterinarians or humane societies may also know of a rehab facility.
The following is a guideline for the daily amount to feed a TRULY orphaned bunny (mother was killed, etc.) that will be about 5 lbs as an adult. It is impossible on the internet to be exact. Please find rehabber.
GENERAL FEEDING OF ORPHANS
Age + Amount (This WILL vary depending on type of rabbit.) Use KMR (Kitten Milk Replacer) for domestics and Meyenberg Goat Milk, regular not low fat for wild ones,or KMR. Add a pinch of acidophilus (AKA Probiotic capsules) to all formula to promote healthy gut flora. Other formulas vary depending on the region of the country. Avoid using Esbilac or any puppy formulas or cow’s milk. Do not add Karo syrup. FEED TWICE A DAY ONLY unless baby is low weight, than three times.
Newborn to One Week: 2 – 2+1/2 cc/ml each feeding (two feedings).
1-2 weeks: 5-7 cc/ml each feeding (two feedings).
(depending on bunny. .may be much LESS if smaller rabbit).
.may be much LESS if smaller rabbit).
2-3 weeks: 7-13 cc/ml each feeding (two feedings). Bunnies whose eyes are still CLOSED need to be stimulated to urinate and defecate before or after each feeding. Again, seek a professional on this. Domestic eyes open at about 10 days of age. Then start introducing them to timothy and oat hay, pellets and water (always add fresh greens for wild ones–dandelion greens, parsley, carrot tops, grated carrots, all fresh, watered down). See below for detail.
3-6 weeks: 13-15 cc/ml each feeding (two feedings–again, may be LESS depending on size of rabbit! A cottontail will take so much LESS–about half of this!.)
Domestics are weaned about 6 weeks. Cottontails wean and release about 3-4 weeks and jackrabbits much later (9+ weeks). Feed only twice a day up to these TOTAL amounts. You may find an eyedropper or syringe easiest to use. Feed them upright, and go slowly watching them lick and swallow so they do not aspirate. For domestic rabbits, if you have a healthy adult rabbit at home and you can collect cecotropes (the soft chain-like droppings that the rabbit usually eats) then these can be mixed with the KMR or goat milk to give the baby bunny normal bacteria for its intestinal tract. Only one cecotrope per day for 4-5 days is needed. This is particularly important for rabbits under one week of age. Acidophilus capsules for humans, opened and sprinkled some in formula, works well too.
For domestic rabbits, if you have a healthy adult rabbit at home and you can collect cecotropes (the soft chain-like droppings that the rabbit usually eats) then these can be mixed with the KMR or goat milk to give the baby bunny normal bacteria for its intestinal tract. Only one cecotrope per day for 4-5 days is needed. This is particularly important for rabbits under one week of age. Acidophilus capsules for humans, opened and sprinkled some in formula, works well too.
After each feeding it is important to make the bunny defecate and urinate (until their eyes are open) to keep the intestinal tract and urinary system running smoothly. Use a cotton ball moistened with warm water and gently stroke the anal area until the bunny starts producing stool and urine and keep stroking until the bunny stops. You are reproducing the behavior of the mother rabbit who would lick her young to stimulate them to go to the bathroom and to keep the nest clean. No need to do this for jackrabbits or if bunny’s eyes are open.
As soon as their eyes are open, you may introduce the bunnies to hay, such as oat and timothy hay, some alfalfa, and pellets, and for wild ones, add dark leafy veggies such as dandelion greens, carrot tops, parsley, grated carrots, etc. Keep the greens fresh, moist, and stand them up in a heavy mug of water. Change greens often. If this is a wild rabbit, you do not need to introduce pellets. If this is a domestic rabbit baby, then you may introduce plain alfalfa pellets at 2 weeks of age (please refer to the handout Care of Rabbits for more information on diet). Wild rabbits should be released as soon as they are eating hay and greens and are approximately 5 inches in body length (for cottontails) and are afraid of you (about 3-4 weeks). Jackrabbits are released much later (9 weeks up). They will be small, but the longer you keep them, the more agitated and difficult to handle they will become, and the less likely their chances for survival in the wild. They may be easily injured in your care as they attempt to get free. For wild bunnies, please do not raise them yourself, but take them to a rehabber! Google your state and wildlife rehabber or see links above.
For wild bunnies, please do not raise them yourself, but take them to a rehabber! Google your state and wildlife rehabber or see links above.
Modified from an original document from :
Midwest Bird & Exotic Animal Hospital
Caring for Newborn Baby Rabbits
IF THESE ARE WILD BABIES
It’s that time of year again. Wild babies everywhere. But are they at risk?
Wild rabbits hide their nests in plain view, often in the middle of your yard, bushes, etc. If you find a nest that has been disturbed, do the best you can to restore it and leave the babies in there. If a dog discovers the nest, do your best to restore it (with grass, leaves, whatever mama has used), make sure the kits are in there, and find a way to keep the dog(s) away from the nest. Mama will return for her babies and taking them away will seriously decrease their chance of survival. If you do not see the mama—DON’T WORRY—they only nurse their babies a few minutes a day, then they stay away so as to not draw predators to the nest.
If a kit is injured or an animal brings you an injured baby, if you have no choice but to help a baby, please do not try to care or it yourself—-get it to a rabbit vet or a wildlife rehabilitator
- Local wildlife rehabilitator: https://www.nwrawildlife.org
- List of rabbit vets: http://rabbit.org/vet-listings/
The best thing you can do for wild babies is to leave them alone (restored to the nest) or, if injured, get them to a rabbit vet or wildlife rehabilitator.
DOMESTIC/PET RABBITS
WHERE TO PUT THE BABIES
Make the babies a soft nest area in a box with clean towels. We like to put one folded towel on the bottom and another bunched on top of that, so the babies can snuggle into it. You can also purchase soft nesting wool from a pet store and put that on top of the towel. You can also take whatever nesting material they were in and put it in the box as well. Cover the box almost entirely with a light towel, making sure that there will be enough air so the babies do not suffocate. Leaving about a one inch gap at the top is usually sufficient. Keep the babies in an out-of-the way, QUIET area, such as an adult’s bedroom. If the room temperature is between 68-72 degrees you will not need to provide extra heat, but if it’s cooler than that you will need to provide extra warmth. Use a heating pad set on low and slip it under one half only of the box. We do it this way so that the babies can move to a cooler area if it gets too warm. DO NOT put babies directly on heating pad, as babies can burn themselves very badly.
Leaving about a one inch gap at the top is usually sufficient. Keep the babies in an out-of-the way, QUIET area, such as an adult’s bedroom. If the room temperature is between 68-72 degrees you will not need to provide extra heat, but if it’s cooler than that you will need to provide extra warmth. Use a heating pad set on low and slip it under one half only of the box. We do it this way so that the babies can move to a cooler area if it gets too warm. DO NOT put babies directly on heating pad, as babies can burn themselves very badly.
If the babies were with their mamma, but she is not caring for them (and you are sure she is ignoring them) you may need to separate her from them so they will not get hurt. Rabbit milk is very caloric and the kittens (baby rabbits) only nurse for a few minutes a day, so if you think that she is not caring for them based only on the fact you don’t see them feed…think again. If you do think they are being neglected, you can check: Are they cold? Are they making crying sounds for more than a few minutes before (or at) feeding time? Are they blue? Is the skin shriveled? Check for dehydration: gently pinch together the skin at the nape of the neck. If it sticks together or stays in a tent, they are dehydrated. A healthy kit has a round belly, is warm, gains weight on a daily basis, and snuggles with its litter mates. If they are dehydrated, cold, losing weight or becoming injured, of course, something must be done
If it sticks together or stays in a tent, they are dehydrated. A healthy kit has a round belly, is warm, gains weight on a daily basis, and snuggles with its litter mates. If they are dehydrated, cold, losing weight or becoming injured, of course, something must be done
WHAT TO FEED THE BABIES
Baby rabbits should be fed Kitten Milk Replacer (KMR) or goat milk, which you can buy at pet stores, or sometimes even a local veterinarian’s office. Because rabbit milk is the most caloric of all mammals, we add in one tablespoon of 100% heavy whipping cream (no sugar) to each can of KMR. Most kits will not nurse from the baby animal bottles you can buy at stores. Instead, use a sterile oral syringe, which can be purchased at most pharmacies. A better alternative are these nipples, which come the a syringe, but you may not be able to find them locally/right away (link).
It is best to feed baby rabbits no more than twice a day, but sometimes it takes more feedings to get an adequate amount into them, especially at first.
How much to feed varies greatly on what breed of rabbit you are feeding, and how big the kit is, but here is a basic guideline for the daily amount to feed a domestic rabbit who will be approximately 5-6 pounds as an adult (average rabbit size). You can increase the amounts as needed for larger breeds.
To help the kits maintain healthy gut bacteria, go to your local health food store (and get a bottle of ACIDOPHILUS. Ask for the capsules that have the “grainy stuff” inside (they are easier to mix than the “powdery stuff”) and add a bit to the formula at each feeding.
ALL amounts below should be divided into two feedings per day.
- Newborn – 1 week
- 4-5 cc formula
- 1-2 weeks
- 10-15 cc formula
- 2-3 weeks
- 15-30 cc formula
- 3-6 weeks, until weaned
- 30 cc formula
HOW DO I DO THIS?
Baby rabbits feed from their mothers while lying on their backs. You may loosely wrap baby in a soft face cloth or hand towel and lay it on your lap or in the crook of your arm. If bunny will NOT eat this way, of course, do the best you can. It is ABSOLUTELY CRUCIAL to let the baby eat at it’s own pace—especially if it is not suckling from the syringe willingly. If you squirt the liquid in too quickly you can aspirate (get liquid in) the lungs and the rabbit will suffocate.
You may loosely wrap baby in a soft face cloth or hand towel and lay it on your lap or in the crook of your arm. If bunny will NOT eat this way, of course, do the best you can. It is ABSOLUTELY CRUCIAL to let the baby eat at it’s own pace—especially if it is not suckling from the syringe willingly. If you squirt the liquid in too quickly you can aspirate (get liquid in) the lungs and the rabbit will suffocate.
Until their eyes open (10 days): After each feeding it is important to make the bunny defecate and urinate to keep the intestinal tract and urinary system running smoothly. Use a soft cloth or a cotton ball moistened with warm water and gently stroke the genital area until the bunny starts producing stool and urine. Keep stroking until the bunny stops. You are replicating the behavior of the mother rabbit who would lick her young to stimulate them to go to the bathroom. The stool will be soft and may be varying shades of green and yellow.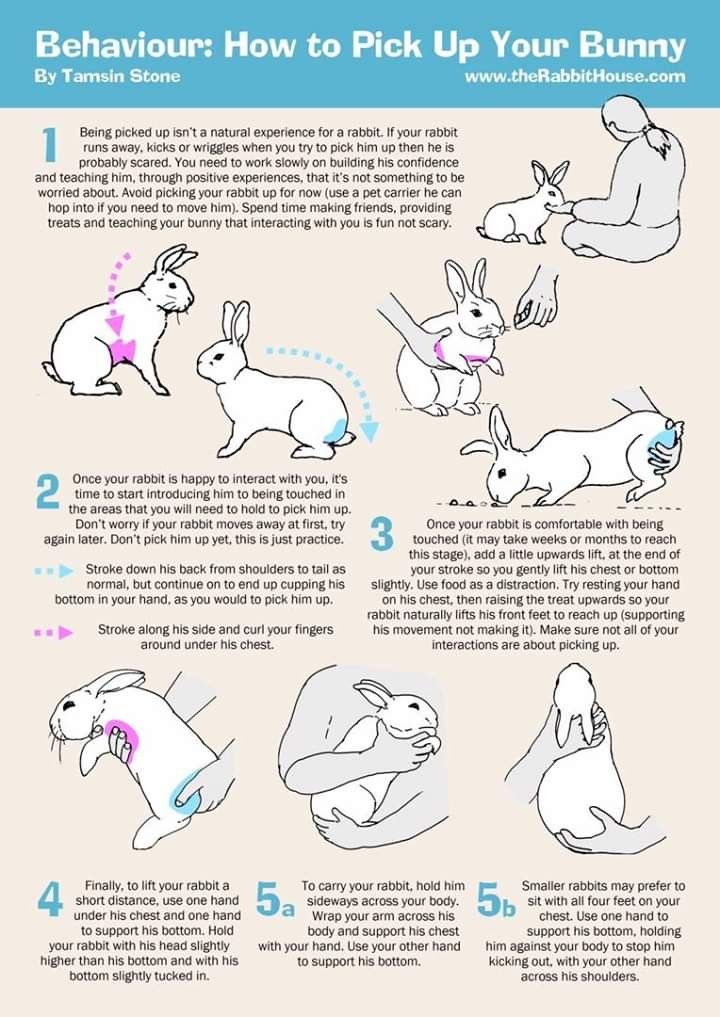 If the urine is brown and gritty, the buns are not adequately hydrated and you need to get them to a rabbit vet ASAP—-it is an emergency. Be sure to clean baby’s mouth with a damp cloth or paper towel, so that no milk dries in the hair.
If the urine is brown and gritty, the buns are not adequately hydrated and you need to get them to a rabbit vet ASAP—-it is an emergency. Be sure to clean baby’s mouth with a damp cloth or paper towel, so that no milk dries in the hair.
Baby rabbit eyes open at about 10 days of age. You may start introducing them to hay and pellets at this point, but no veggies or fruits yet. Just leave some timothy or orchard and alfalfa hay and pellets in a corner of the box where the babies can easily get to them. Make sure it the pellets are plain, high fiber and fresh, with no added goodies such as dried banana chips or seeds. Don’t ever leave a deep water dish in which a baby could drown; instead, use something shallow and rinse and fill it frequently.
If you have any questions, please contact us.
How to feed rabbits at home
Proper feeding of rabbits requires balanced mixtures containing a certain norm of the necessary products and having a high nutritional value.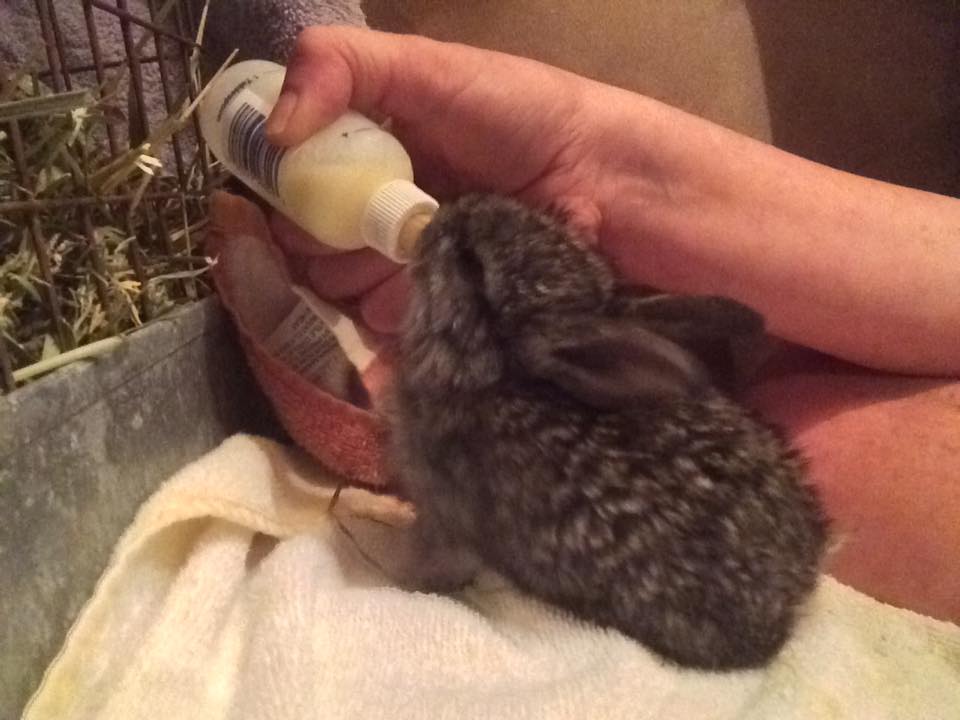 Without observing this condition, it is impossible to achieve good growth and strong immunity in animals. By adjusting the diet of rabbits, you can improve the quality of meat and fur, increase the survival of offspring and maximize the potential of the breed.
Without observing this condition, it is impossible to achieve good growth and strong immunity in animals. By adjusting the diet of rabbits, you can improve the quality of meat and fur, increase the survival of offspring and maximize the potential of the breed.
- What can rabbits eat?
- Benefits of specialty feeds
- Benefits of compound feed produced by MEGAMIX
- Feeding rates and rations
- Self-preparation of feed
- Nuances of feeding rabbits depending on the season
- What should not be fed to rabbits?
What can be fed to rabbits?
The metabolism of rodents is so intense that they need to constantly eat for the proper functioning of all body systems. If the rabbit for some reason stops eating, then during the day there is a malfunction in the digestive tract. This entails serious consequences for health, up to and including death.
Compound feed for rabbits is complete and concentrated. The first one provides all the needs of animals in calories and nutrients. The second is used as a supplement to the main diet. Young rabbits reach a commercial weight of 3.5–4.5 kg, provided that they are properly fed, at the age of 4–5 months, and an adult female brings 30 or more cubs per year. If the diet is balanced and meets the needs of the breed, the rabbit is capable of the next reproductive cycle as early as 3-5 days after birth.
The first one provides all the needs of animals in calories and nutrients. The second is used as a supplement to the main diet. Young rabbits reach a commercial weight of 3.5–4.5 kg, provided that they are properly fed, at the age of 4–5 months, and an adult female brings 30 or more cubs per year. If the diet is balanced and meets the needs of the breed, the rabbit is capable of the next reproductive cycle as early as 3-5 days after birth.
Livestock specialists have repeatedly researched the best way to feed rabbits. The diet of meat and decorative animals should include the following products:
Cereals (concentrated feed) have the highest nutritional value. They contain a large amount of protein and a minimum of water. Oats are considered the best grain, as they are well absorbed, have a positive effect on intestinal motility and reproductive functions, and do not contribute to obesity. It is used in the form of whole or crushed grains. Rye, barley and wheat are offered to rabbits in the form of crushed, mixed with other feeds.
It should be remembered that you can not give a lot of wheat, and it is better to remove the shell from barley. These grains are difficult to digest, often leading to bloating. Many farmers recommend pre-treatment of grain products: soaking, sprouting, steaming or yeasting. Sprouting allows you to increase the amount of vitamins and increase protein digestibility. Yeasting improves the digestibility of fiber, but feeding animals with such grains for more than 5 days in a row is undesirable, as it can provoke fermentation in the intestines.
Green foods form the basis of the rabbit diet from spring to late autumn. This type of food includes: vegetable tops; fodder cabbage; wild herbs; seeded cereals and legumes. Nettle, wormwood, dandelion, couch grass, plantain, quinoa are considered the most suitable wild plants. Freshly cut greens are recommended to be slightly dried and dried in the sun. The tops of fodder and sugar beets, carrots, turnips, rutabaga, Jerusalem artichokes are also suitable as green fodder.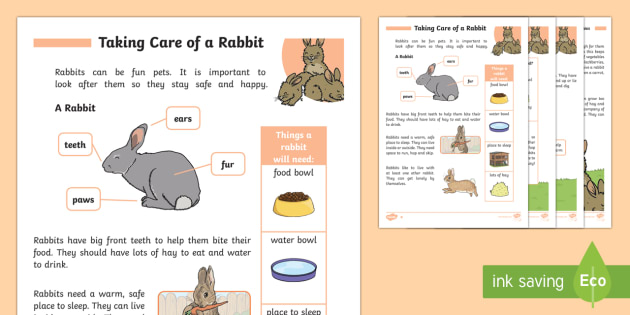 Sugar and fodder beet tops are not recommended for young animals. It has laxative properties, therefore, along with it, animals are advised to give plant foods that have a fixing effect. For these purposes, yarrow, comfrey, branches and leaves of oak and alder are suitable. In the mass of green fodder beet tops should not be more than 30%.
Sugar and fodder beet tops are not recommended for young animals. It has laxative properties, therefore, along with it, animals are advised to give plant foods that have a fixing effect. For these purposes, yarrow, comfrey, branches and leaves of oak and alder are suitable. In the mass of green fodder beet tops should not be more than 30%.
The aerial part of legumes, legumes and cereals is rich in vitamins and minerals, and also contains a large amount of proteins. However, experienced rabbit breeders advise using the above plants in a mixture with other feeds, since herbs alone will not be able to provide good nutrition and can lead to bloating in animals.
The diet of rabbits should be approximately 25% roughage. These include: hay, straw, tree branches. The optimal harvesting time is in spring and summer. Such food is very important, as it creates a feeling of satiety and contains fiber necessary for the normal functioning of the digestive tract.
The main share of roughage is hay. Harvest it using the same herbs as for green fodder. Legume hay has much more plant protein than grain hay, so it is more nutritious. Haylage is under-dried hay pressed into briquettes. Rabbits eat it with gusto, and also love clean straw if it's well dried.
Harvest it using the same herbs as for green fodder. Legume hay has much more plant protein than grain hay, so it is more nutritious. Haylage is under-dried hay pressed into briquettes. Rabbits eat it with gusto, and also love clean straw if it's well dried.
Juicy food (vegetables)
- Potato: high in fast digesting starch. It is recommended to give in boiled form;
- Carrots contain C and B vitamins vital for breeders, pregnant/nursing females and growing rabbits. It is the main source of carotene in winter. The daily norm for an adult animal is up to half a kilogram. Young rabbits are started on portions weighing 20–30 g.
- Cabbage contains many minerals, vitamins C and E. Helps to improve the quality of the skin and fur. Introduced into the diet of animals gradually, used both raw and boiled.
- Zucchini helps to better digest other foods. They are given fresh.
- Pumpkin improves coat quality and has a positive effect on milk production in lactating rabbits.
 It has a good effect on digestion and weight gain in animals. Offered to rabbits both raw and boiled.
It has a good effect on digestion and weight gain in animals. Offered to rabbits both raw and boiled. - Feed and sugar beet improves metabolism and blood quality, improves immunity. Use raw or boiled, no more than 150–200 g for young animals and 250–300 g for adults per day. Excess beets can lead to diarrhea in animals. Table varieties are strictly prohibited.
- The diet of rabbits also includes melons, watermelons, turnips, Jerusalem artichokes, and radishes. However, their nutritional value is not very high.
Processed products of legumes and oilseeds (meal, cake of soybeans, peas, beans, sunflower, hemp, flax) are sources of fatty acids necessary for the body, including essential ones.
The composition of feed mixtures necessarily introduce products of animal origin: meat and bone or fish meal. Meat and bone contains about 40% protein and 14% fat, while fish contains about 45% protein and 7% fat. Flour is mixed into wet food in small portions - 5–10 g per individual.
Also, table salt must be present in the diet of rabbits. The rabbit needs 0.5–1 gram per day. For adults, the rate is increased by 1.5–2 times. When fattening animals, the daily amount of salt is 2-3 grams per individual.
Benefits of specialty foods
Complete nutrient mixtures can be prepared independently, but this is a very time-consuming work. To produce a quality product for feeding rabbits, you need:
- crushers, crushing components to the desired size;
- stocks of various grain crops;
- meat and bone and fish meal;
- protein-vitamin-mineral complexes;
- cake.
It is important to check the quality of incoming raw materials to minimize the risk of mortality. In the process of preparing mixtures for feeding rabbits, it is necessary to know exactly how much and what components are required, and at home or in a small enterprise it is difficult to achieve proportions. Because of this, there is a possibility of an excess of some nutrients and a deficiency of others, which can lead to improper formation of rabbits and young animals.
For the storage of compound feed, it is necessary to maintain normal ventilation in the room, a humidity level of not more than 75% and a temperature of up to 25 ° C. It is desirable to place bags on lattice racks or pallets. For small farms and medium-sized farms, buying ready-made feed can be more profitable than own production. The higher cost of the product is offset by guaranteed quality and time savings.
Benefits of compound feed produced by MEGAMIX
Our compound feeds for rabbits are presented in correctly formulated complete mixtures, which contain all the necessary nutrients:
| universal | for lactating queens |
|---|---|
| Ideal for weaned rabbits and fattening animals. | Also suitable for queens and rabbits. on milk feeding. |
Feed is produced in the form of granules and packaged in convenient packages: standard bags of 25 and 40 kg or big bags for large customers. The composition of the mixtures contains only valuable components that improve productivity, strengthen the immune system, positively affect the quality of the fur and the resulting meat, increase the growth and activity of rabbits.
The composition of the mixtures contains only valuable components that improve productivity, strengthen the immune system, positively affect the quality of the fur and the resulting meat, increase the growth and activity of rabbits.
Thanks to our own science-intensive production, we create recipes that best meet the needs of a particular breed of animal. The quality of incoming raw materials and the final product is carefully checked against more than 280 indicators in our analytical center, accredited to the international standard. Our requirements for commercially available compound feed for rabbits are stricter than GOSTs. All products undergo mandatory certification.
The company closely cooperates with VolGAU. The effectiveness and safety of all feeds are tested in a research center. Due to this, we are able to quickly navigate the needs of customers, clearly analyze each request and select the most profitable option for the customer. Our production facilities are designed to produce up to 180 tons of products annually.
We work not only in the central regions of Russia (Moscow and nearby regions), but also organize delivery to the cities of the Urals, Western Siberia, the North Caucasus, Crimea through an extensive network of dealerships.
Feed mixtures from MEGAMIX are effective for breeding rabbits at home, on medium-sized farms or large complexes. Using them, you will provide the animals with all the necessary trace elements, vitamins and mineral supplements, get a high average daily weight gain and reduce the risk of livestock infection.
Norms and diet
For agricultural breeds (meat and fur)
In summer, one rabbit needs 40-50 grams of concentrated and roughage plus a pound of green. During preparation for mating, the amount of food increases: green for 600 grams, concentrated and coarse - 70-80 grams. For a pregnant female, you will need 550–700 grams of greenery and 70–90 grams concentrated and coarse. A lactating female needs at least a kilogram of greens per day and up to 150 grams of roughage.
In winter, the basis of the diet is succulent food (150–200 grams) plus hay (120–150 grams). The amount of rough and concentrated feed remains the same. During preparation for mating 150-200 grams of juicy, 90-100 grams of concentrated and coarse and 150-200 grams of hay. A pregnant rabbit needs 200-250 grams of juicy, 100-130 grams of coarse and 150-200 grams of hay. A lactating female will need 300-350 grams of juicy, 140-160 concentrated and coarse and 200-250 grams of hay.
Fattening of meat breeds usually occurs in autumn and winter. When fattening, the amount of concentrated feed, bran and root crops (especially boiled potatoes) is gradually increased.
In ornamental breeds, digestion works worse than in agricultural ones. They can be given the following foods.
- Hay is the main feed for ornamental breeds. It should be clean and dry and should be replaced as needed.
- Grass - it can be added to the diet in summer. It is desirable to collect grass away from roads and other sources of pollution.

- Granulated food - 2 tablespoons per day.
- Vegetables and fruits - can be given little by little, in small pieces and only washed and fresh. Radishes, parsley, carrots are good. It is better to exclude beets and cabbage in order to avoid stomach problems.
A complete balanced diet for rabbits, of course, should include the main vitamins:
- A - has a positive effect on the functioning of the nervous and reproductive systems in wards, improves their general physical condition;
- B1 - responsible for the metabolism of carbohydrates in the body, normalizes the activity of the cardiovascular system, indirectly improves the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- B2 - improves the condition of the skin and fur, optimizes the general physical condition of animals;
- B5 - normalizes the digestive system;
- B6 - is responsible for the absorption of proteins and simple proteins, as well as for the enzymatic balance in the body;
- B12 - promotes the absorption of proteins, is extremely important for the health of newborn rabbits;
- C - strengthens the immune system and normalizes the digestive tract;
- D - necessary for the proper development of the eared musculoskeletal system, promotes better absorption of minerals;
- E - is responsible for the development of the muscular system of pets.
 Stabilizes the work of the heart and reproductive system;
Stabilizes the work of the heart and reproductive system; - K is an essential vitamin for rabbit breeding.
Self-feed preparation
The mash is a delicacy for rabbits. The most popular recipe includes:
- boiled potatoes;
- carrots;
- oats;
- germinated wheat;
- table salt;
- bran;
- chopped hay.
The mixer is prepared using a blender or other grinder. To enrich it with biologically active substances, concentrated feed additives are added to it.
Hay is harvested using the same herbs as for green fodder. It is important to mow the plants before they bloom. The resulting raw material is dried on the street, and then allowed to lie down for some time in a well-ventilated place under a canopy (without direct sunlight).
Silage ingredients are crushed to fragments no larger than 1 cm in length. The resulting mass is placed in a sealed barrel and covered with a layer of sawdust 5 cm thick. The resulting substrate is compacted until juice appears and pressed down with a wooden circle, on which a load is placed on top. In the process of silage maturation, the barrels are stored in a moderately warm place, and then removed to a cool room.
The resulting substrate is compacted until juice appears and pressed down with a wooden circle, on which a load is placed on top. In the process of silage maturation, the barrels are stored in a moderately warm place, and then removed to a cool room.
Nuances of feeding rabbits depending on the season
The summer diet of animals should consist of cereals by 30-40%, and in winter and with intensive fattening - by 50-70%. In the summer, green food predominates in the diet of rabbits, but with the onset of cold weather, juicy food - silage and vegetables - become the main part of the menu. The owners who grow vegetables and melons on their plots give the animals various root crops, cabbage, zucchini and pumpkins. Such food contains many vitamins, but little fiber and protein; in lactating rabbits, it contributes to more intense lactation.
When planning the volume of the product harvested for the winter, farmers proceed from the calculation: 40 kg of hay for a rabbit; 10–15 kg per head of potential offspring. If there is not enough hay for all the livestock, then first of all it should be fed to females and lactating females, young animals. For adult males during the dormant period (if mating is not planned), the above product can be replaced with pea, lentil, oat or millet straw. You can’t feed it for a long time, because there are very few nutrients in the straw.
If there is not enough hay for all the livestock, then first of all it should be fed to females and lactating females, young animals. For adult males during the dormant period (if mating is not planned), the above product can be replaced with pea, lentil, oat or millet straw. You can’t feed it for a long time, because there are very few nutrients in the straw.
Branch fodder becomes a good help in winter. Timely harvested young twigs of trees contain quite a lot of vitamins. In addition, rabbits that have a constant opportunity to eat such food are much less likely to express a desire to gnaw on cages. Branches of only certain tree species are suitable for harvesting: willow, willow, maple, linden, acacia, mountain ash, poplar, aspen, ash, oak, alder. The content of nutrients in tree shoots is highest in the first month of summer.
Vitamin supplements are administered most often at the end of winter - in early spring, when there is a shortage of green and succulent fodder. To fill the need for vitamins A and D, animals are given special concentrated preparations or fish oil is added to food. At the same time, the amount of fish oil required by rabbits is calculated depending on their physiological state.
To fill the need for vitamins A and D, animals are given special concentrated preparations or fish oil is added to food. At the same time, the amount of fish oil required by rabbits is calculated depending on their physiological state.
What should not be fed to rabbits?
It is better to refrain from adding birch branches to the diet, as they can lead to kidney disease. The same can be said about the branches of cherries, sweet cherries and plums. They contain hydrocyanic acid, which is quite dangerous for the body of animals. Branches of wild rosemary, buckthorn, bird cherry, apricot and elderberry are strictly forbidden to give to rabbits.
Even beneficial plants in excess can harm rabbits. From freshly cut grass, they have bloating of the intestines. Therefore, before feeding rabbits, it must be dried in direct sunlight. As a rule, an excess of cabbage leads to intestinal upset. It is also not recommended to give dirty vegetables to rabbits. This negatively affects the work of the digestive tract.
Rabbits should not be fed plants with a high concentration of toxins:
- hemlock;
- mustard;
- colza;
- digitalis;
- dope;
- we milk;
- Colchicum.
Buttercup caught in the feed mixture causes serious poisoning. Thrust is also dangerous. This flower is able to paralyze the muscles of the animal. Among the harmful herbs is aconite. Rabbits develop severe salivation, convulsions, and a slow pulse. Aconite poisoning leads to the death of the animal. From the marsh marigold in rabbits, the work of the kidneys is disrupted.
For the most part, the rate of weight gain and the taste of meat depend on proper nutrition. If you follow all the recommendations for feeding rabbits, you can quickly get large carcasses with good fur at the exit and significantly increase the livestock when breeding decorative breeds.
How and what to feed little rabbits of different ages
Feeding rabbits and getting a healthy livestock is not difficult if you work hard. After birth, babies in the first weeks of life receive good nutrition with rabbit milk. Then they move on to food. There are some differences in the diet for babies and adults. Properly selected nutrition will improve the quality of fur and meat , and for this you need to know how to properly feed young animals of different ages. In this article, you will learn how to feed little rabbits, as well as consider all the nuances of artificial feeding.
After birth, babies in the first weeks of life receive good nutrition with rabbit milk. Then they move on to food. There are some differences in the diet for babies and adults. Properly selected nutrition will improve the quality of fur and meat , and for this you need to know how to properly feed young animals of different ages. In this article, you will learn how to feed little rabbits, as well as consider all the nuances of artificial feeding.
Contents
- How to feed rabbits from birth to weaning
- How much food a rabbit needs per day
- How to feed rabbits without a rabbit at home
- Up to 7 days
- After 7 days
- From 20 days up to a month
- One month old and older
- feed
- Winter feeding, %
- Summer feeding, %
What to feed rabbits from birth to weaning
From birth to complementary foods, the main food for them is mother's milk. When the rabbit is behaving normally and she is healthy, then there is no reason to worry. At this time the concern of the rabbit breeder is to provide them with good conditions . This is an abundance of quality food and water. At this time, the female experiences a great load on the body, so you should increase the nutrients in the diet . She has 170 grams of milk per day, or even more. And with it 25 grams of protein. Therefore, for replenishment, she needs more nutritious food than before the lactation period. For a rabbit with an average weight of 5-6 kg, the consumption rate of feed units is 330-700 grams (1 feed unit is equal to 1 kg of oats). The menu should be changed every week.
When the rabbit is behaving normally and she is healthy, then there is no reason to worry. At this time the concern of the rabbit breeder is to provide them with good conditions . This is an abundance of quality food and water. At this time, the female experiences a great load on the body, so you should increase the nutrients in the diet . She has 170 grams of milk per day, or even more. And with it 25 grams of protein. Therefore, for replenishment, she needs more nutritious food than before the lactation period. For a rabbit with an average weight of 5-6 kg, the consumption rate of feed units is 330-700 grams (1 feed unit is equal to 1 kg of oats). The menu should be changed every week.
At this time, the female rabbit should be fed:
- in the summer: clover, alfalfa, oat mixture, herbs;
- in winter: bean hay, boiled potatoes, silage, carrots.

Also in the menu is added a mixture of peas , oats, bran and cake.
How much feed a rabbit needs per day
- from hay 100-300 grams;
- sunflower cake 40-60 grams;
- sunflower grotto 30 grams;
- fodder yeast 5 grams;
- fish oil 4 grams;
- meat and bone meal 7 grams;
- bone meal 4 grams;
- chalk - 3 grams;
- table salt 2 grams.
Be sure to introduce green and succulent foods. The increase in lactation is influenced by the shoots of dill and elecampane.
During the feeding period for the female, it is better to make feed mixtures,%:
Recipe 1:
- oats - 60;
- alfalfa - 30-40;
- mineral additives.
Recipe 2:
- bran - 12;
- corn - 10;
- alfalfa - 10;
- mineral additives -2.

The female rabbit should be given 20 to 500 grams of feed mix per day. On day 20, the amount of food is increased, because the babies begin to eat with their mother.
To increase lactation during this period, you can pour some milk in addition to water . In the morning 0.5 l and in the evening 0.5 l. To train her, use a 5 gram syringe. Pour a little into your mouth and then offer it to her in a bowl. Be careful with milk in the summer so as not to drink it sour. Otherwise, there may be problems with the intestines. Cow's or goat's milk can be replaced with dry or mixtures.
How to feed rabbits without a rabbit at home
Sometimes there are cases when newborn rabbits are left without rabbit milk. How to get out of this situation? In this position, they can be fed artificially, even at home.
Up to 7 days old
Babies up to 7 days old can be fed with cow's milk, goat's milk or powdered milk mixtures.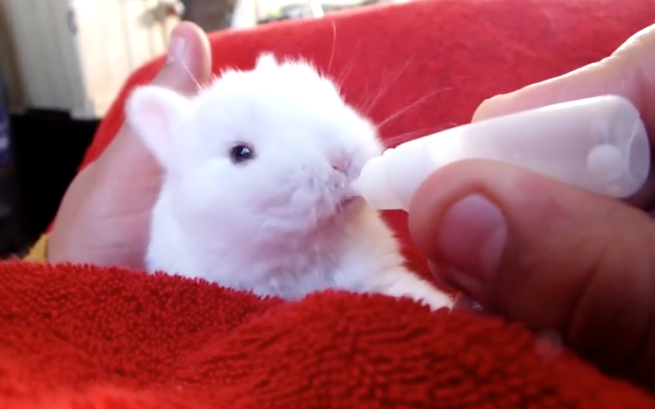 Cow's milk is diluted 1:1 with condensed unsweetened, the milk mixture is made in double concentration, and goat's milk is given in its pure form. Enter milk with a syringe or make a nipple. We wash the penicillin vial and put a nipple on it. We make a nipple from a pipette rubber cap.
Cow's milk is diluted 1:1 with condensed unsweetened, the milk mixture is made in double concentration, and goat's milk is given in its pure form. Enter milk with a syringe or make a nipple. We wash the penicillin vial and put a nipple on it. We make a nipple from a pipette rubber cap.
Baby rabbits need to be fed 3 to 5 times a day.
- once in the early morning;
- 3 times a day;
- once in the evening.
Approximately 1 ml per feeding of .
For artificial feeding of rabbits, goat's milk is preferable. In concentration and composition, it is closer to rabbit milk.
After 7 days
Until 1 week of age milk only. After 7 days of age double the amount of food and reduce feeding to 3 times a day. By 15 days portions are tripled.
Feeding is difficult in the early days of the baby, so take a cotton swab, moisten it and gently wipe the mouth with it. Wait until he licks and continue on. When the rabbit gets used to it, switch to a syringe or a pacifier.
Wait until he licks and continue on. When the rabbit gets used to it, switch to a syringe or a pacifier.
In the first days, the little one needs a tummy massage and hygiene. Wipe the body with a damp cloth. Pay special attention to the anus. Also wipe the muzzle after feeding.
From 20 days to month
From 20 days of age, rabbits can drink milk on their own from bowl . We adhere to the dairy menu until the age of one month. After that, it will be possible to give them high-quality hay, grated carrots and moistened compound feed in small quantities. Feed mixers should be given in small portions, avoiding souring. You can buy herbal granules for feeding rabbits in a veterinary pharmacy. How much food to feed a rabbit? The serving is calculated by the weight of the baby and should be 3% of the mass.
One month old and older
From the moment the milk decreases, they need to drink additional water. First, we force water to drink with the help of a pacifier.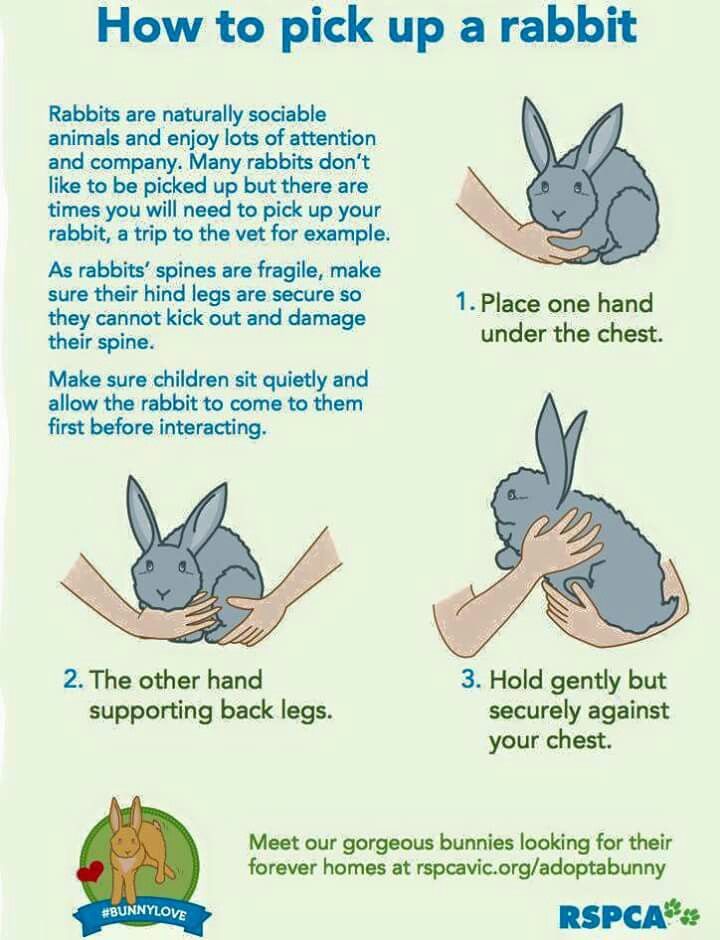 Later, when they begin to drink on their own, the water should be in the bowl at all times. Lack of water threatens rabbits with kidney disease . Until the age of 45 days, milk feeding and a smooth transition to an adult diet are possible.
Later, when they begin to drink on their own, the water should be in the bowl at all times. Lack of water threatens rabbits with kidney disease . Until the age of 45 days, milk feeding and a smooth transition to an adult diet are possible.
A few tips for formula feeding newborn baby rabbits with milk
If such a misfortune happened and the babies were left without maternal care and milk, then rabbits can be fed artificially . Although this process is troublesome and requires great patience. And the result is not 100%, but rather deplorable, but you need to try. Such rabbits are usually retarded in development.
Keep clean when feeding . All nipples and dishes should be scalded with boiling water. Since the babies are naked, they should be kept warm. You can put a heating pad in the drawer where they are kept. When they grow fur, it can be removed.
When they grow fur, it can be removed.
It is better to feed goat milk , but if this is not available, then powdered milk or mixtures for fattening puppies can be purchased at a veterinary pharmacy.
Feed often enough. They should eat 5 times a day in small portions . Before feeding, the baby needs to be helped to empty. Under natural conditions, this is done by the mother, but in this case, you need to do it yourself.
With a damp cotton pad, massage movements, wipe the body . Let's start massaging the tummy. With light pressure, we draw several times from the navel to the tail. We do this procedure until the baby is emptied. Then we wipe the anus and feed the rabbit. Massage for emptying to do within 2 weeks. Then it will empty itself.
It is important to monitor the presence and color of poop. They must be green. If they are not, then the baby needs help.
If it does not empty, it means that it is not getting enough food. You need to add some milk. A well-fed baby behaves calmly. Doesn't bounce in sleep. Doesn't crawl on the box. The tummy is plump and elastic.
You need to add some milk. A well-fed baby behaves calmly. Doesn't bounce in sleep. Doesn't crawl on the box. The tummy is plump and elastic.
By 15 days in the box should be allocated a place where it will be dark . Rabbits by this time like to sleep in a dark place. Cover one corner with a cloth.
If the feeding process is successful, then by the 20th day the baby can drink milk from the saucer . You can also give him finely chopped carrots. Green, quality hay or dried grass. If this happens in winter, then the greens can be grown hydroponically. Babies can also be given hay flour . Gradually, small portions of moistened compound feed should be added to the diet. Boiled thick porridge.
Do not give cabbage leaves, although they eat them with pleasure. The digestive system is not yet formed, so the baby may have bloating and diarrhea. This will most likely lead to death.
This will most likely lead to death.
As already mentioned, cleanliness must be observed. Feed must be fresh . No souring, no mold. Mixture prepare immediately before feeding. Vegetables must be washed.
These tips may help you feed a healthy baby.
How to feed little rabbits after hatching from their mother, how to make food
The laying of rabbits from the mother takes place at different ages from 28 to 45 days . But it is best to do this at the age of 45 days. Jigging at this time reduces the mortality of young animals. Since by this time his digestive system is formed. Together with his mother, he eats hay and other food from the adult diet.
Black rabbits with a rabbit In the beginning, they are given the same food that they ate with their mother. New foods for rabbits, introduced gradually in small portions. It is recommended to drip vitamin B into the water. 1 liter requires 50 ml. It prevents stress.
The diet of rabbits should include:
- dried greens or quality hay;
- boiled potatoes ;
- pumpkin;
- marrows;
- milk powder;
- vitamin preparations if it is winter;
- hay meal;
- grated or chopped carrots ;
- oats;
- moistened compound feed ;
- crushed grain ;
- bone meal;
- fishmeal.
- reverse
During this period it is useful to feed:
- chicory;
- yarrow;
- chamomile;
- St. John's wort;
- dubrovnik;
- burdock;
- tree branches with leaves.
Baby rabbit should receive:
45-60 days:
- 70-125 feed units;
61-90 days:
- 145-170 c.
 u.;
u.;
90-120 days:
- 170-225 c.u.;
Since rabbits grow rapidly during this period, digestible protein should be 18 grams per 100 k.u. Growing up rabbits from 4 months are transferred to an adult diet .
When distributing hay, look carefully for toxic herbs:
- Datura;
- henbane; and many others.
For older rabbits from 4 months of age, change the feed ration . Reduce the proportion of compound feed. It contains a lot of fat, which in large quantities is harmful to animals. They give plenty of vitamin hay, green grass and vegetables.
Winter feeding, %
- hay 10-20;
- compound feed 55-65;
- juicy food 20-30.
Summer feeding, %
- green grass 30-40;
- concentrate 60-70.
Food is distributed 3-4 times a day .