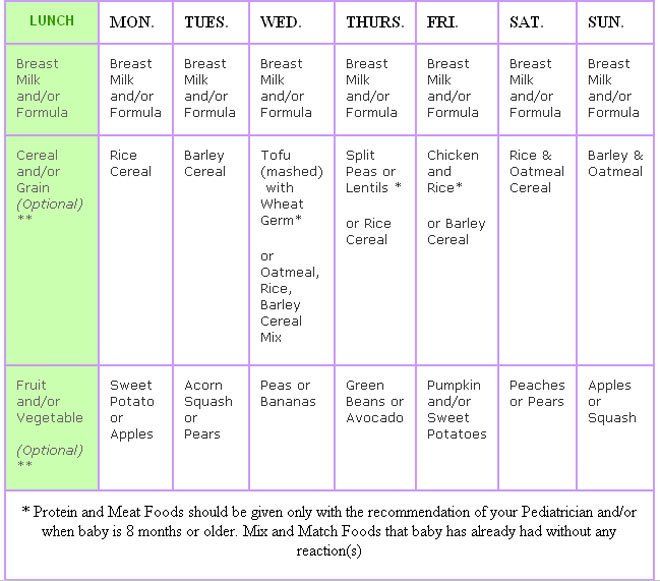
Signs to start feeding baby solids
Introducing solids: why, when, what & how
Solid foods: why babies need them
As babies get older, they need solid food to get enough nutrients for growth and development. These essential nutrients include iron, zinc and others.
For the first 6 months of life, babies use iron stored in their bodies from when they were in the womb. They also get some iron from breastmilk and/or infant formula. But babies’ iron stores go down as they grow. By around 6 months, babies need to start having solid food.
Introducing solids is also important for helping babies learn to eat, giving them experience of new tastes and textures from a range of foods. It develops their teeth and jaws, and it builds other skills that they’ll need later for language development.
Signs that it’s time to introduce solids
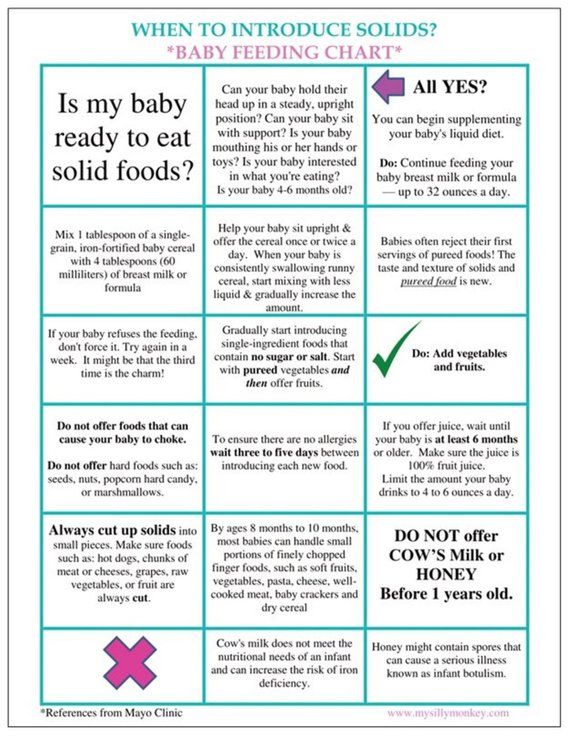
Signs your baby is ready for solids include when your baby:
- has good head and neck control and can sit upright when supported
- shows an interest in food – for example, they look at what’s on your plate
- reaches out for your food
- opens their mouth when you offer them food on a spoon.
Most babies start to show these signs by around 6 months, although this can vary.
It’s recommended not to introduce solids before 4 months.
If your baby is nearing 7 months of age and hasn’t started solids, you might like to get some advice from your child and family health nurse or GP.
The best times of day to introduce solids
When you’re first introducing solids, it’s good to offer solids when you and your baby are both happy and relaxed.
This is often after a feed of breastmilk or formula. Babies will still have room in their tummies for a taste of new foods after a feed of breastmilk or formula. But if they’re really hungry before a feed, they just want the breastmilk or formula that they know satisfies their hunger.
As time passes, you’ll learn when your baby is hungry or full, not interested or tired.
Signs of hunger include your baby:
- getting excited when they see you getting their food ready
- leaning towards you while they’re sitting in the highchair
- opening their mouth as you’re about to feed them.

Signs your baby is no longer interested include:
- turning their head away
- losing interest or getting distracted
- pushing the spoon away
- clamping their mouth shut.
Your baby’s appetite can vary from day to day.
How much food to offer when introducing solids
When you’re first introducing solids, try offering 1-2 teaspoons of food once a day. At first, your baby might have only a small taste and probably won’t swallow much.
As your baby grows, you can increase the amount according to your baby’s appetite and signs.
By 12 months, your baby should be eating around 3 small meals a day, plus breastmilk or infant formula.
The right textures for first foods
When your baby is ready for solids, first foods might be smooth or finely mashed, depending on what baby likes. Over the next weeks and months, your baby can move on to roughly mashed or minced foods and then chopped foods. All foods should be very soft.
All foods should be very soft.
Your baby needs a variety of food textures. This helps your baby learn how to chew, and chewing helps with speech development and self-feeding. It also helps to prevent feeding difficulties as your baby develops. Babies can chew even before they get their first teeth.
By the time your baby is 12 months old, they should be eating the same foods that the rest of the family is eating. But you might still need to chop some foods into smaller pieces and cook vegetables until they’re soft.
To prevent choking, always supervise babies and young children while they’re eating solid food. Avoid nuts, take special care with pieces of meat and check fish for small bones, because these are choking hazards. And if your baby can move around, make sure baby is sitting down while they’re eating. If you sit with your baby while they’re eating, baby is less likely to move around.
Types of food to offer when introducing solids
All new foods are exciting for your baby.
The key is to include iron-rich foods of the right texture in your baby’s first foods. Iron-rich foods include:
- iron-fortified infant cereal
- minced meat, poultry and fish
- cooked tofu and legumes
- mashed, cooked egg (avoid raw or runny egg).
To these iron-rich foods, you can add other healthy foods of the right texture like:
- vegetables – for example, cooked potato, pumpkin, sweet potato, carrot, broccoli or spinach
- fruit – for example, banana, apple, pear, melon or avocado
- grains – for example, oats, bread, rice and pasta
- dairy foods – for example, yoghurt and full-fat cheese.
You can introduce any number of new foods at a time and in any order. When you offer your baby a variety of foods, they can try plenty of new tastes and get a range of nutrients.
Read our tips for introducing solid foods to learn how to get your baby interested in new foods and manage mealtime mess and play.
Breastmilk and infant formula while introducing solids
You should keep breastfeeding or using infant formula until at least 12 months.
When you start introducing solids, breastmilk or infant formula should still be the main source of your baby’s nutrition. Over the next few months, your baby will start having more solids and less milk or formula. The rate that this happens will vary.
By around 9 months, babies have generally developed enough chewing and swallowing skills to move from having milk before solids to having milk after solids.
Here are some signs that your baby is getting enough nutrition from both solids and breastmilk or formula during this time. Your baby:
- has plenty of wet nappies – at least 6-8 wet cloth nappies or 5 very wet disposables in 24 hours
- is alert and mostly happy after and between feeds
- is gaining weight at about the right rate – your child and family health nurse will weigh your baby at your regular check-ups.

From 12 months onwards, solids should be the main source of your baby’s nutrition. Your baby doesn’t need infant formula after 12 months, but you can keep breastfeeding for as long as you and your baby like.
If solid food replaces breastmilk and/or infant formula too quickly, babies can miss out on important nutrition. If you have any concerns about your baby’s feeds or weight, talk to your midwife, child and family health nurse, lactation consultant or GP.
Introducing water
Once your baby has reached 6 months, you can start to offer baby cooled, boiled water in a cup at mealtimes and at other times during the day. This is so your baby can practise drinking from a cup, but baby still doesn’t really need fluids other than breastmilk or formula at this age.
Once your baby has reached 12 months, you can offer fresh tap water without boiling it.
Foods and drinks to avoid while introducing solids
There are some foods to avoid until your baby is a certain age:
- Honey until 12 months – this is to avoid the risk of infant botulism.
- Raw or runny eggs and foods containing raw eggs like home-made mayonnaise until 12 months – bacteria in raw eggs can be harmful to babies.
- Reduced-fat dairy until 2 years – babies need full-fat dairy for growth.
- Whole nuts and similar hard foods until 3 years – these are choking hazards.
There are some drinks to avoid until your baby is a certain age:
- pasteurised full-fat cow’s milk as a main drink until 12 months
- dairy alternatives like soy, goat’s, sheep’s, rice, oat, almond and coconut milk until 2 years, unless your GP or child and family health nurse has recommended these for a particular reason
- unpasteurised milks at all ages
- tea, coffee or sugar-sweetened drinks at all ages
- fruit juice – this should be limited at all ages (whole fruits are better because they have fibre and help babies develop chewing and feeding skills).
Your baby doesn’t need added salt or sugar. Processed or packaged foods with high levels of fat, sugar and/or salt aren’t good for babies and children. These foods include cakes, biscuits, chips and fried foods.
Processed or packaged foods with high levels of fat, sugar and/or salt aren’t good for babies and children. These foods include cakes, biscuits, chips and fried foods.
Food allergy and introducing solids
Introducing allergenic foods early can reduce the risk of your child developing food allergy. Allergenic foods are foods that might cause allergies.
All babies, including babies with a high allergy risk, should try solid foods that might cause allergies from around 6 months of age. These foods include well-cooked egg, peanut butter and other nut butters, wheat (from wheat-based breads, cereals and pasta) and cow’s milk (but not as a main drink).
Once you’ve introduced an allergenic food, it’s a good idea to regularly include it in your baby’s diet.
It’s a good idea to get advice from your GP, child and family health nurse, dietitian, paediatrician or allergy and immunology specialist for the following reasons:
- Your baby already has a food allergy.
- Your baby has severe eczema.
- Your family has a history of food allergy and you’re concerned about starting solids.
- You’re worried about reactions to foods.
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.

- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.

- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.
- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
Introducing Solid Food: Why, When, What and How
Introducing Solid Food: Why Babies Need It
As babies grow older, the need for solid food arises, from which the body will receive enough iron and other nutrients necessary for growth and development.
During the first six months, the baby's body uses the iron stored in the womb. Some iron also comes from breast milk and/or formula. But as the baby grows, the reserves of this substance in the body decrease. And the iron that a child receives from breast milk or formula is already not enough at the age of about six months.
Through the introduction of solid foods, the child also learns to eat, gets to know new tastes and textures of different foods. At the same time, he develops teeth and jaws, and he also acquires skills that will later be needed for language development.
Signs it's time to introduce solid foods
You will know when it's time to introduce solid foods by how your baby develops and behaves.
Your child is ready for solid food if:
- holds head and neck well and can sit upright with support
- shows interest in food - for example, looking at the contents of your plate
- reaching for your food
- opens his mouth when you offer him food from a spoon.

Most children show these signs by about six months, but in general everyone is individual.
It is not recommended to introduce solid foods before four months of age.
If your baby is about seven months old and hasn't started solid foods yet, you can talk to a nurse or pediatrician.
The best time to offer solid food to your baby is when you and he are in a good mood for the first time.
He is also more likely to try new foods after breast milk or formula. The fact is that when a child is really hungry, he only wants milk or formula, because he knows that he will be satisfied. At the same time, there will still be room for other food in his tummy.
Over time, you will learn to tell if your baby is hungry or full, wants to try something or is tired.
Your child is hungry, if:
- brightens up when he sees you cooking for him
- leans towards you while sitting in a highchair
- opens its mouth when you are about to feed it.
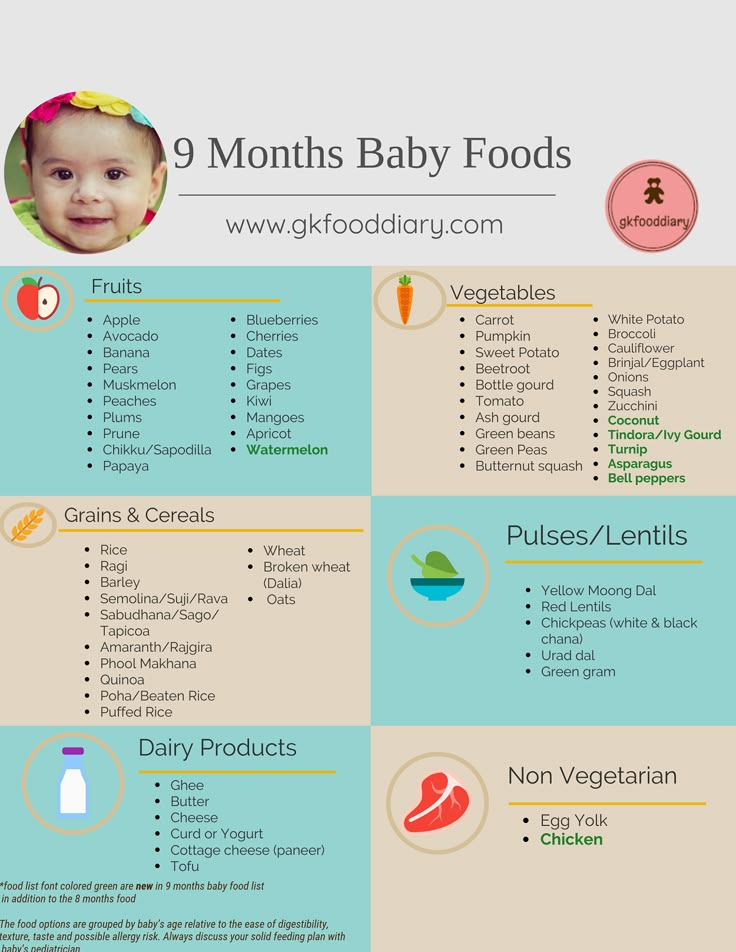
Your child no longer wants to eat if:
- turns away
- loses interest or gets distracted
- repels spoon
- purses his lips.
In what portions should the new food be introduced to the child? Start with 1-2 teaspoons and increase according to your baby's appetite. By 12 months, he should be eating about three small meals a day, plus breast milk or formula.
Consistency of solid food
The first solid food can be smooth, pureed or in soft pieces , depending on your baby's preference. Then the child can quickly move on to finely chopped, and then just to finely chopped foods.
The child needs food of various consistencies. This will help him learn to chew, and chewing, in turn, contributes to the development of speech. It also encourages the child to learn to eat on his own and will prevent eating problems as he develops.
By 12 months, the baby should already be eating the same as the rest of the family. You may have to cut some foods into smaller pieces, and boil the vegetables well.
You may have to cut some foods into smaller pieces, and boil the vegetables well.
Do not leave the child unattended while eating, make sure that he does not choke. Be especially careful with foods such as nuts and small-boned meats, as they are easy to choke on. If the child can already move around, try to seat him while eating. If you sit next to each other while the baby is eating, he will most likely sit more quietly.
Types of foods when introducing solid foods
The child will be happy to try any new food, so there is no need to prepare something “special” for him.
You can introduce solid foods in any order, as long as you include iron-rich foods and cook foods of the right consistency.
Foods rich in iron include:
- iron-fortified baby cereals
- minced meat, poultry and fish
- tofu and legumes, cooked
- mashed or boiled eggs (do not give raw or soft-boiled eggs).
Iron-rich foods can be supplemented with other healthy foods:
- vegetables such as boiled potatoes, carrots or green vegetables such as broccoli
- fruit - e.
 g. banana, apple, melon or avocado
g. banana, apple, melon or avocado - cereals - e.g. oats, bread, rice and pasta
- Dairy products such as yogurt and full fat cheese.
These products can be combined as there is no need to administer only one product at a time. By offering your child a variety of foods, you will allow him to try a variety of new tastes and get a lot of nutrients.
With our solid food introduction tips, you can get your child interested in new foods and make the eating process smoother and playful.
Breast milk and formula when introducing solid food
Continue breastfeeding or formula until at least 12 months while introducing solid food.
If you are unsure if your baby is getting the right amount of milk once solids are introduced, pay attention to his behavior.
For example, if a child has eaten a lot of solid food and is not getting enough or is not getting enough milk, the daily milk feeds may need to be made less frequent but longer. If the baby does not want to eat solid food, he may have had too much milk. This may be a signal that portions of milk should be reduced.
If the baby does not want to eat solid food, he may have had too much milk. This may be a signal that portions of milk should be reduced.
By about nine months of age, babies usually develop enough chewing and swallowing skills to eat solid foods before milk, not after.
Solid food does not replace breast milk or formula. If the transition to solid foods instead of milk and/or formula occurs too quickly, a child may miss an important milestone in their diet.
Water administration
At the age of six months, the child may be offered chilled boiled water in a cup during meals or at other times. This is to help your baby learn to drink from a cup, but at this age, he still doesn't need liquids other than breast milk or formula. When the child is one year old, he can be offered fresh tap water without boiling.
Foods and drinks to avoid
Some foods should not be given to children under a certain age:
- honey under 12 months to avoid the risk of infant botulism
- raw eggs, soft-boiled eggs, and products containing raw eggs, such as homemade mayonnaise, up to 12 months - bacteria in raw eggs may be harmful to infants
- skim milk products up to two years
- Whole nuts and similar hard foods up to three years - due to risk of choking.

Also, up to a certain age, children should not be given certain drinks :
- pasteurized whole cow's milk as a main drink up to 12 months
- soy, goat and sheep milk up to two years (fortified soy products may be given up to two years)
- rice, oatmeal, almond or coconut milk up to two years of age, unless advised otherwise by a pediatrician or nurse
- Unpasteurized milk of all kinds, tea, coffee or sugar-sweetened beverages for all ages
- fruit juice - should be limited at any age (fruits contain the nutrients a child needs).
Salt and sugar should not be added to baby food. Infants and young children are not suitable for highly processed foods and packaged foods that are high in fat, sugar and/or salt. These include cakes, cookies, chips and fried foods.
Food allergy and introduction of solid foods
Early introduction of allergenic foods may reduce risk development of food allergy in a child.
All children, including children at high risk of allergies, should try allergenic foods from about six months of age . These foods include hard-boiled eggs, peanut butter, wheat (in wheat bread, cereals, and pasta), and cow's milk (but not as a staple drink).
It is recommended to consult a physician, health visitor, nutritionist, pediatrician, allergist or immunologist if:
- the child already has a food allergy
- you have a family history of food allergies and are concerned about introducing solid foods to your child
- you are worried about his reaction to the products.
Children with severe eczema and children of parents with food allergies are more likely to develop food allergies. But most children with food allergies do not have food allergy parents.
Solid food | Tervisliku toitumise informatsioon
From the age of 6 months, the baby should be supplemented with breast milk to provide with the necessary amount of energy and nutrients. As you grow older, you can gradually switch to regular food (cooking it without frying, and also without adding salt and sugar). Children over 1 year of age, in addition to regular food and complementary foods, can continue to drink breast milk, but by the age of two, the child should completely switch to a common table. Exposure of a child to grain-containing foods during breastfeeding may protect him from gluten intolerance in the future. When offering a child complementary foods or regular food, care should be taken, to have a varied diet . Both during breastfeeding and during the transition to regular food, the baby may experience gases or allergies .
As you grow older, you can gradually switch to regular food (cooking it without frying, and also without adding salt and sugar). Children over 1 year of age, in addition to regular food and complementary foods, can continue to drink breast milk, but by the age of two, the child should completely switch to a common table. Exposure of a child to grain-containing foods during breastfeeding may protect him from gluten intolerance in the future. When offering a child complementary foods or regular food, care should be taken, to have a varied diet . Both during breastfeeding and during the transition to regular food, the baby may experience gases or allergies .
For children over two years of age, the same nutritional guidelines apply as adults, but the recommended serving sizes are smaller.
Children under three years of age (actually, a person of any age) do not need salty or sweet snacks, carbonated drinks, deep fried and/or very sweet and salty foods!
By the sixth month of life, the infant's eating habits and digestive system are mature enough to offer more solid foods in addition to breast milk. Proteins, carbohydrates and fats contained in regular food are different from the easily digestible sugars, fats and proteins that enter the baby's body with breast milk. Therefore, a so-called certain familiarization period is needed so that the baby's digestive system has time to get used to a new type of food. If the baby is breastfed as often as before, then these feeds cover about 2/3 of the energy needed by an 8-month-old baby. The remaining approximately 200 kilocalories should come from the various macronutrients found in complementary food ingredients, i.e. proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Complementary foods are needed so that the child can slowly move to the common table, as well as to obtain the nutrients necessary for age. Complementary foods for babies are a completely unfamiliar thing. It differs significantly from breast milk and will take time to learn how to eat it.
Proteins, carbohydrates and fats contained in regular food are different from the easily digestible sugars, fats and proteins that enter the baby's body with breast milk. Therefore, a so-called certain familiarization period is needed so that the baby's digestive system has time to get used to a new type of food. If the baby is breastfed as often as before, then these feeds cover about 2/3 of the energy needed by an 8-month-old baby. The remaining approximately 200 kilocalories should come from the various macronutrients found in complementary food ingredients, i.e. proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Complementary foods are needed so that the child can slowly move to the common table, as well as to obtain the nutrients necessary for age. Complementary foods for babies are a completely unfamiliar thing. It differs significantly from breast milk and will take time to learn how to eat it.
Proper complementary foods are food that is hard enough to eat with a spoon, contains all the important foods (except sweets), is rich in nutrients and does not contain salt or sugar. Complementary foods should always be offered to the child from a spoon and never from a bottle, as in this case the child will never understand what to eat in an upright position using a spoon. In addition, bottle feeding contains too much water, so it may not provide enough energy and nutrients. As the child grows older, you can allow him to put pieces of food in his mouth with his fingers. Simultaneously with the gradual introduction of solid food into the baby's diet, his interest in breast milk gradually begins to fade. This is completely natural and as the first birthday approaches, you can start to slowly reduce the number of breastfeeds. All children are different, so their preferences and needs are also different, but it is important that the child's diet is varied and covers all the nutritional needs of a growing body for life and development.
Complementary foods should always be offered to the child from a spoon and never from a bottle, as in this case the child will never understand what to eat in an upright position using a spoon. In addition, bottle feeding contains too much water, so it may not provide enough energy and nutrients. As the child grows older, you can allow him to put pieces of food in his mouth with his fingers. Simultaneously with the gradual introduction of solid food into the baby's diet, his interest in breast milk gradually begins to fade. This is completely natural and as the first birthday approaches, you can start to slowly reduce the number of breastfeeds. All children are different, so their preferences and needs are also different, but it is important that the child's diet is varied and covers all the nutritional needs of a growing body for life and development.
Complementary foods for babies by months:
0-6 months
6-8 months
9-11 months
substances can be markedly reduced.
World Health Organization recommendations for the introduction of complementary foods for children aged 6-23 months.
| Age (in months) | Frequency Frequency | The portion for 1 feeding | Consistency of food |
| 6 | 9000 9000 or 2 times quantity | Finely pounded or pureed | |
| 6-8 | 2-3 feedings per day 9 0239 to 1 DL | Trucified or pureed | |
|
| 3-4 feeding per day 1-2 Open 1-2 | Crowned or finely busy | |
| 12-2-23 | 3-4 feeding per day 1-2 snacks | 2-2.5 DL | 9000 242 |
The recommendations in the table are general and give an idea of how much a child could eat on average, however the exact amount and frequency of feedings may vary from child to child.