Baby off food and milk teething
Feeding and teething: how to help them with the pain | Baby & toddler articles & support
Your child might have just started weaning when teething creates a stumbling block. Here we see how teething can affect eating, and how to get through it.
One symptom connected with teething is a decreased appetite for solid foods (Macknin et al, 2000; Lyttle et al, 2015; Eisenstadt et al, 2017). And guess what? You’re likely to start weaning your little one around the six-month mark – the exact same time many babies cut their first teeth (eyes roll again) (Lyttle et al, 2015).
So why do they start fussing all of a sudden? It will come as no surprise that teething causes a lot of discomfort (Eisenstadt et al, 2017).
Where’s my baby’s appetite gone?
Just like us adults can go off our foods when we’re feeling under the weather, so can our little ones. The gums swell and are tender to touch just before a tooth breaks through (Ashley, 2001). So anything in your little one’s mouth could cause more pain.
That said, not all babies lose their appetite when teething. Like with everything else, they’re all different. In fact, the science shows only around one third of teething babies lose their appetite (Macknin et al, 2000).
When will my baby’s teething affect their appetite?
Interestingly, some studies show children lose their appetite with teething only when their canines come through, not when their incisors or molars emerge (Memarpour et al, 2015). Generally, these canines – the pointy ones either side of the front four – appear when your little one is 16 to 22 months old (NHS Choices, 2016a; NHS Devon, 2018).
We know from parents we speak to that many encounter food fussiness earlier than the 16 to 22 month mark. So our practical tips can apply whatever your baby’s age over six months, when weaning starts (NHS Choices, 2018). This guide shows you what to do if your baby is struggling to juggle tooth pain and munching.
Which foods are best when they are teething?
If your baby goes on a feeding strike as they start to cut some teeth, the following should help. It is a case of trial and error here, there’s no right answer. Experiment and see what they seem most comfortable with the following types of foods.
It is a case of trial and error here, there’s no right answer. Experiment and see what they seem most comfortable with the following types of foods.
1. Soft foods
Much like us adults might eat nothing but soup after a painful procedure at the dentists, babies might just want to stick with soft foods and purees. Anything they can slurp from a spoon with minimal contact with their gums. A fruit or vegetable puree, or a soft risotto or macaroni cheese (blitzed or slightly overcooked for minimal chewing) could be just the comfort food they need right now.
2. Cool foods
Chilled foods can take the heat out of those burning gums (Ashley, 2001). Yogurt is an easy option here. A ready-made pouch popped in the fridge. Or try some fruit or veg straight from the fridge such as cucumber sticks, a whole strawberry or avocado mushed up.
Just remember foods containing meat, or prepared in advance will need reheating for food hygiene reasons so might not be suitable (NHS Choices, 2015). And make sure you stay with them while they’re eating to watch out for choking.
And make sure you stay with them while they’re eating to watch out for choking.
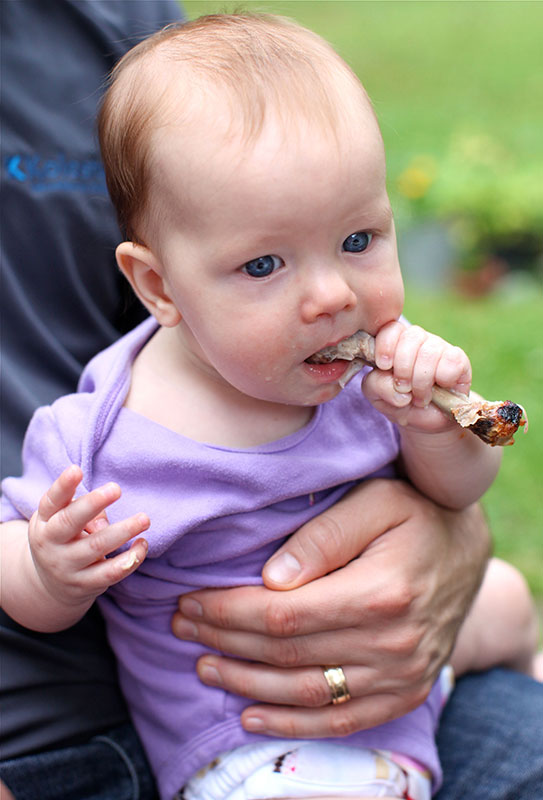
3. Hard foods
To chew and bite down on have been proven to provide relief in around half of teething babies. Why? Their firmness provides counterpressure to a rising tooth (Memarpour et al, 2015).
Try carrot sticks, whole green beans or sugar snap peas, sliced pepper, breadsticks or bread crusts for babies over six months (Ashley, 2001). As above, just ensure you are on watch to avoid them choking on the chunkier items.
Avoid rusks, because nearly all brands contain some sugar. And sugar can cause tooth decay, even if your child only has a few small teeth (NHS, 2016b). You can read more about how to ease their pain with hard foods and teether toys here.
Does it matter if they are not eating as much as usual?
Try not to worry if not much is going in at any one mealtime. If they are still drinking their usual milk, they’ll be getting nutrients from that. That said, if their hunger strike seems to last more than a few days and you’re worried, see your GP or health visitor.
Try to keep them hydrated. While some babies want to suck and therefore breast or bottle-feed more during a bout of teething (Macknin et al, 2000), others go off the idea. If they are refusing milk or drinking less than usual, try to get them to sip some water, or add milk to their purees. Some parents we speak to also make breast or formula milk lollipops to get milk into their little ones, and soothe their gums at the same time. Win, win.
If they are chewing down on everything, including their bottle teat, try a teether toy instead, which might be more sturdy. If your baby is chewing down on your nipple (hideous), then read our article on feeding and biting.
When will the fussing end?
Your baby will probably have a reduced appetite for solids for the five days ahead of a tooth peeping through, the day it surfaces and for three days afterwards (Macknin et al, 2000). So in general, your baby should be more into their food again in just over a week. That is, unless another tooth is on its way (. ..you guessed it, another eye roll).
..you guessed it, another eye roll).
Further information
Our support line offers practical and emotional support with feeding your baby and general enquiries for parents, members and volunteers: 0300 330 0700.
You might find attending one of NCT's Early Days groups helpful as they give you the opportunity to explore different approaches to important parenting issues with a qualified group leader and other new parents in your area.
Make friends with other parents-to-be and new parents in your local area for support and friendship by seeing what NCT activities are happening nearby.
For guidance on how to look after those teeth once they appear (and what foods and drinks they should avoid) read our article on brushing baby’s teethand why teeth hygiene is important for babies.
NCT has partnered with the British Red Cross to offer courses in baby first aid.
Teething Baby Not Eating? Try These This to Get Your Tot Fed
NewFolks may earn a commission when you buy through links on our site.![]()
What to know if your baby doesn't seem as hungry while teething
By Sarah Prager
Teething is both an exciting and painful time for both you and your baby. Your tot will be ready to try more textures and different foods, so mealtime becomes more fun. But it also means screaming and crying all while those teeth are coming in. One not-so-fun side effect of teething is a baby losing their appetite.
Contents
- Do babies eat less when teething?
- Solutions for a teething baby who is not eating
It’s upsetting to see them uncomfortable and in pain when cutting new teeth. The good news is that there are ways to help your baby through the teething process while encouraging your teething baby to eat. Once you establish that teething is the cause of baby’s refusal to eat, either by a pediatric visit or feeling that shark tooth jutting out, there are some tried-and-trusted strategies to get them to eat. What should you do when your teething baby isn’t eating as much as they normally do? Let’s get to the root of the problem.
What should you do when your teething baby isn’t eating as much as they normally do? Let’s get to the root of the problem.
Do babies eat less when teething?
Yes, babies may eat less when their mouths are sensitive from teething. Dr. Dina Kulik told Today’s Parent, “It’s OK, and normal, for babies to eat a bit less during teething.”
Eating becomes uncomfortable or painful for teething babies to press their gums into food when their gums are so sensitive. Babies may also not like the feel of utensils clanging against their sore gums. Instead of eating, they may want to chew on teethers because it brings a bit of relief to their gum discomfort.
“As long as your baby is drinking fluids, the reduced appetite is not a concern,” Dr. Kulik said. “Just keep offering food and your baby will feed again when the pain is gone.”
A red flag is if a baby is also refusing liquids. If your teething baby won’t eat or drink, it’s important to talk to the pediatrician to make sure there isn’t something else going on.
Solutions for a teething baby who is not eating
Use a mesh feeder
A mesh feeder lets your baby gum food for an extended time without having to take bites. Mesh feeders are great for frozen foods, iced cubes of puree, milk, or a smoothie. The texture of the mesh and the cold from the chilled foods feels soothing on your child’s gums. The big bonus of mesh feeders is the baby will be slowly taking in some calories.
Give some Tylenol or Ibuprofen
If your child is four months or older, you could offer acetaminophen (Tylenol). At 6 months old, babies are ready for ibuprofen (Motrin). Both acetaminophen and ibuprofen provide some relief from the pain of teething. Pain relief could help your baby feel up to eating. Consult with a doctor before using either product to relieve teething pain. Numbing gels applied directly to the gums are not recommended.
Try going back to purees
Even if your baby has graduated from purees to more solid foods, while the gums are sensitive from teething, they might not want to chew. Break out the baby food again and keep anything that needs to be chewed in the cabinet until the tooth has come through. Soft foods like soup, mashes, yogurt, applesauce, hummus, scrambled eggs, and purees are great options.
Break out the baby food again and keep anything that needs to be chewed in the cabinet until the tooth has come through. Soft foods like soup, mashes, yogurt, applesauce, hummus, scrambled eggs, and purees are great options.
Provide something to gnaw on
Because everyone is different, babies may want something hard to chew on instead of soft foods. Sometimes, babies want to rub their gums against where the tooth is trying to burst through. Foods like carrot sticks or whole green beans are good for this. To avoid choking, a baby should be under supervision while seated in a highchair.
Push liquids
Staying hydrated is important, but you could also get your baby’s caloric intake in with liquids as well. Make smoothies with veggies, healthy fats, and protein powder hidden in with the fruits, making it a complete meal. Drinking a cool smoothie will be soothing on tiny gums.
Make it all cold
Chill any food before serving it to baby. Whatever you would give at room temperature, even things like crackers, put it in the fridge for a bit first. Anything frozen is perfect for a teething baby. Hello, popsicles! Make your own popsicles from a kale smoothie for a healthy twist.
Anything frozen is perfect for a teething baby. Hello, popsicles! Make your own popsicles from a kale smoothie for a healthy twist.
Numb first, eat next
Let baby chew on a cold teether before mealtime so their gums are numbed up to reduce pain while eating. Numbing the sore gums with a cold teether before mealtime may make food more inviting. They’ll be more likely to want to eat if they get to chew on something icy first.
The good news about a teething baby not eating as much is that it rarely goes on long enough to cause health issues. If you have concerns though, check with the pediatrician, as babies dehydrate quickly.
Dealing with a teething tot isn’t the most fun part of parenting. And a hungry, teething baby is about as bad as it gets. But with these helpful tips, you and your little one just might find the trick that makes eating a soothing experience.
Editors' Recommendations
- How many calories should I let my teen eat per day? The answer is complicated
- Should I wake baby from a long nap? 3 times it’s okay
- Can you take cold medicine while nursing? What you need to know about what to avoid
- 6 best Facebook groups for nursing moms
- Help! My teenager is vaping! Why this is a high-level parenting emergency
what to do if the teeth are climbing and the baby has a poor appetite
Published: 05/06/2022
Reading time: 2 min.
Number of reads: 52659
The author of the article: Ponomareva Yuliya Vladimirovna
Pediatrician, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Allergist-Immunologist
The appearance of milk teeth in a baby is a difficult stage in the life of both a child and all family members. This is one of the most common causes of restlessness, moody behavior and poor appetite in an infant in the first year of life. Let's discuss how parents need to behave in order to help the baby get through this difficult period.
Contents: Hide
- Timing of teeth
- Changes in health
- Refusal to eat
- General rules
- Baby porridge
- Practical tips
Terms of appearance of teeth
The formation of teeth occurs in utero, that is, the baby is born already with a full set of teeth, which are then waiting for their time to erupt. The timing and pace of teething is an individual process, which depends primarily on heredity, as well as on external factors, such as the quality of drinking water and the nature of nutrition. For the first 3-4 months, the baby is exclusively breastfed, and the baby does not need teeth yet. By the 4th month of life, the baby is already deficient in the nutrients of breast milk, the stage of the start of the introduction of complementary foods begins. At this age, many children begin to appear the first milk teeth. However, the timing of the onset of eruption can be shifted to the second half of life, this is also a variant of the norm. On average, by the 12th month of life, a child has 8 teeth and 20 by 2 years.
For the first 3-4 months, the baby is exclusively breastfed, and the baby does not need teeth yet. By the 4th month of life, the baby is already deficient in the nutrients of breast milk, the stage of the start of the introduction of complementary foods begins. At this age, many children begin to appear the first milk teeth. However, the timing of the onset of eruption can be shifted to the second half of life, this is also a variant of the norm. On average, by the 12th month of life, a child has 8 teeth and 20 by 2 years.
Health changes
The most common teething symptoms are increased salivation and itchy gums. During this period, the child pulls in his mouth and gnaws his own fingers and any objects that come across. In addition, the appearance of teeth is often accompanied by an increase in body temperature, changes in the stool and a decrease in appetite. The temperature can be above 38 ° C and disturb the child for several days. To make sure that changes in the baby's health are associated with the appearance of milk teeth, carefully examine the child's oral cavity. On examination, you will find redness and swelling of the gums at the site of the new tooth, and the child will respond even to a slight pressure on this area. Against the background of teething, the immune defense of the baby is often reduced, which leads to the appearance of symptoms of a viral or bacterial infection. Therefore, changes in the state of health of the crumbs can only be indirectly associated with teething. In every ambiguous situation, do not neglect the advice of a pediatrician.
On examination, you will find redness and swelling of the gums at the site of the new tooth, and the child will respond even to a slight pressure on this area. Against the background of teething, the immune defense of the baby is often reduced, which leads to the appearance of symptoms of a viral or bacterial infection. Therefore, changes in the state of health of the crumbs can only be indirectly associated with teething. In every ambiguous situation, do not neglect the advice of a pediatrician.
Refusal to eat
Teething in babies is often accompanied by eating disorders - children become selective in choosing food, and often completely refuse food. Since the appearance of milk teeth is a long process, many parents of babies are concerned that during the period when teeth are being cut, the child does not eat almost anything. The contact of food with the gums increases pain, and the child does not perceive any food well. "How and what to feed the baby?" - this is the most pressing issue for parents of infants in the first year of life. Try to follow the general recommendations during this period, as well as some practical tips to help keep the child from being hungry.
Try to follow the general recommendations during this period, as well as some practical tips to help keep the child from being hungry.
General rules
Despite the difficult situation, do not force-feed. Forced eating can provoke disruption of the digestive tract and be the cause of improper eating behavior in the future. During this period, it is better to adhere to a free feeding regime according to the principle - often, but in small portions. If the mother is breastfeeding, then expect the frequency of feedings to change. The child has a need for frequent application, not only to satisfy hunger, but also for emotional calm. In the acute phase, refuse to introduce complementary foods and choose foods that minimally irritate the oral mucosa. During this period, salivation is increased in babies, therefore, to restore the water balance, periodically offer the baby drinking water for babies, allowed from birth. The baby has a desire to gnaw and bite everything, but during this period it is better to refuse solid food as much as possible, since sharp edges can additionally injure the mucous membrane and only worsen the situation. Among complementary foods, the most optimal choice during teething are cereal complementary foods.
Among complementary foods, the most optimal choice during teething are cereal complementary foods.
Children's porridge
What are the advantages of choosing children's porridge as a priority in the baby's diet during the period of the appearance of milk teeth? Firstly, it is a highly nutritious product - the combination of milk and cereals meets the needs of the child for energy and nutrients, even with a relatively small amount of the finished product. Secondly, the appropriate consistency of commercially produced baby cereals facilitates the assimilation of complementary foods. Bebi Premium baby cereals for children over 4 months of age have a homogenized degree of grinding, which does not require additional gum grinding and reduces the load on the jaw apparatus. In addition, they are easily and without lumps diluted with water or breast milk at room temperature, which also reduces the severity of pain compared to warmer food. Fruit and vegetable complementary foods, despite the appropriate puree-like structure, are rich in organic acids, which can be a source of irritation of the delicate mucous membrane of the baby's gums. During this period, another important advantage of the Bebi Premium line of children's cereals is the reduced sugar content. Sugar is a good breeding ground for microbes that live in the oral cavity, its excess intake can increase the inflammatory process in the gums.
During this period, another important advantage of the Bebi Premium line of children's cereals is the reduced sugar content. Sugar is a good breeding ground for microbes that live in the oral cavity, its excess intake can increase the inflammatory process in the gums.
Practical advice
The pharmaceutical market offers a variety of topical gum pain relievers approved for use in children. However, it is recommended to use them very carefully and in consultation with the pediatrician in cases where pain significantly affects the condition of the crumbs. Be careful when using them, as swallowing the gel with painkillers can lead to severe toxic reactions. Safe aids are special teethers. Among them, the most effective are devices with a cooling gel or water inside. Offer the baby teethers before the next meal, and then he will eat complementary foods more calmly. Another simple and useful procedure is to massage the gums in the direction from the center to the corners of the mouth, avoiding impact on the eruption zone. Massage improves blood flow, activates growth processes and reduces tension in the gum area. Remember, teething is a natural physiological process, and the task of parents is to help the baby to overcome this difficult life stage as comfortably as possible.
Rate the article
(Number of votes: 14, average 4.7)
Share with friends:
Symptoms of teething in children under one year old and ways to alleviate them
In the first year of life, the child develops rapidly. He learns to sit, crawl, walk. And he also has something that indicates the general physiological development, the maturation of the digestive system. He is preparing to move from eating exclusively milk or formula to a new stage - to the use of semi-solid and solid foods and the appearance of first milk teeth .
The eruption of the first milk teeth is influenced by genetic characteristics, health, nutrition and other factors. Even the dependence of teething in infants on the region of residence has been established. So, in the northern regions of Russia, there is a frequent deviation from the average dates towards a later eruption of [1] .
Even the dependence of teething in infants on the region of residence has been established. So, in the northern regions of Russia, there is a frequent deviation from the average dates towards a later eruption of [1] .
On average, the first baby tooth appears at 6-7 months. Within three years, all 20 milk teeth will take their place in the dentition. In some babies, teething begins at 4-5 months, someone waits up to 10-12 months. All of this is within the normal range of [2] .
There are several theories explaining the process of teething [2] :
-
Hunter's theory - pushing the tooth out of the bone alveolus occurs due to the pressure of growing roots;
-
Yasvoin's theory - the appearance of a tooth above the gum provokes processes of differentiation in the tissue of the dental papilla;
-
Katz's theory - an increase in tissue pressure in the area of the bottom of the alveoli directs the tooth to the surface.

But none of them can fully explain this complex mechanism.
By the time the tooth erupts, there is resorption of the bone covering the crown of the tooth. The same processes are noted in the gum. During the growth of the tooth root, the bone is also rebuilt and the dental alveoli gradually deepen. At the same time, morphological changes in the tissues surrounding the tooth occur: increased blood flow, changes in vascular permeability, increased production of the main substance of the pulp and periodontium"Can the physiological process of teething in infants be pathological?" Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Chief Pediatrician of the Central Federal District of the Russian Federation, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation Zakharova I. N. [2]
It is not surprising that the appearance of teeth causes discomfort in children at any age, but this process is especially difficult for babies.
Symptoms of teething in a child
The appearance of milk teeth is a natural physiological process, however, a number of children develop a symptom complex, which, according to the International Classification of Diseases, is classified as teething syndrome (ICD code - K00.7). Numerous surveys of young children say that the most common symptoms accompanying the appearance of teeth are:
-
increased salivation — processes in the oral cavity are activated;
-
irritability - the child experiences severe discomfort and cannot report it otherwise than by changing behavior;
-
sleep disturbance - the pain is so severe that the baby cannot sleep or often wakes up during the night;
-
itching of the gums - children try to compensate for it by trying to bite the breast or nipple, by trying to keep hands, toys, clothes in their mouths.
Such harbingers of the appearance of a tooth occur in 35-60% of children. But some babies may have non-specific symptoms [2] :
On average, symptoms appear 5-8 days before the appearance of a tooth. When teething several teeth at the same time, this, as a rule, increases the discomfort.
Even if the child's symptoms are very similar to those of teething, a specialist consultation is necessary. Be sure to consult a doctor if diarrhea or fever persists for a long time.
Ways to alleviate discomfort
To ease the teething of a baby, it is necessary:
-
provide additional attention and care from parents;
-
if the child is breastfed, breastfeed more frequently as this has a slight sedative effect;
-
purchase several silicone teethers that can be cooled and offered to the baby during the day;
-
massage the gums with a finger wrapped in a clean gauze pad or with a special silicone nozzle;
-
blot drool in time with a clean tissue to avoid irritation of the skin around the mouth;
-
if necessary and in agreement with the doctor, use medicines.

To date, there are pharmacological and non-pharmacological methods of therapy for the eruption of temporary teeth.
Topical preparations
Pediatricians prescribe gels and ointments as symptomatic relief for severe discomfort associated with teething.
Such teething gels and ointments with proven effectiveness are divided into 3 groups [1] :
-
Preparations with analgesic effect based on anesthetic (lidocaine, choline, benzocaine). Sometimes lidocaine-based preparations include anti-inflammatory or antiseptic components, providing a combined effect of the gel.
-
Medicines based on anti-inflammatory or antiseptic agents.
-
Preparations based on extracts of medicinal plants. They use extracts of Roman chamomile, boswellia, aloe, marshmallow, Indian ivy, medicinal rhubarb, calendula and other components of plant origin.
Homeopathic teething products are also produced, but their effectiveness has not been scientifically proven [1] .
Systemic drugs
In severe pain syndrome, hyperthermia, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used, which reduce body temperature and have a systemic analgesic effect. The pediatrician should select the dosage and the drug suitable for the child.
Distractions
These include: the gum massage described above and baby teethers that help your baby temporarily relieve itchy gums.
Inspection of erupted teeth
Swelling and redness of the gums gradually subside as the infant's teeth erupt and grow, but should be monitored. Normally, the teeth should be evenly located in the dentition, not have whitish or colored spots, irregularities on the enamel.
Violation of the timing, pairing and sequence of eruption of milk teeth can serve as a marker of various diseases and disorders.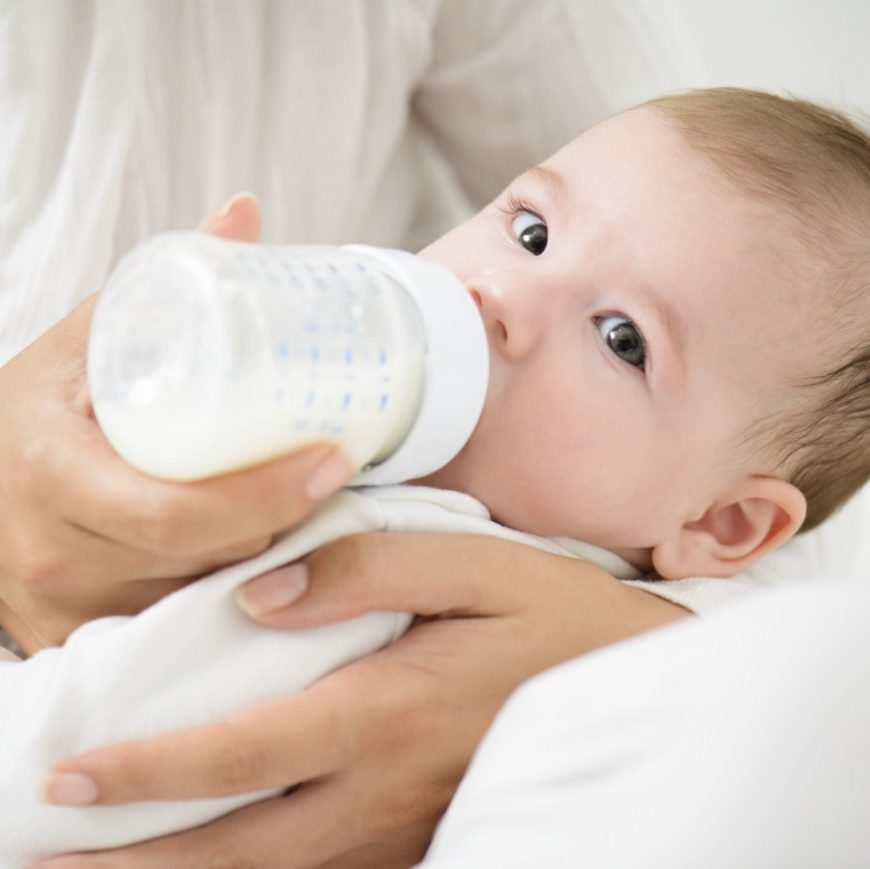 For example, rickets or hypothyroidism [2] . It is important to record the date of appearance of each tooth and its location in the mouth. It is convenient to do this with photos saved in a separate folder on your smartphone.
For example, rickets or hypothyroidism [2] . It is important to record the date of appearance of each tooth and its location in the mouth. It is convenient to do this with photos saved in a separate folder on your smartphone.
Erupted Tooth Care Instructions
To clean baby's teeth, use special silicone fingertips with soft bristles. Toothpaste should be labeled as suitable for young children and free of substances that are harmful if swallowed: high concentrations of fluoride, parabens, sodium lauryl sulfate.
As soon as the first tooth shows above the gum line, it needs special care . Enamel has not yet fully formed, it is very thin, so children's caries develops rapidly. Only 10% of children manage to avoid caries and adults practically fail [5] . Therefore, do not postpone the preventive fight against it.
To maintain the health of milk teeth, some of which will remain with the child until the age of 10-12, it is important to visit the dentist regularly once every 3-4 months.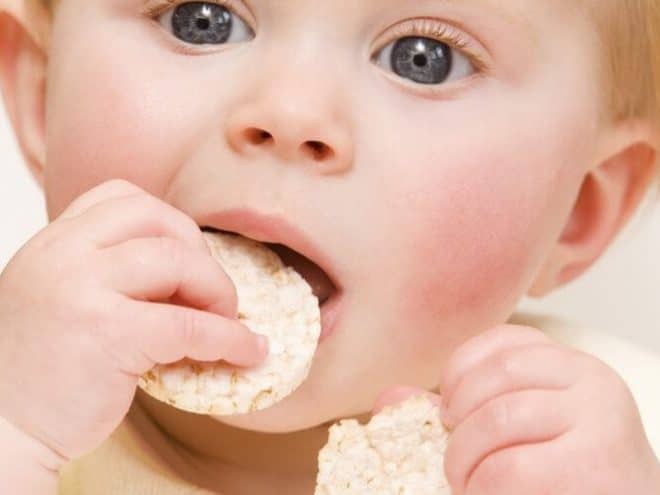 After a year, you need to visit an orthodontist to make sure that the bite develops correctly.
After a year, you need to visit an orthodontist to make sure that the bite develops correctly.
List of sources
1. Zaplatnikov A. L., Kasyanova A. N., Maykova I. D. Teething syndrome in infants: a new look at an old problem 2018 // https://www.rmj.ru /articles/pediatriya/Sindrom_prorezyvaniya_zubov_u_mladencev_novyy_vzglyad_na_staruyu_problemu/ (Accessed 05/28/2020).
2. Zakharova IN, Kholodova IN, Dmitrieva Yu. A., Morozova NV, Mozzhukhina MV, Kholodov DI Can the physiological process of teething in infants be pathological? 2016 // https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/mozhet-li-fiziologicheskiy-protsess-prorezyvaniya-zubov-u-mladentsev-byt-patologicheskim (date of access: 05/28/2020).
3. Kleschenko E. I., Zhdanova I. A., Lukisha A. N., Krakovets I. V., Smychkova E. V., Kartavtseva A. V. Symptoms of teething in infants: condition or disease? 2017 // https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/simptomy-prorezyvaniya-zubov-u-mladentsev-sostoyanie-ili-bolezn (date of access: 05/28/2020).