Vitamin d foods list for babies
5 Vitamin D-Rich Foods That Are Safe For Babies
Life
Christin Lola/Fotolia
by Lauren Schumacker
Vitamin D is an important nutrient for people of all ages. You can get vitamin D from exposure to sunlight, which is helpful during the warm and sunny months. But people — especially babies — don't typically spend all that much time in direct sunlight, even in the warmer months. Because they're often shaded and probably don't yet take a daily multivitamin, vitamin D rich foods that are safe for babies can be an important component of their diet.
Vitamin D has always been important. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), it's a powerful, fat-soluble vitamin that helps boost calcium absorption, provides immune system support, promotes healthy cell growth, and helps reduce inflammation. Basically, it's essential. But it has gotten some more attention recently with the American Academy of Pediatrics noting the results of a recent study that found babies might not be getting enough vitamin D from their diet.
or infants, the AAP recommended daily liquid vitamin D supplements, particularly if they are breast-fed. But for babies who are a bit older, there are foods they can be fed that will help boost vitamin D intake. Adding the following baby-safe, vitamin D rich foods can mean healthier babies and healthier kids down the line.
1
Milk
Devanath/PixabayIf you're looking to up your baby's vitamin D intake and they're old enough for milk, vitamin D-fortified milk could be just what you're looking for. According to the NIH, nearly all milk sold in the U.S. is fortified with vitamin D. Milk is also extremely versatile. You can use instead of water in oatmeal or add a bit of chocolate syrup for something a little different.
2
Yogurt
NeuPaddy/PixabayFortified yogurt is a good source of both vitamin D and calcium, according to Parents. Win-win. Additionally, Baby Center noted that many babies can begin to tolerate yogurt at about four to six months of age.
Win-win. Additionally, Baby Center noted that many babies can begin to tolerate yogurt at about four to six months of age.
3
Salmon
zephious/PixabayFatty fish like salmon is a good source of vitamin D, according to the National Institutes of Health. You can start introducing fish into your baby's diet at six months, according to Parenting.
4
Egg
Tookapic/PexelsAccording to the Mayo Clinic, eggs are a good source of naturally occurring vitamin D. Babies can start eating egg yolks at around nine months, according to Parents. While egg yolk allergies aren't overly common, watch for any potential signs of allergy.
5
Cereal
ponce_photography/PixabayMany older babies and toddlers love snacking on ready-to-eat cereals. According to BabyCenter, vitamin D-fortified, ready-to-eat cereal can up your baby's intake of the essential vitamin.
Vitamin D in your child's diet
Vitamin D is crucial for children's good health and development. Read on to find out how much vitamin D your child needs, which sources are the best, and how to avoid getting too little or too much.
Read on to find out how much vitamin D your child needs, which sources are the best, and how to avoid getting too little or too much.
Find out more: Ten important nutrients for children
Why vitamin D is important
Vitamin D helps the body absorb minerals like calcium and builds strong teeth and bones. According to researcher Michael F. Holick, professor of medicine, physiology, and biophysics at Boston University School of Medicine, vitamin D deficiency can not only cause rickets (a disease that can lead to bone deformity and fractures), it can also keep a child from reaching her genetically programmed height and peak bone mass.
Vitamin D also functions as a hormone with many other jobs in the body, including regulation of the immune system, insulin production, and cell growth.
How much vitamin D does my child need?
Infants up to 12 months old need 400 international units (IU), or 10 micrograms (mcg), a day. Children older than 1 need 600 IU, or 15 mcg, a day.
Your child doesn't have to get enough vitamin D every day. Instead, aim to get the recommended amount as an average over the course of a few days or a week.
The best sources of vitamin D
Vitamin D is called the "sunshine vitamin" because the body can produce it when the skin is exposed to sunlight. But your child's body isn't able to make vitamin D when covered with clothing or sunscreen to block the sun's rays. Other obstacles to vitamin D production from sun exposure include smog, clouds, dark skin, and geographic location.
Though it's hard to estimate how much time a person needs to spend in the sun to make the recommended amount of vitamin D, some researchers say spending 5 to 30 minutes outside between 10 a.m. and 3 p.m. at least twice a week should do it.
But experts warn that UV radiation from the sun is the main cause of skin cancer, and it's hard to judge whether you can get enough vitamin D from the sun without increasing your risk of a potentially deadly skin cancer. So consider finding other ways to get the vitamin D you need.
So consider finding other ways to get the vitamin D you need.
Advertisement | page continues below
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that all infants, children, and teens take vitamin D supplements of 400 IU each day. Kids who are too young for chewable vitamins can take liquid supplements.
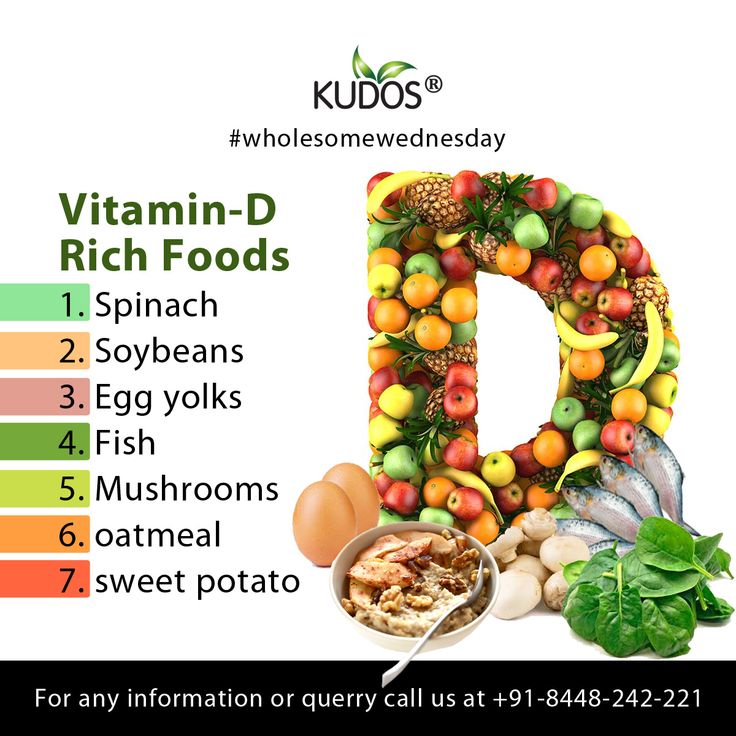
Some of the best food sources of vitamin D:
- 1 ounce salmon: 102 IU
- 6 ounces fortified yogurt: 80 IU
- 1 ounce canned tuna, drained and packed in oil: 66 IU
- 1/2 cup orange juice, fortified with 25 percent of daily value for vitamin D: 50 IU
- 1/2 cup fortified milk (whole, low-fat, or skim): 49 IU
- one slice fortified American cheese: 40 IU
- 1/2 cup fortified, ready-to-eat cereal: 19 IU
- 1 ounce mackerel: 11.6 IU
- 1/2 large egg yolk: 10 IU
- 1/2 teaspoon fortified margarine: 10 IU
- 1/2 ounce Swiss cheese: 6 IU
The amount of vitamin D in a food varies somewhat, depending on the brand of the product.
Kids may eat more or less than the amounts shown, given their age and appetite. Estimate the nutrient content accordingly.
Can my child get too much vitamin D?
It's unlikely but possible. On the contrary, many health experts are concerned that the current recommended amount is too low and that children actually need much more.
That said, vitamin D can be harmful if you get too much. According to the Office of Dietary Supplements (a department of the National Institutes of Health), the safe upper limit for infants up to 12 months old is 1,000 to 1,500 IU daily. For kids 1 to 8 years old, the safe upper limit is 2,500 to 3,000 IU each day.
Vitamin D is stored in body tissue, so it's best not to get more than what health experts recommend. (Vitamin C, by contrast, isn't stored in the body – any excess is simply eliminated in urine.)
To be safe, if you have a very young child, stick to the 400 IUs recommended as an infant supplement. More than 400 IUs may be fine for an older child, but check with your child's doctor to be sure.
what foods contain, the norm, deficiency and excess of vitamin D, symptoms and diseases associated with vitamin deficiency.
December 18, 2019 January 17, 2022
The importance of vitamin D for the body cannot be overestimated. It is responsible for a number of important biochemical processes:
- helps the absorption of calcium and phosphorus, "opening" the cells of bone tissue, teeth and nails to receive these minerals;
- normalizes blood sugar levels; nine0008
- speeds up metabolism;
- synthesizes monocytes, which cleanse the blood;
- stimulates the synthesis of a number of hormones;
- improves the transmission of impulses between neurons;
- affects the development of the embryo.
Proper intake of vitamin D strengthens bones and muscles, improves blood composition, eliminates dry hair and skin, reduces the risk of oncology and diabetes, improves immunity, working capacity, concentration, improves thyroid and heart function, regulates arterial pressure. nine0003
nine0003
Types of vitamin D
Vitamin D, or calciferol, is the general name for a group of biologically active substances - fat-soluble vitamins D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6. Of these, two are beneficial to human health:
- ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) and
- cholecalciferol (vitamin D3).
Ergocalciferol enters the body from the outside - along with plant foods (juices, cereals, mushrooms).
But cholecalciferol is synthesized by the body itself under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. That's why it's also called a "natural" vitamin. In addition, it is found in food of animal origin - fatty fish, yolks, butter, etc. According to scientific research, D3 is involved in human life by about 30% more actively, which means that this type of calciferol is especially useful. nine0003
Vitamin D deficiency
It is known that vitamin D is synthesized by the body when it hits the skin at a certain angle, which is observed from 11 am to 2 pm. This time for children may coincide with lunch or sleep, while for adults it is necessary for work. Factors that lower vitamin D levels include constant use of sunscreen in the summer and bad habits such as smoking and drinking too much alcohol. nine0003
This time for children may coincide with lunch or sleep, while for adults it is necessary for work. Factors that lower vitamin D levels include constant use of sunscreen in the summer and bad habits such as smoking and drinking too much alcohol. nine0003
Symptoms in adults
Vitamin D deficiency can be detected through clinical and laboratory tests. And the signal that it is time to go to the doctor should be the following symptoms:
- chronic fatigue,
- irritability, nervousness,
- problems with stool,
- sleep disorder,
- caries,
- vision loss8,
- bone mass and bone fragility,
- aching pain in bones and joints,
- increased sweating of the occipital region,
- cramps, pulling muscles,
- dryness, skin peeling,
- alopecia,
- Witting appetite, anorexia, anorexia, anorexia,
- ,
- frequent respiratory tract infections.
As we can see, the symptoms from this list are not specific. And on their basis it can be difficult to make an accurate diagnosis. Therefore, those who suspect that they have calciferol vitamin deficiency should be tested for 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25 (OH) D). If your indicator is in the range of 30-100 ng / ml, there is no need to worry. A reading of less than 20-30 ng/mL is indicative of vitamin D deficiency, and less than 10 ng/mL is diagnosed as a deficiency, in which case immediate action should be taken. Read more about the importance of vitamin D for women. nine0003
And on their basis it can be difficult to make an accurate diagnosis. Therefore, those who suspect that they have calciferol vitamin deficiency should be tested for 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25 (OH) D). If your indicator is in the range of 30-100 ng / ml, there is no need to worry. A reading of less than 20-30 ng/mL is indicative of vitamin D deficiency, and less than 10 ng/mL is diagnosed as a deficiency, in which case immediate action should be taken. Read more about the importance of vitamin D for women. nine0003
Symptoms in children
Calciferol is involved in the development of the embryo and the formation of innate immunity, so children should receive this vitamin before they are born, during the prenatal period. In childhood, when the child's skeleton, teeth and muscular body are actively developing, an adequate level of vitamin D is very important.
Among the symptoms of a lack of this vitamin in children are:
- increased tearfulness, excitability and sleep disturbances; nine0008
- stunting;
- slowing down the closure of the fontanel;
- weight loss;
- profuse sweating, especially during sleep;
- rickets, changes in the skeletal system (crooked legs, enlarged head, flat occiput, too prominent forehead).

Read more about vitamin D for children.
Risk groups
- Patients with diseases of the liver, kidneys and intestines . Vitamin D is activated in the liver and kidneys, so in people with diseases of these organs, the process is disrupted.
- Dark skinned . A large amount of melanin in dark or tanned skin protects it from UV rays, which reduces the volume of synthesized cholecalciferol.
- Pregnant and lactating women. The developing skeleton of the embryo requires a large amount of calcium and calciferol - it receives them from the mother's body. During lactation, calcium is also washed out of the body, so nursing mothers, as a rule, lack vitamin D and are advised to take vitamin complexes. nine0008
- People over the age of 60. Fat absorption by the intestines deteriorates with age, which affects the absorption of fat-soluble vitamin D.
- Overweight . Being a fat-soluble vitamin, calciferol dissolves in adipose tissue without having time to participate in a number of biochemical processes.
 Thus, the need for vitamin D is higher in obese people.
Thus, the need for vitamin D is higher in obese people. - Vegetarians . This is easily explained by their lack of animal foods containing vitamin D in their diet.
Too much vitamin D
Too much vitamin D is often the cause of too much calciferol. In this case, hypervitaminosis occurs, that is, a state when the hydroxyvitamin D index exceeds 100 ng / ml.
Calcium salts begin to be deposited in muscles, internal organs, skin, which negatively affects their condition and work. Hypervitaminosis provokes visual impairment, kidney failure and the appearance of stones. nine0035 The enthusiasm of some young mothers for vitamins can lead to an excess of calciferol in the child's body. Therefore, the treatment and choice of medicines for the child should be carried out as directed by the pediatrician. It takes into account the appearance of the newborn, as well as the type of feeding on which he is. For example, if you feed your child with milk formulas, then vitamin D is already included in their composition in the right amount, which means that you do not need to use drugs to prevent its deficiency. While mother's milk, especially in winter, may contain insufficient amounts of this vitamin. nine0003
While mother's milk, especially in winter, may contain insufficient amounts of this vitamin. nine0003
Among the signs of excess calciferol in children and adults:
- insomnia;
- frequent urination, diarrhea and vomiting;
- skin rashes;
- muscle cramps;
- irritability.
In addition, in children, an excess of vitamin D increases the symptoms of other diseases. Skin rashes or loose stools are sometimes mistaken for an allergy to vitamin D. In fact, this is just an overdose that disrupts the liver and causes reactions similar to allergic ones. nine0003
How to Increase Your Vitamin D Levels
You can increase your calciferol levels by sunbathing or UV lamps, or by eating vitamin D-rich foods or NUTRILITE™ Vitamin D* dietary supplements.
Learn more about NUTRILITE™ Vitamin D
UV Rays
The easiest, most natural way to boost your vitamin D levels is to spend more time in the sun. The ultraviolet spectrum of sunlight consists of three fractions of rays: UV-A, UV-B and UV-C. The synthesis of cholecalciferol requires B-fraction rays that do not pass through a glass window. Therefore, it is recommended to catch them only in the open air. It should also be remembered that clouds and urban smog are capable of retaining up to 50% of ultraviolet radiation. nine0035 The minimum duration of sunbathing should be 20-30 minutes per day from 11 am to 2 pm. Unfortunately, it is during these hours in the summer that the likelihood of getting a sunburn is high. And the use of sunscreens with an SPF factor above 8 blocks the production of vitamin D. Therefore, it is necessary to measure the danger and benefits of such a tan.
The ultraviolet spectrum of sunlight consists of three fractions of rays: UV-A, UV-B and UV-C. The synthesis of cholecalciferol requires B-fraction rays that do not pass through a glass window. Therefore, it is recommended to catch them only in the open air. It should also be remembered that clouds and urban smog are capable of retaining up to 50% of ultraviolet radiation. nine0035 The minimum duration of sunbathing should be 20-30 minutes per day from 11 am to 2 pm. Unfortunately, it is during these hours in the summer that the likelihood of getting a sunburn is high. And the use of sunscreens with an SPF factor above 8 blocks the production of vitamin D. Therefore, it is necessary to measure the danger and benefits of such a tan.
If there is no opportunity to be in the sun, you can use the solarium. The rays of UV lamps are not equivalent to the sun, but partially compensate for the deficiency of natural ultraviolet radiation. However, the unreasonable use of a solarium can provoke premature skin aging, pigmentation, and even the appearance of melanoma. nine0003
nine0003
What foods contain vitamin D?
List of products with a high content of vitamin D:
- Fish oil
- Cod liver
- Gorbusha and other oily fish
- 9000
- Evalal yolk 9000 9000 9000 Solid Simp
- rheumatoid arthritis,
- oncology,
- hypertension,
- migraine,
- diabetes mellitus,
- atherosclerosis,
- diseases of the cardiovascular system,
- immunodeficiency,
- allergies,
- periodontal disease,
- risk of preterm birth.

The table shows the amount of cholecalciferol contained in 100 grams of products. nine0035 NUTRILITE Omega-3 with Vitamin D is a jelly lozenge for children that is easy to swallow, dissolves quickly, is well absorbed and does not leave an unpleasant aftertaste. One lozenge covers up to 80% of your daily vitamin D intake.
NUTRILITE Children's Chewable Lozenges contain calcium, magnesium and vitamin D to help your baby grow. In one lozenge - approximately 30% of the daily requirement of calciferol.
Calcium, magnesium, vitamin D complex NUTRILITE - dietary supplement for adults. nine0003
By itself, calcium intake cannot guarantee that it will go exactly where we expect - into the bone tissue.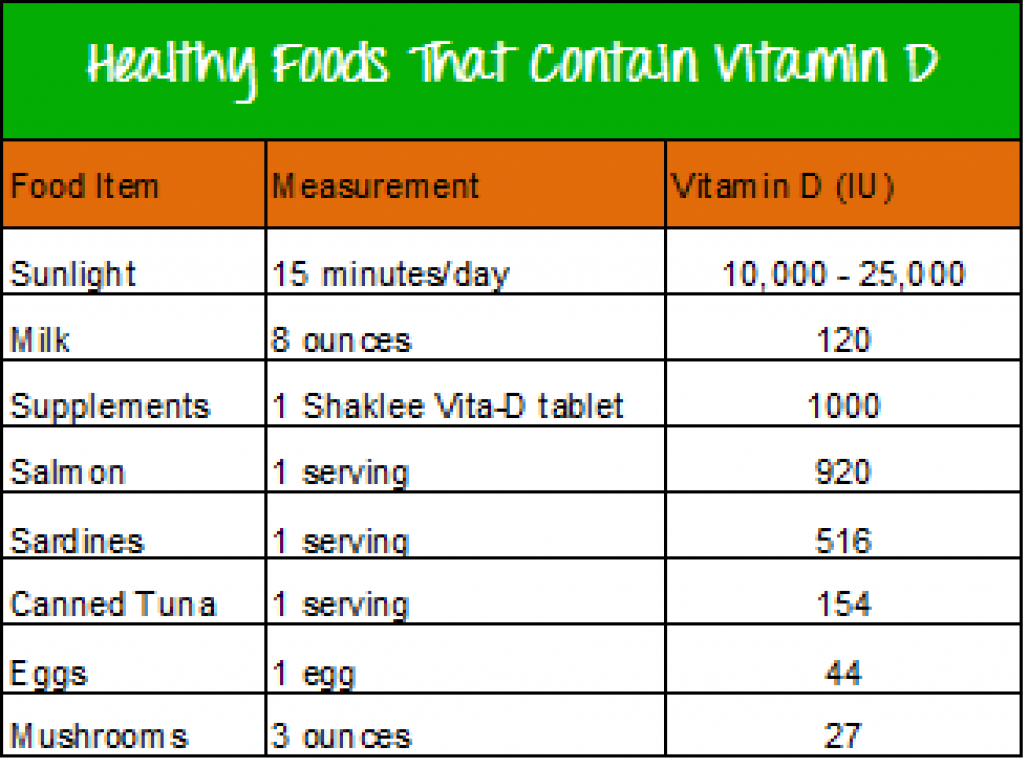 Without faithful helpers, magnesium and vitamin D, it can "get lost" and deposited in the walls of blood vessels or atherosclerotic plaques, thereby bringing cardiovascular complications closer. It is very important that the complex works - three components simultaneously in certain proportions. Vitamin D, which is actually not a vitamin, but a prohormone, regulates the level of calcium in the blood. If there is too little calcium, it contributes to the destruction of the bone and leaching of calcium from it. If vitamin D "determines" that there is enough calcium, the latter will be taken up by osteoblasts (bone cells). Magnesium is needed to stabilize the process. The "Great Trinity" guarantees us beautiful hair, strong bones, strong nails and teeth. nine0003
Without faithful helpers, magnesium and vitamin D, it can "get lost" and deposited in the walls of blood vessels or atherosclerotic plaques, thereby bringing cardiovascular complications closer. It is very important that the complex works - three components simultaneously in certain proportions. Vitamin D, which is actually not a vitamin, but a prohormone, regulates the level of calcium in the blood. If there is too little calcium, it contributes to the destruction of the bone and leaching of calcium from it. If vitamin D "determines" that there is enough calcium, the latter will be taken up by osteoblasts (bone cells). Magnesium is needed to stabilize the process. The "Great Trinity" guarantees us beautiful hair, strong bones, strong nails and teeth. nine0003
Dmitry Semiryadov , Dietitian, federal expert of the brand Nutrilite
Regular use of this drug keeps bones strong and reduces the risk of fractures. The drug is suitable for older people, as well as those who play sports and want to maintain flexibility and mobility. Each tablet contains the daily amount of calciferol.
Each tablet contains the daily amount of calciferol.
It is convenient to purchase drugs at the lowest cost through the Amway website. Just choose the products you need and arrange delivery to your city. nine0003
Daily Value
The required daily intake of cholecalciferol for a healthy adult is 15 micrograms, or 600 IU, which is equivalent to about 100 grams of salmon.
For children under three years of age, doctors prescribe up to 400 IU of vitamin per day to prevent rickets. For children older than three years, the daily intake of calciferod is 600 IU.
The ratio of patients to the recommended daily dose of vitamin D3 (in IU) is shown in this table. nine0200 600
Constant absence of vitamin D
More than a hundred years have passed since the discovery of vitamin D. But every year, scientists learn about its new features. Its role in life processes is very great. Therefore, it is so important to monitor the level of this substance in the body.
*NUTRILITE™ dietary supplements are not medicines. There are contraindications. Consult with a specialist.
**Product availability may change. The product images shown may differ from their actual appearance. Detailed information about the goods can be found by calling 8-800-080-55-08 or on the website kz.amway.com.
Also see:
- Vitamin D for children
- Vitamin D for women
- What foods contain Omega-3
- Vitamins for women
- Vitamins for women over 30
- Vitamins for women over 40 the most famous of which are cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) and ergocalciferol (vitamin D2). The first is produced by the body under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, and also comes with food, the second is found only in food.
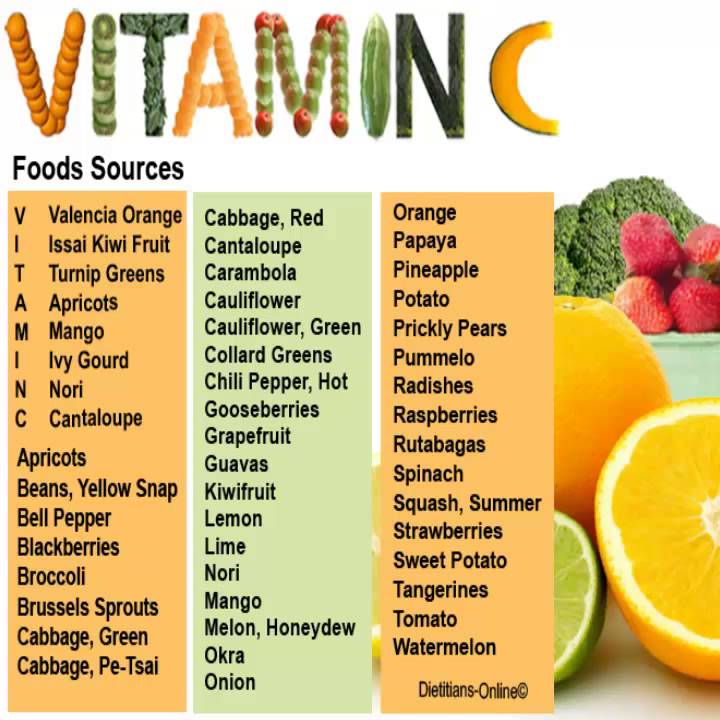 nine0003
nine0003 Unfortunately, many people are deficient in this micronutrient. The results of a large-scale study conducted in 2016 at the Cork Center for Vitamin D and Nutrition Research, University College Cork (Ireland) led by Professor K.D. Cashman showed that 40.4% of the population of European countries have a deficiency of vitamin D in the blood serum, and 13% of people experience a pronounced deficiency of this micronutrient, which carries a high risk of clinical manifestations. This is due to the fact that the majority of the European population is in the zone of low insolation. nine0003
Taking into account the obtained data, the issue of replenishment of the “sunshine” vitamin through food becomes topical. Everyone knows that there is a lot of vitamin D in foods containing fish oil, but it can also be found in mushrooms, eggs and meat, dairy and plant foods. In this article, we will consider which foods contain vitamin D for introducing it into the diet and compile a list of champions in terms of its content.

Benefits for the body
The main function of vitamin D is participation in the metabolism of phosphorus and calcium. It ensures normal growth of bone tissue, prevents the occurrence of rickets and osteoporosis, and is responsible for the strength of teeth and nails. nine0003
The latest scientific evidence has proven the significant effect of vitamin D on the immune system and increase the protective properties of the body, which is especially important during colds and viral diseases. Calciferol improves cognitive functions, helps with nervous and psychological disorders, facilitates the course of autoimmune diseases (psoriasis), and prevents the growth of cancer cells.
Which foods contain the most vitamin D
It is known that approximately 90% of vitamin D is synthesized in the skin under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. Unfortunately, not everyone can sunbathe all summer to accumulate enough of it, and doctors warn about the dangers of prolonged exposure to the sun due to the risk of skin cancer.
 Thus, to prevent a deficiency of the “sunshine” vitamin, two options remain: introduce foods rich in this nutrient into the diet, or take dietary supplements in various forms. So, let's look at which foods contain the most vitamin D.
Thus, to prevent a deficiency of the “sunshine” vitamin, two options remain: introduce foods rich in this nutrient into the diet, or take dietary supplements in various forms. So, let's look at which foods contain the most vitamin D. Fish oil
Known and unloved by many since childhood, fish oil contains the largest amount of vitamins D2 and D3: 100 g of the product contains 250 mcg or 2500% of the daily requirement, and a teaspoon (5 ml) of cod liver oil contains it 56%. In addition, this product is one of the best sources of retinol - a growth vitamin for children, as well as omega-3 fatty acids - an important nutrient for heart, vascular and brain health. Fish oil can be bought in different forms of release, as well as with various flavoring and aromatic additives. However, due to the high toxicity of vitamin A, taking fish oil in large quantities is not recommended. nine0003
Fatty fish
The top vitamin D-rich food is fish, with salmon topping the list.
 The amount of D2 and D3 is very dependent on the habitat of the animals: the concentration in a wild individual is much higher than in artificially grown. So, in a 100-gram piece of fish caught in natural conditions, contains 247% of the daily norm, and in the "farm" - only 32%.
The amount of D2 and D3 is very dependent on the habitat of the animals: the concentration in a wild individual is much higher than in artificially grown. So, in a 100-gram piece of fish caught in natural conditions, contains 247% of the daily norm, and in the "farm" - only 32%. What other fish contains the most vitamin D? Interestingly, the most common herring, sardines and mackerel are also an excellent source of it, regardless of the cooking option. 100 g of fresh Atlantic herring contains 1600 IU of the "sunshine" vitamin, which is almost 4 times higher than the daily norm, in canned fish - 22%, and in marinated - 14%. Large amounts of calciferol are found in other varieties of fatty fish: chum salmon, pink salmon, halibut, as well as in canned tuna (34% DV in 100 g). The disadvantage of canned fish is the presence of sodium and a harmful toxin - methylmercury, which limits their use. nine0003
Oysters are rich in vitamin D from seafood. This gourmet food contains very few calories, but many important nutrients, including up to 80% of the daily value of calciferol in just two shellfish.
Forest mushrooms
For those who do not like fish, generous nature offers an alternative option - forest mushrooms, which are an excellent source of vitamin D. Interestingly, they, like humans, are able to synthesize a micronutrient under the influence of sunlight, but unlike us , mushrooms produce less efficient calciferol (vitamin D2). Some types of forest mushrooms contain up to 2300 IU per 100 grams, which is almost three times the daily value. Commercial mushrooms grown in the dark contain very little of this nutrient, but when exposed to UV radiation can provide up to 450 IU of vitamin D2 per 100 grams. nine0003
Whole eggs
Eggs are an excellent source of vitamin D3. One egg yolk contains 37 IU or 5% of the daily value. At the same time, the amount directly depends on the exposure of the chicken to the sun and the content of the vitamin in the chicken feed. By analogy with mushrooms, free-range domestic laying hens produce eggs with a vitamin D content 3-4 times higher than those grown in cramped and enclosed spaces.

Herbal products
Despite the fact that vegetables and fruits contain almost no calciferol, some manufacturers produce juices enriched with this micronutrient. Such food is especially suitable for people who are lactose intolerant or allergic to milk. For example, a glass of fortified orange juice may contain 100 IU of ergocalciferol, or 12% of the Daily Value. nine0003
Vitamin D can also be found in other plant foods such as fortified cereals, soy, almond, coconut or rice milk. Half a cup of fortified oatmeal provides up to 17% of the daily micronutrient value, 100g of fortified tofu provides 13%, and a cup of soy milk provides up to 30%, which is a good way to increase your daily intake. A small amount of vitamin D contains potatoes, parsley, as well as some herbs: alfalfa, dandelion, nettle and horsetail.
Table 1. Foods high in vitamin D (D3 and D2)
Product name Vitamin D in 100 g percentage of daily needs Fish oil (from the liver of the explosion) 9030 μg2500% 9 90% 9 90% 9 90% 9 90% 9020 Mackerel 16.  3 mcg
3 mcg 163%0208 Dietary supplements
Vitamin D can be obtained in three ways: sun exposure, food sources and dietary supplements. The latter option is convenient and affordable, therefore it is today a very popular way to prevent the “sunshine” vitamin.
Vitamin D is available in different dosages and forms:
- oily
- aqueous
- fish oil in dark glass or capsules
- medicinal solutions
- chewable tablets
- regular tablets.
The fat-soluble (oil) form is very popular for many vitamins, in which the active ingredient is dissolved in oil. However, the bioavailability of such vitamin D directly depends on the state of the gastrointestinal tract of the person who takes it. For example, chronic pancreatic disease significantly reduces micronutrient absorption.
An alternative to the oil form is the water form. It is a ready-to-use micellar solution of vitamin D that is easily digested in the intestines and is the preferred source of energy and resources.
 nine0003
nine0003 Vitamin D supplements
Vitamin D capsules
Vitamin D3 2500 IU 150 mg capsule №90
Source of vitamin D, has a general strengthening effect on the body, maintains the required level of calcium in the body, promotes the absorption of phosphorus.
Vitamin D3 2500 IU 120 gelatin capsules TM Vansiton / Vansiton
Strengthens bone tissue, reduces the risk of osteoporosis, promotes the creation of immune cells, supports the functioning of the lungs and the cardiovascular system, increases the level of serotonin in the body. nine0035
Vitamin D3 1000 IU 100 softgels TM Country Life
Promotes calcium absorption, healthy teeth and nails, normal functioning of the immune system. A vegan product made from lanolin. The capsules contain cholecalciferol, a natural form of vitamin D3 that is most easily absorbed and utilized.
Causes of deficiency and daily intake of vitamin D
The authors of a study published in the journal “Science of the Total Environment” analyzed how long it takes to be in the sun to synthesize a daily dose of vitamin D3 without significant damage to health.
 It turned out that in July a person can be in the sun no more than 29min., in January - 130 min. at noon with maximum light and 10% open skin, and in October - 30 min.
It turned out that in July a person can be in the sun no more than 29min., in January - 130 min. at noon with maximum light and 10% open skin, and in October - 30 min. However, it is not enough just to stay in the sun, it is necessary that the rays fall on the surface of the skin at a certain angle, which in the European part is observed in spring and summer from 12:00 to 16:00. But it is precisely this time that doctors consider the most harmful for sunbathing, fraught with photodermatosis and the risk of skin cancer. The use of sunscreen blocks the formation of vitamin D, which leads to its deficiency even in the summer. nine0003
Potential indicators of vitamin D deficiency are:
- living in geographic latitudes with a small number of sunny days per year
- air pollution
- vitamin deficiency in the diet and semi-finished products).
- lactose intolerance, dairy allergy
- constant use of sunscreen
- overweight
- taking drugs that reduce the bioavailability of vitamin D
- long-term diets of low-fat foods
- chronic diseases that reduce the absorption of all vitamins by the body (cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, biliary dyskinesia, kidney and thyroid diseases).

Vitamin D deficiency can be diagnosed by taking a blood test. According to the clinical recommendations of endocrinologists, it is advisable to use the following interpretation of the concentrations of this micronutrient in the body in practice:
✔ less than 10 (less than 25 nmol/l) - severe deficiency, characterized by an increased risk of rickets, osteomalacia, secondary hyperparathyroidism, myopathy, falls and fractures;
✔ less than 20 ng / ml (less than 50 nmol / l) - micronutrient deficiency, causes an increased risk of bone loss, secondary hyperparathyroidism, falls and fractures;
✔ 20 to 30 ng/ml (50 to 75 nmol/l) - vitamin deficiency associated with low risk of bone loss and secondary hyperparateriosis, neutral effect on falls and fractures; nine0003
✔ from 30 ng/ml (from 75 nmol/l) - adequate D level, optimal suppression of parathyroid hormone and bone loss, reduction in falls and fractures by 20%;
✔ above 150 ng/ml (above 375 nmol/l) - levels with possible manifestation of vitamin D toxicity, hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria, nephrocalcinosis, calciphylaxis.

Given the latest scientific data on the significant impact of this nutrient on the body's susceptibility to viral infections, such knowledge will be useful to every person. nine0035
For the prevention of vitamin D deficiency without an appropriate test, it is recommended to take a therapeutic dose. For children under 3 years old, today it is 500 IU, from 3 to 12 years old - 1000 IU, over 12 years old and adults - 2000 IU. During viral infections, at the risk of oncological and autoimmune diseases, as well as in the fight against excess weight, the dosage should be higher and determined by the doctor.
Daily Values for Vitamin D from the American Society of Endocrinology (2011 data). nine0003
Conclusion
Research on the positive effects of vitamin D on human health is ongoing, but due to the already proven benefits, doctors strongly recommend taking it for therapeutic or prophylactic purposes with food or supplements.