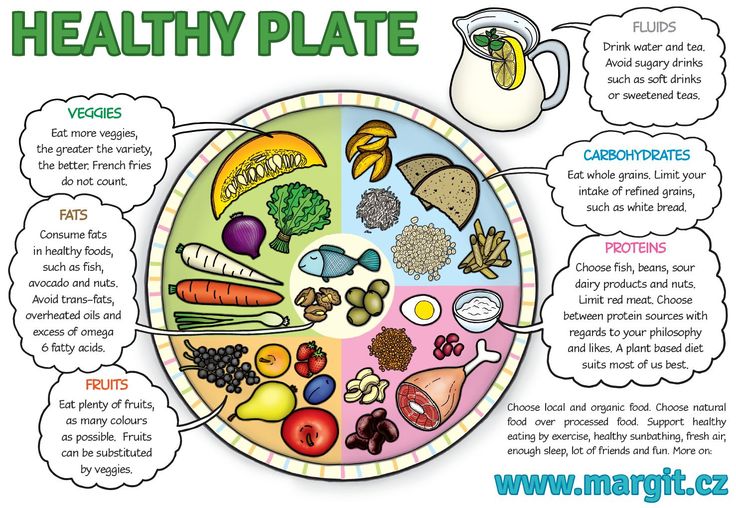
When can baby bunnies eat food
How to feed them – The Little Hay Company
Baby rabbits and diet
You can hear the patter of tiny paws - a baby rabbit has come into your life. It’s an exciting time, but what do you feed a baby rabbit? What’s the best diet for a baby rabbit? How much should you feed your baby rabbit? Let's look at these and a host of other baby rabbit related questions to help you give them the best start in life.
A note: What are baby rabbits called?
It’s a lesser-known fact that baby rabbits are not officially called bunnies. They are called kittens. Bit confusing, we know. The female rabbit known as the doe gives birth (kindling), and the baby rabbits are called kittens or kits.
Baby rabbit’s diet from birth to adulthood
When a baby rabbit is born, it will first feed on its mother milk. This is why you should not get your rabbit from its Mother before a minimum of 8-weeks has passed. This time is crucial and helps start your baby on a healthy path.
From around 2-3 weeks old, baby bunnies start to nibble at the hay around the nest and in 3-4 weeks, baby rabbits start eating the same food as their Mum, whilst still taking her milk.
Weaning occurs at around 6-8 weeks old as their digestive system adapts from liquids to solids.
As with all young animals, baby bunnies will be very sensitive to change. Their stomachs like consistency, so it’s a good idea to keep them on the same food they have been used to and make any changes gradually.
Once your rabbit is an adult, it will eat mainly hay (like our Timothy Hay or Meadow Hay) with additional good treats like green leaves and vegetables for variety and extra goodness.
Baby rabbits and moving homes
We all know how moving home is one of the most stressful things you can do. Your baby rabbit will feel the same. It is a good idea to know in advance exactly what food your baby rabbit has been eating so you can get a supply ready for them in their new home. This will help ease the transition and make your bunny feel more at home. You can slowly change their food if it is not of the best quality, but best to do this slowly rather than changing the food they are accustomed to overnight.
If you do not know what your baby bunny has been eating, then the safest bet is to offer a quality hay like our Timothy Hay and water as they settle in.
Wild and abandoned baby rabbits
It is not always easy to know if a nest of baby rabbits has been abandoned. The mother will stay away from the nest during the day to avoid alerting predators to its position, only returning under the cover of darkness.
Wild rabbits can survive on their own after 3-weeks, so even though they look small, they may be completely healthy and not orphaned. It is best to leave them alone.
If you hang around a nest and move things around, you are more likely to make the Mother abandon the nest, as she feels it is no longer safe. It's always best to keep your distance.
Convinced the rabbit's nest is abandoned? Then you can do a simple test. Leave a piece of natural string or fibre over the nest, so that if the Mother returns in the night (which she definitely would) she will disturb it. When you check again in the morning, if it is where you left it, then chances are the nest has been abandoned. The best thing you can do is phone a specialist rescue centre.
When you check again in the morning, if it is where you left it, then chances are the nest has been abandoned. The best thing you can do is phone a specialist rescue centre.
Young rabbits’ diet
A young rabbit will need lots of good food to help it grow strong and healthy. In the wild, they will eat a variety of grasses and succulents. With you at home, most young rabbits are fed with a mix of hay and pellets.
Alfalfa Hay is ideal for a growing bunny as it is rich in protein and calcium and tastes great. They will eat this happily and voraciously. As they get older, too much protein and calcium in the Alfalfa Hay will cause problems with their bladder and make them overweight.
A good approach as they get older is to combine Alfalfa Hay with another hay source like Timothy Hay, Rye Grass Hay or Meadow Hay and then gradually reduce the amount of Alfalfa Hay in the diet until you stop it completely.
Baby rabbit food list
A baby rabbit (up to 6-8 months old) can eat a variety of food.
Alfalfa hay should be available to your growing bunny every day. Give a chunk of hay roughly the same size as your bunny. You can also give your bunny an egg cup full of pellets once a day whilst they are growing. These are usually alfalfa-based pellets (not containing extra seeds or anything else). Again, these alfalfa pellets should be slowly weaned from your rabbit once they are around 6-months old and no longer need the extra calcium and protein.
As Alfalfa hay and pellets are quite tasty, moving them to Timothy Hay or Rye Grass Hay can take a bit of perseverance, but it is the best thing for your bunny and should take a few months, there's no need to rush it.
The other food source to slowly introduce is green leaves. A small amount at first (one or two leaves) and only slowly building up or adding new green leaves as you progress.
Green leaves to try: Basil, broccoli leaves, butter lettuce, cabbage, dandelion greens, dill, kale, mint, oregano, parsley, spinach, watercress, rosemary, carrot tops and others. With such a range, you can find out your rabbit's favoured green leaf with a bit of experimentation and keep them interested with variety.
With such a range, you can find out your rabbit's favoured green leaf with a bit of experimentation and keep them interested with variety.
Hay for baby rabbits
Baby rabbits will start to nibble on hay after a few weeks and then should be moved to a diet full of hay after they are weaned from their mother’s milk. The type of hay they eat is important.
Alfalfa hay is ideal hay for baby bunnies as it is richer in calcium (which helps their bones grow strong) and protein which gives them the energy they need to grow up healthily. Alfalfa hay also tastes good to a baby bunny. This is also its downfall. As your bunny gets bigger and enters adulthood, everything that makes alfalfa hay good for them as a baby is bad for them as an adult. Too much calcium will cause bladder issues and too much protein will make them overweight. This creates additional health issues for rabbits.
Timothy hay and Meadow hay or another adult type of hay have less calcium and protein, so is much healthier for your bunny. Learn all about all the different hay types for your bunny. The trick is to move your young rabbit over to Timothy Hay without them missing Alfalfa hay too much. To do this takes time but is essential. Start the process slowly by adding more Timothy Hay and taking out some Alfalfa, over a few months complete the process until there is no alfalfa hay being given to your bunny at all.
Learn all about all the different hay types for your bunny. The trick is to move your young rabbit over to Timothy Hay without them missing Alfalfa hay too much. To do this takes time but is essential. Start the process slowly by adding more Timothy Hay and taking out some Alfalfa, over a few months complete the process until there is no alfalfa hay being given to your bunny at all.
Dry pellets for your baby rabbit
Should I feed unlimited pellets?
In short, no. A baby rabbit will love eating pellets and giving them an unending supply will create problems with their diet. A quality hay diet like the Timothy Hay created by The Little Hay Co. mixed with alfalfa hay whilst they are young is the best for your rabbit, with pellets added for extra nutrients. A baby rabbit will usually only have an egg cup full of pellets when young, with this only increasing a little as they get bigger. Moving a rabbit onto hay as soon as possible is more natural and will help with their teeth health. Hay naturally wears down their teeth to a manageable and healthy size.
Hay naturally wears down their teeth to a manageable and healthy size.
Changing dry food/pellets
You should swap out your pellets daily, so they always have a fresh supply. You will probably find most young bunnies eat all the pellets they are offered anyway, but if any are leftover, swap them out with new fresh ones.
Fresh fruits and vegetables for baby rabbits
When can a baby rabbit have fresh foods?
Around 3-months is a good time to introduce fresh foods to your rabbit. Ideally, you should introduce fresh food to a rabbit one at a time. This will allow you the chance to see which ones they like most and if any affect their digestive system in negative ways.
Which fresh fruits and vegetables are suitable for a baby rabbit?
Leafy greens are an excellent fresh food to give a baby rabbit. Carrot tops, dandelion leaves, kale, spinach, spring greens, herbs like parsley or basil, watercress, broccoli greens and cilantro can be offered to baby rabbits in moderation.
Can baby rabbits eat grapes, apples, bananas?
Giving a baby rabbit fruit is a little trickier. Fresh fruit often contains too much sugar for a baby rabbit, so should only be offered as a treat once a week. These treats for rabbits include apple (without seeds), banana, strawberries, blackberries, raspberries, cranberries, cherries (no seeds), melon, grapes, orange and nectarine.
At what age can rabbits eat grass?
Baby rabbits can usually eat grass after about 8-weeks. They’ll probably pick at grass or hay whilst still feeding on their Mother's milk and will transition across to hay completely at around 8-weeks. Fresh grass is not always practical for a bunny owner, hay (which is dried grass) is usually the main diet of all rabbits.
Should I give meat to a baby rabbit?
No. Rabbits are herbivores and do not ever eat meat.
Can baby rabbits drink water?
Baby rabbits are getting milk from their mother, but at around 3-4 weeks old, they will start to drink small amounts of water too. As they grow and their diet changes, so will their water intake. Hay is dry, so a rabbit eating hay will want more water than a rabbit eating fresh leafy greens. But all animals need fresh water to survive, so it should be a plentiful resource to your bunny.
As they grow and their diet changes, so will their water intake. Hay is dry, so a rabbit eating hay will want more water than a rabbit eating fresh leafy greens. But all animals need fresh water to survive, so it should be a plentiful resource to your bunny.
How often should I feed a baby bunny?
As you should have picked up your bunny after it has weaned from its mother and not before 8-weeks old, your bunny will already be eating hay and pellets and fresh greens. A ball about the same size as your bunny is the right amount of hay each day. The fresh food should be limited and slowly added over time.
If your baby rabbit is refusing to eat?
A rabbit’s digestive system needs to work constantly to avoid health problems, so any interruption in eating habits needs addressing quickly. If your rabbit is eating a small amount, they may be bored, so you can try to tempt them with leafy greens and remove the pellets. If they are still not interested in any food, you should get them checked by your nearest specialist.
Transitioning into adult rabbits
Rabbits grow fast to help them survive in the wild. The period a rabbit is a baby is short. After 3-weeks a wild rabbit will leave the nest, fend for itself and return at night. A baby rabbit should stay with its mother for 8-weeks to get all the protection her milk offers at this critical life stage.
The transition into adulthood is quick, after 6-8 months they will be eating a quality Timothy Hay, begging for treats and still starring in your latest Instagram posts.
What To Feed Baby Rabbits — Rabbit Care Tips
The first six months of a rabbit’s life are pivotal to their long-term health. At this key stage of their development, a rabbit is constantly growing. Their diet needs to reflect this fact. Ensuring that your baby rabbit is sufficiently nourished will mean healthy bones and muscle mass into adulthood.
Hay and water are essential foods. Baby rabbits need more protein, so give them pellets and alfalfa hay. Your rabbit should be weaned. If not, use kitten or goat milk to imitate their mother’s milk.
Your rabbit should be weaned. If not, use kitten or goat milk to imitate their mother’s milk.
Make sure that you get a baby rabbit into good eating habits. It’s tempting to overfeed young rabbits, but this can lead to obesity in later life. When their growth spurts subside, your rabbit needs less protein and more fiber. We will explain what the optimal diet plan for a baby rabbit is. You should also read our comprehensive guide to caring for baby rabbits.
New owners are sometimes surprised to learn what baby rabbits eat. Excessive carrots and iceberg lettuce can cause health issues. Instead, domesticated rabbits mainly sustain themselves on hay.
This replicates the experience of wild bunnies, which graze on grass all day. It would be impossible to provide a pet rabbit with enough grass to sustain itself. Hay is a substitute, and pet rabbits munch on it throughout the day.
In addition to hay, rabbits enjoy fresh fruit and vegetables and specialist pellets. The former must be offered sparingly. Too many vegetables can cause a stomach upset.
The former must be offered sparingly. Too many vegetables can cause a stomach upset.
Pellets are also optional once a rabbit reaches adulthood. Pellets are critical for young and baby rabbits, as they provide a range of vitamins and nutrients. They’re also calorific. Pellets must be reduced in quantity as the rabbit gets older. Don’t panic if your rabbit has stopped eating pellets.
Hydration is also just as important to a rabbit. Bunnies must always have access to fresh water. You can provide this in a bowl, or a bottle that’s attached to their hutch.
What to Feed Pet Rabbits
The three core elements of a rabbit’s diet are pellets, hay, and fresh vegetables. If we were to draw a diagram of a bunny’s needs, hay would be at the base as the most critical.
This is because a rabbit’s digestive tract is engineered to process the fiber found in grass. There are several different types of hay available, each with slightly different qualities.
- Grass Hay (aka Meadow Hay or Timothy Hay).
 This is the most popular hay feed among rabbit owners. This hay is fresh grass that has been cut and dried out. This means that it replicates a wild rabbit’s diet.
This is the most popular hay feed among rabbit owners. This hay is fresh grass that has been cut and dried out. This means that it replicates a wild rabbit’s diet. - Oat Hay. This hay is made up of oat grass, which is harvested before blooming. Once the oat blooms, this hay no longer contains any nutritional value for a rabbit. It can be used as bedding, though.
- Alfalfa Hay. This is a little different; it’s a legume, rather than grass. Alfalfa hay is usually fed to larger animals. It contains more protein and calcium than other hays, so it leads to weight gain.
Pellets are considered to be an essential part of a rabbit’s diet. Many claim that pellets are unnecessary for adult rabbits though, and are just empty calories.
If your rabbit is looking overweight, pellets should be sacrificed. Adult rabbits can happily sustain themselves on hay alone. Pellets are essential for helping a young rabbit grow, though.
These should always be kept as a treat, especially fruit. Rabbits love sweet tastes, so they enjoy berries, raisins, parsnips, and carrots. Their bodies are not designed to process carbs, though.
Rabbits love sweet tastes, so they enjoy berries, raisins, parsnips, and carrots. Their bodies are not designed to process carbs, though.
A rabbit can enjoy a tablespoon of fresh fruit and vegetables for every 2 lbs. of their body weight.
Again, an overweight rabbit should not receive any fruit and veg for a while. Rabbits do not necessarily need these to flourish. They’ll get all the vitamins they need from hay.
Baby Rabbit Feeding Guide
Young bunnies need to eat more, as they are continually growing. Baby rabbits also use food to stay warm ahead of the first shedding of their fur. Here’s some info on when baby rabbits get fur.
The diet of baby rabbits adjusts steadily as they grow. They’ll start eating solid hay at around 2 weeks of age. This will be supplemented by milk from their mother, though. By the time they reach 4 weeks, baby rabbits eat pellets and hay.
Feed alfalfa hay to a baby rabbit. The protein and calcium found within will help them grow strong muscles and bones. Also mix in some standard hay, though. This will make the transition easier when your rabbit reaches adulthood.
Also mix in some standard hay, though. This will make the transition easier when your rabbit reaches adulthood.
You should also ensure that you pick up pellets designed especially for young rabbits. These will provide everything that a growing bunny needs.
Whatever you decide to feed your baby rabbit, keep it consistent. Any bunny is sensitive to changes in diet, but young rabbits are especially so. Don’t chop and change unless it’s strictly necessary.
Baby Rabbit Food List
Before you even bring your rabbit home, you should pull together a shopping list. Healthy food for baby rabbits is pivotal, so don’t make any best guesses after their arrival.
You’ll need to buy hay in advance. Prioritize alfalfa hay, but get some traditional meadow hay too. Your bunny cannot eat alfalfa hay forever, so don’t let them get too attached to the taste.
You’ll also need pellets. Have a chat with a clerk in your local pet store, and get the ideal pellets for your bunny. There will be numerous options, tailored to different life stages.
There will be numerous options, tailored to different life stages.
Avoid the temptation to buy a huge bag of pellets. You may be told that baby rabbits can eat unlimited pellets. Pellets can grow moldy quite quickly. Smaller bags are preferred.
Pellets
It’s advisable to make pellets part of your baby rabbit’s meal plan. These will help your young bunny grow up happy and healthy. Both quality and quantity should be carefully managed, though.
Tread carefully around claims that baby rabbits can eat unlimited pellets. In theory, this is correct. The ever-growing body of a bunny will cope with the calories consumed while they’re so young.
All the same, this is teaching your bunny bad habits. They’ll grow accustomed to having a constant supply of pellets. If you remove this option as an adult, they’ll grow distressed. It’s better to teach a young rabbit to enjoy hay early.
Also, ensure that you pick up the highest quality pellets possible. They should make up at least 22% fiber. Protein should not amount to more than 14%. Avoid anything with more than 1% calcium, as this can be harmful.
Protein should not amount to more than 14%. Avoid anything with more than 1% calcium, as this can be harmful.
Don’t be tempted by muesli-based pellets. These will be tastier, as they contain nuts and seeds. A baby rabbit will pick out the nutrient-deficient fun ingredients, and ignore the rest.
Hay
Alfalfa hay is ideal for baby rabbits. For the first months of their life, a rabbit will enjoy the protein in this hay. As pellets also contain alfalfa, your baby bunny will be in good health.
Even though alfalfa hay is good for baby rabbits, it shouldn’t be all they have. Aim for a ratio of around 60:40, mixing alfalfa with traditional grass hay. This will make the eventual transition to meadow hay only less jarring.
Another thing to remember is that your rabbit’s hutch will be filled with hay. They’ll sleep on it, and generally surround themselves with the substance. This also means that your rabbit will pee and poop in their hay.
As baby bunnies have immature brains and bladders, they take a while to be litter trained. This needs to be handled with care. Urine can turn hay moldy, and moldy hay is toxic to rabbits. Clean their hutch regularly.
This needs to be handled with care. Urine can turn hay moldy, and moldy hay is toxic to rabbits. Clean their hutch regularly.
It’s vital that your baby rabbit sees hay as a source of pleasure. Get them into the habit of grazing on hay as early as possible. Incorporate it into playtime, and exercise.
Fresh Fruit and Vegetables
In the past, popular opinion dictated that baby rabbits should not be fed fresh food. This is because young bunnies have particularly sensitive digestive tracts. The truth is, fresh fruit and vegetables are fine in moderation.
The misconception that fresh vegetables are dangerous to baby bunnies arose through a lack of education. Feeding a rabbit of any age-inappropriate vegetables will cause stomach upsets. A bunny needs time to adjust to dietary changes.
When bringing home a baby rabbit, learn what fresh food their mother enjoyed. Once the bunny reached 4 weeks of age, they would have nibbled on these vegetables too. Their stomachs will be able to cope with them in small doses.
Fresh vegetables will also help a young rabbit manage the size of their teeth. Rabbit teeth never stop growing. By crunching on tough, solid vegetables, they’ll be filed down.
Fruit is best avoided in baby rabbits, unless used as training treats. Offer small amounts of vegetable as a treat, once your bunny has eaten sufficient hay.
Should I Give a Baby Rabbit Meat?
Meat must be avoided. While baby bunnies need protein, they don’t need meat. They’ll suffer from an excess of protein, and experience stomach upsets as a result.
Your rabbit may develop a taste for meat. A little won’t kill them, but it will make them uncomfortable. A rabbit’s digestion is engineered to process fiber, not protein. The older they get, the more problematic this will become.
Rabbits are herbivores. They do not want or need to eat meat. Babies are no exception to this rule.
Can Baby Rabbits Drink Water?
Baby rabbits can drink water. It should be actively encouraged.
Rabbits will start to hydrate from their mother’s water source at around 3 weeks old. As baby bunnies eat more dry food, water becomes particularly important. They need to hydrate regularly to stay healthy.
It’s vital to learn how your baby rabbit enjoys drinking. Some bunnies find water bottles fun. Others would rather lap from a bowl. Encourage your pet to drink in whatever way they prefer.
If you use a bowl, ensure that it’s heavy and shallow. Baby rabbits are playful and curious. They will splash around in water if they can. This can turn their hay moldy, and wet rabbits suffer a drop in body temperature.
Can Baby Rabbits Drink Cow Milk?
Baby rabbits drink milk from their mother’s until they’re 8 weeks old. A bunny should never be separated from their mother before this. If you’re offered a rabbit younger than 8 weeks by a breeder, walk away.
If you must provide a rabbit with milk, don’t use cow milk. This is too dense in calcium. The closest equivalent is kitten milk. Warm goat milk will be suitable in a pinch.
The closest equivalent is kitten milk. Warm goat milk will be suitable in a pinch.
Rabbit milk contains more calories than kitten milk, though. As a result, mix in a tablespoon of sugar-free heavy cream. Baby bunnies should be fed milk twice a day.
Also, don’t forget that baby rabbits are not sustained on milk alone. Once they reach 2 weeks, they also need water and solids. Failing to provide these will leave a rabbit malnourished.
How Can I Tell if My Baby Rabbit’s Diet is Healthy?
Young rabbits need to nap regularly, but they’ll be energetic in between. If your young rabbit is lethargic, it may be due to dietary deficiency.
Another way to check on a rabbit’s condition is their droppings. Rabbit poop is a fine way to assess your bunny’s digestive health. Rabbit’s produce two types of poop:
- Pellets, which will be littered throughout their cage.
- Cecotropes, which are bunches of fecal matter that the rabbit eats.
A healthy poop pellet will be light brown, and will crumble when picked up. If your rabbit’s feces pellets are dark, it suggests they’re eating too much protein.
If your rabbit’s feces pellets are dark, it suggests they’re eating too much protein.
Diarrhea in a baby rabbit is a medical emergency. This condition can be fatal in hours. Administer the first aid suggested by the University of Miami, and make an urgent vet appointment.
My Baby Rabbit Eats Too Fast
This is nothing to worry about. Even if it leads to hiccups, these will pass in a short period of time.
The main reason that baby rabbits eat quickly is food insecurity. Until they get into a strict routine, bunnies worry about when they’ll be fed. They’ll guzzle food in case they don’t receive any more.
Rabbits that share a hutch are particularly likely to eat fast. They’ll be worried that another, older bunny will eat their share otherwise.
Also, remember that baby rabbits are always growing. This means that they’ll be hungry pretty much constantly. Once they establish a routine, they’ll calm down.
My Baby Rabbit is Not Feeding
If your baby rabbit is refusing to eat, it’s essential to find out why. A rabbit not eating at any age is worrying. This goes double when the bunny is young.
A rabbit not eating at any age is worrying. This goes double when the bunny is young.
A young rabbit eating less as they reach adulthood is not as concerning. As they grow older, rabbits need fewer calories. They may take to eating more hay than pellets. This is a good thing. Don’t let them eat too much alfalfa hay, though.
You should also check that your bunny is not just being stubborn. If you have changed their diet, they may be holding out for a favorite. This needs to be managed carefully.
Baby rabbits need to eat, but if you cave too quickly, you’re setting a dangerous precedent. They’ll refuse to eat anything that doesn’t like into adulthood.
Move the bowl around in the first instance. If a rabbit feels a draught, it will put them off eating. Food that’s too close to a preferred elimination spot will also deter a bunny from eating. Rabbit pee has an overpowering smell.
Also, ensure that your baby rabbit is not anxious. Being separated from their mother and siblings can be distressing. Offer plenty of TLC and a welcoming home environment to help your bunny settle.
Offer plenty of TLC and a welcoming home environment to help your bunny settle.
Spaying or neutering young rabbits also leads to behavioral changes. Your bunny may temporarily lose their appetite. This should pass quickly. Observe them, and take action is necessary.
Alternative Food for Baby Rabbits
If your baby rabbit is refusing to eat, you’ll need to offer the formula. This is often easier said than done. Seek professional help to ensure your bunny is sufficiently nourished.
Use kitten or goat milk if you cannot source rabbit-specific milk. Zooh Corner recommends feeding milk at the following quantities, at least twice a day. If your rabbit will not eat hay or pellets, they’ll need more:
- 1 – 2 Weeks of Age – 10 – 15 cubic cm
- 2 – 3 Weeks of Age – 15 – 30 cubic cm
- 3 – 8 Weeks of Age – 30 cubic cm
You can pick up a syringe to provide this milk from a pet store. Many baby rabbits will not take to this, though. Bunny-savvy suppliers will stock a product called the Miracle Nipple. This imitates the nursing experience.
Many baby rabbits will not take to this, though. Bunny-savvy suppliers will stock a product called the Miracle Nipple. This imitates the nursing experience.
This is not a permanent solution, though. You must learn why your rabbit is not eating, and resolve the issue.
Feeding a baby rabbit is largely similar to nourishing an adult equivalent. Young bunnies eat more, and show more interest in pellets.
What’s most important is that you get your rabbit into good habits surrounding food. Like any animal, a rabbit’s formative experiences will play a significant role in their adult persona.
Help a rabbit eat appropriately while they’re young, and they’ll reach adulthood in a healthy condition. From there, you can enjoy a long and happy relationship.
How to feed rabbits at home
Proper feeding of rabbits requires balanced mixtures containing a certain norm of the necessary products and having a high nutritional value. Without observing this condition, it is impossible to achieve good growth and strong immunity in animals. By adjusting the diet of rabbits, you can improve the quality of meat and fur, increase the survival of offspring and maximize the potential of the breed.
By adjusting the diet of rabbits, you can improve the quality of meat and fur, increase the survival of offspring and maximize the potential of the breed.
- What can rabbits eat?
- Benefits of specialty feeds
- Benefits of compound feed produced by MEGAMIX
- Feeding rates and rations
- Self-preparation of feed
- Nuances of feeding rabbits depending on the season
- What should not be fed to rabbits?
What can be fed to rabbits?
The metabolism of rodents is so intense that they need to constantly eat for the proper functioning of all body systems. If the rabbit for some reason stops eating, then during the day there is a malfunction in the digestive tract. This entails serious consequences for health, up to and including death.
Compound feed for rabbits is complete and concentrated. The first one provides all the needs of animals in calories and nutrients. The second is used as a supplement to the main diet. Young rabbits reach a commercial weight of 3.5–4.5 kg, provided that they are properly fed, at the age of 4–5 months, and an adult female brings 30 or more cubs per year. If the diet is balanced and meets the needs of the breed, the rabbit is capable of the next reproductive cycle as early as 3-5 days after birth.
Young rabbits reach a commercial weight of 3.5–4.5 kg, provided that they are properly fed, at the age of 4–5 months, and an adult female brings 30 or more cubs per year. If the diet is balanced and meets the needs of the breed, the rabbit is capable of the next reproductive cycle as early as 3-5 days after birth.
Livestock specialists have repeatedly researched the best way to feed rabbits. The diet of meat and decorative animals should include the following products:
Cereals (concentrated feed) have the highest nutritional value. They contain a large amount of protein and a minimum of water. Oats are considered the best grain, as they are well absorbed, have a positive effect on intestinal motility and reproductive functions, and do not contribute to obesity. It is used in the form of whole or crushed grains. Rye, barley and wheat are offered to rabbits in the form of crushed, mixed with other feeds.
It should be remembered that you can not give a lot of wheat, and it is better to remove the shell from barley. These grains are difficult to digest, often leading to bloating. Many farmers recommend pre-treatment of grain products: soaking, sprouting, steaming or yeasting. Sprouting allows you to increase the amount of vitamins and increase protein digestibility. Yeasting improves the digestibility of fiber, but feeding animals with such grains for more than 5 days in a row is undesirable, as it can provoke fermentation in the intestines.
These grains are difficult to digest, often leading to bloating. Many farmers recommend pre-treatment of grain products: soaking, sprouting, steaming or yeasting. Sprouting allows you to increase the amount of vitamins and increase protein digestibility. Yeasting improves the digestibility of fiber, but feeding animals with such grains for more than 5 days in a row is undesirable, as it can provoke fermentation in the intestines.
Green foods form the basis of the rabbit diet from spring to late autumn. This type of food includes: vegetable tops; fodder cabbage; wild herbs; seeded cereals and legumes. Nettle, wormwood, dandelion, couch grass, plantain, quinoa are considered the most suitable wild plants. Freshly cut greens are recommended to be slightly dried and dried in the sun. The tops of fodder and sugar beets, carrots, turnips, rutabaga, Jerusalem artichokes are also suitable as green fodder. Sugar and fodder beet tops are not recommended for young animals. It has laxative properties, therefore, along with it, animals are advised to give plant foods that have a fixing effect.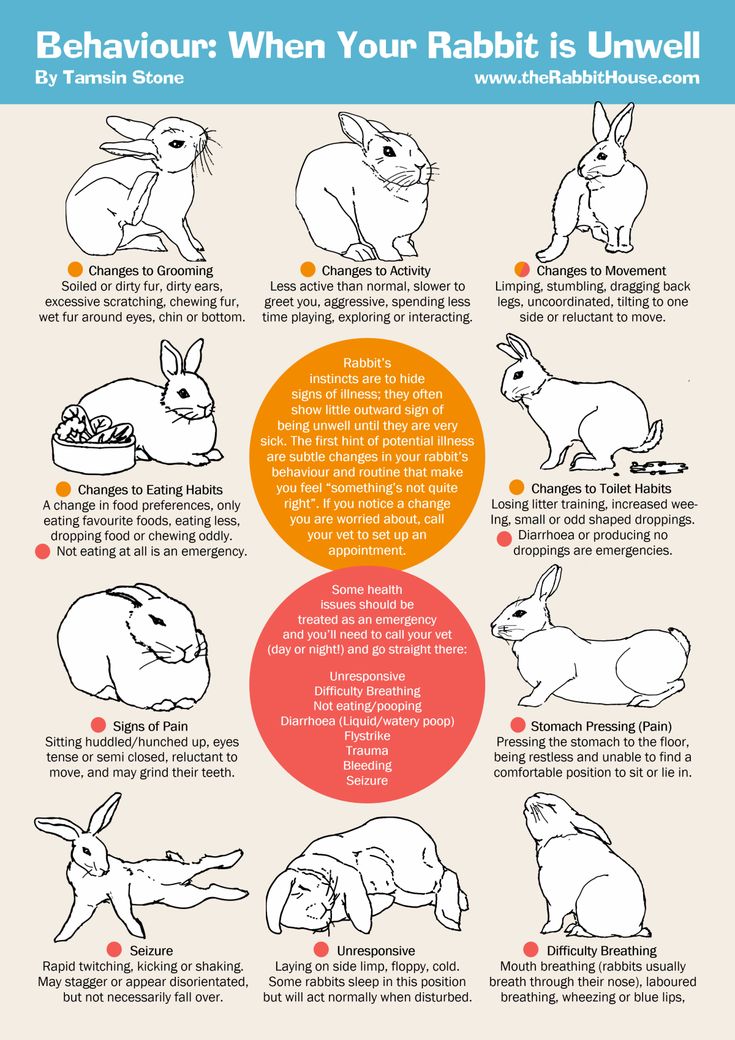 For these purposes, yarrow, comfrey, branches and leaves of oak and alder are suitable. In the mass of green fodder beet tops should not be more than 30%.
For these purposes, yarrow, comfrey, branches and leaves of oak and alder are suitable. In the mass of green fodder beet tops should not be more than 30%.
The aerial part of legumes, legumes and cereals is rich in vitamins and minerals, and also contains a large amount of proteins. However, experienced rabbit breeders advise using the above plants in a mixture with other feeds, since herbs alone will not be able to provide good nutrition and can lead to bloating in animals.
The diet of rabbits should be approximately 25% roughage. These include: hay, straw, tree branches. The optimal harvesting time is in spring and summer. Such food is very important, as it creates a feeling of satiety and contains fiber necessary for the normal functioning of the digestive tract.
The main share of roughage is hay. Harvest it using the same herbs as for green fodder. Legume hay has much more plant protein than grain hay, so it is more nutritious. Haylage is under-dried hay pressed into briquettes. Rabbits eat it with gusto, and also love clean straw if it's well dried.
Rabbits eat it with gusto, and also love clean straw if it's well dried.
Juicy food (vegetables)
- Potato: high in fast digesting starch. It is recommended to give in boiled form;
- Carrots contain C and B vitamins vital for breeders, pregnant/nursing females and growing rabbits. It is the main source of carotene in winter. The daily norm for an adult animal is up to half a kilogram. Young rabbits are started on portions weighing 20–30 g.
- Cabbage contains many minerals, vitamins C and E. Helps to improve the quality of the skin and fur. Introduced into the diet of animals gradually, used both raw and boiled.
- Zucchini helps to better digest other foods. They are given fresh.
- Pumpkin improves coat quality and has a positive effect on milk production in lactating rabbits. It has a good effect on digestion and weight gain in animals. Offered to rabbits both raw and boiled.
- Feed and sugar beet improves metabolism and blood quality, improves immunity.
 Use raw or boiled, no more than 150–200 g for young animals and 250–300 g for adults per day. Excess beets can lead to diarrhea in animals. Table varieties are strictly prohibited.
Use raw or boiled, no more than 150–200 g for young animals and 250–300 g for adults per day. Excess beets can lead to diarrhea in animals. Table varieties are strictly prohibited. - The diet of rabbits also includes melons, watermelons, turnips, Jerusalem artichokes, and radishes. However, their nutritional value is not very high.
Processed products of legumes and oilseeds (meal, cake of soybeans, peas, beans, sunflower, hemp, flax) are sources of fatty acids necessary for the body, including essential ones.
The composition of feed mixtures necessarily introduce products of animal origin: meat and bone or fish meal. Meat and bone contains about 40% protein and 14% fat, while fish contains about 45% protein and 7% fat. Flour is mixed into wet food in small portions - 5–10 g per individual.
Also, table salt must be present in the diet of rabbits. The rabbit needs 0.5–1 gram per day. For adults, the rate is increased by 1.5–2 times. When fattening animals, the daily amount of salt is 2-3 grams per individual.
Benefits of specialty foods
Complete nutrient mixtures can be prepared independently, but this is a very time-consuming work. To produce a quality product for feeding rabbits, you need:
- crushers, crushing components to the desired size;
- stocks of various grain crops;
- meat and bone and fish meal;
- protein-vitamin-mineral complexes;
- cake.
It is important to check the quality of incoming raw materials to minimize the risk of mortality. In the process of preparing mixtures for feeding rabbits, it is necessary to know exactly how much and what components are required, and at home or in a small enterprise it is difficult to achieve proportions. Because of this, there is a possibility of an excess of some nutrients and a deficiency of others, which can lead to improper formation of rabbits and young animals.
For the storage of compound feed, it is necessary to maintain normal ventilation in the room, a humidity level of not more than 75% and a temperature of up to 25 ° C. It is desirable to place bags on lattice racks or pallets. For small farms and medium-sized farms, buying ready-made feed can be more profitable than own production. The higher cost of the product is offset by guaranteed quality and time savings.
It is desirable to place bags on lattice racks or pallets. For small farms and medium-sized farms, buying ready-made feed can be more profitable than own production. The higher cost of the product is offset by guaranteed quality and time savings.
Benefits of compound feed produced by MEGAMIX
Our compound feeds for rabbits are presented in correctly formulated complete mixtures, which contain all the necessary nutrients:
| universal | for lactating queens |
|---|---|
| Ideal for weaned rabbits and fattening animals. | Also suitable for queens and rabbits. on milk feeding. |
Feed is produced in the form of granules and packaged in convenient packages: standard bags of 25 and 40 kg or big bags for large customers. The composition of the mixtures contains only valuable components that improve productivity, strengthen the immune system, positively affect the quality of the fur and the resulting meat, increase the growth and activity of rabbits.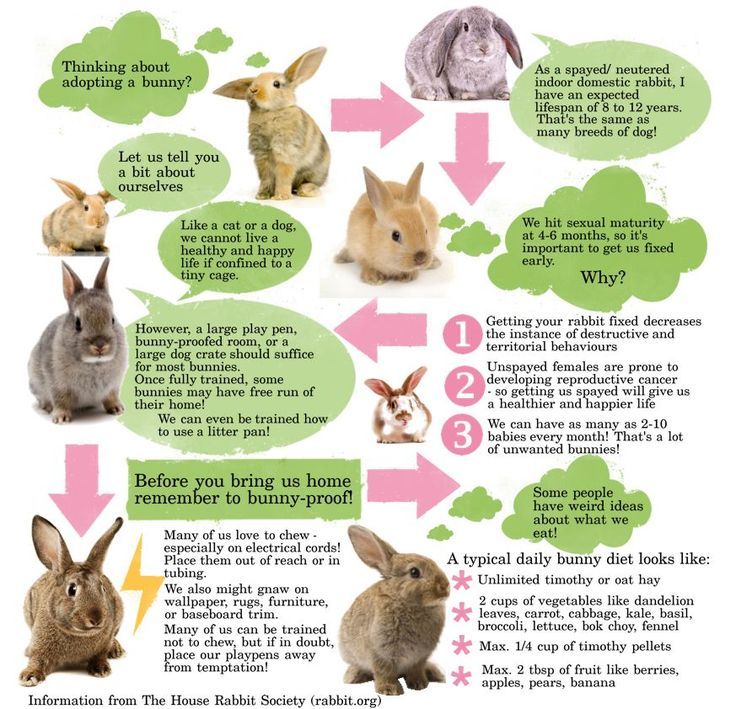
Thanks to our own science-intensive production, we create recipes that best meet the needs of a particular breed of animal. The quality of incoming raw materials and the final product is carefully checked against more than 280 indicators in our analytical center, accredited to the international standard. Our requirements for commercially available compound feed for rabbits are stricter than GOSTs. All products undergo mandatory certification.
The company closely cooperates with VolGAU. The effectiveness and safety of all feeds are tested in a research center. Due to this, we are able to quickly navigate the needs of customers, clearly analyze each request and select the most profitable option for the customer. Our production facilities are designed to produce up to 180 tons of products annually.
We work not only in the central regions of Russia (Moscow and nearby regions), but also organize delivery to the cities of the Urals, Western Siberia, the North Caucasus, Crimea through an extensive network of dealerships.
Feed mixtures from MEGAMIX are effective for breeding rabbits at home, on medium-sized farms or large complexes. Using them, you will provide the animals with all the necessary trace elements, vitamins and mineral supplements, get a high average daily weight gain and reduce the risk of livestock infection.
Norms and diet
For agricultural breeds (meat and fur)
In summer, one rabbit needs 40-50 grams of concentrated and roughage plus a pound of green. During preparation for mating, the amount of food increases: green for 600 grams, concentrated and coarse - 70-80 grams. For a pregnant female, you will need 550–700 grams of greenery and 70–90 grams concentrated and coarse. A lactating female needs at least a kilogram of greens per day and up to 150 grams of roughage.
In winter, the basis of the diet is succulent food (150–200 grams) plus hay (120–150 grams). The amount of rough and concentrated feed remains the same. During preparation for mating 150-200 grams of juicy, 90-100 grams of concentrated and coarse and 150-200 grams of hay. A pregnant rabbit needs 200-250 grams of juicy, 100-130 grams of coarse and 150-200 grams of hay. A lactating female will need 300-350 grams of juicy, 140-160 concentrated and coarse and 200-250 grams of hay.
A pregnant rabbit needs 200-250 grams of juicy, 100-130 grams of coarse and 150-200 grams of hay. A lactating female will need 300-350 grams of juicy, 140-160 concentrated and coarse and 200-250 grams of hay.
Fattening of meat breeds usually occurs in autumn and winter. When fattening, the amount of concentrated feed, bran and root crops (especially boiled potatoes) is gradually increased.
In ornamental breeds, digestion works worse than in agricultural ones. They can be given the following foods.
- Hay is the main feed for ornamental breeds. It should be clean and dry and should be replaced as needed.
- Grass - it can be added to the diet in summer. It is desirable to collect grass away from roads and other sources of pollution.
- Granulated food - 2 tablespoons per day.
- Vegetables and fruits - can be given little by little, in small pieces and only washed and fresh. Radishes, parsley, carrots are good. It is better to exclude beets and cabbage in order to avoid stomach problems.

A complete balanced diet for rabbits, of course, should include the main vitamins:
- A - has a positive effect on the functioning of the nervous and reproductive systems in wards, improves their general physical condition;
- B1 - responsible for the metabolism of carbohydrates in the body, normalizes the activity of the cardiovascular system, indirectly improves the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- B2 - improves the condition of the skin and fur, optimizes the general physical condition of animals;
- B5 - normalizes the digestive system;
- B6 - is responsible for the absorption of proteins and simple proteins, as well as for the enzymatic balance in the body;
- B12 - promotes the absorption of proteins, is extremely important for the health of newborn rabbits;
- C - strengthens the immune system and normalizes the digestive tract;
- D - necessary for the proper development of the eared musculoskeletal system, promotes better absorption of minerals;
- E - is responsible for the development of the muscular system of pets.
 Stabilizes the work of the heart and reproductive system;
Stabilizes the work of the heart and reproductive system; - K is an essential vitamin for rabbit breeding.
Self-feed preparation
The mash is a delicacy for rabbits. The most popular recipe includes:
- boiled potatoes;
- carrots;
- oats;
- germinated wheat;
- table salt;
- bran;
- chopped hay.
The mixer is prepared using a blender or other chopper. To enrich it with biologically active substances, concentrated feed additives are added to it.
Hay is harvested using the same herbs as for green fodder. It is important to mow the plants before they bloom. The resulting raw material is dried on the street, and then allowed to lie down for some time in a well-ventilated place under a canopy (without direct sunlight).
Silage ingredients are crushed to fragments no larger than 1 cm in length. The resulting mass is placed in a sealed barrel and covered with a layer of sawdust 5 cm thick. The resulting substrate is compacted until juice appears and pressed down with a wooden circle, on which a load is placed on top. In the process of silage maturation, the barrels are stored in a moderately warm place, and then removed to a cool room.
The resulting substrate is compacted until juice appears and pressed down with a wooden circle, on which a load is placed on top. In the process of silage maturation, the barrels are stored in a moderately warm place, and then removed to a cool room.
Nuances of feeding rabbits depending on the season
The summer diet of animals should consist of cereals by 30-40%, and in winter and with intensive fattening - by 50-70%. In the summer, green food predominates in the diet of rabbits, but with the onset of cold weather, juicy food - silage and vegetables - become the main part of the menu. The owners who grow vegetables and melons on their plots give the animals various root crops, cabbage, zucchini and pumpkins. Such food contains many vitamins, but little fiber and protein; in lactating rabbits, it contributes to more intense lactation.
When planning the volume of the product harvested for the winter, farmers proceed from the calculation: 40 kg of hay for a rabbit; 10–15 kg per head of potential offspring. If there is not enough hay for all the livestock, then first of all it should be fed to females and lactating females, young animals. For adult males during the dormant period (if mating is not planned), the above product can be replaced with pea, lentil, oat or millet straw. You can’t feed it for a long time, because there are very few nutrients in the straw.
If there is not enough hay for all the livestock, then first of all it should be fed to females and lactating females, young animals. For adult males during the dormant period (if mating is not planned), the above product can be replaced with pea, lentil, oat or millet straw. You can’t feed it for a long time, because there are very few nutrients in the straw.
Branch fodder becomes a good help in winter. Timely harvested young twigs of trees contain quite a lot of vitamins. In addition, rabbits that have a constant opportunity to eat such food are much less likely to express a desire to gnaw on cages. Branches of only certain tree species are suitable for harvesting: willow, willow, maple, linden, acacia, mountain ash, poplar, aspen, ash, oak, alder. The content of nutrients in tree shoots is highest in the first month of summer.
Vitamin supplements are administered most often at the end of winter - in early spring, when there is a shortage of green and succulent fodder. To fill the need for vitamins A and D, animals are given special concentrated preparations or fish oil is added to food. At the same time, the amount of fish oil required by rabbits is calculated depending on their physiological state.
To fill the need for vitamins A and D, animals are given special concentrated preparations or fish oil is added to food. At the same time, the amount of fish oil required by rabbits is calculated depending on their physiological state.
What should not be fed to rabbits?
It is better to refrain from adding birch branches to the diet, as they can lead to kidney disease. The same can be said about the branches of cherries, sweet cherries and plums. They contain hydrocyanic acid, which is quite dangerous for the body of animals. Branches of wild rosemary, buckthorn, bird cherry, apricot and elderberry are strictly forbidden to give to rabbits.
Even beneficial plants in excess can harm rabbits. From freshly cut grass, they have bloating of the intestines. Therefore, before feeding rabbits, it must be dried in direct sunlight. As a rule, an excess of cabbage leads to intestinal upset. It is also not recommended to give dirty vegetables to rabbits. This negatively affects the work of the digestive tract.
Rabbits should not be fed plants with a high concentration of toxins:
- hemlock;
- mustard;
- colza;
- digitalis;
- dope;
- we milk;
- Colchicum.
Buttercup caught in the feed mixture causes serious poisoning. Thrust is also dangerous. This flower is able to paralyze the muscles of the animal. Among the harmful herbs is aconite. Rabbits develop severe salivation, convulsions, and a slow pulse. Aconite poisoning leads to the death of the animal. From the marsh marigold in rabbits, the work of the kidneys is disrupted.
For the most part, the rate of weight gain and the taste of meat depend on proper nutrition. If you follow all the recommendations for feeding rabbits, you can quickly get large carcasses with good fur at the exit and significantly increase the livestock when breeding decorative breeds.
weekly, monthly and after jigging
Little rabbits, like all babies in the animal kingdom, need a balanced diet.
In the first days and weeks, their life is completely dependent on mother's milk. And then the whole responsibility falls on the shoulders of a person. There are several options for feeding little rabbits and how to organize their diet at different ages.
At home, the most difficult thing is the proper nutrition of young animals after birth. All the most important elements for life at first come to animals with colostrum and rabbit milk. But even if the mother does not feed the kids, you can create the most complete diet for them. Young animals after the first weeks of life, for example, at the age of 14-20 days, it is already easier to keep, but there are some nuances. So, let's find out how to feed rabbits in different periods of their lives.
Contents
- 1 from birth to week
- 2 complementary foods of two -week babies
- 3 How to feed menstruation rabbits
- 4 after a suction from mother
- 5 two -month
- 6 videos “Rabbits eat salad along with rabbit”
- 9000 6.
 1 similar articles similar articles
1 similar articles similar articles
Birth to one week old
From the very birth, the main food of rabbits is mother's milk. If the female behaves normally, she is healthy and feeds the babies well, there is no cause for concern. During this period, the task of a person is to monitor the relationship between mother and newborn children as much as possible. Otherwise, there will be little milk and artificial feeding will be needed.
If a mother for various reasons does not feed her cubs, then improvised means will already be used. Small rabbits that are less than seven days old can be given milk or formula milk. Milk is taken from goat or cow, at the rate of 1 ml for each feeding. In total, babies eat five times a day with an 8-hour night break. The number of daily feedings is at least 3, plus one in the late evening and one in the early morning.
At the age of one week, apart from milk, nothing else is included in the diet of rabbits.

At the end of the first week, babies are already covered in down, becoming heavier, ideally they should double their birth weight. Young animals eat the same amount as at birth, however, after 7 days, you can slightly increase the amount of food for feeding. An important clarification: cow's milk is mixed 1:1 with condensed milk and so given, and goat's milk is given in its pure form. The milk mixture at home is diluted twice as concentrated as indicated on the jar.
Complementary foods 9 weeks old0021
Small rabbits that are already 14 days old are fed more intensively. At this time, you need to look to see if they have enough mother's milk. If not, the babies squeak and constantly reach for the nipples of the rabbit, it is worth turning on the feeding. Like week-old babies, they are fed only milk, they do not offer other food. You also need to feed babies if they are stunted and not gaining weight.
If during this period, the female no longer feeds, then we switch to artificial feeding. The number of feedings is reduced to 3 per day. Young animals after two weeks from about 20 days will already be able to drink from a saucer, so you will not need a nipple or syringe. Strong young animals already weigh 500 grams by this age, and by 20 days already almost 600 (consider the breed). A milk ration will be necessary for rabbits at least until they are one month old.
The number of feedings is reduced to 3 per day. Young animals after two weeks from about 20 days will already be able to drink from a saucer, so you will not need a nipple or syringe. Strong young animals already weigh 500 grams by this age, and by 20 days already almost 600 (consider the breed). A milk ration will be necessary for rabbits at least until they are one month old.
From birth to three weeks of age, rabbits are fed exclusively with mother's milk or are artificially fed with milk mixtures. From 17-20 days you can offer them fresh hay in small quantities, as well as a little finely grated fresh carrots.
If the children are kept together with the rabbit and feed on her milk, the transition to adult food will be smoother and more natural. The rabbits will instinctively eat what is good for them if the female leads by example.
How to feed monthly rabbits
Young rabbits after the age of 20 days and up to a month can already chew their own food. This is due to the fact that after a 20-day milestone, the teeth of the rodents will partially change, part of the milk ones will be replaced by permanent ones. For monthly pets, milk is no longer so necessary, in the diet it takes about 25%. Strengthened rabbits begin to give more hay, green mash, bran, dried wild plants. After a month, many breeders generally transfer their rabbits to an adult diet.
This is due to the fact that after a 20-day milestone, the teeth of the rodents will partially change, part of the milk ones will be replaced by permanent ones. For monthly pets, milk is no longer so necessary, in the diet it takes about 25%. Strengthened rabbits begin to give more hay, green mash, bran, dried wild plants. After a month, many breeders generally transfer their rabbits to an adult diet.
Ever since the gradual decrease in the milk content and the increase in the proportion of solid and succulent feed, babies also need clean water. The more rabbits drink, the less kidney problems they will have. Young animals must be forced to drink (from a syringe), if they do not drink themselves. Until the age of 30-45 days, it is better to compensate for the liquid not with water, but with milk, especially in winter.
After weaning from mother
After jigging rabbits from their mother (and this happens at different times, but not earlier than 20-24 days), you need to carefully monitor their digestion. Having ceased to receive part of the enzymes with milk from the mother, grown-up babies learn to digest coarser food. From the age of 20 days, the rabbits fed by their mother try a little adult food. Therefore, after jigging, the process of adaptation to coarser, juicier or green food goes naturally.
Having ceased to receive part of the enzymes with milk from the mother, grown-up babies learn to digest coarser food. From the age of 20 days, the rabbits fed by their mother try a little adult food. Therefore, after jigging, the process of adaptation to coarser, juicier or green food goes naturally.
During this period, animals are boldly given vegetables and cereals. Good soft hay is also introduced, a small amount of grass pellets (about 3% of the rabbit's weight per day). You can give young animals cooled grain brewed with boiling water, greens of wild plants, a little bran. When more than 20 days have passed since jigging, the rabbits can be completely transferred to an adult diet. In the morning they give dry food, more moist food - in the middle of the day.
Bimonthly
So, your rabbits are no longer a week, not 20 days, or even a month, but two whole - how to feed two-month-old individuals? Here the matter is small - just arrange for them the right diet with plenty of fiber.