Baby brain development food in womb
Are you pregnant? 8 simple things you can do to have an intelligent baby | Health
It is every parent’s dream that her/his baby grows up to be healthy and intelligent. Sure, mother’s diet, genes and emotions play a part in developing a growing baby’s intelligence, but what about tips for creating a smarter, happier baby? Are there any?
“Inherited genes play a major role in determining intelligence and personality, but the right lifestyle choices can help ensure those genes are programmed in the womb,” gynaecologist Ratnabali Ghosh says.
Researchers now estimate that only half of IQ is down to genes - the rest is influenced by a baby’s environment.
So, what are you waiting for?
To ensure your baby inherits your braininess, start now, as we bring you eight tips that ensure your baby is smart and intelligent.
By the third trimester, your baby can memorise sounds she/he hears regularly. (iStockphoto)1. Start a storytime habit
When does learning begin? Psychologist and parenting expert Polly Sengupta says the foundations for language begin in the womb and, by the third trimester, your baby can memorise sounds she/he hears regularly.
According to an article in parenting website Babble, researchers asked mothers to read a passage from The Cat In The Hat (a children’s book written and illustrated by Theodor Geisel under the pen name Dr Seuss and first published in 1957) repeatedly to their unborn babies. After birth, the babies recognised that passage when they heard it.
Iron found in leafy vegetables, like spinach, helps the flow of oxygen to the baby’s brain cells. (Shutterstock)2. Eat healthy
Omega 3 fatty acids are absolutely essential for baby’s brain development. Make certain you include foods that have a good content of omega 3, such as, fish, soybeans and spinach, in your diet. Also, iron found in leafy vegetables, like spinach, helps the flow of oxygen to the baby’s brain cells.
“Include nuts such as almonds and walnuts in your diet during your pregnancy. Walnuts are essential for brain development of adults and babies alike. Almonds are a good source of niacin, protein and energy and helps in the overall brain development of the baby,” Ghosh says.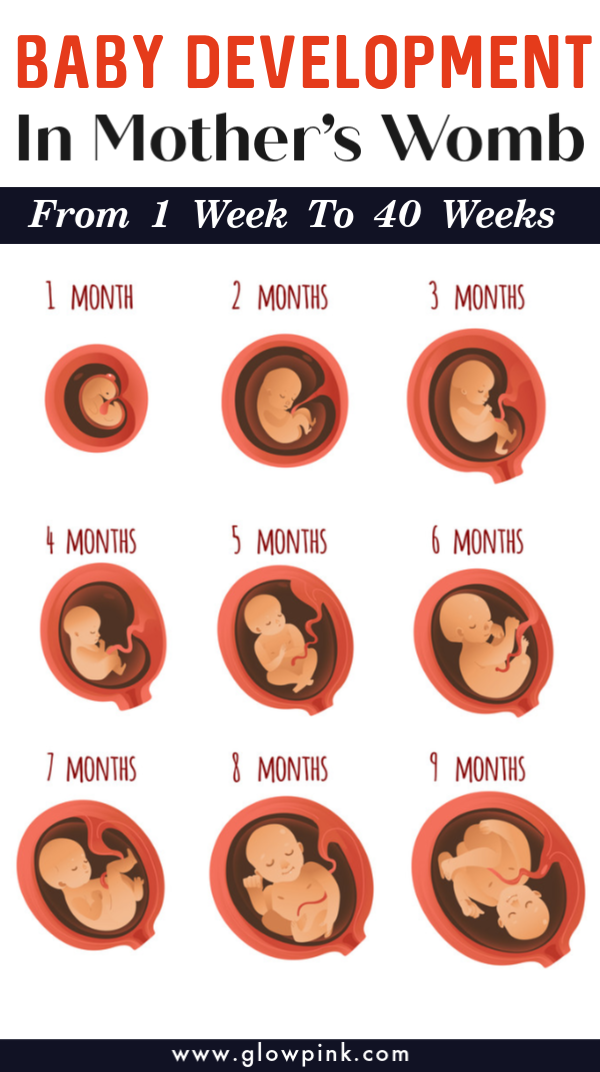
And if you want your baby to have the gourmet palate of an intellect, get adventurous at dinnertime, Ghosh suggests, as your baby’s taste buds develop from around 12 weeks. In one study, babies of mums who drank carrot juice while pregnant showed a preference for carrots once born.
Staying fit and active is all the more important during pregnancy. (Shutterstock)3. Stay fit and active
Love the endorphin boost you get from exercise? Well, so does your baby. Staying fit and active is all the more important during pregnancy. Fight the urge to laze around and get off the couch if you want to make your baby smarter, Ghosh says.
“Hormones released during exercise cross the placenta, bathing your baby in feel-good chemicals for up to a couple of hours. Plus, as exercise increases the flow of blood around your body, including to the womb. Hence, your baby’s development is given a boost,” she says.
If you weren’t exercising before getting pregnant, stick to lightweight exercises and brisk walks, as it has been proven that mothers who are active during pregnancy have smarter children, she adds. Latest research also suggests exercise during pregnancy can increase neurons in your baby’s hippocampus - the learning and memory part of the brain - by 40%.
Latest research also suggests exercise during pregnancy can increase neurons in your baby’s hippocampus - the learning and memory part of the brain - by 40%.
4. Play music and get talking
As the baby grows in her/his mother’s womb, she/he begins to hear and even respond to sound. She/he may not understand what you are saying but stimulating your baby by talking or even singing can help with her/his brain development, says Sengupta.
“You can even ask you partner to speak to your belly and feel the baby respond in return,” she says, adding, “From time to time listen to soothing music or even nursery rhymes.”
Perhaps the most important education of all - you can shape your baby’s music taste.
“Unborn babies love music - it helps trigger happy chemicals, like serotonin, which encourage her/him to be calm and even increase concentration power. After the birth, your baby remembers and relives all those good feelings associated with the music each time she/he hears it,” Sengupta says. That means: After your baby’s born, sing the same rhymes to quieten and soothe her/him.
After the birth, your baby remembers and relives all those good feelings associated with the music each time she/he hears it,” Sengupta says. That means: After your baby’s born, sing the same rhymes to quieten and soothe her/him.
5. Keep thyroid levels in check
Thyroid is essential for the body. During pregnancy if your thyroid level is unstable it can affect the baby: Deficiency of thyroid in the mother can affect the intelligence quotient of the baby.
“Try to eat a well-balanced and healthy diet, which contains ample amount of sodium. Include iodised salt and yogurt in your diet in case you feel you do not get the required amount of iodine in your diet,” Ghosh says.
You must take additional supplements for the well-being of the baby and a smooth delivery. (Shutterstock)6. Don’t ignore the supplements
During pregnancy your body needs extra nourishment. Though a wholesome meal will provide you with ample nutrition,you must take additional supplements for the well-being of the baby and a smooth delivery.
Though a wholesome meal will provide you with ample nutrition,you must take additional supplements for the well-being of the baby and a smooth delivery.
“There are a lot of prenatal supplements available in the markets such as vitamins and supplements containing folic acid. Both of these elements play a crucial role in the development of the brain cells of the baby. However, it is necessary that you consult your doctor before taking any supplements,” Ghosh says.
All you need to do is soak some sunshine up for 20 minutes a day. (Shutterstock)7. Get a little sunshine
Never before has vitamin D been so important. All you need to do is soak some sunshine up for 20 minutes a day.
“We test the pregnant mums who come to our clinic for vitamin D, and more than half of them are deficient. That’s due to a combination of a lack of sunlight and not getting enough vitamin D in their diet.” Ghosh says.
Most of the vitamin D we rely on to grow healthy and strong bones comes from the sun, though it can also be found in a few foods like oily fish and eggs. This nutrient is essential for helping your baby develop strong bones and heart, and researchers have also started investigating a link between a lack of vitamin D in pregnant women and autism.
This nutrient is essential for helping your baby develop strong bones and heart, and researchers have also started investigating a link between a lack of vitamin D in pregnant women and autism.
8. Gently massage your tummy
According to a Time magazine article, rubbing your belly gently is also a good stimulation for the baby.
“A baby, still in the womb, can feel your touch. From around 20 weeks, your baby will feel you touching your bump and stroking it can send calming messages to her/his nervous system, Sengupta says.
Research suggests an unborn baby can even distinguish between her/his mother and father’s touch. Pass some almond oil: this is the best excuse for a massage ever.
What’s more? Your unborn baby even has sense of smell. Sengupta suggests you try and smell fresh flowers, fruits and other such soothing fragrances whenever you can, as these exercises will also help with the baby’s brain stimulation.
Follow @htlifeandstyle for more
SHARE THIS ARTICLE ON
9 Foods To Boost Your Baby's Brain Development During Pregnancy – feedmomandme
Written by: Co-Founder Amanda Capriglione, RDN, CDN
Medically Reviewed by Dr. Nicole Palmer, DO
In this article
Every parent naturally wants their baby to be healthy and grow up to be smart. Scientific research suggests that your diet during pregnancy can help boost fetal brain development. Optimal nutrient intake will not only have you flourishing but also your growing baby. We will be discussing the nutrients and foods that help boost a baby’s brain development while pregnant.
1. TAKE YOUR DAILY PRENATAL VITAMIN
Taking a daily complete prenatal plus DHA multivitamin will help you get those extra nutrients you may not be getting in your everyday diet. Look for a prenatal with DHA and Choline, both essential for baby’s brain development. We recommend taking Feed Mom & Me Complete Prenatal + DHA Multivitamin.
We recommend taking Feed Mom & Me Complete Prenatal + DHA Multivitamin.
Vitamins supplements are meant to supplement your well-rounded diet regimen. They help enhance your intake of nutrients and vitamins along with your everyday food intake. Vitamin supplements aren’t meant to be used in place of real food.
For more information on prenatal vitamins, please check out our Benefits of Feed Mom & Me Complete Prenatal with DHA Multivitamin Blog. To purchase our Prenatal Vitamins, click here! You got this mama, you and your little one are going to thrive!
2. OMEGA 3, LIKE DHAActive forms of omega-3 fatty acids are docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), which are vitally important for your developing baby’s brain & retina during pregnancy. DHA is the critical component of the cell membrane in the brain, eyes, and nervous system. It also supports the development of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem.
The fetal’s brain growth accelerates during your second trimester and continues growth for several years after birth. During pregnancy and lactation, it is recommended women’s daily intake of at least 200 mg of DHA. Both DHA and EPA are primarily derived from seafood and algae. Consuming 1 to 2 servings of seafood per week and a daily prenatal with DHA will help with your omega-3 intake.
During pregnancy and lactation, it is recommended women’s daily intake of at least 200 mg of DHA. Both DHA and EPA are primarily derived from seafood and algae. Consuming 1 to 2 servings of seafood per week and a daily prenatal with DHA will help with your omega-3 intake.
- Fish such as Salmon, Mackerel, Tuna, Herring, and Sardines. (No more than 12 ounces per week)
- Fortified Eggs
- Flax and Chia Seeds
★ A good prenatal vitamin with natural DHA will smell a little fishy.
Read more on DHA in our blog, All You Need To Know About Prenatal Vitamins And DHA.
3. CHOLINECholine is vital for the proper development of your baby’s brain and spinal cord. It also helps form the neurotransmitters in the brain, which the nervous system uses to transmit messages between neurons, and/or neurons to muscles. It also influences lifelong memory functions for your developing baby.
BEST FOODS RICH IN CHOLINE FOR PREGNANT WOMEN:
Read more on choline in our blog, Choline during pregnancy.
4. VITAMIN B COMPLEXVitamin B complex plays a critical role during pregnancy for your developing baby’s brain. They help aid the production of numerous aspects of brain function, including energy production, DNA/RNA synthesis/repair, genomic and non-genomic methylation, and the synthesis of numerous neurochemicals and signaling molecules. They can also be considered a potent antioxidant capable of protecting the brain’s cellular membranes.
BEST FOODS RICH IN VITAMIN B COMPLEX FOR PREGNANT WOMEN:- Poultry, Lean Beef, and Meat.

- Fish such as Tuna and Salmon. (No more than 12 ounces per week)
- Dairy Products such as Eggs, Milk, Yogurt
- Nuts and Seeds such as Peanuts, Sunflower Seeds, Hazelnuts, Pistachios, Cashew Nuts
- Legumes such as Chickpeas, Black-Eyed peas, and Kidney Beans
- Whole Grains such as Whole Wheat, Brown Rice, and Oats.
- Enriched and Fortified Foods such as many Breads and Cereals.
- Vegetables such as Mushrooms (especially shiitakes), Avocados, Potatoes, Asparagus, and Brussels Sprouts and Broccoli.
- Leafy Vegetables such as Spinach and Mustard Greens.
- Fruits such as Papaya, Oranges, and Banana.
- Dried fruits such as Apricots and Prunes.
5. ANTIOXIDANTS
Antioxidants protect your developing baby’s brain tissues and cellular membranes from damage and free radicals. Free radicals are unstable atoms that can damage cells. Produce contains the most amounts of antioxidants that are good for you and your baby. Try to consume seven servings of well-washed fruits and vegetables daily.
Try to consume seven servings of well-washed fruits and vegetables daily.
- Dark Chocolate
- Pecans
- Berries such as Blueberries, Strawberries, Raspberries, and Goji Berries
- Vegetables such as Artichokes, Broccoli, Asparagus, and Squash
- Leafy Vegetables such as Kale, Spinach, Cabbage, Lettuce, Collard Greens
- Root Vegetables such as Carrots, Beets, Radish
- Legumes such as Beans and Peas
- Avocados
★ Dark-colored produce often has more antioxidants.
6. IRONIron is one of the critical nutrients in developing a healthy baby. It helps your body produce hemoglobin, a protein that carries oxygen through your red blood cells, delivering life-sustaining oxygen to your baby. Oxygen helps flourish your developing baby’s brain growth. Make sure you stay hydrated when consuming iron to help avoid constipation. Check out our blog on the Top 15 Foods to Help Naturally Relieve Pregnancy Constipation.
- Lean Meat, and Poultry.
- Iron-fortified Breakfast Cereals and Breads.
- Legumes such as White Beans, Lentils, Spinach, Kidney Beans, Peas, and Edamame.
- Dried Fruits such as Raisins, Apricots, Peaches, and Prunes.
- Leafy Greens such as Spinach, Kale, Broccoli, and Collards Greens.
Read more on iron in our blog, Iron during pregnancy.
7. PROTEINEvery cell in your body requires protein’s numerous amino acids to help your body make new cells and repair cells. Research has shown that proteins are essential for the function of brain cells and the development of your baby’s brain.
BEST FOODS RICH IN PROTEIN FOR PREGNANT WOMEN:- Poultry
- Fish such as Salmon & Shrimp
- Dairy such as Eggs, Milk
- Legumes such as Beans, Lentils, Split Peas.
- Nuts & Seed such as Peanuts, Walnuts, Cashews, Pistachios, and almonds
- Whole grains
 IODINE
IODINE Your thyroid needs iodine to produce triiodothyronine & thyroxine hormones in both your developing baby and you during pregnancy. Iodine plays a crucial role in aiding the formation of your growing baby’s cerebral cortex and neocortex, visual and auditory cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellum. The fetal thyroid is not fully active up until the 20th week of pregnancy; therefore, your baby is entirely dependent on maternal thyroxine supply.
BEST FOODS RICH IN IODINE FOR PREGNANT WOMEN:- Seafood & Fish such as Cod, Tuna, Seaweed, and Shrimp.
- Dairy products such as Milk, Yogurt, and Cheese.
- Iodized salt
Read more on iodine in our blog, The importance of iodine during pregnancy.
9. ZINCZinc is a key micronutrient that helps with the rapid growth and development of cells and tissue. Aiding the development of the brain's hippocampal and cerebellar. Making it essential for your baby’s brain development.
Making it essential for your baby’s brain development.
REFERENCE
- https://www.feedmomandme.com/products/complete-prenatal-vitamin-with-dha
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3046737/#B3
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26828517/
- https://www.feedmomandme.com/blog/15-foods-to-help-pregnancy-constipation
- https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2006/09/060905225522.htm
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23062035/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3506421/#:~:text=Zinc%20is%20essential%20for%20normal,on%20the%20offspring's%20nervous%20system.
- https://feedmomandme.com/blogs/mama-blog/all-you-need-to-know-about-prenatal-vitamins-and-dha
- https://feedmomandme.com/blogs/mama-blog/importance-of-choline-during-pregnancy
- https://feedmomandme.com/blogs/mama-blog/iron-during-pregnancy
- https://feedmomandme.com/blogs/mama-blog/the-importance-of-iodine-during-pregnancy
How nutrition affects the intelligence of a child
We use cookies
to improve our experience!
Good
Author: Vera Yakubson
January 20, 2022
2177 views
In the first years of a child's life, more than 1 million new neural connections appear every second. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention writes that the human brain develops throughout life, but the first 8 years can lay the foundation for future health, learning and success in general.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention writes that the human brain develops throughout life, but the first 8 years can lay the foundation for future health, learning and success in general.
The formation and development of the brain is influenced by many different factors, among them the nutrients that the child begins to receive in the womb. We figure out what kind of nutrition is needed for the development of intelligence and how to provide it.
In order for the brain to develop, various nutrients must be supplied to the body. Here are the elements that are most actively involved in the formation of the brain:
In order for the brain to develop, various nutrients must enter the body. Here are the elements that are most actively involved in the formation of the brain:
- protein - found in meat, fish, eggs, legumes and nuts;
- zinc - meat, fish, dairy products and nuts;
- iron - meat, legumes, dark leafy vegetables;
- choline - meat, dairy products and eggs;
- folic acid - liver, spinach;
- iodine - seafood, seaweed, iodized salt;
- vitamin A - liver, carrot, spinach;
- vitamin D - oily fish and fortified foods;
- vitamin B6 - organ meats, fish, potatoes, fruit;
- vitamin B12 - meat, fish, eggs, dairy products;
- polyunsaturated fatty acids, including omega-3 fatty fish and certain vegetable oils
Malnutrition refers to a lack of protein and calories, as well as a low amount of micronutrients in food. Lack of nutrition slows down the development of the child, including the formation of intelligence.
Lack of nutrition slows down the development of the child, including the formation of intelligence.
In 2020, 149 million children under 5 were stunted due to malnutrition. Growth retardation is associated with deterioration in the cognitive development of children. For example, a study of 40,000 Indian families found that non-malnourished children who are of normal height for their age are more likely to be able to write than their stunted peers.
Unlike general malnutrition, the impact of individual nutrient deficiencies on intelligence is not so obvious. The effects of iron, iodine, zinc, choline, B vitamins, and polyunsaturated fatty acids on brain development have been well studied in animals. Studies have shown that the lack of these substances slows down all the basic processes of brain formation.
Human studies of micronutrient deficiencies present ethical challenges. No one will specially not feed children, and if there is already a shortage, then usually there is not one, but several. In addition, the development of such children is almost always influenced by other factors: poverty, low education of parents, high levels of stress.
In addition, the development of such children is almost always influenced by other factors: poverty, low education of parents, high levels of stress.
The effects of iron, iodine and zinc deficiency on cognitive development are best studied. Iron deficiency during fetal development and after birth leads to the formation of iron deficiency anemia. Research shows that children who were anemic before age 2 have cognitive retardation and poor school performance until age 19.
The baby's brain is still being formed in the womb, and her diet can affect the process.
Folic acid deficiency in the diet of a pregnant woman leads to malformations of the neural tube - the basis of the future brain.
Iron, iodine and vitamin D are elements that also affect intrauterine brain development. A lack of iodine can lead to cretinism, a deficiency of thyroid hormones, which leads to a delay in physical and mental development.
The need for nutrients during pregnancy is higher, so you need to pay extra attention to your diet. It is better to minimize "empty calories" - processed food, sweets and saturated fats.
If you have any doubts that you are getting enough micronutrients from food, you should discuss your diet and the need to take prenatal vitamins with your doctor.
The connection between breastfeeding and the development of the child's nervous system has been proven in numerous studies. A 2015 meta-analysis found that even after adjusting for maternal cognition, breastfed babies had a 2.62 higher IQ. Without this adjustment, the difference was 3.44 points.
Most studies use different versions of IQ tests to measure intelligence. These tests are not the ultimate truth, but they allow you to compare the results of mental activity of different people. Scientists also use academic performance to assess children's cognitive abilities.
Whether the duration of breastfeeding affects the child's intelligence is not yet clear. A 2012 Cochrane review found that the duration of breastfeeding (three, four or six months) does not affect a child's cognitive function. A 2018 review cites two studies that have shown that longer breastfeeding has a positive effect on children's IQ.
To assess the impact of nutrition on the intelligence of children, it is necessary to track their development over several years. To do this, scientists take data from longitudinal cohort studies - when they observe a large number of people for a long time. An example of such a study is ALSPAC, or Children of the Nineties. At the end of 1991 In early 1992, scientists from the UK enrolled 14,000 pregnant women. Scientists are still monitoring the children born then, collecting data on the influence of genetic and external factors on development and health.
A 2011 ALSPAC study found that a healthy diet at age 3 resulted in an IQ increase at age 8. 5. The healthy diet in this study included fruits, vegetables, rice, pasta, and fish. In contrast, children who ate a lot of processed foods high in sugar and fat had lower IQs.
5. The healthy diet in this study included fruits, vegetables, rice, pasta, and fish. In contrast, children who ate a lot of processed foods high in sugar and fat had lower IQs.
Useful substances are best obtained from food, and not in the form of dietary supplements. A balanced diet that includes all food groups provides enough macro and micronutrients for full brain development. The only exception may be vitamin D, which is very scarce in food. It is recommended to give it to children soon after birth as a supplement: according to American standards, 400-600 international units, according to Russian - 1000-1500.
Studies on the effectiveness of iodine, iron and other supplements on cognitive development show conflicting results. They are mainly effective for children with general malnutrition. Under normal conditions, they can have the opposite effect. For example, one study looked at the cognitive development of children who ate iron-fortified infant formula.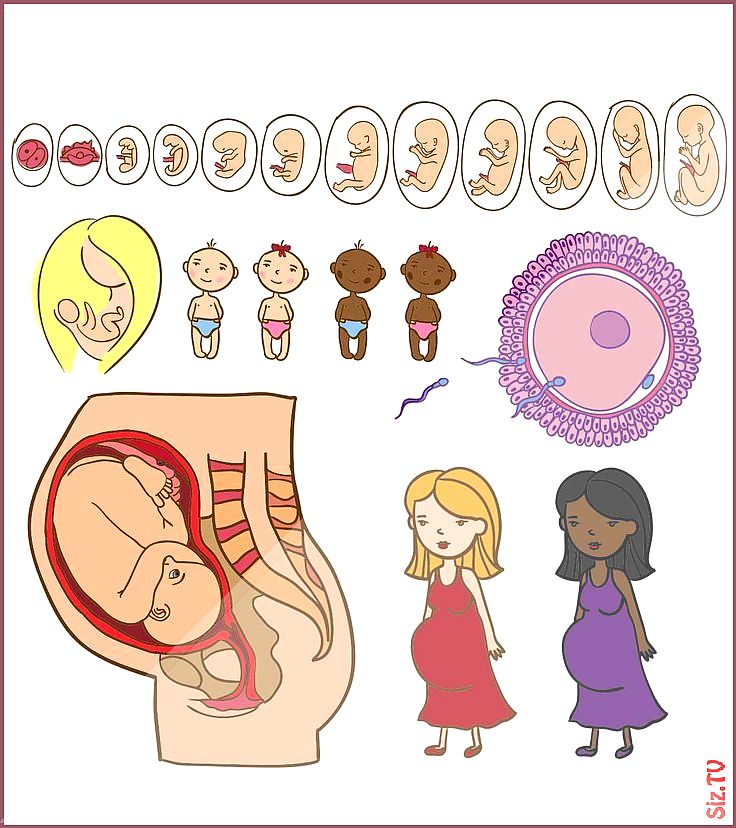 Children who initially had low hemoglobin had higher IQs after 10 years, and children with high hemoglobin had lower ones.
Children who initially had low hemoglobin had higher IQs after 10 years, and children with high hemoglobin had lower ones.
The recipe for growing a genius has not been invented yet. But there are nutritional recommendations that will give the baby's brain the opportunity to develop to its full potential:
- Eat well during pregnancy; If there is a shortage, make up.
- Breastfeed if possible.
- Give your child vitamin D from birth.
- Feed your child a varied and regular diet that includes foods from the five food groups: vegetables, fruits, whole grains, dairy, and protein.
- If you can't get all the nutrients in your diet, talk to your doctor about taking vitamins.
Topics
Food
Children's health
Choice of editorial office
Hearing check
→
Are there any benefits from long-term storage products
1172 View
Food September 6, 2022
5 Sources of Protein for Vegetarians and Vegans
919 views
Food
July 25, 2022
Hearing test
→
Is it true that Ivan tea is healthy, but Coke has only chemistry?
1869 views
Food
July 21, 2022
→
Su-Vid-is it dangerous to eat such food
797 Views
Food
July 2022
How to help the children's brain to develop correctly
48 What determines the harmonious development of the child's brain? Answering this question, scientists name a whole range of factors - from the nature of nutrition and the safety of the social environment to diseases suffered in infancy and injuries received. Of course, the course of pregnancy is also of great importance.
Of course, the course of pregnancy is also of great importance.
Generally speaking, caring for a child's brain health should begin at the planning stage. It is in order to prevent possible violations of its - the brain - development, that doctors prescribe folic acid to expectant mothers (it must be taken before conception and continued after pregnancy) and preventive vaccinations: against influenza, whooping cough, rubella. It is also recommended to stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
How is nutrition related to brain development?
It seems that the postulate about the importance of proper nutrition of the child has been adopted by all modern parents. But what is behind it? How is nutrition related to the brain? And here's how: it turns out that brain development can be disrupted if the child does not receive the necessary nutrients. As a result, we may experience defective development of the sheath of nerve fibers (myelin) and/or insufficient size of the brain itself.
Of course, we remember that the intellectual potential depends not only on the size of the brain. But if the size is reduced due to malnutrition, this can lead to a decrease in the child's ability to acquire knowledge and communicate adequately.
Insufficient nutritional intake slows down the growth of the fetal and newborn brain. And this has long-term consequences: it negatively affects the behavior of the child, including his benevolence. That's how food is associated with brain development!
However, do not be alarmed: if a nursing mother and her child are not in conditions of starvation - whether for social reasons or due to some unnatural diet - the likelihood of underweight infant brain mass is minimal.
What happens to the baby's brain during and after pregnancy?
How do nutrients get to the fetus during pregnancy? When it enters the stomach of the expectant mother, food under the influence of enzymes begins to decompose to the smallest particles, which are absorbed by the intestinal villi and enter the blood of a pregnant woman. Since the mother and fetus have a single bloodstream, the fetal body also receives useful substances. That's why it's so important to include seasonal fruits and vegetables, poultry, beef, nuts, and whole grain flours in your diet during pregnancy. Add 10-12 extra grams of protein to your daily diet during pregnancy - for example, in the form of low-fat cottage cheese, cheese, lactic acid products - and the proteins will become the “bricks” for building new cells in the developing body of the fetus.
Since the mother and fetus have a single bloodstream, the fetal body also receives useful substances. That's why it's so important to include seasonal fruits and vegetables, poultry, beef, nuts, and whole grain flours in your diet during pregnancy. Add 10-12 extra grams of protein to your daily diet during pregnancy - for example, in the form of low-fat cottage cheese, cheese, lactic acid products - and the proteins will become the “bricks” for building new cells in the developing body of the fetus.
And if both the unborn child and the mother definitely need proteins, then such an important component of a healthy diet as polyunsaturated fatty acids during pregnancy is needed mainly by a woman. The fact is that during pregnancy they do not have a significant impact on the fetal brain and its future intellectual potential, but they allow you to increase the elasticity of the birth canal, which will be relevant during childbirth.
How does nutrition affect the brain of a baby under six months?
Try breastfeeding, it's the best way to get all the nutrients your baby needs. In addition, in breastfed children, the processes of formation of the white matter of the brain occur more intensively. Perhaps this is facilitated by breast milk lipids - arachidonic (ARA) and docosahexaenoic (DHA) fatty acids. They are actively involved in the early development of the nervous system, the formation of myelin (the main component of the white matter of the brain) and the formation of connections between neurons.
In addition, in breastfed children, the processes of formation of the white matter of the brain occur more intensively. Perhaps this is facilitated by breast milk lipids - arachidonic (ARA) and docosahexaenoic (DHA) fatty acids. They are actively involved in the early development of the nervous system, the formation of myelin (the main component of the white matter of the brain) and the formation of connections between neurons.
However, if breastfeeding is not possible, there is no need to panic. The need of the child (and his brain!) in fatty acids can be met with the help of breast milk substitutes. When choosing a mixture, pay attention to those that are enriched with fatty acids. The more long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids ( look for ARA and DHA on the package) in a child's diet, the better: they have a beneficial effect on the development of the nervous system and the functions of the whole organism as a whole.
How to feed a child so that his brain develops well?
Experts recommend that your baby start introducing complementary foods (that is, new foods other than breast milk and formula) when he is six months old. This is important not only because the child needs to grow and gain a healthy weight, but also for the development of the brain: proteins, unsaturated fats, carbohydrates, macro- and microelements - nerve cells use all these components for their functional activity and as a building material.
This is important not only because the child needs to grow and gain a healthy weight, but also for the development of the brain: proteins, unsaturated fats, carbohydrates, macro- and microelements - nerve cells use all these components for their functional activity and as a building material.
How do you know when it's time to introduce complementary foods? As a rule, you can start when the baby demonstrates a set of the following skills:
- sits with little or no support;
- good head control;
- shows food interest, that is, opens his mouth and leans forward when food is offered to him.
There are many schemes for the introduction of complementary foods, but the classic recommendations are: you should start with monocomponent cereals or vegetables. By seven to eight months, the diet can be diversified: in addition to vegetables and cereals, offer your baby meat (or other proteins), fruits, vegetables, yogurts, cheese. Take a closer look at the new types of cereals - multi-component: they contain a sufficient amount of ingredients that contribute to the development of the brain.
Take a closer look at the new types of cereals - multi-component: they contain a sufficient amount of ingredients that contribute to the development of the brain.
Despite the fact that fish and greens are not the most favorite foods for children, you should still try to teach your child to eat them. Not only because it will help expand the menu and establish healthy eating habits. Fish and greens contain folic acid and polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are the physical foundation for the formation of intelligence.
Pay attention to vegetable oil: if the fatty acids from olive go directly to the brain cells for their quality work, then the components of sunflower oil can be involved in inflammatory processes that we would like to avoid.
What is a stimulating environment and what does a child's brain have to do with it?
The results of many years of research show that in the first year of life, the child's social environment can also influence the development of the brain. Under its influence, such a property of the brain as neural plasticity is formed - the ability to physically change in response to the acquired experience. The more attention and care a child receives, the more whole person he grows and the better his brain develops. In contrast, childhood malnutrition and lifelong abuse reduce the activity of a gene that protects the brain from exposure to stress hormones.
Under its influence, such a property of the brain as neural plasticity is formed - the ability to physically change in response to the acquired experience. The more attention and care a child receives, the more whole person he grows and the better his brain develops. In contrast, childhood malnutrition and lifelong abuse reduce the activity of a gene that protects the brain from exposure to stress hormones.
What needs to be done to create the right environment around the child? Here are its main components:
- parental attention - eye contact and a sense of security contribute to the formation of new connections between brain neurons, which will later be involved in the process of learning and establishing contacts with new people;
- communication with the family is the child's first experience of communication; if it is positive, then the child gets used to generating positive emotions, forms a positive emotional intelligence; in turn, the negative emotions that a child experiences if they are shouted at, subjected to emotional and physical violence, make the child withdrawn, closed to new knowledge and the realization of their potential;
- games and communication - the child should be able to look at pictures and objects, hear a variety of sounds and speech, touch different things; this stimulates various analyzers, involves certain parts of the cerebral cortex in the active functioning.












