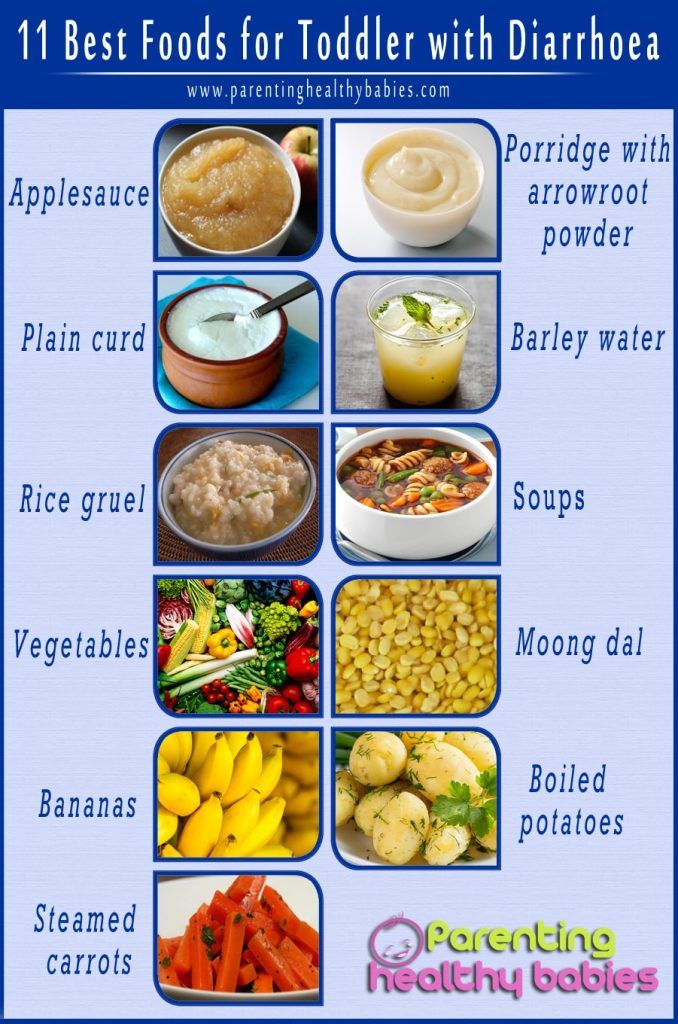
What food to give a baby with diarrhea and vomiting
Vomiting and Diarrhea in Children
Am Fam Physician. 2001;63(4):775-776
What causes vomiting and diarrhea?
Vomiting (throwing up) and diarrhea (frequent, watery bowel movements) can be caused by viruses, bacteria, parasites, foods that are hard to digest (such as too many sweets) and other things.
Can vomiting and diarrhea be dangerous for children?
They can be. Vomiting and diarrhea can be harmful to children because they can cause dehydration. Dehydration occurs when too much fluid is lost from the body. Young babies can become dehydrated very quickly, but dehydration can occur in a child of any age. Signs of dehydration include:
Irritability
Not eating as well as usual
Weight loss
Not urinating (“peeing”) as often as usual
Urine that is darker than usual
Fast heartbeat
Dry mouth
Thirst (babies may show thirst by crying and being irritable and eager to drink when something is offered)
Sunken eyes
No tears when crying
Sunken soft spot in babies younger than 18 months
Skin that isn't as springy as usual
How can I prevent dehydration?
If your child has had several bouts of vomiting or diarrhea, he or she will need to drink fluids to replace those lost with vomiting and diarrhea. Encourage your child older than two years to drink water and other clear fluids. Ask your doctor about giving your baby or toddler oral rehydration solution (ORS), which contains the right mix of salt, sugar, potassium and other elements to help replace lost body fluids.
Ask your doctor about giving your baby or toddler oral rehydration solution (ORS), which contains the right mix of salt, sugar, potassium and other elements to help replace lost body fluids.
What can I give my older child to drink?
Children older than two years can have drinks such as apple juice, chicken broth, sports drinks (Gatorade), ginger ale or tea. Plain water can cause problems, such as lowering the amount of salt or sugar in the blood.
Should I give my child ORS?
If your child is younger than two years and you are worried that he or she is dehydrated, ask your doctor about using ORS. ORS comes as a powder that you mix with water, or a liquid that is already mixed and as frozen popsicles.
Brands of ORS include Pedialyte, Rice-Lyte, Rehydralyte and the World Health Organization's Oral Rehydration Solution (WHO-ORS). Ask your doctor about which one to use.
Should I feed my child during sickness?
Yes. Even though eating may cause the amount of diarrhea to increase, your child will be able to get some nutrients from the food. This may prevent your child from losing too much weight and help your child get better quicker.
This may prevent your child from losing too much weight and help your child get better quicker.
Breast-fed babies. If you are breast-feeding, keep breast-feeding while you give ORS.
Formula-fed babies. If you have been giving your baby formula, some doctors suggest switching from formula to ORS for up to 12 to 24 hours and then switching back to giving formula. Talk to your doctor about what to do.
Children on food. Children should begin eating within about 12 to 24 hours after starting to take ORS. Avoid foods with a lot of sugar and fat, such as ice cream, gelatin, pudding and fried foods.
If your child has had diarrhea, dairy products are best avoided for three to seven days. Sometimes bland foods are recommended for the first 24 hours. Foods that are bland include bananas, rice, applesauce, toast and unsweetened cereals. If these foods don't bother your child, other foods can be added over the next 48 hours. Most children can return to normal eating habits in about three days after the vomiting and diarrhea stop.
Most children can return to normal eating habits in about three days after the vomiting and diarrhea stop.
Should I give my child medicine to stop diarrhea?
This usually isn't needed. Diarrhea doesn't usually last long. If it is caused by an infection, diarrhea is a way for the body to get rid of the infection. Giving medicines that stop diarrhea may interfere with the body's efforts to get rid of the infection. Antibiotics are usually not necessary either. Talk to your family doctor if you think your child needs medicine.
Call your doctor if your child is vomiting or has diarrhea and:
Is younger than six months.
Is older than six months and has a fever higher than 101.4°F.
Has signs of dehydration.
Has been vomiting longer than eight hours or is vomiting with great force.
Has stools that are bloody or slimy.
Has blood or green slime in the vomit.
Hasn't passed urine in eight hours.

Could have swallowed something that could be a poison.
Has a stiff neck.
Is listless or unusually sleepy.
Has had tummy pain for more than two hours.
Diet for Vomiting and Diarrhea (Infant/Toddler)
Vomiting and diarrhea are common in babies and young children. They can quickly lose too much fluid and become dehydrated. This is the loss of too much water and minerals from the body. This can be serious and even life threatening. When this occurs, body fluids must be replaced. This is done by giving small amounts of liquids often.
For babies, breastmilk or formula is the best fluid. Breastmilk can help reduce how serious the diarrhea is. But if your child shows signs of dehydration, their healthcare provider may tell you to use an oral rehydration solution. This can replace lost minerals called electrolytes. It can be used in addition to breast or bottle feedings. Oral rehydration solution may also reduce vomiting and diarrhea. You can buy it at grocery stores and pharmacies without a prescription.
It can be used in addition to breast or bottle feedings. Oral rehydration solution may also reduce vomiting and diarrhea. You can buy it at grocery stores and pharmacies without a prescription.
In cases of severe dehydration or vomiting, a child may need to go to a hospital to have IV (intravenous) fluids.
Giving liquids and feeding
For breast or formula feedings:
-
Continue the breast or formula feedings. Do this unless your healthcare provider says otherwise.
-
If you use formula, the healthcare provider may tell you to try a different kind of formula. A common cause of vomiting in newborns is a problem with formula.
-
Give your baby short, frequent feedings. Feed every 30 minutes for 5 to 10 minutes at a time over a period of 2 to 3 hours. This will help give your baby more fluids.

-
If vomiting or diarrhea doesn't stop, the provider may tell you to give a formula with no lactose, or low lactose. Lactose is a milk sugar that can be hard to digest. Follow the provider's advice about what type of formula to give your baby.
If using oral rehydration solution:
-
Follow the healthcare provider's instructions when giving the solution to your baby. Oral rehydration solution may be alternated with breast or formula feedings.
-
Use only prepared, purchased oral rehydration solution. Don't make your own solution.
-
Give your baby short, frequent feedings. Feed every 30 minutes for 2 to 3 hours. This will help replace lost electrolytes.
-
If vomiting or diarrhea gets better after 2 to 3 hours, you can stop the oral rehydration solution.
 Resume breastmilk or full-strength formula for all feedings.
Resume breastmilk or full-strength formula for all feedings.
For children on solid foods:
-
Follow the diet your child's healthcare provider advises.
-
If desired and tolerated, your child may eat regular food.
-
If unable to eat regular food, your child can drink clear liquids such as water, or suck on ice chips. Don't give high-sugar fluids such as juice or soda. Give small amounts of food and drink often.
-
If clear liquids are tolerated, slowly increase the amount. Alternate these fluids with oral rehydration solution as your healthcare provider advises.
-
Your child can start a regular diet 12 to 24 hours after diarrhea or vomiting has stopped.
 Continue to give plenty of clear liquids.
Continue to give plenty of clear liquids.
Follow-up care
Follow up with your child’s healthcare provider, or as advised. If a stool sample was taken or cultures were done, call the healthcare provider for the results as instructed.
Call 911
Call 911 if your child has any of these symptoms:
When to get medical advice
Call your child’s healthcare provider right away if any of these occur:
-
Fever (see "Fever and children" below)
-
Belly (abdominal) pain that gets worse
-
Constant lower right abdominal pain
-
Repeated vomiting after the first 2 hours on liquids
-
Occasional vomiting for more than 24 hours
-
Continued severe diarrhea for more than 24 hours
-
Blood in vomit or stool (black or red color)
-
Refusal to drink or feed
-
Dark urine or no urine for 8 hours, no tears when crying, sunken eyes, or dry mouth
-
Fussiness or crying that can't be soothed
-
Abnormal drowsiness
-
New rash
-
More than 8 diarrhea stools in 8 hours
-
Diarrhea lasts more than 1 week on antibiotics
Fever and children
Use a digital thermometer to check your child’s temperature.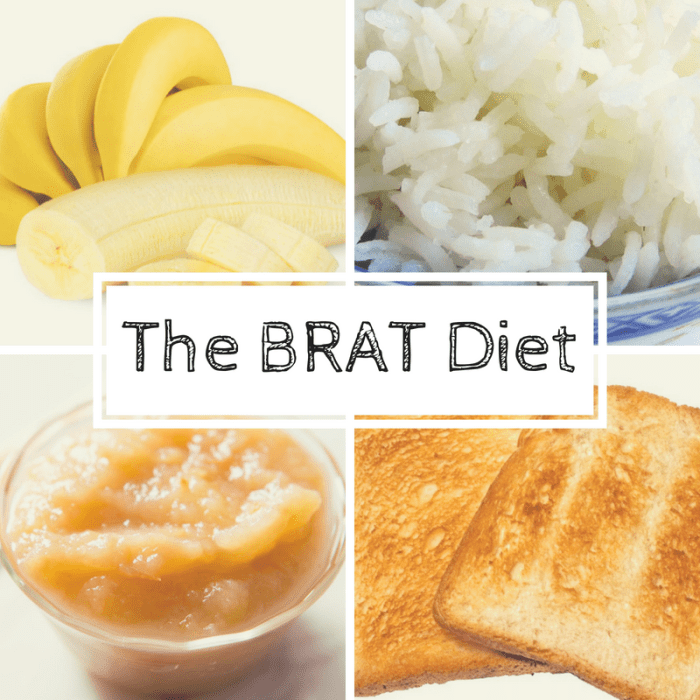 Don’t use a mercury thermometer. There are different kinds and uses of digital thermometers. They include:
Don’t use a mercury thermometer. There are different kinds and uses of digital thermometers. They include:
-
Rectal. For children younger than 3 years, a rectal temperature is the most accurate.
-
Forehead (temporal). This works for children age 3 months and older. If a child under 3 months old has signs of illness, this can be used for a first pass. The provider may want to confirm with a rectal temperature.
-
Ear (tympanic). Ear temperatures are accurate after 6 months of age, but not before.
-
Armpit (axillary). This is the least reliable but may be used for a first pass to check a child of any age with signs of illness.
 The provider may want to confirm with a rectal temperature.
The provider may want to confirm with a rectal temperature. -
Mouth (oral). Don’t use a thermometer in your child’s mouth until they are at least 4 years old.
Use the rectal thermometer with care. Follow the product maker’s directions for correct use. Insert it gently. Label it and make sure it’s not used in the mouth. It may pass on germs from the stool. If you don’t feel OK using a rectal thermometer, ask the healthcare provider what type to use instead. When you talk with any healthcare provider about your child’s fever, tell them which type you used.
Below are guidelines to know if your young child has a fever. Your child’s healthcare provider may give you different numbers for your child. Follow your provider’s specific instructions.
Fever readings for a baby under 3 months old:
Fever readings for a child age 3 months to 36 months (3 years):
-
Rectal, forehead, or ear: 102°F (38.
 9°C) or higher
9°C) or higher -
Armpit: 101°F (38.3°C) or higher
Call the healthcare provider in these cases:
-
Repeated temperature of 104°F (40°C) or higher in a child of any age
-
Fever of 100.4° F (38° C) or higher in baby younger than 3 months
-
Fever that lasts more than 24 hours in a child under age 2
-
Fever that lasts for 3 days in a child age 2 or older
© 2000-2022 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.
Was this helpful?
Yes No
Tell us more.
Check all that apply.
Wrong topic—not what I was looking for.
It was hard to understand.
It didn't answer any of my questions.
I still don't know what to do next.
Other.
NEXT ▶
Last question: How confident are you filling out medical forms by yourself?
Not at all A little Somewhat Quite a bit Extremely
Thank You!
Diet for diarrhea in a 1-year-old child
When a child is sick, it is always a serious test for a family. Moreover, if the baby has vomiting, frequent loose stools, fever, he refuses to eat. In such cases, parents naturally face the question: what to do?
Moreover, if the baby has vomiting, frequent loose stools, fever, he refuses to eat. In such cases, parents naturally face the question: what to do?
The first thing to do is to see a doctor. In most cases, this condition is associated with an acute intestinal infection and can lead to serious consequences for the baby. And timely treatment allows you to quickly deal with the problem.
The second significant issue facing the parents of a sick child is the issue of proper nutrition. Unfortunately, you can still find recommendations for stopping feeding a child during diarrhea, but this should not be done categorically.
Important!
It has been proven that "water-tea" breaks and starvation diets significantly weaken the protective functions of the child's body and lead to a delay in recovery processes in the intestines. Therefore, at present, most pediatricians insist on the mandatory continuation of the child's nutrition in case of acute intestinal infections, but with the obligatory consideration of the latest achievements in nutrition.
The main principles for managing the nutrition of a child with diarrhea should be:
| Phased | The development of the disease has a staging, each stage must correspond to certain approaches to diet therapy |
| Accounting for the age of the child | Each age should have its own products and its own schemes for their purpose |
| Accounting for the severity of the disease |
There are three main stages of diet therapy. The first stage corresponds to the acute period of the disease, when the maximum manifestations of the disease are noted (vomiting, loose stools, fever), and the child may refuse his usual diet. During this period, proper nutrition is an integral part of treatment. And the success of treatment largely depends on the correct organization of diet therapy in a child.
The second stage is the recovery period.![]() There are no longer those manifestations of the disease that were noted in the baby in the acute period, the child has an appetite, he becomes more active, but it must be remembered that any acute intestinal infection leads to significant changes in the child's body. This is a violation of the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract, and dysfunction of enzyme systems, bile secretion and other digestive processes. It takes time to restore the correct functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, which requires a sparing diet at this stage. Violation of the diet during this period can lead to the formation of a chronic pathology of the gastrointestinal tract.
There are no longer those manifestations of the disease that were noted in the baby in the acute period, the child has an appetite, he becomes more active, but it must be remembered that any acute intestinal infection leads to significant changes in the child's body. This is a violation of the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract, and dysfunction of enzyme systems, bile secretion and other digestive processes. It takes time to restore the correct functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, which requires a sparing diet at this stage. Violation of the diet during this period can lead to the formation of a chronic pathology of the gastrointestinal tract.
The third stage of diet therapy is aimed at a gradual transition to the usual diet for this baby. Breastfed babies should continue to breastfeed. If the baby is bottle-fed, the doctor will prescribe a formula that matches the baby's condition. In children older than one year, it is necessary to exclude whole milk from the diet, they are also shown the appointment of fermented milk products as a diet therapy, the favorable properties of which are due to a number of positive qualities: the presence of lactic acid gives the product pronounced bactericidal properties and inhibits the growth of pathogenic microflora, the positive effect of these products on intestinal microbiocenosis, the secretory function of the digestive glands and intestinal motility, and they also have immunomodulatory properties.
One of the important components of diet therapy is the use of dairy-free cereals with pro- and synbiotics. Clinical studies have shown that the appointment of this diet therapy contributes to a more rapid relief of the main symptoms of intestinal dysfunction, as well as the restoration of intestinal microflora.
Choose foods for the diet
It is most correct to start with rice porridge, as it has pronounced sorption properties and helps to stop diarrhea. As the child recovers, oatmeal and buckwheat porridge can be included in the diet.
Vegetables and fruits are an important component in the first stage of diet therapy. Preference should be given to products that contain pectin (baked apple, boiled carrots), as they contribute to the sorption of pathogens and their toxins. At the first stage of diet therapy, the use of fresh vegetables and fruits, as well as juices, is not shown.
The second stage - the patient's condition improves, the child becomes active, appetite improves, and in some children it even becomes elevated, which is often perceived by parents as a signal for increased nutrition. It is absolutely impossible to do this, since the child's body has not yet recovered from the disease. During this period, it is necessary to continue eating sour-milk, lactose-free and low-lactose products. An obligatory component of diet therapy is the use of nutrition with probiotics.
It is absolutely impossible to do this, since the child's body has not yet recovered from the disease. During this period, it is necessary to continue eating sour-milk, lactose-free and low-lactose products. An obligatory component of diet therapy is the use of nutrition with probiotics.
The third stage is the gradual expansion of the diet according to the age of the child. At this stage, the most justified is the widespread use of probiotic foods in order to restore and maintain the function of the gastrointestinal tract and its microbiocenosis.
What to feed a child with diarrhea at first?
- freshly cooked rice;
- bananas;
- natural apple juice;
- boiled potatoes;
- boiled chicken meat;
- crackers and stale bread;
- lean fish;
- weak tea.
Diet for vomiting in a child, nutrition menu after vomiting
How to feed a child after vomiting and diarrhea? This question is asked by all parents, since food poisoning happens periodically to everyone. No one is 100% protected from them. Even when preparing food on your own, you cannot be sure of the quality of the products and that the baby will not eat something in kindergarten or school, and even with dirty hands. In this article, we told you what you can eat after a child vomits, when you need to start eating, what foods you can eat, and which ones should be discarded for a while.
No one is 100% protected from them. Even when preparing food on your own, you cannot be sure of the quality of the products and that the baby will not eat something in kindergarten or school, and even with dirty hands. In this article, we told you what you can eat after a child vomits, when you need to start eating, what foods you can eat, and which ones should be discarded for a while.
Causes of vomiting and diarrhea
Vomiting and diarrhea are common symptoms in children of different age groups. They can be signs of a functional failure in the body, an inflammatory or infectious process, intoxication or poisoning.
Any episode of nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea in a child requires parental attention. It is necessary to monitor the condition of the baby, try not to miss any other symptoms.
- Food poisoning. It can develop due to the consumption of stale and poor-quality food, as well as due to the child's failure to follow the basics of personal hygiene.
 Poisoning is manifested by nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, increased formation of gases in the intestines, and abdominal pain. This state can proceed without temperature.
Poisoning is manifested by nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, increased formation of gases in the intestines, and abdominal pain. This state can proceed without temperature. - Intestinal infection (salmonellosis, dysentery, rotavirus infection, etc.). These diseases are caused by pathogenic microorganisms that can even be found in fresh foods. For example, the source of salmonellosis are eggs, dairy or meat products. Intestinal infection is manifested by profuse watery diarrhea, which may be streaked with blood, mucus, nausea, severe abdominal pain and fever. If left untreated, severe dehydration develops.
- Acetonemic syndrome is a condition in which the level of ketone bodies in the blood rises. This disease develops in children under 7 years of age. A characteristic symptom is the smell of acetone from the baby's mouth and from his urine.
- Child overheating, heatstroke or sunstroke. This condition can be manifested by vomiting, tachycardia, and one-time diarrhea may occur.
 Children under 6 years of age are more sensitive to the influence of the sun and high temperatures. Due to the high sweating, they develop an electrolyte failure and rapid fluid loss.
Children under 6 years of age are more sensitive to the influence of the sun and high temperatures. Due to the high sweating, they develop an electrolyte failure and rapid fluid loss. - Inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (pancreatitis, gastritis, cholecystitis). These pathologies were previously considered more "adult". But over the past 10-20 years, their age category has changed dramatically. Poor quality food, ecology, chemicals "rejuvenated" these diseases. For example, cases of chronic gastritis in a baby at the age of 4 years or pancreatitis at 2 years old are not uncommon.
- Food intolerance, food allergy. For example, a baby's digestive system may not be able to digest dairy products or gluten. Most often, such individual characteristics are detected in a child at an early age, and parents, knowing about them, carefully compose the diet.
The child may vomit from a feeling of disgust for something or during crying, a nervous experience. Children under 5 years of age often vomit against the background of high temperature with SARS and influenza. It is necessary to monitor the condition of your baby, try to understand the cause of the symptoms that have arisen in him.
Children under 5 years of age often vomit against the background of high temperature with SARS and influenza. It is necessary to monitor the condition of your baby, try to understand the cause of the symptoms that have arisen in him.
Basic nutrition rules for diarrhea and vomiting
Diet after vomiting in a child is not required if this symptom is due to disgust, crying or SARS. In all other cases, it is necessary to draw up a specific menu for the child after vomiting and carefully monitor his diet.
Feeding a child with vomiting and diarrhea, according to the latest WHO protocols, can be started as early as the first day of illness. Scientists have proven that hunger does not contribute to a quick recovery. However, eating with nausea and with a complete lack of appetite is also not worth it. Thus, it is possible to provoke a repeated vomiting attack.
Here are some general guidelines to follow when thinking about what to eat after your baby has vomited:
- Feed your baby often.
 Breaks between meals should not exceed 3 hours. If the child is under 3 years old, he should eat every 2 hours. Food should be given in small portions. A single amount of food should not exceed the volume of the child's fist.
Breaks between meals should not exceed 3 hours. If the child is under 3 years old, he should eat every 2 hours. Food should be given in small portions. A single amount of food should not exceed the volume of the child's fist. - All food and drink must be at neutral (room) temperature. Hot, cold can irritate the gastric mucosa, cause nausea, abdominal pain.
- All nutrition after vomiting and diarrhea should not only be dietary and light, but also meet the energy needs of the baby's body. The child needs energy to recover.
- Do not force your child to eat if he is sick on the first day of illness. But you can't go hungry for a long time. You can feel sick from hunger and irritation of the stomach walls with hydrochloric acid.
- Eating during vomiting is categorically contraindicated, you can start feeding the baby only after it stops. If he vomits, begin to give a little to drink table water. It is best to drink it in a sip every 5-10 minutes. This mode of drinking will help start the digestive system, will not allow dehydration to increase.

- The best way to cook baby food is in a double boiler. It can also be boiled or stewed. All dishes should not be spicy or very salty. Spices, seasonings and flavor enhancers are prohibited.
What to eat when vomiting and diarrhea
Food on the first day of illness is very limited. In case of poisoning, you can feed the baby only with rice water, dried white bread or biscuit simple cookies. You can also eat oatmeal cooked to a slimy consistency.
In case of acute gastritis, pancreatitis or intestinal infection, you can start eating only after the permission of your doctor.
- Low-fat chicken broth made from the loin. You can add some carrots, salt to it.
- Boiled lean chicken, turkey or rabbit.
- Oven or microwave baked apples.
- Dried white bread.
- Biscuits.
- Boiled potatoes, carrots, beets, zucchini.
- Bananas.
- Low-fat varieties of hard cheese, cottage cheese, dairy products.

- Buckwheat, oatmeal, rice porridge.
- Boiled eggs, steam omelet.
A small amount of refined vegetable oil can be added to ready meals. Butter, margarine, mayonnaise should be discarded for the period of diet therapy.
In addition to food, special attention should be paid to feeding the baby. The liquid is necessary to reduce the intoxication syndrome and to normalize the water and electrolyte balance.
Give your child plain table water to drink after vomiting and diarrhea. Then he can drink alkaline mineral water, such as Borjomi, black sweet tea, compote.
What not to eat
- Milk (other than breast milk) is a forbidden food product in case of digestive tract malfunction. You can start drinking milk only after 2 weeks.
- Fatty varieties of meat and fish, as well as broths cooked on their basis.
- Chocolate, flour confectionery, fresh bread.
- All sausages, pates.
- Meat by-products.

- Shop semi-finished products.
- Carbonated drinks, coffee, cocoa.
- Juices (store-bought and freshly squeezed).
- Various sauces, tomato paste.
- Cabbage, garlic, onion.
- Citrus and exotic fruits.
- Fat varieties of hard cheese and fermented milk products.
- Fried, fatty, smoked, spicy.
How to choose and buy baby products
Baby food should be safe first and foremost. A weakened children's body is very sensitive to any toxins, preservatives, and low-quality products can cause an exacerbation of the disease or re-food poisoning.
- Buy all products only at official points of sale (shops, markets). Spontaneous bazaars are dangerous places where the goods are not checked and controlled by no one.
- Please check the date of manufacture before purchasing any product. When purchasing meat or fish, do not hesitate to smell it.
- Do not buy ready-made meals for your baby at a cookery or restaurant.
 Only by preparing food on your own, you can safely give it to your child, without doubting the quality of the products and the cleanliness of the hands preparing the dish.
Only by preparing food on your own, you can safely give it to your child, without doubting the quality of the products and the cleanliness of the hands preparing the dish. - Avoid frozen and prepared foods. There is nothing useful left in them. For example, meat becomes useless when frozen, its structural proteins are destroyed and cannot provide the body with the necessary amino acids.
Nausea, diarrhea and vomiting are symptoms that you should always watch out for. Dietary nutrition is a necessary component in the treatment of diseases of the digestive tract, which can be manifested by these symptoms.
Do not try to self-medicate, consult a doctor about the list of allowed and prohibited foods for your child. You can eat a little already in the first day, after the onset of the disease.
All food you give your child must meet his daily energy needs and be safe for his body.
Feeding a child after vomiting: what can and cannot be eaten?
After poisoning, the baby needs special nutrition. This will help him recover faster, improve his well-being. To contribute to a speedy recovery, you need to know what you can feed the child after vomiting, and what is forbidden to give. The principles of nutrition depend on the age that has passed since the time of poisoning. It is necessary to prepare food in special conditions.
This will help him recover faster, improve his well-being. To contribute to a speedy recovery, you need to know what you can feed the child after vomiting, and what is forbidden to give. The principles of nutrition depend on the age that has passed since the time of poisoning. It is necessary to prepare food in special conditions.
Nutrition during vomiting
Poisoning is not the only cause of the gag reflex. But in childhood, in most cases, it leads to rejection of food, diarrhea.
What else causes not eating in childhood:
- intestinal infections;
- gastritis, ulcer;
- reflux;
- head injury, high intracranial pressure;
- sun and heat stroke;
- appendicitis;
- CNS diseases;
You need to know what to eat after a child vomits. But already during it, help should be provided.
Nutrition during an acute condition:
- An important component of first aid is the observance of the drinking regimen.
 Diarrhea and fever increase fluid loss from the body. The balance needs to be restored. In this case, you can not force the baby to drink large amounts of water. This will lead to increased vomiting. You need to drink often and in small sips. The optimal break between fluid intake is every half an hour.
Diarrhea and fever increase fluid loss from the body. The balance needs to be restored. In this case, you can not force the baby to drink large amounts of water. This will lead to increased vomiting. You need to drink often and in small sips. The optimal break between fluid intake is every half an hour. - Too cold or hot liquid is poorly absorbed by the body. Refrigerator water or just brewed tea won't keep you hydrated.
- Do not make tea sweet. Sweets should be avoided.
- In addition to water, it is useful to drink unsweetened dried fruit compotes.
- Regidron or Humana helps to restore the balance.
Important! It is not recommended to feed the baby during vomiting.
Feeding after vomiting in the first days
It will be right to find out what to feed the child after vomiting, depending on the time elapsed after it. On the first day, the body is not ready to accept heavy food. But gradually you need to restore the old nutrition. This must be done correctly so as not to disrupt digestion.
This must be done correctly so as not to disrupt digestion.
Important! If there is bile or an admixture of blood in the vomit, you should immediately consult a doctor!
First day
Feeding the child after vomiting on the first day, when the symptom of poisoning has not yet passed, should be minimal. The kid will not show initiative in eating, as there will be no appetite. Observing the principles of nutrition in the first day, you need to take into account the desires of the baby.
How to feed a baby on the first day of poisoning:
- On the first day, be sure to keep the amount of water you drink. Vomiting with diarrhea helps to remove pathogenic organisms from the body. Along with this, a person loses a lot of fluid and substances necessary for normal functioning. Doctors say that no liquid can replace clean drinking water. But children willingly use juices and compotes. It is not recommended to give sugar on the first day. Rosehip broth is not sweet, it will also remove nausea.

- For the first 6-7 hours, the minor should drink a moderate amount of water. Only then slowly reduce it. It is recommended to add salt to the drink.
- It is on the first day that Regidron or analogues are used.
- After 6 hours, you can include food in the diet. Receptions should be 5-7, but in small portions.
- The kid is given biscuit cookies, puree soup, a baked apple. It is forbidden to eat raw vegetables, thick cereals, dairy products. You can not drink fruit juices, even natural ones.
The second day after vomiting
The second day after the rejection of food is accompanied by relief of the baby's well-being. There is an appetite. There is an opportunity to diversify the food. But parents still need to follow the diet. The body is not ready to return to the previous diet.
How to feed a child on the second day in case of poisoning and vomiting:
- On the second day they give liquid porridge.
 Rice or wheat.
Rice or wheat. - From fruits, apples are allowed, but must be pureed. Vegetables are cooked only. Carrots or broccoli.
- In addition to biscuits, the patient is given white bread crackers. It is recommended to soften them before feeding the baby.
- It is still allowed to drink dried fruit compotes, rosehip decoction. It is recommended to give chamomile tea, it soothes, has an anti-inflammatory effect.
Important! The day after the exacerbation, appetite begins to improve. This is a sign that he is on the mend. If in the future the baby does not show a desire to eat, consult a doctor.
The third day after vomiting
The menu of the third day is diverse, the choice of food depends on the causes of indigestion. You don't have to give up on the diet.
What to give the child on the third day after vomiting:
- Natural fruit juice is introduced into the diet. The purchased product should be with a minimum amount of additives.

- You can not return to the usual amount of food. With each dose, the portions are increased gradually.
- If the cause of the symptom is not poisoning, the child is given low-fat cottage cheese, natural yogurt. It is important that the dairy product is of high quality.
- Kashi is given in liquid form. Milk is added if there is no poisoning poisoning.
- Soups are given on a vegetable basis. They may contain small amounts of grains.
- Kissels are added to the drink. It is important that they are not acidic, as they will irritate the gastric mucosa.
- Fish and meat are given boiled. It is recommended to take low-fat varieties.
Dried fruit compotes remain on the menu. It is a source of essential vitamins. It is allowed to make kissel from rose hips.
Fourth and fifth days
The fourth and fifth days after vomiting gradually return the baby to the previous diet. By this time, the stomach is ready to accept heavier food. These are ordinary soups, rice, buckwheat, fresh fruits and vegetables.
These are ordinary soups, rice, buckwheat, fresh fruits and vegetables.
How to feed a baby on the fourth and fifth days after poisoning:
- 4 days after the acute period, the amount of food should be enough to satisfy the patient's hunger. Portions are the usual size.
- The food should be lean. Any kind of meat and fish is stewed or boiled.
- From drinks, sweet tea, ordinary compotes are allowed. But it is better to refuse sweet soda. It irritates the mucous.
The baby's condition still needs close monitoring. The baby should be given as much food as he needs. But it is important not to lead to overeating.
How to prepare food for a child after vomiting
What is important is what to feed the child with diarrhea and vomiting, and how to prepare food.
It should be as light, safe, useful as possible:
- Food should be cooked without spices. A moderate amount of salt is allowed, it retains water in the body, which is necessary for recovery.

- Food must not be fried. The optimal processing method is boiling, baking, steaming. In this case, the heat treatment should be sufficient. The child's body is weakened and susceptible to pathogens.
- Wash fruits and vegetables well before feeding them. It is recommended to remove the skin.
- In the first days, the products are ground with a blender or other available method.
- The temperature should be comfortable and close to body temperature.
Important! Dishes must be fresh.
What foods can you eat?
What can a small child eat in case of poisoning and vomiting:
- Cereals (oatmeal, buckwheat, rice).
- Lean meats.
- Lean fish.
- White bread.
- Processed vegetables.
- Banana and apple fruit.
- After 3 days kefir, yogurt, cottage cheese, more fatty milk (if there was no diarrhea).
- Tea, rosehip decoction, dried fruit compote.

What foods are not allowed
When poisoning occurs, you need to eat foods that are well absorbed. Most of them can immediately be excluded from the list.
What not to feed the baby:
- Pearl barley, barley groats, millet porridge, legumes.
- Pasta.
- Fatty meat, lard, sausages.
- Smoked products, canned food.
- Raw vegetables and fruits.
- Cookies, cakes, rolls.
- Chocolate and other sweets.
- Fast food.
Peculiarities of feeding children up to a year
How to feed a child after a year with vomiting and after vomiting is easier to decide. What about babies under 12 months old? At this age, it is necessary to consult a doctor. Nutrition will depend on the type of feeding.
How to feed a child up to a year:
- When breastfeeding, the breast is given more often than before. But in small portions. This will aid in better absorption.

- If it is necessary to switch to a mixture, changes are made gradually.
- Complementary foods are refused or portions are reduced.
- Formula-fed 7 meals in small portions.
Doctor Komarovsky's advice
Doctor Komarovsky also answered mothers' questions about what to feed the child immediately after poisoning and vomiting. He claims that the babies are on a special diet. If the condition is accompanied by fever, swelling and other symptoms, you should go to the doctor. In any case, hospitalization is required at the age of 3 years.
Nutrition advice:
- Do not give food during vomiting.
- Drink small portions (2-3 sips), but often.
- Drinking temperature - room temperature.
- Add salt water, rosehip tea, dried fruit compote to the diet.
- Take Enterosgel.
In case of vomiting, it is necessary to prepare dietary food for the child. It is based on a special drinking regime, the exclusion of heavy and irritating food. It is necessary to increase portions gradually. Under the age of 3 years, with vomiting, a doctor's consultation is required.
It is necessary to increase portions gradually. Under the age of 3 years, with vomiting, a doctor's consultation is required.
Feeding a child after vomiting: do's and don'ts
Vomiting in a child most often occurs due to food poisoning, but it can also be provoked by infectious diseases: scarlet fever, rotavirus.
There are other causes of vomiting: head injuries, severe stress, stomach diseases.
In case of repeated vomiting of the child, it is necessary to see a doctor, otherwise dehydration of the body can lead to undesirable consequences, up to death. The correct diet after vomiting is also important.
What to give immediately after vomiting
If the child starts vomiting, it is better not to feed him for the first day. The digestive system needs time to recover.
But, if this is a one-time vomiting that appeared due to severe stress, the diet may not be changed. When vomiting, a person loses a lot of fluid, especially if it is accompanied by diarrhea.
It is important to make up for this loss. How to properly solder when vomiting:
- Don't force your baby to drink a lot of water. Drinking must be fractional and frequent. A child can drink just a few sips, this will be enough.
- Do not give him too cold or hot drinks, the temperature of the liquid should be the same as body temperature. Then the liquid will be well absorbed and dehydration will not begin.
- Do not put sugar, jam or other sweets, even honey, in your drink. If the baby refuses to drink water, give him juice to drink, but before that, dilute it with water so that it becomes transparent.
- Solder with solutions for oral rehydration: Regidron, Hydrovit, Gastrolit, the drug is prescribed by a doctor, mineral water without gas, dried fruit compote, weak tea, rosehip broth.
Day 2 Diet
Do not force your child to eat if he does not want to. You need to feed only if there is an appetite. Your body will tell you when it is ready to eat.
The diet is selected depending on the cause of vomiting. Diet is always individual.
We will tell you about the rules of nutrition common to all diseases. But you will receive exact recommendations only from your doctor.
Nutritional considerations
If it is poisoning or a rotavirus infection, the child's gastrointestinal tract may be affected. To restore their work, observe the following rules:
- Don't force your baby to eat, don't ask him to eat everything on the plate if he doesn't want to.
- He should eat little, but often, every 2 or 2.5 hours, 5-6 times a day.
- The first days he is allowed only liquid or semi-liquid meals.
- Do not give your child hot or cold food.
- Prohibited are dishes that contain aggressive components that damage the mucous membrane.
What to feed
On the 2nd day, if the patient is already better, he does not suffer from vomiting, feed him buckwheat or rice porridge. Porridge should be liquid and boiled. It is better to cook them in water or milk diluted with water. Well, if the cereal is ground, then it will not irritate the stomach.
Porridge should be liquid and boiled. It is better to cook them in water or milk diluted with water. Well, if the cereal is ground, then it will not irritate the stomach.
During the recovery period
The recovery period of the child's body depends on the type of disease, its severity, and the immune system. But usually after 2 weeks after the onset of the disease, the child returns to the usual diet. Until that time, you will have to follow a strict diet.
It is advisable to feed your baby only liquid or semi-liquid foods. Boil food, bake, or stew, steam. Do not give your baby fried foods. All pickles, marinades, canned food, any sauces, spices, food with dyes are prohibited.
What to feed a child:
- Soups. Vegetarian soups are best, but low-fat meat broths are also allowed. Add grated cereals to them. All vegetables should be finely chopped. Put vegetables without coarse fiber in the soup: carrots, potatoes, cauliflower, zucchini.
 You can add meatballs, quenelles.
You can add meatballs, quenelles. - Kashi. Only liquid and boiled. Boil on water, you can add 1/3 of milk. Corn, millet, barley and barley porridges are not allowed. Grate buckwheat and rice. You can put a piece of butter in the porridge.
- Meat and fish, preferably in the form of a soufflé.
Nuances of nutrition for children under one year old
If a child under one year old falls ill, you need to show him to the pediatrician. The doctor will not only prescribe the necessary medications, but also discuss the feeding regimen with you. If the baby is breastfed, he needs to be breastfed much more often than before. In this case, the milk will come in small portions, which is why it is better absorbed.
Sometimes the doctor advises to give up breastfeeding for a while and switch to lactose-free formulas. But even then it is impossible to abruptly transfer the child to the mixture, the transition should be gradual.
And it is better to do this only on the recommendation of a doctor, in case of emergency, otherwise it will be difficult to return to natural feeding later.
It is better to refuse complementary foods during the period of illness, but when the baby gets better, it can be introduced in small portions.
If the child is bottle-fed, he should eat more often, about 7-8 times a day if the condition is moderate, and 5-6 times a day if he feels better. The amount of the mixture, respectively, is reduced, it is better to check the exact numbers with the doctor.
What foods can you eat
To quickly restore the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, you need to choose foods that promote its healing:
- cereals, but not all, oatmeal, buckwheat and rice are allowed;
- lean meat: chicken, rabbit soufflé;
- marine lean fish;
- bread - only white, dried, you can cracker;
- cooked vegetables: boiled beets, carrots, cauliflower or broccoli;
- bananas and baked apples;
- fermented milk products: kefir, yogurt, in 2-3 days - cottage cheese;
- it is useful to drink dried fruit compotes, fruit jelly, rosehip tea, weak slightly sweetened tea.

What foods are prohibited
The child's menu during this recovery period is not very diverse, many foods are prohibited:
It would be difficult for a healthy child to follow this diet. But if the baby has suffered a serious illness or has been poisoned, he will probably have a poor appetite, so it will not be difficult to persuade him to eat right.
A therapeutic diet will provide the child with all the necessary nutrients, unload the gastrointestinal tract as much as possible, and help him recover faster.
If you abandon the diet, there is a high risk of developing chronic inflammation of the digestive organs, later you will have to treat the child's stomach.
Diet after vomiting in children
Hello, moms and dads! Today I wrote an article about the features of the diet after vomiting in children. After all, many still do not know about the diet of a little man after poisoning ...
A child's nutrition requires a particularly careful approach, since the child's body is not yet able to fully process many new products for him, as well as low-quality or stale products. If a child vomits, then the body is fighting and rejecting unacceptable food. As a rule, during such a period, it greatly weakens, and parents need to think about the right diet.
Feeding in case of poisoning
The diet after vomiting in children should be carefully thought out in a complex way, since the work of many organs is disrupted, and requires restoration. During poisoning, vomiting may be accompanied by diarrhea and rising temperature, which together lead to significant fluid loss.
Therefore, the child needs to be provided with plenty of fluids throughout the day. It can be a rosehip decoction, dried fruit compote or herbal tea.
It can be a rosehip decoction, dried fruit compote or herbal tea.
Until the vomiting finally stops, this will be enough. Of course, you should consult with your doctor to determine the cause of poor health (food poisoning, nervous stress, bactericidal infection that has entered the body, concussion, etc.). From food, it is worth limiting yourself to soaked crackers or dry cookies.
Diet for the second day
After the first day, when the vomiting finally stops, the child should be fed little by little, even if he does not want to and is capricious. After the experience, the baby may simply be afraid to eat something so that vomiting does not happen again. But parents should set him up for the fact that it is necessary to eat a little bit in order to restore strength.
From the diet it is necessary to exclude heavy foods that a weakened child's body cannot cope with, namely: meat, fish, fruit juices, sausages, smoked meats, pastries, carbonated water, sweets, vegetable and sunflower oil.
Legumes, vegetable salads (fresh or pickled), oranges, corn, cheese, eggs, fatty foods, whole milk are not recommended for the first few days.
During the diet after vomiting in children, it is planned to take in small proportions such products as one-day kefir, baked apples, bananas, yogurts without additives, sugar-free cereals (except for millet, eggs, barley), boiled carrots and broccoli.
It is also necessary to continue drinking plenty of water. You can purchase medical solutions at a pharmacy, such as Glucosolan, Rihydron, etc., but take them strictly according to the instructions. Daily portions of these drugs are calculated based on the weight of the child.
If "overdone" vomiting may recur.
During the first days, all food is prepared for the child in such a way as not to injure the lining of the stomach. Therefore, it is boiled, steamed, but by no means fried. Porridge from cereals is brought to full boil. All food is crushed or rubbed through a sieve. Rice and hercules decoctions are especially useful during this period. It is undesirable to give hot food, which can injure the stomach.
Rice and hercules decoctions are especially useful during this period. It is undesirable to give hot food, which can injure the stomach.
Diet after vomiting in children on the second or third day
When your baby is a little stronger and appetite starts to return, the number of meals in small portions can be increased up to 7-8 times a day.
During this period, foods such as minced boiled meat (protein helps to remove toxins from the body), cottage cheese, but not more than 30 g, vegetable puree, baked or steamed dishes are introduced into the diet.
Chicken broth with a small amount of homemade croutons will help the child recover.
On the third day, steamed fish or meat cutlets are gradually included in the diet, and rice or buckwheat is served as a side dish. Rich sources of carbohydrates are baked apples, which must be included in the diet.
The best enveloping effect for the walls of the stomach will create kissel, so it is a good product in the diet.
Features of nutrition of infants after vomiting
If the baby, in addition to breast milk, receives artificial complementary foods, it is better to refuse it for the time of feeling unwell.
When he is fully bottle-fed, buckwheat or rice milk formulas are fine.
Children from six months and beyond can cook porridge in water with buckwheat in a ratio of 1:1, and, starting from 8 months, gradually give vegetable puree, meat soufflé, provided that vomiting has already stopped.
Gag reflex in babies can be caused by teething. As a rule, vomiting is short or single. The first days the child needs to be given food in small portions, dividing it into 7-8 meals. Be sure to include dried fruit compote in your diet, which will restore the balance of potassium in the body. You can give rice porridge, diluted milk.
A child's vomiting diet may vary in length depending on the cause of the malaise. A longer and more scrupulous approach requires feeding a child after a serious food poisoning.
In any case, before engaging in self-treatment and self-formation of a diet, it is worth consulting a doctor and, if necessary, passing the appropriate tests.
Please note that vomiting may be caused by a child's intolerance to certain foods, such as dairy. In this case, they should be completely excluded.
Diet during and after vomiting in a child, what can and cannot be fed / Mama66.ru
The child's nutrition should be approached very responsibly. Toddlers react sharply to food that is offered to them for the first time. If products of dubious quality penetrate into the children's stomach, serious consequences for the body can occur. When a child vomits, this means that the internal defense is working: the body is trying to rid the stomach of harmful elements.
Help for a child should be comprehensive. After the vomiting reaction is stopped, parents must decide for themselves the natural question: how to feed the child after vomiting. There was a malfunction of the internal organs. In this case, it is required to support a weak body and restore normal digestion.
In this case, it is required to support a weak body and restore normal digestion.
Feeding during vomiting
When adults detect vomiting reactions in a child, they often state that he has diarrhea (diarrhea), which is accompanied by an increase in the baby's body temperature.
This is a signal that the child is losing a lot of fluid. You can fill its deficiency by providing the patient with plenty of water. In other words, a diet for diarrhea and vomiting begins with drinking plenty of water.
During the first 24 hours, you need to drink the baby in an alternating mode:
- herbal and black tea;
- rosehip decoction;
- mineral or lightly salted water;
- dried fruit compote.
On the second day, it is recommended to start feeding the baby if the vomiting has stopped.
It is important for parents to take into account that the diet depends on the causes of vomiting. If there was a non-compliance with the diet or the child suffered some kind of stress, then after two days you can return to the usual food for the child.
In case of food poisoning or disorders of the nervous system, nutrition should be taken more seriously. It is possible that the advice of a doctor will come in handy.
Read more: How to stop vomiting in a child →
Nutrition after vomiting in the first days
When vomiting was stopped, the question arises - can the baby eat? Here, experts are extremely unanimous: it is necessary to eat.
How foods affect the baby's stomach
At first, to restore the body, the child needs a sparing diet. Children's stomach is not ready to take regular food right away. Parents are encouraged to think about how difficult to digest foods do not get into the weakened food tract. These include:
- meat and fish dishes;
- fruit juices;
- grapes, pears, plums;
- any sweets;
- fresh pastries and all flour products;
- raw vegetables;
- fats in the form of sunflower and butter;
- millet, barley and pearl barley;
- sausages and smoked products;
- carbonated water.
On the first day, an abundance of drinking is a powerful weapon against malaise: boil rose hips, prepare weak, slightly sweetened tea, or make a medical saline solution. It can be Glucosolan, Oralit or Regidron. For every kilogram of body weight, a child can be given no more than 170 g of solution. Servings should be 1-2 teaspoon, otherwise there is a risk of resumption of vomiting.
The work of the stomach will improve quickly if the child is offered to eat in small portions:
- bananas;
- baked apples;
- dried fruit decoction;
- boiled broccoli and carrots;
- plain yoghurts;
- kefir without oxidation.
Features of cooking for a child after vomiting
The main task of the products that the child consumes 24-48 hours after vomiting is to be well absorbed and not irritate the mucous membrane of the child's stomach. For this purpose, food for the baby is crushed with a blender or with a strainer.
Cereals should be brought to a boiled state, for small children they can be rubbed into jelly. Rice and hercules decoctions will have a beneficial effect on the work of the child's gastric tract. Puree and any kind of porridge should not contain sugar. The most valuable is freshly prepared food.
All food that parents give the child to eat in the very first days after vomiting is stewed, boiled, or steamed. Hot food is extremely undesirable, however, like cold food, the delicate walls of the stomach can be injured.
And don't forget: a child won't want to eat right away.
Diet
After 48 hours, you can enter the children's menu:
- Curd mass, not more than 20 g.
- Vegetable puree.
- Liquid or semi-liquid dishes (fat-free soups).
- Foods rich in protein (chopped boiled meat).
- Baked or steamed dishes.
Do not force your child to eat against his will!
The child should eat at least 7 times a day every 2. 5 hours. Any amount of food eaten by the baby can be regarded as the norm. Every day the child's appetite will improve.
5 hours. Any amount of food eaten by the baby can be regarded as the norm. Every day the child's appetite will improve.
Return to a normal diet occurs 4-5 days after the end of vomiting. Diet and a sparing diet require a cycle of 2-3 weeks after the illness.
Peculiarities of nutrition of children under one year old
Children who are breastfed with complementary foods do not need additional nutrition during vomiting. Formula-fed babies digest rice and buckwheat mixtures in milk well.
Six-month-old children benefit from porridge made from buckwheat and rice. They should be boiled in water and milk in a ratio of 1: 1. Complementary foods are allowed to be included in the menu of babies at the end of vomiting: this should be done gradually. The nutrition of a child at the age of 7-8 months implies the presence, in addition to cereals, meat soufflé, vegetable puree, airy cream soup.
Parents will act very wisely if they trust the needs of the child himself, and will not put pressure on him in terms of the quality and quantity of food. Let the baby eat as much as he wants and what he wants.
Let the baby eat as much as he wants and what he wants.
Irina Khubetsova,
especially for Mama66.ru
How to feed a child after vomiting: diet and nutrition rules .
The reflex removal of undigested or partially digested foods with gastric juice through the mouth or nose is called vomiting.
Doctors have been studying this reaction for many years and have come to the conclusion that it is a protective ability to get rid of dangerous, excess food with the help of a gag reflex. The famous doctor Komarovsky noticed: a person needs vomiting, you should not be afraid of it.
At temperature, poisoning, it is accompanied by acute diarrhea. Dehydration of a weakened child's body is inevitable.
Doctors identify several main causes that cause vomiting in a one-year-old baby. Particular attention should be paid to the signs of a reaction (what kind of food you ate, medications taken, possible stresses, injuries, illnesses), then inform your doctor. The most common causes are:
The most common causes are:
- food poisoning;
- excess food;
- unfamiliar food;
- fever;
- concussion;
- teething;
- the use of seasonings and hot spices in the diet of an infant;
- stress;
- antibiotic treatment.
What to do in case of vomiting in a baby
In a single case of nausea, vomiting, a special diet that restores immunity is not required. With the help of a reflex, the small stomach gets rid of harmful toxic substances that accumulate in the intestinal tract. If the attacks are repeated, vomiting is accompanied by diarrhea, the parent must know and take the necessary measures to help.
The first obligatory action for nausea (from 2 times a day) in children is to call an ambulance doctor at home. The doctor will determine the cause, prescribe the appropriate treatment. Before the ambulance arrives, the baby is soldered with liquid to prevent dehydration.
Antiemetics should not be taken. The body is cleansed of pathogenic microflora, it cannot be prevented. Do not forcefully try to feed, the baby will agree to eat when the attack stops.
List of drinks recommended by doctors for vomiting, diarrhea:
- meat, vegetable broth;
- dried fruit compote;
- still mineral water;
- rice water;
- sweet tea;
- kissel.
To give the baby a drink, pour liquid into a bottle. Frequent portions are given to drink. When he refuses to suck from a bottle, drink from a teaspoon 2-3 tablespoons of liquid every 10 minutes.
Poisoning: causes and consequences
Food poisoning - intoxication of the digestive tract by eating spoiled or improperly cooked food. This type of infection is the most common case among one-year-old children.
Infection is not spread by eating fresh, edible, properly prepared foods. Observing proper care for the baby, personal hygiene, eating fresh vegetables and fruits washed in warm water with soap, the infection will not bother the baby. If the rules are not observed, harmful microorganisms enter the body with food:
If the rules are not observed, harmful microorganisms enter the body with food:
- staphylococci;
- E. coli;
- proteus;
- Klebsiella.
When they enter the immature microflora of a child's body, pathogens spread rapidly, causing intoxication, salmonellosis, dysentery, escherichiosis, and other dangerous infections. Diseases are dangerous, without appropriate treatment lead to adverse consequences.
Symptoms of poisoning
Strong symptoms of poisoning in a child:
- sharp pains in the stomach;
- sudden deterioration in well-being;
- pale complexion;
- diarrhea;
- fever;
- nausea;
- frequent vomiting.
The baby is very sick, diarrhea appears. The temperature may rise or fall. The described symptoms require an immediate examination by a doctor. Symptoms may occur at normal temperatures.
When the disease is exacerbated, children have no appetite, Dr. Komarovsky recommends constantly giving the baby water-salt solutions, compotes, kissels to drink.
Komarovsky recommends constantly giving the baby water-salt solutions, compotes, kissels to drink.
When restoring digestion, the properties of products to be absorbed by the body are taken into account. The wrong diet will lead to indigestion.
Restorative Diet for Children
Breastfed infants under one year of age should not receive complementary foods. Mother's milk is an easily digestible product containing vitamins and microelements necessary to restore digestion. Resume the introduction of complementary foods after complete recovery.
A bottle-fed one-year-old baby is more difficult to properly feed after vomiting. In the early days, products that create a positive microflora in the body and are quickly absorbed in the intestinal tract are acceptable. In a year, you can not feed the baby with solid food that can irritate the intestinal mucosa.
Liquid, semi-liquid vegetable broths, low-fat meat pates for baby food. Milk porridge from rice, buckwheat, fat-free cottage cheese, vegetable puree. You can feed a child with a banana, a baked apple, fresh kefir, boiled carrots, dried fruit compote. Dried fruits are a good substitute for sweets.
You can feed a child with a banana, a baked apple, fresh kefir, boiled carrots, dried fruit compote. Dried fruits are a good substitute for sweets.
Baby's menu to restore digestion
Food from the menu is divided into 7 meals, after vomiting the child does not eat everything at a time. You need to feed after 2-3 hours. When a child refuses to eat, you can not force. It is better to drink sweet tea.
- For breakfast - liquid oatmeal, kefir.
- Baked apple for afternoon tea.
- At lunch, buckwheat porridge and chicken broth, jelly.
- First dinner. Low-fat baby cottage cheese, banana. Sweet tea.
- Second dinner. Semi-liquid rice porridge with boiled fish, egg, kefir.
- At the end of the day offer low-fat yoghurt with breadcrumbs.
The menu is expanded depending on the taste needs of the child. Prohibited foods for a child during a recovery diet:
- sausages;
- smoked products;
- canned food;
- legumes;
- fruit juices;
- raw fruits, vegetables;
- fatty meats, lard;
- fried;
- sunflower, cream fats.

Diarrhea Diet
Feeding an infant with diarrhea should not contain food that relaxes the gastrointestinal tract. Beetroot is a strong laxative vegetable, it should not be used. Products are excluded from food: prunes, potatoes, desserts, freshly squeezed juices, chocolate and sweets. Milk, milk mixtures will aggravate the situation.
In case of diarrhea, the child should be fed rice liquid milk-free porridge, breadcrumbs soaked in water. Soup in white broth will help restore digestion. Banana contains potassium, the fruit should be included in the daily diet.
It is forbidden to feed fresh fruits to babies. Baked apples, on the contrary, are recommended after diarrhea, nausea. After kefir, the microflora improves.
Doctors recommend taking bifidobacteria after poisoning to restore beneficial intestinal flora.
Rules of nutrition
During the recovery diet, the regime changes fundamentally. Food is consumed in small portions every 2-3 hours. Refuse cold and hot. The portion size does not exceed the size of a fist. The mode helps the stomach digest food faster and does not burden the liver and pancreas.
Refuse cold and hot. The portion size does not exceed the size of a fist. The mode helps the stomach digest food faster and does not burden the liver and pancreas.
Frequent consumption of liquid in the form of compotes, jelly, yogurt, sweet tea will restore the water balance in the body and help the stomach recover. Adhere to diet should be 10-14 days.
After graduation, the child should not be allowed to eat forbidden food. It is necessary to introduce the usual diet gradually, one species every two days, observing the condition of the child.
If he experiences discomfort from the product, do not give it again.
In order to memorize what foods were introduced, what the child has a negative reaction to, start a notebook and write down all observations there. The reaction of the body to the introduced products is diverse.
You can find out that the food is not suitable for the baby by colic, rashes on the face, liquid or, on the contrary, excessively hard stools.