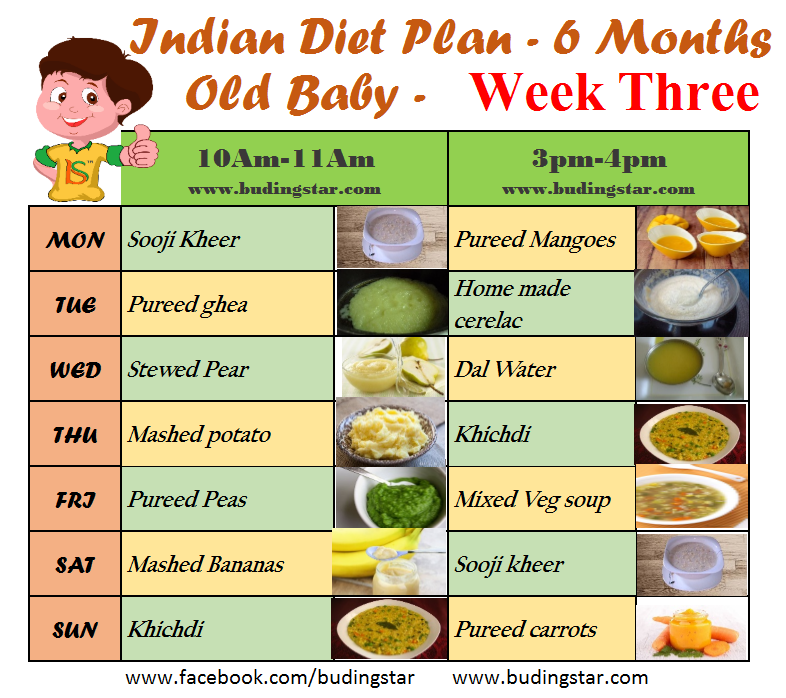
Types of food for 7 month old baby
What To Feed Your Baby | 7 to 9 mths | Weaning
Baby's age
- Around 6 months
- 7 - 9 months
- 10 - 12 months
- 12 months+
7 - 9 months
By now, your baby will have had some good practice learning how to eat! Eat together as much as possible – they learn a lot from watching you.
Your baby will gradually move towards eating 3 meals a day (breakfast, lunch and tea). Offering a wide variety of different foods is important to ensure they get enough energy and nutrients (such as iron). Babies don't need salt or sugar added to their food (or cooking water) – salty food isn't good for their kidneys and sugar can cause tooth decay.
Remember, it may take 10 tries or even more for your baby to get used to new foods, flavours and textures. There'll be days when they eat more, some when they eat less, and then days when they reject everything! Don't worry – this is perfectly normal. Just be patient, keep offering a variety of foods, even the ones they don't seem to like, and let them get used to it in their own time.
Babies under 12 months don't need snacks, if you think your baby is hungry in between meals, offer extra milk feeds instead.
Smooth or lumpy?
Hopefully your baby will now be more confident exploring new textures. Offer more mashed, lumpier foods as well as a variety of finger foods. Giving your baby finger foods helps them learn to feed themselves, develop hand-eye co-ordination and learn to bite off, chew and swallow small pieces of soft food.
Babies take different amounts of time to get used to lumps, but it's an important skill they need to learn. Just keep offering them lumpy textures and finger foods and stay with them so you can be sure they are swallowing it safely.
What is baby-led weaning?
Baby-led weaning means offering your baby only finger foods and letting them feed themselves from the start (rather than spoon feeding them puréed or mashed food). You can offer a range of small, finger-sized, pieces of food.
You can offer a range of small, finger-sized, pieces of food.
Some parents prefer baby-led weaning to spoon feeding, while others combine a bit of both. There's no right or wrong way – the most important thing is that your baby eats well and gets all the nutrients they need.
Should I still give my baby breast milk or first infant formula?
Yes. Breast milk or first infant formula is still important for energy and nutrients during the first year, and should be their main drink until 12 months. You can continue breastfeeding for as long as you both want. As time goes on and your baby eats more solids, they may naturally want less breast milk or first infant formula.
If you're breastfeeding, your baby will adapt their feeds according to how much food they're having. Formula-fed babies may need around 600ml of milk a day, but just use this as a guide. Remember your baby's tummy is tiny and fills up quickly, so offer milk feeds after solids and don't force them to finish the bottle.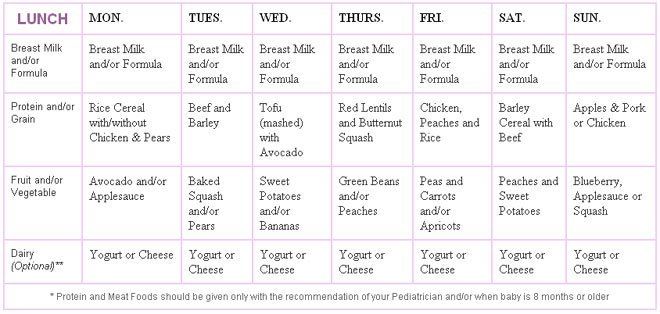
Drinks?
A Cheat Sheet for Parents
7-month-old baby food: What’s right?
Just like with adults, every child is slightly different and thus has a unique appetite. Babies are born with the innate ability to self-regulate feeding capacity. In other words, they know when they are finished or full.
You’ve probably already taken note of this during breastfeeding. They’ll latch on when they’re hungry and stop when they’re satisfied. If you’ve had trouble with this, consider looking into how to use a nipple shield while breastfeeding to address latching issues.
You’ll likely be able to tell when your baby is ready for solid food, since they’ll show obvious signs of agitation and hunger after breastfeeding. Usually, this happens at about the 6-month mark, and baby food for a 7-month-old frequently starts to consist of more solid foods. The signs of readiness for solid foods include hand-to-mouth coordination, decreased tongue protrusion reflex, sitting without support, and opening mouth to spoon. You may continue breastfeeding, as well, until you decide an appropriate time to stop.
You may continue breastfeeding, as well, until you decide an appropriate time to stop.
Perhaps you’ve already been feeding your baby solids for a month or so, but you want to make sure you have your information straight, or maybe you’ve been wondering how many jars of baby food for a 7-month-old is appropriate. You’ve come to the right place. Let’s take a closer look.
I love Flo! I got pregnant with my last baby with ease because of this app! It is very accurate when it comes to predicting your period dates. I used other apps, and it was so frustrating. Flo is #1!
Baby food list for a 7-month-old
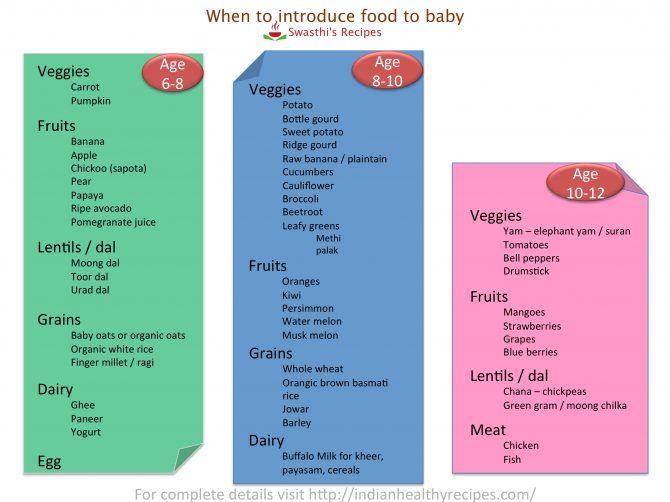
When you’re ready to start feeding your baby solid food, you’ve got an array of options to choose from. These foods help ensure that your baby gets sufficient amounts of the nutrients and vitamins they need to continue down the road of healthy development.
Before you dive into the list, make sure you only introduce a little bit of one food at a time — about 1–2 tablespoons to start is good. New foods should be introduced individually and about a week apart in order to identify any allergies and intolerance the baby may have. It’s best to introduce foods from most bland to sweetest.
New foods should be introduced individually and about a week apart in order to identify any allergies and intolerance the baby may have. It’s best to introduce foods from most bland to sweetest.
If you haven’t already started feeding your child solids, start with the following baby food for your 7-month-old:
- Pea puree: Peas have iron, protein, calcium, Vitamin A, and Vitamin C, which are all important for encouraging and promoting the healthy development of your child.
- Baby brown rice cereal: This cereal is easy to digest and it’s unlikely that your child will suffer an allergic reaction to it.
- Baked sweet potato puree: Adults benefits from sweet potatoes, so it shouldn’t come as a surprise that your baby will benefit from this antioxidant, nutrient, and vitamin blend.
- Banana Puree: Bananas are easy to digest and won’t upset the stomach. However, avoid feeding your child too much, as a lot of banana can result in constipation, which isn’t fun for you or your baby.
- Carrot Puree: Babies usually love carrot puree because of the sweet taste. It’s also packed full of antioxidants and various vitamins and minerals.
- Avocado Puree: This can provide a pleasant texture and introduce good fats into your child’s diet.
If you’ve already introduced solid baby food for your 7-month-old, you may begin slowly presenting more thick purees and foods to your child’s diet, including:
- Pumpkin thyme puree: It’s loaded with iron, potassium, and beta carotene.
- Varieties of veggies: Puree different vegetable combinations, such as spinach with yams.
- Fruits: New fruits may include pears, papayas, and blueberries. Blend them into a puree for easy eating.
Avoid foods that are choking risks, including small fruits, raw vegetables, nuts, candy, gum, and whole grapes. Children under the age of five are at risk of choking on grapes and similarly shaped foods, and parents should cut them in half or quarters.
How to know if your baby is ready for solids
Most babies are ready for solid foods by 6 months of age. Yet, there are tell-tale signs that can help you determine if it’s the right time to introduce them.
Certain developmental stages should be reached before you feed your baby solid foods. They should be able to sit up unsupported, as well as keep their head stable and upright. Your baby should not be pushing the solid food out of their mouth, and they should have good hand-to-mouth coordination.
You may also be ready to alter your 7-month-old baby food menu when your child begins taking increasingly longer breastfeeding sessions. They may still seem hungry after your normal duration, indicating that it’s time to start introducing other foods besides breast milk.
If your 7-month-old isn’t ready for solids, don’t panic. It’s absolutely normal for different babies to be ready at different times. Most babies’ development won’t be impacted if they continue with just breast milk until 9–12 months of age.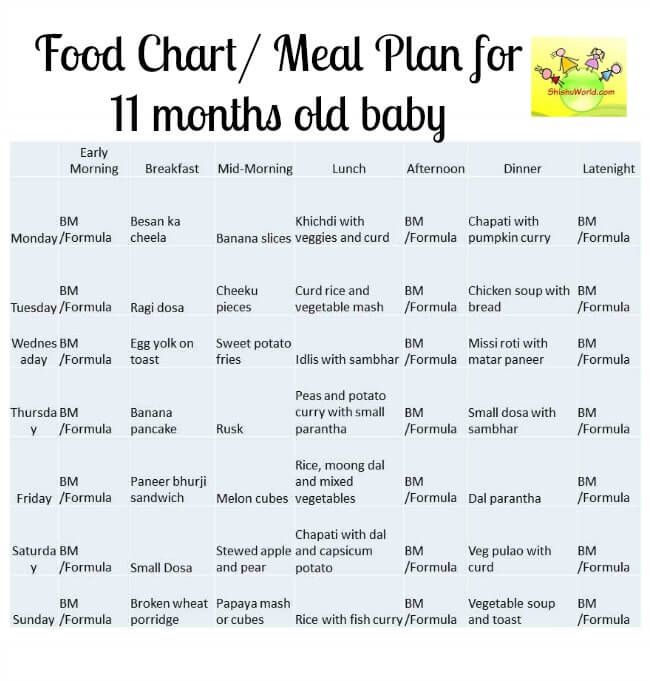
7-month-old baby food recipes
If your baby is all set and ready to eat solids, it’s cooking time. There are a variety of 7-month-old baby food recipes you can begin to create, including the following three. Similar to storing breast milk, these purees can be frozen but should be used within about six months.
- Pea puree: This one is great for newbies to solid food. In other words, if your child has just begun eating solids, this is a good one to start with — and it’s simple. Take 3 cups of frozen peas and half a cup of breast milk. Boil water, lower the heat, and add the peas, steaming them for about 15 minutes. Blend the peas and the breast milk in a food processor, filtering any lumps that remain using a strainer. Freeze the batch in an ice cube tray. When you’re ready to feed your little one, simply take out one pea puree ice cube and heat it up until warm. Make sure it’s not too hot!
- Spinach and white yam puree: You’ll need about a half pound of washed spinach and a half pound of white yams, as well as either 1.
 5 cups of water or sodium-free vegetable broth. Chop up the yams into small cubes. Bring them to a boil in the liquid of your choice, then let them simmer for about 10–15 minutes. Put the spinach in and wait until the spinach is cooked, which should only take a few minutes. Remove the mixture from the heat, then blend it all in a food processor. You can freeze it in a similar way to the pea puree recipe.
5 cups of water or sodium-free vegetable broth. Chop up the yams into small cubes. Bring them to a boil in the liquid of your choice, then let them simmer for about 10–15 minutes. Put the spinach in and wait until the spinach is cooked, which should only take a few minutes. Remove the mixture from the heat, then blend it all in a food processor. You can freeze it in a similar way to the pea puree recipe. - Blueberry and beet mash-up: Grab 2 mid-sized beets and a half cup of fresh or frozen blueberries. Remove the skin of the beets and chop them up into small cubes. Place the cubes in a saucepan with the blueberries, and pour just enough water to cover the contents. Cover and cook for about 10–15 minutes on medium-high heat. Make sure the beets are tender before removing them from the heat. Blend everything in a food processor and freeze them similar to the above recipes.
How much baby food does a 7-month-old need?
Now, you’re probably wondering how much baby food for a 7-month-old is enough? The answer is that it varies depending on the baby. While all babies are a bit different, a typical 7-month-old will have three meals a day. These meals may be anywhere from less than a tablespoon to two tablespoons in size. Some babies may consume up to eight or twelve tablespoons per day; it depends on their size and appetite.
While all babies are a bit different, a typical 7-month-old will have three meals a day. These meals may be anywhere from less than a tablespoon to two tablespoons in size. Some babies may consume up to eight or twelve tablespoons per day; it depends on their size and appetite.
In terms of breastfeeding, usually a 7-month-old baby nurses for 3–4 hours a day. Your baby may consume a total of about 25 ounces of breast milk every day at this age.
The daily caloric requirements for babies aged 7–9 months is around 825 kcal/day for boys and around 765 kcal/day for girls.
7-month-old baby food menu: Feeding tips
Lastly, let’s leave you with some feeding tips and tricks regarding 7-month-old baby food.
Strict guidelines don’t exist for baby food or when to feed your baby. It depends on where your baby is at in development, though most doctors recommend steering clear of processed foods and sticking to simple purees as outlined above.
Some foods should be avoided. 7-month-old baby food to avoid includes honey, cow’s milk, raw vegetables, nuts, small fruits, candy, gum, and any other food that could pose a choking hazard.
Don’t force it. The general rule is to feed at the earliest sign of hunger and stop at the earliest sign of satiety. If your child doesn’t want solid food, they may not be ready or may not be hungry.
If you’re struggling with it, allow your baby to handle a small spoon after breastfeeding. This may help your child associate the spoonfed foods with the comfort that comes with breastfeeding.
Ensure your child is sitting upright. This prevents choking. Consider using a high chair if necessary.
If you’re having trouble breastfeeding or notice you feel sore on one side, consider switching positions. Various breastfeeding positions exist and can make the whole process easier for you and your baby.
Check with your healthcare provider before attempting to feed your baby solid foods. Your doctor knows what is good for you and your baby and can give good advice regarding your specific situation. Doctors are able to offer advice and recommendations on medicine you can take while breastfeeding, other breastfeeding issues or problems, the types of foods that are safe for you and your baby, how much solid food you should start with when feeding your child, and what foods you should stay away from at the 7 month mark.
Enjoy this time and explore foods that you know are safe to feed your little one at 7-months-old. Don’t forget to introduce only small amounts of new foods at first and remember that every baby is unique. If your child isn’t ready for solid foods yet, it’s not necessarily a reason to panic. Every child develops at their own pace. Before you know it, they’ll be eating all on their own!
Complementary foods at 7 months, what foods to introduce into complementary foods for a child from the network of months
02. 08.2022
08.2022
≈ 6 min read time
Contents
- How do you know when it's time for your baby to expand complementary foods? nine0009 What foods are too early to introduce at 7 months
- How to continue introducing complementary foods at 7 months - features and general rules nine0009 Complementary feeding regimen at 7 months
- The diet of a child on breastfeeding and artificial feeding - what is the difference?
- Sample food menu nine0010
- What to do if the child refuses complementary foods?
If complementary foods started from six months, as the World Health Organization advises, then by 7 months the baby is already “experienced” enough to try new, more “difficult” foods for digestion.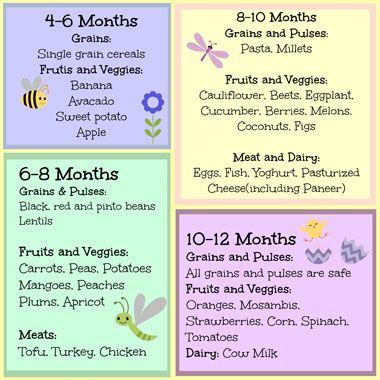 For example, only from this age can one offer a chicken egg yolk. nine0003
For example, only from this age can one offer a chicken egg yolk. nine0003
It is extremely important that the menu expands: during this period, taste preferences are already laid that will remain with a person for life.
A growing child's nutritional needs are constantly increasing, but their amount must be strictly verified. For example, with a lack of protein in the diet, the development of a child may suffer, but an excess of protein negatively affects the functioning of the kidneys. And the need for calories per kg of body weight from 7 months is even slightly reduced compared to earlier, infancy. True, the baby gains weight, therefore, of course, consumes more and more calories. nine0003
Energy and nutrient requirements of a 7-month-old baby (per kg of body weight)
| Energy | Squirrels | Fats | Carbohydrates |
|---|---|---|---|
| 110 kcal nine0003 | 2. | 5.5 g | 13 g |
You can understand that you need to introduce new products by certain signs. Your baby:
- willingly eats different types of vegetables, as well as not only gluten-free, but also gluten-free cereals;
- eats not only single-component, but also multi-component products - for example, cereals from different types of cereals;
- "mastered" different types of meat and fruit purees.
The child's digestive system continues to change. In particular, the length of the intestine increases, and by 7 months the small intestine “becomes” in the same place as in an adult. However, the consistency of food should still remain homogeneous, homogeneous.
- Juices . The National Feeding Optimization Program advises introducing them after the main complementary foods. Juices have insufficient nutritional value to cover the needs of a growing organism.
 In addition, if you give your child juice between feedings, the risk of caries may increase, and excess of the norm creates the preconditions for excess weight.
In addition, if you give your child juice between feedings, the risk of caries may increase, and excess of the norm creates the preconditions for excess weight. - Unadapted kefir, yoghurt, biolact . Their turn will come only from 8 months. Cottage cheese can be administered earlier, but after consulting with the pediatrician. nine0010
- Fish puree . For a child of this age, meat has more nutritional value than fish, so you also need to wait another month with it.
- Cow's milk . Due to the high protein content, which differs significantly from breast milk protein, experts do not recommend offering this product for the entire 1st year of life.
The main fundamentally new product at the age of seven months is the egg yolk. Previously, nutritionists were wary of the fact that the egg contains cholesterol, the excess of which can be potentially dangerous for the heart and blood vessels. But now science has confirmed that eggs do not increase plasma cholesterol levels. nine0003
nine0003
The egg contains:
- fats;
- proteins;
- vitamin A, B vitamins;
- iron, phosphorus, zinc.
However, 2% of babies are allergic to eggs. That is why the product is administered no earlier than 7 months of age. And only the yolk: the molecules that can cause intolerance are concentrated in the protein. But vitamins and minerals are in the yolk. Already by the age of 3, hypersensitivity to the product disappears in half of the kids. nine0003
The pattern of continuing complementary foods is already familiar:
- we offer an unfamiliar product in the 1st half of the day - there will be time to follow the reaction;
- offer a small amount, the product must be crushed. If the baby refuses, you can mix a little new product with an already familiar one;
- in 5-7 days we increase the portion of the new product to the volume recommended in 7 months - no more than 1/4 of the yolk; nine0010
- we give only one new product at a time;
- we do not introduce a new dish during stressful circumstances: illnesses, vaccinations, moving.
 You have to wait 3-5 days.
You have to wait 3-5 days.
When expanding the diet with new cereals, vegetable and fruit purees, meat, it is better to use the products of licensed companies. It is ready to use and passed the safety control at the proper level.
The complementary feeding regimen at 7 months is five times feeding. The first morning and the last evening - breastfeeding or infant formula. At other feedings, mother's milk or mixture is present as supplementary food. nine0003
Complementary feeding chart at 7 months
| Dishes and products | Weight (g, ml) |
|---|---|
| vegetable puree | 150 |
| Porridge nine0058 | 150 |
| Meat puree industrial production / boiled meat | 40–50/ 20–30 |
| fruit puree | 70 | nine0051
| Yolk | 1/4 |
It is recommended to add oil to vegetables - 5 g per day, to cereals - 4 g per day.
Important: dosages are approximate, it is necessary to focus on the satiety and food interest of the child.
Domestic pediatricians recommend continuing breastfeeding up to 1.5-2 years, and WHO experts - up to 2 years and even longer. Breast milk is the ideal food for a baby, it is called the “child health programming factor”. Therefore, although mother's milk no longer provides all the nutritional needs of a 7-month-old baby, it continues to fulfill its protective functions. The "contribution" of mother's milk to the health of a child from six months to a year is at least half of the nutrients. Therefore, it must necessarily be preserved against the background of the introduction of complementary foods. nine0003
It is advised to resort to artificial mixtures when breastfeeding is excluded. Manufacturers, when developing mixtures, are guided by the composition of breast milk, but it is simply technically impossible to repeat it in full. Modern infant formula does not contain as many biologically active substances as in breast milk.
It is believed that the scientifically proven ability of a particular mixture to reduce the risk of allergies, prevent acute intestinal infections and provide the baby with additional functional benefits is much more important - so that growth and development, if possible, do not lag behind and "go" at the same pace as with breastfeeding. nine0003
There are some peculiarities in the introduction of complementary foods.
Complementary foods at 7 months breastfed
Complementary feeding at 7 months with breastfeeding suggests that every time after the baby has tried a new food, it must be applied to the breast. Even if he is already full, this will help maintain lactation.
In addition, breast milk has the ability to influence the taste preferences of the baby. This is explained by the fact that in the mother's milk there is a taste of the products that she eats. If the child does not want to try new food, you can first “introduce” the baby indirectly: the mother can add products to her menu that she wants to introduce into the child’s menu. If he does not accept the offer the first time, this is absolutely normal. You need to methodically offer to try the next feeding - and so many times. nine0003
If he does not accept the offer the first time, this is absolutely normal. You need to methodically offer to try the next feeding - and so many times. nine0003
Formula-fed complementary foods at 7 months
Complementary foods at 7 months on artificial feeding are introduced in the same way as in breastfed babies. Moreover, it is interesting that modern infant formulas take into account how the composition of mother's milk changes with the growth of the baby. For example, the amount of protein in it is gradually reduced - and milk formulas recommended for a child after six months may also contain less protein. But some vitamins and minerals will be added to them compared to mixtures for an earlier age. nine0003
By the second half of the year of life, the baby "met" almost all the key complementary foods, albeit in the form of puree or thick slurry. Therefore, the approximate menu of complementary foods at 7 months is already varied enough to make it possible to alternate dishes, not often repeating, and offer new tastes.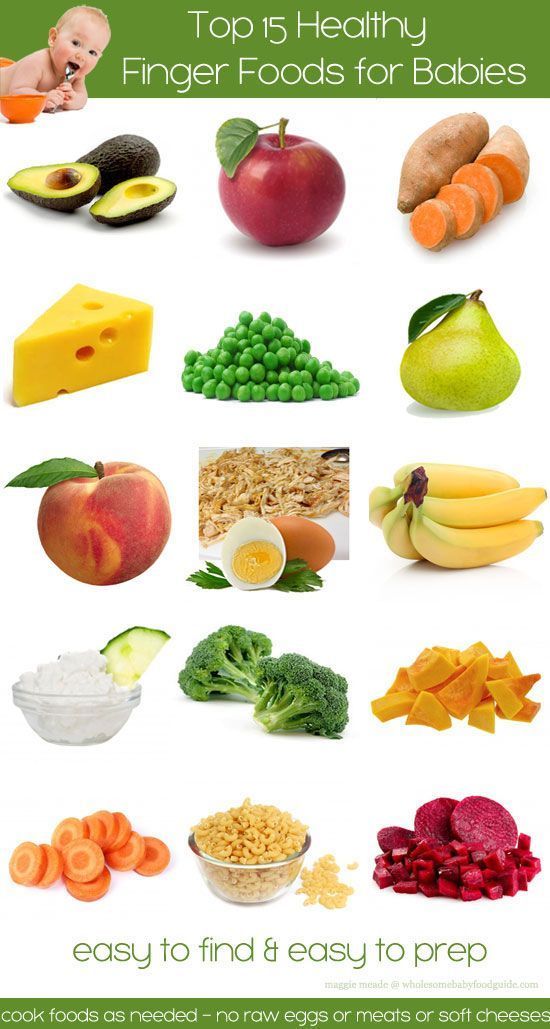
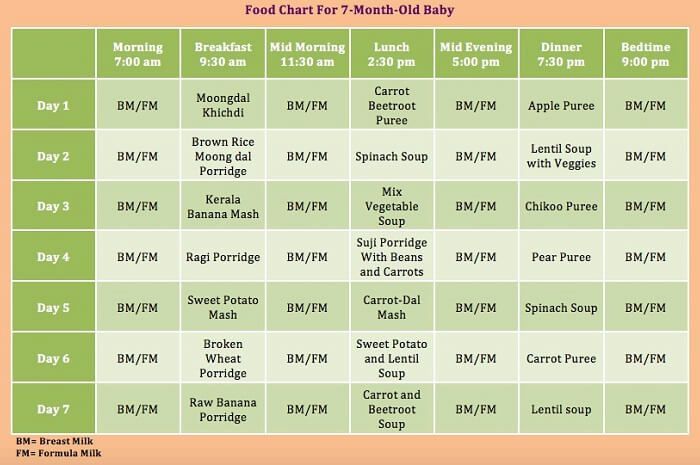
Complementary foods at 7 months. Menu for the day
| 6.00 1st feeding nine0058 | Breast milk or infant formula | 200 ml |
| 10.00 2nd feeding |
| 150 g
1/2 teaspoon 1/4 piece
50 ml nine0058 |
| 14.00 3rd feeding |
| 150 g 1 teaspoon 40–50 g |
nine0002 18. 00 00 4th feeding |
| 70 g 1–2 pcs. 130 ml |
| 22.00 nine0003 5th feeding | Breast milk or infant formula | 200 ml |
Weekly menu
Experts from the Union of Pediatricians of Russia advise distributing products in the diet of a seven-month-old baby in such a way that “you get a prototype menu for an already grown child with breakfast and lunch.” nine0003
If we take into account that the day begins and ends with breastfeeding or artificial formula, then between them the feeding of a child at 7 months can be varied (by supplementing with breast milk / formula) like this:
| Day of the week | Morning | Day | Evening nine0003 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monday | Rice porridge cooked with breast milk or infant formula + butter + boiled egg yolk
| Zucchini puree + vegetable oil + turkey puree | Apple puree + complementary breast milk/infant formula nine0003 |
| Tuesday | Buckwheat porridge cooked with breast milk or infant formula + butter + boiled egg yolk | Puree of several vegetables + vegetable oil + puree of rabbit | Pear puree + complementary breast milk/infant formula nine0003 |
| Wednesday | Multi-grain porridge made with breast milk or infant formula + butter + boiled egg yolk | Broccoli puree + vegetable oil + chicken puree | Mixed fruit puree + complementary breast milk/infant formula nine0003 |
| Thursday | Oatmeal cooked with breast milk or infant formula + butter + boiled egg yolk | Puree from different types of vegetables + vegetable oil + beef puree | Peach Puree + Complementary Breast Milk/Infant Formula nine0003 |
| Friday | Multi-grain porridge made with breast milk or infant formula + butter + boiled egg yolk | Pumpkin puree + vegetable oil + different types of meat puree | Vegetable and fruit puree + complementary breast milk/infant formula nine0003 |
| Saturday | Corn porridge cooked with breast milk or infant formula + butter + boiled egg yolk | Puree from different types of vegetables + vegetable oil + turkey puree | Apple puree + complementary breast milk/infant formula nine0003 |
| Sunday | Wheat porridge cooked with breast milk or infant formula + butter + boiled egg yolk | Carrot puree + vegetable oil + rabbit puree | Pear puree + complementary breast milk/infant formula nine0003 |
The kid may refuse a particular product, happy to try others. But it can also refuse complementary foods in general.
But it can also refuse complementary foods in general.
If the baby refuses some new foods, this is completely normal. According to experts, this is one of the manifestations of the so-called. "neophobia", "fear of the new". There is an assumption that evolution has formed it as a defense mechanism to protect the baby from possible poisoning. But in infancy, this mechanism can make it difficult to expand the diet. Studies have shown that most foods that children refuse will be more favorably received if they are offered repeatedly, and sometimes a dozen times. nine0003
But sometimes a child does not eat complementary foods for 7 months, i.e. unwilling in principle to switch to food other than mother's milk or formula. Experts believe that the ideal age to start complementary foods is 4-6 months and call this interval the "tolerance window" when new foods are introduced as easily as possible. Those. starting to introduce complementary foods to a seven-month-old baby is already some lag behind the “schedule” recommended by doctors.
The reason for refusal may be: nine0003
- diseases;
- difficulty swallowing;
- food intolerance;
- improper feeding.
Be sure to check with your pediatrician. Due to the delayed feeding, the baby will lack nutrients that are extremely important for growth and development, it will be more difficult for him to master the skill of chewing and swallowing thick food. In addition, new foods will then have to be introduced at a faster pace, and this will increase the burden on the immune system. nine0003
References
- The program for optimizing the feeding of children in the first year of life in the Russian Federation. Moscow, 2019. https://minzdrav.midural.ru/uploads/document/4908/optimizatsii-vskarmlivaniya-detej-pervogo-goda-zhizni.pdf
- Approximate diet of a child at the age of 6 months.
 Union of Pediatricians of Russia https://www.pediatr-russia.ru/parents_information/soveti-roditelyam/ratsiony-pitaniya-v-razlichnye-vozrastnye-periody/7%20%D0%BC%D0%B5%D1%81%D1 %8F%D1%86%D0%B5%D0%B2.pdf
Union of Pediatricians of Russia https://www.pediatr-russia.ru/parents_information/soveti-roditelyam/ratsiony-pitaniya-v-razlichnye-vozrastnye-periody/7%20%D0%BC%D0%B5%D1%81%D1 %8F%D1%86%D0%B5%D0%B2.pdf - Age features of the digestive system. Sechenov University. https://www.sechenov.ru/upload/iblock/32e/lektsiya-_3-vozrastnye-osobennosti-anatomii-pishchevaritelnoy-sistemy.pdf
- Nutrition of children of the first year: topical issues and new trends. Ed. I.N. Zakharova https://remedium.ru/doctor/pediatrics/Pitanie_detey_pervogo_goda_aktualnye_voprosy_i_novye_trendy/
- HE. Komarova, A.I. Khavkin. Causes of food refusal in young children: differential diagnostic search and methods of correction. Questions of modern pediatrics. 2014 https://vsp.spr-journal.
 ru/jour/article/view/194/121
ru/jour/article/view/194/121 - I.N. Zakharova, Yu.A. Dmitriev. Neophobia in infants: how to form their taste preferences? Questions of modern pediatrics. 2013 https://vsp.spr-journal.ru/jour/article/view/257/185
- Sophie Rehault-Godbert,* Nicolas Guyot, and Yves Nys. The Golden Egg: Nutritional Value, Bioactivities, and Emerging Benefits for Human Health. Nutrients.2019 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6470839/
Baby menu at 7 months: what is possible and what is not yet
— Anastasia Ivanovna, what are the nutritional features of children at 7 months? nine0123
— The menu of a baby at seven months is different from the menu of a newborn and a baby at one year old. This difference exists due to the fact that a number of body systems, including the gastrointestinal tract and oral cavity, have not yet been formed in a newborn, he is only learning to suck.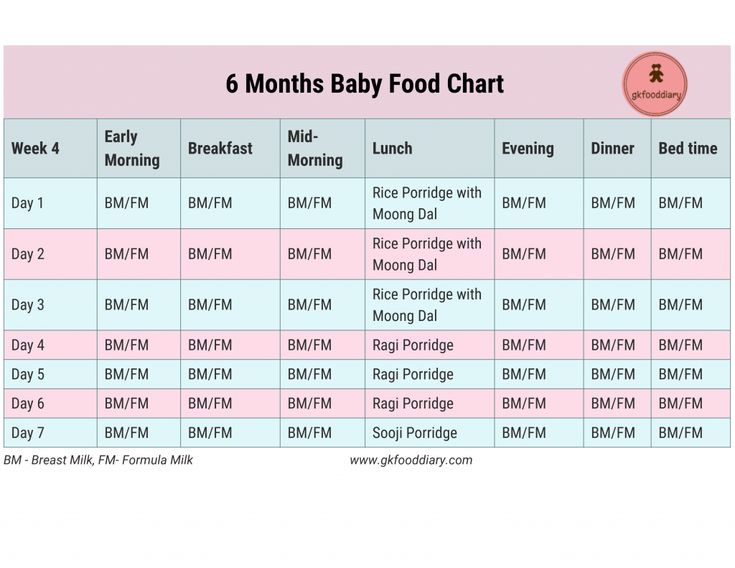 From four to six months, the diet begins to include complementary foods - food that is different from breast milk or infant formula. In the year of the child, in ideal conditions, they are transferred to a common table.
From four to six months, the diet begins to include complementary foods - food that is different from breast milk or infant formula. In the year of the child, in ideal conditions, they are transferred to a common table.
Some pediatricians recommend introducing complementary foods from five to six months, sometimes even from four. But the enzymatic system of the baby's body has not yet been formed, so pedagogical complementary foods are possible at four or five months, and pediatric complementary foods by six months. nine0003
— How to combine breastfeeding or bottle feeding with complementary foods?
— Pediatricians and nutritionists recommend separating these meals and giving the main dairy food and complementary foods in separate meals so that the child understands what he is eating.
If complementary foods started at 4-5 months
— What rules of baby food should parents know?
— The functions of the gastrointestinal tract are formed in such a way that the body needs to adapt to the incoming products.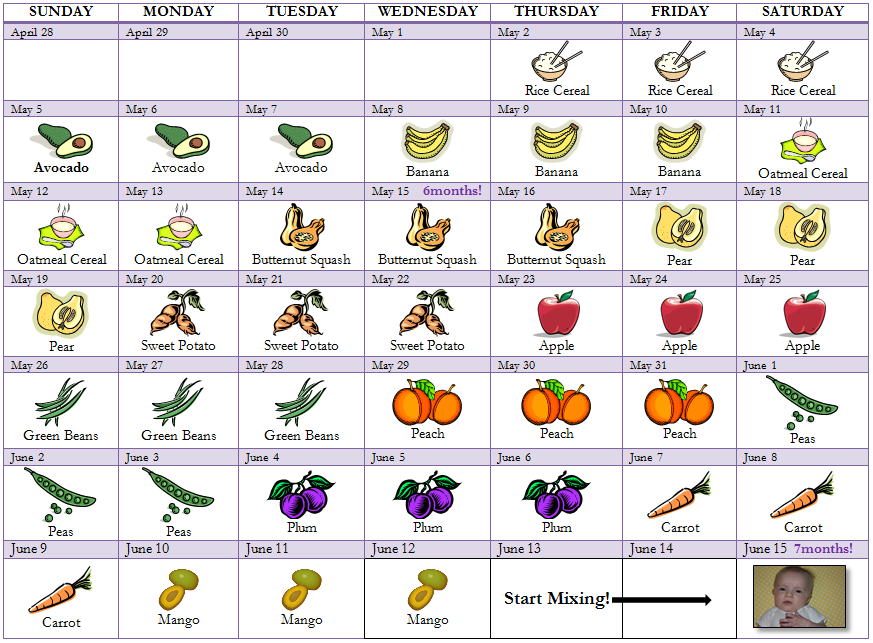 With proper complementary foods, it is important to monitor the child's condition in the food diary and, if necessary, consult a doctor. nine0003
With proper complementary foods, it is important to monitor the child's condition in the food diary and, if necessary, consult a doctor. nine0003
Basic feeding recommendations for seven-month-old babies
- One new product is given in small doses at the beginning of the day every four days to monitor for allergies, constipation, peeling and other reactions.
- One new product can be given per feeding.
- Water is best offered between feedings and not given with complementary foods.
- Do not force-feed: if the child refuses a certain dish, it can be offered at another time and in a different form. nine0010
- The child is not given unfamiliar food when he is not in a very good mood, teething, or has just been vaccinated.
- How to identify food allergies and find the allergen?
- Observant mothers will see or hear the problem. The baby will have something on the body, constipation or indigestion will begin. A restless child will cry. To track the allergen, it is advisable to keep a food diary and keep your finger on the pulse. If there is a connection with the pediatrician, ask questions and, taking into account the vaccination calendar, the physiology of the development of your child, offer him certain products so as not to once again provoke an immune response. nine0003
A restless child will cry. To track the allergen, it is advisable to keep a food diary and keep your finger on the pulse. If there is a connection with the pediatrician, ask questions and, taking into account the vaccination calendar, the physiology of the development of your child, offer him certain products so as not to once again provoke an immune response. nine0003
What foods can be given at 7 months?
- What purees and cereals can be given at 7 months?
- If this is the first complementary food for a baby, then monocomponent purees, dairy-free and milk porridges with one cereal in the composition are good: they are easier to digest and it is easier to track the body's reaction by them.
— In what order can complementary foods be given?
— If your baby is overweight by seven months, it is better to feed him vegetable puree. If everything is in order with weight, then preference can be given to cereals. All new products are introduced gradually: they begin to feed in the amount of 5-10 g, gradually increasing the volume to 50 g. By seven months, a portion of porridge at one time can reach up to 200 g. The third option for complementary foods, if parents want, can be fruit. It is in this sequence, because fruits are sweet, and the child does not always eat unleavened vegetables or cereals after them. nine0003
By seven months, a portion of porridge at one time can reach up to 200 g. The third option for complementary foods, if parents want, can be fruit. It is in this sequence, because fruits are sweet, and the child does not always eat unleavened vegetables or cereals after them. nine0003
Each product will also have its own processing specifics:
- vegetables and fruits are given in the form of puree;
- purchased cereals are prepared according to the instructions;
- homemade porridges are boiled in water, then milk or mixture is added if desired;
- cottage cheese is properly stored in the refrigerator, tracking the expiration date;
- dairy, vegetable broths are brought to a single consistency (puréed) so that the child develops the correct perception of the product. nine0010
— How many times to feed a child at 7 months and how much food to give?
- You need to focus on five feedings per day. If your baby cannot tolerate the interval between meals, it is worth supplementing with breast or formula after the introduction of complementary foods.
How to calculate the amount of complementary foods
A child at seven months should weigh about eight kilograms. 1/8 of the child's weight is the daily amount of food, that is, approximately a kilogram of food, taking into account all feedings, or 200 grams per meal. nine0003
Sample menu for a 7-month-old baby (Russian Federation)
— At what age can semi-solid and solid foods be introduced into a child's diet?
- By 6 months, most babies are ready for a new food: the baby realizes that something is hard in his mouth. By the age of seven months, the skill of palmar grip is formed: the child is able to hold solid food in his hand, and he can be given biscuits and crackers to grind. Allergists and pediatricians consider 6-10 months as the optimal period to begin the introduction of semi-solid and solid foods.

 9 g
9 g