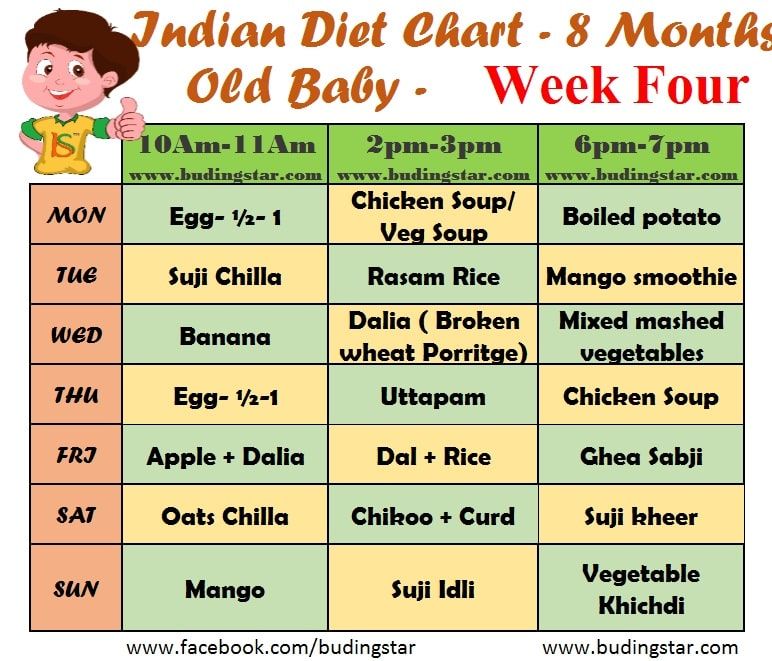
What foods do you give baby first
Feeding Your 4- to 7-Month-Old (for Parents)
Most babies this age are ready to try solid foods. Experts recommend starting solid foods when a baby is about 6 months old, depending on the baby's readiness and nutritional needs.
Be sure to check with your doctor before giving any solid foods.
Is My Baby Ready to Eat Solid Foods?
How can you tell if your baby is ready for solids? Here are a few hints:
- Does your baby swallow food or push it out of their mouth? Babies have a natural tongue-thrust reflex that pushes food back out. Wait until this reflex disappears (typically when babies are 4–6 months old).
- Can your baby support their own head? To eat solid food, an infant needs good head and neck control and should be able to sit up.
- Is your baby interested in food? Babies who stare, reach and grab, and open their mouths for food are ready to try solid foods.
If your doctor gives the go-ahead but your baby seems frustrated or uninterested in solid foods, try waiting a few days before trying again. Breast milk and formula will still meet nutritional needs as your baby learns to eat solid foods. But after 6 months, babies need the added nutrition — like iron and zinc — that solid foods provide.
Do not add cereal or other food to your baby's bottle because it can lead to too much weight gain.
Watch for signs that your child is hungry or full. Respond to these cues and let your child stop when full. A child who is full may suck with less enthusiasm, stop, or turn away from the breast or the bottle. With solid foods, they may turn away, refuse to open their mouth, or spit the food out.
How Should I Start Feeding My Baby Solid Foods?
When your baby is ready and the doctor says it’s OK to try solid foods, pick a time of day when your baby is not tired or cranky. You want your baby to be a little hungry, but not so hungry that they’re upset. So you might want to give your baby a little breast milk or formula first.
Have your baby sit supported in your lap or in a high chair with a safety strap.
Most babies' first food is iron-fortified infant single-grain cereal mixed with breast milk or formula. Place the spoon near your baby's lips, and let the baby smell and taste it. Don't be surprised if this first spoonful is rejected. Wait a minute and try again. Most food offered to your baby at this age will end up on the baby's chin, bib, or high-chair tray. Again, this is just an introduction.
When your little one gets the hang of eating cereal off a spoon, it may be time to try single-ingredient puréed meat, vegetables, or fruit. The order in which you give them doesn't matter, but go slow. Offer foods that are high in iron and zinc — such as meat, poultry, eggs, and beans — especially if your baby is breastfeeding. Try one food at a time and wait several days before trying something else new. This will let you identify any foods that your baby may be allergic to.
Which Foods Should I Avoid?
Foods that are more likely to cause allergies can be among the foods you introduce to your baby. These include peanuts, eggs, cow’s milk, seafood, nuts, wheat, and soy. Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies. Talk to your doctor if you’re concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
These include peanuts, eggs, cow’s milk, seafood, nuts, wheat, and soy. Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies. Talk to your doctor if you’re concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
Infants with severe eczema or egg allergies are more likely to have allergies to peanuts. Talk to your doctor about how and when to introduce these foods to your child.
Possible signs of food allergy or allergic reactions include:
- rash
- bloating or an increase in gassiness
- diarrhea
- vomiting
Get medical care right away if your baby has a more severe allergic reaction, like hives, drooling, wheezing, or trouble breathing.
If your child has any type of reaction to a food, don't offer that food again until you talk with your doctor.
Babies shouldn't have:
- foods with added sugars and no-calorie sweeteners
- high-sodium foods
- honey, until after the first birthday.
 It can cause botulism in babies.
It can cause botulism in babies. - unpasteurized juice, milk, yogurt, or cheese
- regular cow's milk or soy beverages before 12 months instead of breast milk or formula. It’s OK to offer pasteurized yogurt and cheese.
- foods that may cause choking, such as hot dogs, raw carrots, grapes, popcorn, and nuts
Tips for Feeding Your Baby Solid Foods
With the hectic pace of family life, most parents try commercially prepared baby foods at first. They come in small, convenient containers, and manufacturers must meet strict safety and nutrition guidelines.
If you prepare your own baby foods at home, here are some things to keep in mind:
- Follow the rules for food safety, including washing your hands well and often.
- To preserve the nutrients in your baby's food, cook it in ways that keep the most vitamins and minerals. Try steaming or baking fruits and vegetables instead of boiling, which washes away the nutrients.
- Freeze portions that you aren't going to use right away.

- Whether you buy the baby food or make it yourself, texture and consistency are important. At first, babies should have finely puréed single-ingredient foods. (Just applesauce, for example, not apples and pears mixed together.)
- After your baby is eating individual foods, it's OK to offer a puréed mix of two foods. As babies get older, they will learn to eat a greater variety of tastes and textures.
- If you use prepared baby food in jars, spoon some of the food into a bowl to feed your baby. Do not feed your baby right from the jar — bacteria from the baby's mouth can contaminate the remaining food. If you refrigerate opened jars of baby food, it's best to throw away anything not eaten within a day or two.
- Around 6 months of age is a good time for your baby to try a cup. You might need to try a few cups to find one that works for your child. Use water at first to avoid messy clean-ups. Do not give juice to infants younger than 12 months.
Over the next few months, introduce a variety of foods from all the food groups. If your baby doesn't seem to like something, don’t give up. It can take 8 to 10 tries or more before babies learn to like new foods.
If your baby doesn't seem to like something, don’t give up. It can take 8 to 10 tries or more before babies learn to like new foods.
Do's and Don'ts for Baby's First Foods
Breastfeeding has been shown to improve infant, child and maternal health outcomes and help control healthcare costs, but how long should breastfeeding last and when should parents introduce solid foods?
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend exclusive breastfeeding, meaning the infant receives only breast milk, during the first six months of life for optimal nutrition and health benefits.
Once solid foods are introduced, health professionals recommend continuing breastfeeding through 12 months of age and, after that, as desired by mother and baby. Introducing your baby to solid foods is an exciting milestone. When you start introducing children to the world of solid foods, you are helping them shape their relationship with food and establish a healthy eating style. The timing for introducing solid foods will depend on the infant, but it is not recommended before the age of four months or after the age of six months.
Not sure how to get your baby started on solid foods? Consider these helpful tips.
Is Your Baby Ready to Transition?
Each child's readiness for solid food depends on their own rate of development. Signs a baby may be ready to start solid foods include sitting up with minimal support, demonstrating good head control, bringing objects to the mouth or grasping at small objects. Check with your pediatrician before starting solid foods.
Getting Started With Solids
Solid foods may be introduced in any order. However, puréed meats, poultry, beans and iron-fortified cereals are recommended as first foods, especially if your baby has been primarily breastfed, since they provide key nutrients. Only one new single-ingredient food should be introduced at a time.
Softer textures are very important when first introducing foods. Infants usually start with pureed or mashed foods around six months. As infants develop chewing and motor skills, they are able to handle items like soft pieces of fruit and finger foods. As the child ages, a variety of healthful foods is encouraged.
As the child ages, a variety of healthful foods is encouraged.
Weaning From Breastfeeding
When deciding if you should wean your baby to a bottle or a cup, consider their developmental readiness. Between 7 and 8 months, most infants will drink small amounts of liquid from a cup or a glass when someone else holds it. Older babies and toddlers often have the coordination to drink fluids from a cup by themselves.
If your baby is under 12 months of age and you are not continuing to breastfeed, wean from breast milk to iron-fortified infant formula. If your baby is 12 months or older, whole cow’s milk is appropriate.
Food Safety Do’s and Don’ts
Food safety concerns for infants and toddlers include food allergies, choking and risks for foodborne illness. Keep the following safety tips in mind:
Do talk with your pediatrician about the risk of food allergies. Introducing one new food at a time, every several days, allows time to monitor for allergic reactions. Current evidence does not indicate needing to wait beyond 4 to 6 months before introducing potential allergy-causing foods such as eggs, dairy, soy, peanuts and fish. In fact, introducing peanut-containing foods as early as 4 to 6 months of age may help prevent a peanut allergy. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends introducing potentially allergenic foods when other complementary foods are introduced to an infant’s diet. Parents with concerns about food allergies should discuss how to include these foods with their pediatrician.
Current evidence does not indicate needing to wait beyond 4 to 6 months before introducing potential allergy-causing foods such as eggs, dairy, soy, peanuts and fish. In fact, introducing peanut-containing foods as early as 4 to 6 months of age may help prevent a peanut allergy. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends introducing potentially allergenic foods when other complementary foods are introduced to an infant’s diet. Parents with concerns about food allergies should discuss how to include these foods with their pediatrician.
Don’t feed your baby solid foods from a bottle. It can be a choking hazard and despite a popular misconception, putting cereal in a baby's bottle won't help with sleeping through the night. Other foods that are considered to be choking hazards are listed below.
Do supervise your child while eating. Infants should be able to sit upright and face forward when you first introduce solid foods. This makes swallowing easier and choking less likely.
Don’t feed directly from the jar of food but instead spoon some food into a separate dish first. Feeding directly from the jar may introduce bacteria from your baby's mouth to the spoon and back into the food, creating a food safety issue.
Don’t feed honey to children under 12 months of age due to the risk of foodborne illness.
Examples of appropriate solid foods listed by age:
6 months:
- Well-cooked and pureed meat, poultry or beans
- Ground, cooked, single-grain cereal or infant cereal with breast milk or formula
- Cooked and pureed vegetables
- Mashed banana or avocado
9 months:
- Well-cooked, minced or finely chopped meat, poultry or beans
- A variety of cooked vegetables cut into small, ½ inch pieces, such as squash and green beans
- Sliced and quartered bananas or small pieces of other soft fruits
12 months:
- Soft, shredded meat, poultry or fish
- Small pieces of cooked vegetables
- Small pieces of soft, easy to chew fruits
- Mixed food dishes the family is eating in appropriately sized pieces
Not recommended for those under 4 years of age due to the risk of choking:
- Popcorn and whole kernel corn
- Nuts and seeds
- Large chunks of meat, poultry and cheese
- Candy, gum drops and jelly beans
- Hard, raw fruits or vegetables such as apples, celery and carrots
- Whole grapes and cherry tomatoes, unless cut into quarters
- Hot dogs, unless cut into strips and age appropriate, bite-size pieces
- Sticky foods, such as peanut butter, which can get stuck in the back of the mouth – peanut butter is okay if spread thinly on bread
For toddlers and preschoolers, chop grapes, meat, poultry, hot dogs and raw vegetables and fruits into small pieces (about ½ inch or smaller).
Nurturing Healthy Relationships with Food
Establishing a positive feeding relationship during infancy can have lifetime benefits. Keep in mind that children are responsible for how much and whether they eat so always wait for your baby to pay attention to each spoonful before you feed them. Don't be afraid to let your baby touch the food in the dish and on the spoon. You wouldn't want to eat something if you didn't know anything about it, would you? In addition, know the cues that your baby is done eating. A common cue babies are full is head turning.
Whatever happens, don't get discouraged and enjoy the experience. With a little patience and creativity, you can make your baby's first solid food eating experience fun for everyone involved!
Tags
- Tag 1
Find a Nutrition Expert
Looking for credible nutrition information and recommendations? The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics' network of credentialed food and nutrition practitioners are ready to help!
See Directory
What foods are needed in a child's diet in winter
The main rules for a child's healthy diet in winter .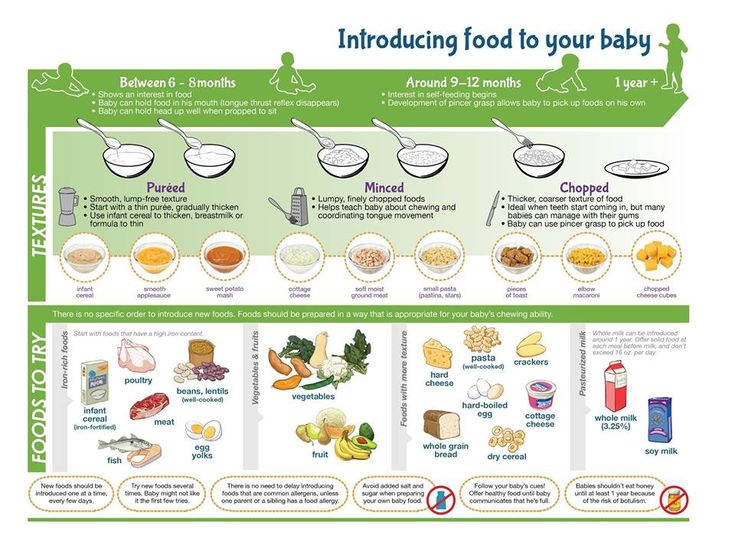 ..
..
Winter can be a real problem for parents: due to the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the child's body and external causes, small children can get sick significantly in the cold season more often. Nutrition plays an important role in maintaining health: at any time of the year, and especially in winter, it is important that it be balanced.
Basic rules for a healthy diet for children in winter
Outdoors in winter, the body expends a lot of energy in order to maintain body temperature, so it is better to build the menu in such a way that the diet contains easy-to-digest, but satisfying, tasty and healthy dishes. For example, you can include vegetables that contain, among other things, also dietary fiber, which will support your child's digestion. In particular, it is known that root vegetables containing a large amount of starch will help the body get additional energy , therefore, you can safely include carrots, potatoes, onions and beets in your daily diet.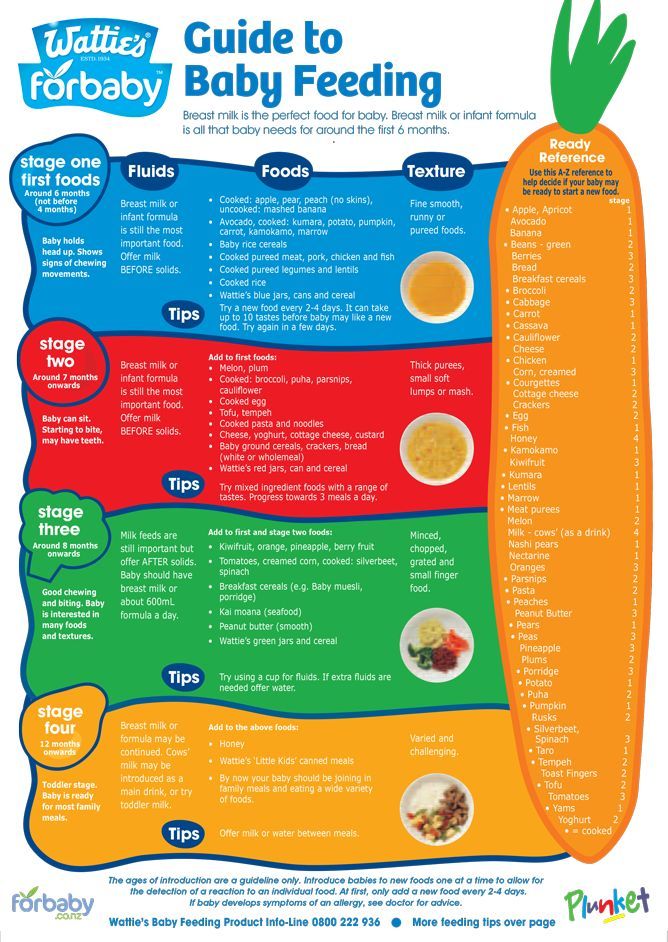 First courses, for example, soups made from them, will help to warm up after a long walk and not only. And dark orange veggies like sweet potatoes, pumpkins, and carrots will replenish your diet with beta-carotene, an antioxidant that helps protect your cells from environmental damage.
First courses, for example, soups made from them, will help to warm up after a long walk and not only. And dark orange veggies like sweet potatoes, pumpkins, and carrots will replenish your diet with beta-carotene, an antioxidant that helps protect your cells from environmental damage.
Regularly introduce children to new flavors and foods and don't give up if they don't hit their plate right away. The more varied the diet, the better: grains, vegetables, fruits and berries, meat, fish, dairy and sour-milk products, legumes, animal and vegetable fats, eggs, flavoring foods, such as greens - all these food groups should be included in the child's diet and adult.
As for the cooking method, preference should be given to baking, stewing, steaming or boiled food. Fried food has nothing to do with healthy nutrition for a child.
Supplementary meals are also important: they will help if the child cannot bear the breaks between main meals. It is better that these are not empty calories due to sweets, but something useful. For example, fruit and berry purees, children's fruit snacks, children's cereal bars, children's drinking porridge with inulin, children's milkshake, children's fermented milk drink or cottage cheese.
For example, fruit and berry purees, children's fruit snacks, children's cereal bars, children's drinking porridge with inulin, children's milkshake, children's fermented milk drink or cottage cheese.
Top 3 foods that are essential in the diet in winter
- Foods high in calcium, magnesium, potassium.
Pay attention to foods that contain a lot of calcium and magnesium (spinach, sesame, dill, cheese, nuts, cereals, broccoli and others) - they fill the body with energy, helping to warm up. Potassium-rich foods also work. Most of all it is in seaweed, prunes, raisins, peas, potatoes, oatmeal, beets, black currants. Rich in potassium and beef, cod, hake, mackerel, squid fillet.
- Source of vitamins A, C, E, D
Vitamins also protect our body. We can and should get them, first of all, from food. For example, vitamin A is found in butter, liver, and eggs. Record holders for the content of vitamin C are rose hips and currants, fresh apples, broccoli, cauliflower and white cabbage, sea buckthorn, greens. Vitamin E is found in vegetable oil and some grains, as well as seeds and seeds. Vitamin D is also important for harmonious development, the production of which is facilitated by such a rare sun in the autumn-winter period. One of the important functions of vitamin D is participation in the proper functioning of the immune system. In conditions of insufficient sunlight, it is important not to forget to take vitamin D in the dosage recommended by a specialist.
Vitamin E is found in vegetable oil and some grains, as well as seeds and seeds. Vitamin D is also important for harmonious development, the production of which is facilitated by such a rare sun in the autumn-winter period. One of the important functions of vitamin D is participation in the proper functioning of the immune system. In conditions of insufficient sunlight, it is important not to forget to take vitamin D in the dosage recommended by a specialist.
- Dairy products
At an early age, fermented milk products supplement the child's diet with important nutrients and help in the formation of the intestinal microflora of the baby. For example, fermented milk products "FrutoNyanya" Immuno Baby is a fermented milk product that helps strengthen immunity in babies from 8 months. It is enriched with probiotics - live beneficial microorganisms that strengthen the immune system and support digestion. They fight pathogenic bacteria, improve the absorption of essential substances by the body. It has been clinically proven that fermented milk products can positively influence the body's defenses when consumed regularly. And if the microflora is in order, then there will be less chance of getting sick and .
It has been clinically proven that fermented milk products can positively influence the body's defenses when consumed regularly. And if the microflora is in order, then there will be less chance of getting sick and .
what can be given, what fruits and vegetables, how to feed a 7-month-old baby on breast or artificial feeding
Healthy nutrition allows the baby to grow and develop properly. Despite the fact that breast milk remains the basis of the diet, complementary foods also become important for the child. Acquaintance with new products should be carried out carefully, starting with a small amount, monitoring the reaction and getting used to changes in nutrition. What can you eat at 7 months? The list is replenished with fruits and vegetables, cereals and mashed meats, and you can drink children's tea or water.
Content: Hide
- Acquaintance with new products
- Features of the introduction of new products in the menu of new products
- Approximate food mode in 7 months
- In what form to give products
- DISCOUS OF 7 months
- Important recommendation
Getting to know new products
You need to start feeding your baby gradually, moving from simple to complex.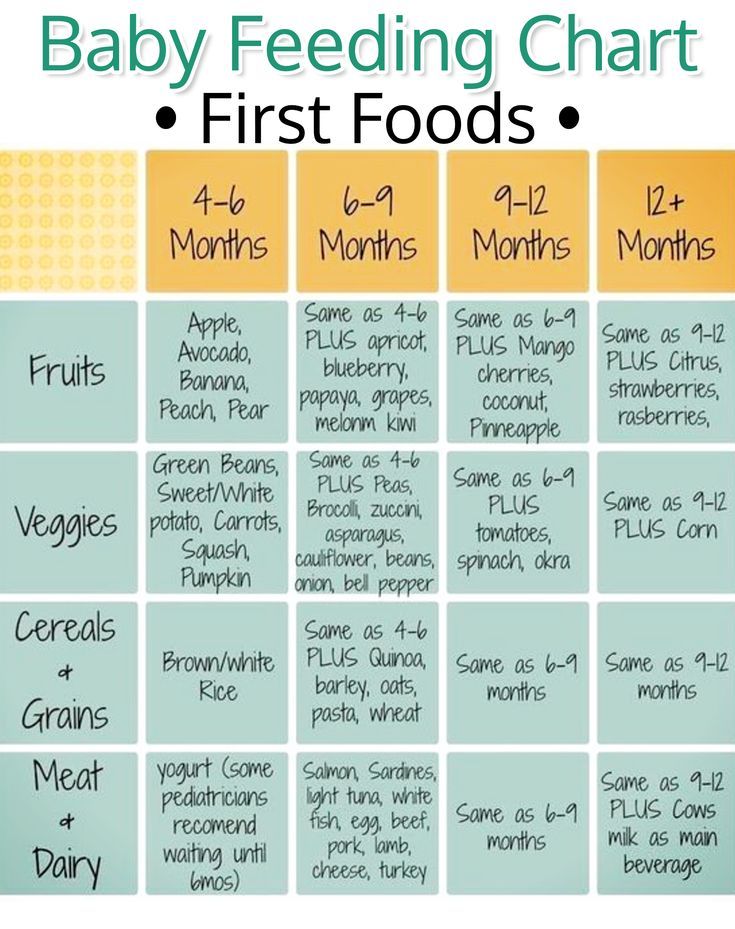 At first, it is better to use one-component products - vegetable purees or cereals. Fruits should be introduced after them, as a pleasant addition to the main course. Over time, you can add new ingredients, increase portions and make the consistency thicker, with pieces of fruit or vegetables. At the same time, the feeding scheme for each baby is individual.
At first, it is better to use one-component products - vegetable purees or cereals. Fruits should be introduced after them, as a pleasant addition to the main course. Over time, you can add new ingredients, increase portions and make the consistency thicker, with pieces of fruit or vegetables. At the same time, the feeding scheme for each baby is individual.
Features of the introduction of new products in the menu
Pay close attention to the signals your child gives you. He is probably already full if:
- turns away from the spoon and closes his mouth;
- is easily distracted by extraneous factors;
- pushes and tries to throw food away;
- starts to eat much more slowly.
It is normal if the amount of food varies from feeding to feeding. However, if the child has become restless, an intestinal disorder or a rash has appeared, then complementary foods should be discontinued and wait until all symptoms disappear, and then offer another product. Bad experiences should also be reported to the pediatrician.
Approximate diet
The child should have a clear daily routine, this also applies to the organization of nutrition. As a rule, children eat five times a day. An example menu might look like this:
First meal. Occurs at 6 am and consists of mother's milk or special formula if the baby is formula-fed. Doctors usually recommend that you breastfeed your baby for as long as possible, if possible, and add supplemental foods gradually.
Second meal. At 10 am it's time for the children's breakfast. The basis for it is porridge. Also, a child at 7 months old can eat boiled chicken yolk - this is a source of vitamin B12, selenium and phosphorus. During breakfast, you can offer your baby a new product. The child is already hungry enough to try it, and mom will have time to track the reaction throughout the day.
Third meal. Lunch usually starts at 2 p.m. - this is the most satisfying meal, followed by a walk.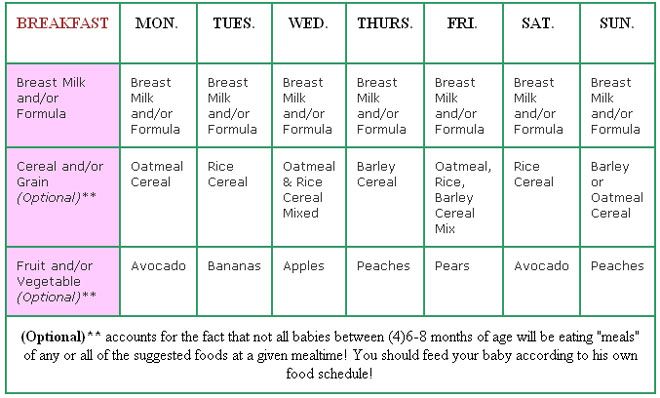 If in the morning you did not give the baby unfamiliar foods, then you can introduce something new into the diet. Vegetable and / or meat puree, porridge with a vegetable component are suitable for lunch, if the child did not receive porridge in the morning.
If in the morning you did not give the baby unfamiliar foods, then you can introduce something new into the diet. Vegetable and / or meat puree, porridge with a vegetable component are suitable for lunch, if the child did not receive porridge in the morning.
Fourth meal. At 6 pm, afternoon tea time. Unfamiliar products should not be present here. The main task of this meal is to replenish the energy spent in the morning and on a walk. Bebi milk porridges contain natural fruit additives and biscuits. The dish is balanced in terms of the composition of nutrients (fats, proteins, carbohydrates) and gives strength for an active evening.
Fifth meal. At 10 pm, the regimen is completed with mother's milk or IV formula. Feeding something else is not worth it in order to exclude overeating, as well as the possible consequences of getting to know new products.
Read also: Complementary foods and dishes
How to give food
The list of what a child can eat at 7 months is already quite wide, compared with crumbs up to six months. Preparing a dish for a baby is not difficult at all. If you decide to feed your child mashed vegetables, then they need to be peeled, boiled and chopped in a blender. Fruit puree is even easier: they don't need to be boiled, although some can be baked beforehand. Particularly hard foods can first be passed through a meat grinder, and then use a blender. Soft fruits are easy enough to grate. If you are giving egg yolk, boil the eggs for at least 15 minutes.
Preparing a dish for a baby is not difficult at all. If you decide to feed your child mashed vegetables, then they need to be peeled, boiled and chopped in a blender. Fruit puree is even easier: they don't need to be boiled, although some can be baked beforehand. Particularly hard foods can first be passed through a meat grinder, and then use a blender. Soft fruits are easy enough to grate. If you are giving egg yolk, boil the eggs for at least 15 minutes.
Why is self-catering not always appropriate? Pediatricians recommend using cereals, mashed potatoes and other industrial products when organizing the nutrition of a child at 7 months. Such complementary foods are produced taking into account strict hygienic requirements, have the necessary degree of grinding and a verified composition, including vitamins, and, if necessary, are enriched with minerals, pre- and probiotics, omega-3 and other biologically active components.
Baby's diet at 7 months
Porridge. At the age of 7 months, porridge is already a familiar product in the baby's diet. During this period, the volume of complementary foods per day is 150 g. Dairy cereals or fruit and cereals, dessert (for an afternoon snack), vegetable and probiotic-enriched porridges of industrial production are selected.
At the age of 7 months, porridge is already a familiar product in the baby's diet. During this period, the volume of complementary foods per day is 150 g. Dairy cereals or fruit and cereals, dessert (for an afternoon snack), vegetable and probiotic-enriched porridges of industrial production are selected.
Vegetable puree. First foods must have soft dietary fiber. Zucchini, pumpkin, broccoli or cauliflower will do. Later, you can add carrots, beets, potatoes. Legumes are recommended to be introduced after 8 months as they can contribute to gas and bloating. Puree for a child should not contain salt or spices. You need to feed the baby gradually, starting with one teaspoon and gradually increasing the portion. For 7 months, the average volume is about 150 g.
Meat puree. If the child is prone to skin allergic reactions to complementary foods, then a rabbit or turkey is a good place to start. If you are allergic to milk proteins, beef and veal should be excluded. With iron deficiency, rabbit meat is recommended - it contains a lot of this substance. Meat puree should be combined with vegetable puree and given at lunchtime. In this combination, iron is well absorbed. In the first days, you can dilute the puree with vegetable broth or breast milk - a familiar taste will help speed up adaptation to new products.
With iron deficiency, rabbit meat is recommended - it contains a lot of this substance. Meat puree should be combined with vegetable puree and given at lunchtime. In this combination, iron is well absorbed. In the first days, you can dilute the puree with vegetable broth or breast milk - a familiar taste will help speed up adaptation to new products.
Fruit puree. It is introduced after the child has become acquainted with cereals, vegetables and meat. For the first time, apple or pear puree is suitable - they are easier to digest. Apricots, bananas, plums and berries are medium allergenic foods, so the baby is introduced to them later. Melon, strawberries and citrus fruits can be given at the age of about one year. If you choose ready-made products, then pay attention to the composition: it is better if the puree does not contain sugar, starch and other additional components.
Baby biscuits. It can be given as a treat. Ordinary sweets are not suitable for a child at this age, as well as bread or crackers, to which he can reach. You need to choose specialized products designed specifically for babies. They are introduced into the diet in the same way as other types of complementary foods, given in the morning and monitoring the reaction.
You need to choose specialized products designed specifically for babies. They are introduced into the diet in the same way as other types of complementary foods, given in the morning and monitoring the reaction.
Drinks
A 7-month-old baby should only drink water and baby tea. As for regular tea, WHO does not recommend its consumption by infants and young children. This is due to the fact that such a drink contains tannins, as well as other compounds that bind iron and other minerals, which reduces their bioavailability.
Experts also recommend delaying juices. So, in the “Program for optimizing the feeding of children in the first year of life in the Russian Federation”, the following is said about the drink: “Given their insignificant nutritional value, it is advisable to prescribe only after the introduction of all the main types of complementary foods. In addition, the use of juices, especially between meals, increases the risk of tooth decay. A large volume of juices (above the recommended amount) can serve as a risk factor for overweight in the future.