Best angle to bottle feed a baby
Everything You Want to Know
Bottle-feeding an infant is not rocket science, but it’s not necessarily easy either. Some babies take to the bottle like champs, while others require a bit more coaxing. In fact, introducing a bottle can be a process of trial and error.
This seemingly simple undertaking is made exponentially more challenging by the staggering plethora of bottle options, varying nipple flows, different formula types, and multiple feeding positions.
Yes, there’s a whole lot more to bottle-feeding than what meets the eye, so don’t be discouraged if your wee one is a bit fussy at first. You’ll soon find the routine — and products — that work for your little one. In the meantime, we’ve got you covered with all the bottle basics.
Once your bottle is prepared and at the ideal temperature (find more details on these below), it’s time to start feeding your baby.
- First, find a position that’s comfortable for you and safe for your baby.
- Hold the bottle at a horizontal angle so that your little one has to gently suck to get the milk.
- Be sure that the milk fills the entire nipple so that your baby isn’t gulping lots of air, which may result in gas and fussiness.
- You’ll want to take breaks every few minutes to gently burp baby. If they seem particularly squirmy during a feeding, they may have a gas bubble; take a pause and gently rub or pat their back.
- Use this opportunity to bond with your baby. Hold them close, look into their wide eyes, sing soft songs, and make feeding time a happy time.
Be sure to pace your feeding. You can’t expect — nor do you want — a new baby to chug a bottle down in 5 minutes flat. It may take a while, and that’s a good thing.
You want a baby to regulate their own hunger, so slow down and allow an infant to go at their own speed. Be sure to follow their cues, pause to burp or reposition them, and put the bottle down if they seem bothered or disinterested. You can try again in a few minutes.
And if they seem to want a top off? Go ahead and offer a free refill if it seems necessary.![]()
There are several positions you can try for bottle-feeding. Make sure you’re both comfortable so it’s a pleasant experience. Find a suitable place to sit comfortably, use pillows to support your arms if needed, and cozy up together during feeds.
Here are a few options to try:
Cradle your baby
When you think of holding a newborn baby, you probably envision yourself cradling them in the nook of your arm. This is a great position for feeding your wee one a bottle. Rest their head in your elbow bend, and tilt them up so they’re at a comfortable angle. This position is ideal for some bonus skin-to-skin contact.
Sitting position
Sit down and place baby upright in your lap with their back against your stomach and chest. This position is especially encouraged for infants with reflux. Just be sure that you’re tipping the bottle to completely fill the nipple with milk.
Rest baby on your legs
Sit or lay down, and prop your baby on your legs with their back against your thighs and their head near your bent knees. This position allows for eye contact and interaction.
This position allows for eye contact and interaction.
Use a feeding pillow
Nursing pillows aren’t just for breastfeeding. Some babies enjoy being positioned on a pillow for mealtime. A traditional C-shaped nursing pillow works great for this purpose, allowing baby to relax and be comfortable during a feed.
While this option frees up your arms, you’ll still need to hold the bottle for your baby. Propping or rigging a hands-free situation has potentially dangerous consequences.
Once a baby is old enough and expresses interest in holding the bottle themselves (somewhere around 6–10 months of age), you can let them try. Just be sure to stay close and monitor them carefully.
Whatever position you try, make sure that your little one is angled, with their head raised. You don’t ever want your baby to be lying down flat while eating. This could enable milk to travel into the inner ear, potentially causing an ear infection.
Of course, feeding baby the bottle might be the easy part.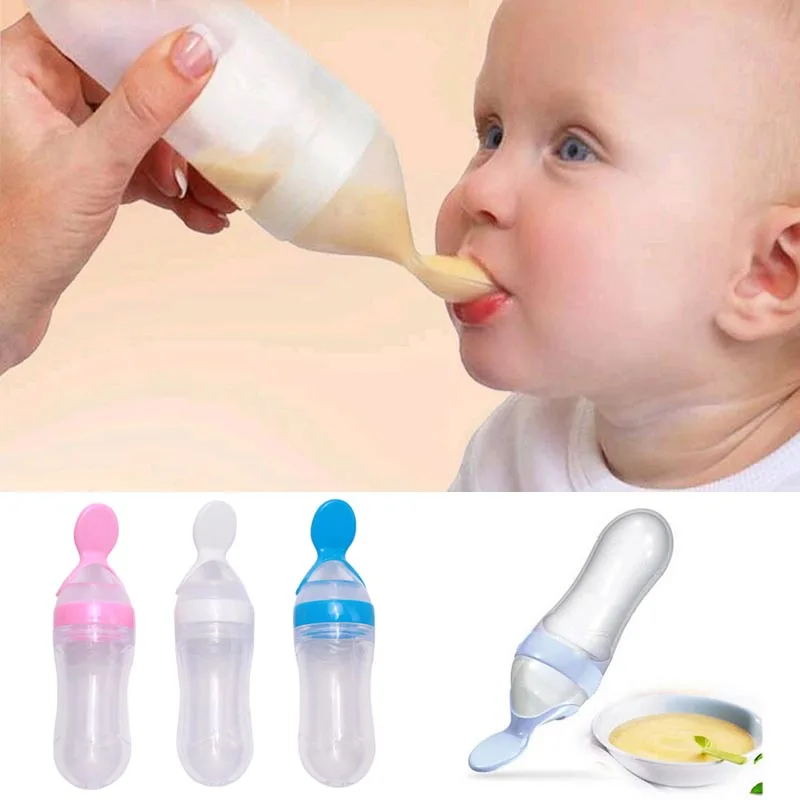 Picking the right vessel to hold your breast milk or formula can be a whole other complicated story. The information below can help you master the art of preparing the perfect bottle for your baby.
Picking the right vessel to hold your breast milk or formula can be a whole other complicated story. The information below can help you master the art of preparing the perfect bottle for your baby.
Choose the right bottle for your baby
If you’ve ever browsed the feeding section of a baby store, you know that bottle options are seemingly endless.
There are bottles designed for colicky babies, gassy babies, and breastfed babies. It’s daunting. The confounding truth is that some babies will take any old bottle you throw at them, while others will be far more discerning.
You might have to try a few different brands to find “the one” for your baby. If you have a gassy guzzler, you could go with one that uses a venting system. If you’ve been exclusively nursing up until now, you can try one that more readily resembles the shape and feel of mama’s breast.
You may also want to pick a bottle that has fewer parts to clean and reassemble. You’ll appreciate the lack of steps during that 2 a. m. feeding session.
m. feeding session.
Furthermore, start with a slow-flow nipple, and upgrade when your baby seems eager to get more milk, faster.
Prepare your formula or breast milk bottle
Feeding with formula? There are three types to choose from: powder, concentrate, and ready-to-pour.
Ready-to-pour formula is the easiest (and, yes, most expensive) option of the three. It involves no preparation and is as simple as opening and pouring it. You can purchase small, individual bottles that come with nipples, which are especially useful for those early infant feedings, or opt for larger bottles that need to be refrigerated. Either way, it’s fairly foolproof.
When using powder, you’ll need to measure out portions and mix them well with suitable water. It’s important to follow the directions and use the recommend water-to-formula ratio. Using too much water can dilute the nutrients; using not enough can cause dehydration. Both of these possibilities can have dangerous consequences, so use caution and care.
Similarly, concentrate formulas require a safe water source. Once again, measuring appropriately is key.
If you’re breastfeeding, preparing a bottle is pretty straightforward. Just pour pumped fresh or frozen breast milk into a bottle, and warm it up (if refrigerated and desired). Be sure to double-check the pump date, though; thawed and/or refrigerated breast milk has a short shelf life.
Warm your bottle
Some babies will take a bottle straight out of the refrigerator, but many prefer their milk slightly warmed.
The best way to warm up a cold formula or breast milk bottle is by submerging it in a cup of hot water for a few minutes. You can also use a bottle warmer. Test the milk temperature on your wrist before serving it to your baby.
Be sure to never microwave a bottle. This can cause an uneven temperature throughout and create hot spots that could burn baby’s mouth.
How long is a bottle good for?
It may seem painful to throw away precious pumped liquid gold or chuck expensive formula. Yet, at some point or another, you’ll probably watch wistfully as you pour some unused bottle milk down the drain.
Yet, at some point or another, you’ll probably watch wistfully as you pour some unused bottle milk down the drain.
If you’re using expressed breast milk, there are some important time frames to remember. Breast milk can be frozen for up to 6 to 12 months and refrigerated for 4 days. (If it has been thawed, though, you should use it within 24 hours.) Once you begin feeding a breast milk bottle, it’s safe for up to 2 hours.
A prepared bottle of formula can be refrigerated for 24 hours. Once baby has taken a sip from a bottle of formula, it must be used within 1 hour. Bacteria multiply quickly on milk-based products, so be sure to check the clock.
It may feel like you’re constantly preparing bottles, but don’t worry, this feeding frenzy phase will soon pass.
Yes, in the early days of parenthood, you’ll be feeding your little one every 2 to 4 hours. As a newborn, your baby will likely consume around 2 ounces per feed.
As they get older, the feedings may become spaced out, and the amount in each bottle will increase. Around the 2-month mark, your baby may start drinking 4 to 6 ounces each feeding. By 6 months, they’ll probably take in about 8 ounces.
Around the 2-month mark, your baby may start drinking 4 to 6 ounces each feeding. By 6 months, they’ll probably take in about 8 ounces.
Don’t feel tethered to a strict feeding schedule. It’s best to feed a baby when they seem hungry. Babies go through rapid growth spurts and may need to feed more frequently. Look for hunger cues to determine whether your little one is hankering for a bottle.
Your baby may be hungry if they begin gumming on their hands, sucking on their tongue, or rooting. Rub your finger or a bottle nipple at the side of their cheek or mouth, if they turn toward it, they’re probably ready for a feeding. Give that bottle a go!
If you’re a nursing mama, you may feel especially nervous about introducing a bottle. Rest assured that with a little patience and time, your baby will eventually get the hang of it.
Still, before you offer a bottle, you’ll want to feel confident that nursing has been well established. As such, you should consider waiting 2 to 3 weeks after your baby is born to introduce the bottle to avoid potential nipple confusion and ensure that your milk supply is adequate.
If you need to transition your baby to the bottle before returning to work, cushion in some extra time to normalize this routine. While your breastfed baby may happily accept the first bottle you offer, they may also turn their tiny nose up at it. Spare yourself and your baby unnecessary pressure, and give yourselves some wiggle room to adjust.
And if your baby does resist the bottle? Walk out of the room and have a partner or caregiver try. Your baby knows that you have the real deal under your shirt, and they may respond more readily to someone else.
Furthermore, don’t try to introduce the bottle when your little one is impatiently ravenous. Wait until they’re in a pleasant mood, and offer a bit when their tummies aren’t entirely empty. You may get a better reaction.
Even if you plan to be home and available to nurse around the clock, you should still try to introduce the occasional bottle. It’s good to know that your baby will accept it in a pinch.
Bottle-feeding has its challenges and rewards. There are a few other tips to keep in mind to help set you and your baby up for success.
Washing and sterilizing bottles
You may want to sterilize your bottles before their first use. You can do this with a steam sterilizer or in the dishwasher.
Sanitizing them between uses is probably unnecessary, but you do want to ensure that you always have a clean supply on hand — lest you have to wash one in the middle of the night while a crying baby impatiently awaits their bottle.
That said, a bottle requires a thorough scrubbing between uses, especially if it has pieces and parts with nooks and crannies. You can, of course, also use your trusty dishwasher. Either way, it’s smart to at least pour out any unused formula or breastmilk right away and give the bottle a quick rinse after a feeding session.
Mixing breast milk and formula
Want to slowly introduce formula to your breastfed baby? You can mix breast milk and formula in the same bottle. This can get baby more readily adjusted to the unique flavor of formula.
This can get baby more readily adjusted to the unique flavor of formula.
Just be sure to prepare the formula separately. If you’re using powder or concentrate formula, you’ll still need to add water first; don’t use breast milk as a liquid substitute. Once the formula is prepared, pour in the breast milk.
Finally, heed the time restrictions. While breast milk on its own can be used for up to 2 hours, the addition of formula means the bottle is only good for 60 minutes.
Adding cereal to a bottle
Has a well-meaning grandparent suggested adding cereal to your baby’s bottle?
Generally speaking, doctors advise against this practice. While many people assume it will keep their baby fuller for longer — and even help them sleep for a longer chunk of time — it can have a few negative consequences, including excessive weight gain and constipation.
Occasionally, doctors will recommend adding a bit of oatmeal cereal to a bottle to help a baby with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Talk to your pediatrician before making this decision on your own.
Talk to your pediatrician before making this decision on your own.
No doubt, the idea of bottle service takes on a whole new meaning these days, but you’re going to love this new adventure.
And while it may seem like a lot to take in, bottle-feeding your baby will soon become second nature. You may encounter some hurdles or missteps along the way, but you’ll quickly discover what works for you and your baby.
Good luck, you’ve got this!
How to Bottle-Feed a Baby
Whether you’re breastfeeding, formula-feeding or doing a combination of both, chances are you’ll eventually use a bottle with your infant. No big deal, right? But while images of a parent blissfully holding a bottle make the process look easy, there’s a learning curve when it comes to proper bottle-feeding. Here, everything you need to know about how to bottle-feed a baby safely and happily.
In this article:
How to choose the right bottle and nipple
How to make a baby bottle
Best bottle-feeding positions
What is pace feeding?
How to get baby to take a bottle
When to wean baby off the bottle
How to Choose the Right Bottle and Nipple
When it comes to figuring out how to bottle-feed a baby, selecting an appropriate bottle and nipple is step one. If people gifted you a bunch of bottles at your baby shower, you may want to hold off before opening and sterilizing them until baby is born, or at least take out just a few to try in the early days of feeding. Why? Because you won’t know what kind of bottle is best until you figure out what baby’s feeding needs are.
If people gifted you a bunch of bottles at your baby shower, you may want to hold off before opening and sterilizing them until baby is born, or at least take out just a few to try in the early days of feeding. Why? Because you won’t know what kind of bottle is best until you figure out what baby’s feeding needs are.
“Certain bottles work better for certain babies,” explains Jamie O’Day, BSN, RN, CLC, a registered nurse, certified lactation consultant and cofounder of Boston NAPS, a pre- and postnatal resource center in the Boston area. “For example, some babies who have issues with gas may do better with a bottle that has a filtration system, like a Doctor Brown’s style bottle, while babies who are used to being breastfed may have more success drinking from a bottle that aims to mimic the shape and feel of a mother’s breast, like the Comotomo.”
That said, O’Day has a universal tip for all parents: Look for a bottle that’s easy to take apart and clean. That generally means a nice wide neck and the fewest parts possible. “Proper cleaning is so important, so I always tell parents to choose the simplest bottle, which may just have a nipple, bottle and collar,” she says. If your child seems happy and easily takes the bottle, then there’s no need to switch.
“Proper cleaning is so important, so I always tell parents to choose the simplest bottle, which may just have a nipple, bottle and collar,” she says. If your child seems happy and easily takes the bottle, then there’s no need to switch.
Of course, it’s not just the bottle that you have to consider. It’s also important to pay attention to the flow of the nipple, which varies based on infant age. Generally speaking, young babies need a slower flow, while older babies who’ve mastered the art of bottle-feeding can handle a faster flow. The nipple may be called “slow flow,” “medium flow” or “fast flow” or may be numbered from one to three, with one being the slowest flow. There is no standard of flow between different brands, but most newborns should begin on level one or slow flow.
So how can you tell when it’s time to change the nipple size? That depends. Some infants happily use the same flow nipple throughout their infancy, while others may need a faster flow nipple. “If you notice your child taking a long time to finish a bottle, or losing interest midway through feedings, a faster flow nipple may be needed,” O’Day says, adding that this might happen at around 3 or 4 months of age, with another potential upgrade around 6 or 7 months.![]()
If your infant finishes a bottle quickly (say, under five minutes), seems gassy or cranky, or spits up a lot of milk right after feedings, it may be time to go back to a slower-flow nipple. Your pediatrician can also help determine if it may be time to switch the flow of the nipple.
How to Make a Baby Bottle
If you’re wondering how to bottle-feed a baby, you’re probably new to prepping baby bottles. Take a new skill, add in sleep deprivation and sprinkle in some very real safety concerns and you’ve got the somewhat daunting process of making a baby bottle (at least at first). Don’t despair. By reading directions, following the advice of a pediatrician and making sure to err on the side of caution, you’ll get the hang of it in no time.
How to make a baby bottle with formula
Baby formula comes in three different forms: ready-to-feed, concentrate and powder. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that babies under 3 months start off with ready-to-feed formula because of the small but real risk of cronobacter, a bacteria that can live in powdered infant formula.
• Preparing ready-to-feed formula: These require very little prep, since they come ready to be poured into a bottle and fed to an infant. Some ready-to-feed formulas come in bottles that can accomodate disposable nipples—all you need to do is screw a nipple on, feed and discard.
• Preparing concentrate formula: To prepare a baby body with this liquid formula, you’ll need to add water. It’s important to read the directions to learn the right ratio of water to concentrate. As for what type of water should you use, that depends on where you live, your pediatrician’s recommendation and your own wishes. If your tap water is safe, feel free to use it—just run it for several minutes before you fill the bottle to remove any trace contaminants in the water. You can also use filtered water, bottled water or boiled (and cooled) tap water.
• Preparing powdered formula: Just like concentrate, it’s important to follow directions on the right ratio of scoops of powder to ounces of water, says Carmen Baker-Clark, an International Board Certified Lactation Consultant (IBCLC) in Hoboken, New Jersey. When using powdered formula, make sure to shake well so the liquid isn’t clumpy. “Some parents notice powdered formulas may make their infant more gassy, more prone to spit-up or more constipated. A lot of this is due to the bottle preparation. For example, not shaking enough can create uneven consistency that may be harder for baby to digest,” Baker-Clark explains.
When using powdered formula, make sure to shake well so the liquid isn’t clumpy. “Some parents notice powdered formulas may make their infant more gassy, more prone to spit-up or more constipated. A lot of this is due to the bottle preparation. For example, not shaking enough can create uneven consistency that may be harder for baby to digest,” Baker-Clark explains.
Regardless of what kind of formula you choose, Baker-Clark recommends sticking with the same brand or being deliberate as you try new ones, instead of just using whatever formula is on sale. While all infant formulas are regulated by the FDA and must pass the same nutrient tests, babies may react differently to various brands of formula. If an infant has frequent reflux, crying episodes or seems uncomfortable after a feeding, speak with your pediatrician. Your child may have an allergy or intolerance and may need a special formula.
Whether you warm the bottle up is up to you. “Many infants have no problem taking a cold bottle and the advantage is that you then don’t need to warm a bottle when you’re on the go,” Baker-Clark says. Once a formula bottle has been made and the nipple has touched baby’s lips, the bottle is good for an hour. But if the bottle isn’t used, a bottle may be refrigerated for a day, O’Day says. Some parents like to prepare and refrigerate a bottle in advance to make middle-of-the-night feedings easier, while others may prepare a pitcher to use during the day.
Once a formula bottle has been made and the nipple has touched baby’s lips, the bottle is good for an hour. But if the bottle isn’t used, a bottle may be refrigerated for a day, O’Day says. Some parents like to prepare and refrigerate a bottle in advance to make middle-of-the-night feedings easier, while others may prepare a pitcher to use during the day.
How to make a baby bottle with breast milk
Preparing a bottle of breast milk is of course much more straightforward, since the milk itself is ready to go. But when grabbing a bag of breast milk to use, it’s important to keep an eye on when it was pumped and how it’s been stored since. According to breast milk storage guidelines, it’s safe to use freshly pumped milk that’s been stored at room temperature for up to four hours, in the fridge for up to four days or in the freezer for up to 12 months. Always use the oldest milk first. If baby doesn’t finish a bottle, you can offer it again within two hours of the last feeding.
Before giving baby the bottle, you can warm the milk up by placing the bottle (or milk storage bag) in a cup of warm water for a few minutes, or pop the bottle into a bottle warmer. Whatever you do, steer clear of the microwave, which can cause dangerous hot spots.
Best Bottle-Feeding Positions
How you hold your little one during a feeding is a crucial part of knowing how to bottle-feed a baby properly. Chances are, you’ve come across loads of images of parents bottle-feeding babies—but the positions you sometimes see in photos or on TV may not actually be the best for baby. For one, forget about laying baby across your lap. “Have you ever easily drank something while you lay on your back?” O’Day asks. (Answer: no.) “It’s the same for baby.” Not only can a back position lead to reflux, but it may also cause ear infections. Try these bottle-feeding positions instead:
• Cradle baby in your arms. This is the classic position you probably think of when you imagine giving baby a bottle. In this bottle-feeding position, baby’s head rests in the crook of your arm as you hold her head and chest at a slight incline—close to your chest is great.
In this bottle-feeding position, baby’s head rests in the crook of your arm as you hold her head and chest at a slight incline—close to your chest is great.
• Hold baby upright. Instead of lying down, baby should be almost in a seated position, with his head on your chest or in the crook of your arm. “This position can work especially well for infants who have reflux,” Baker-Clark says. Tilt the bottle so the milk completely fills the nipple, since a nipple filled only halfway with milk may lead to baby gulping some air, which can lead to gassiness or reflux.
• Use a pillow. A nursing pillow can be helpful in keeping baby’s chest and head propped up at an angle. Bonus: It can give your arms a break too as you cradle baby in your lap.
• Switch sides. Regardless of whether you’re breastfeeding or bottle-feeding exclusively, switching baby from one side to another can help prevent your little one from developing a side preference and can give your arms a break. Switching sides can also naturally pace a feeding session and can give baby a chance to decide whether or not he’s full before the bottle is finished.
Switching sides can also naturally pace a feeding session and can give baby a chance to decide whether or not he’s full before the bottle is finished.
As baby gets older, she may toy with holding the bottle. That’s fine, if she wants to, but it’s not a developmental milestone. “She may want to hold the bottle at 6 months, so you can let her, but you should still be close by, holding her and supervising her,” O’Day says. And if baby doesn’t show any interest in holding her bottle? As long as she’s reached other developmental milestones, like reaching or grasping for toys, it’s totally normal if your older infant wants his bottle served to him.
What is Pace Feeding?
You may have heard of “pace feeding” and wondered how to bottle-feed a baby using this method. “Paced bottle-feeding is where you follow baby’s cues and allow for breaks,” Baker-Clark says. “Taking the bottle away and re-offering it benefits both breastfed and exclusively bottle-fed babies.”
Pace feeding helps babies learn to regulate their hunger and allows ample time for digestion. It can also cue you into baby’s biorhythm, O’Day says. You may find baby doesn’t uniformly eat the same size bottle at each time of day. For example, maybe he’s extra hungry in the morning and drinks 8 ounces, but prefers 4-ounce bottles post-nap. Paying attention to baby’s cues can help you clue into her unique needs and natural schedule.
It can also cue you into baby’s biorhythm, O’Day says. You may find baby doesn’t uniformly eat the same size bottle at each time of day. For example, maybe he’s extra hungry in the morning and drinks 8 ounces, but prefers 4-ounce bottles post-nap. Paying attention to baby’s cues can help you clue into her unique needs and natural schedule.
Plus, paced bottle-feeding makes a feeding session—which can last about 15 to 20 minutes—a great time for baby and his caregiver to bond. Here, some tips for how to pace feed:
• Hold the bottle at a horizontal angle. When the bottle is held horizontally, baby has to work to pull milk from the bottle, instead of the milk dripping into her mouth.
• Give baby some breaks. Instead of pulling the bottle away from baby’s mouth, lean the bottle back so the milk leaves the nipple. That way, baby has a chance to catch his breath. If he seems like he’s still rooting for milk, offer him more.
• Burp mid-feed. “If baby is pulling away, seems fussy or seems to be playing with the nipple with her mouth, give her a burp,” O’Day says. Then offer the bottle again.
“If baby is pulling away, seems fussy or seems to be playing with the nipple with her mouth, give her a burp,” O’Day says. Then offer the bottle again.
How to Get Baby to Take a Bottle
Even if you’re planning to exclusively breastfeed, at some point you’ll likely need some pointers on how to get baby to take a bottle. “I tell my clients to introduce baby to a bottle once breastfeeding has been established, which depends on each mother-baby dyad, but on average, it’s around one month,” O’Day says. “Even if they’re not planning to regularly bottle-feed, doing so can give peace of mind if an emergency comes up, and can also be a way for mom to get a break.”
Some babies take a bottle no problem—after all, sucking is an instinctive reflex, which is why bottle-fed babies tend to get the hang of it in the first few days of life. But other breastfed babies may initially be reluctant to take a bottle. And sometimes breastfed babies have no issue taking a bottle when they’re one month old, but if a bottle hasn’t been regularly offered, by 3 or 4 months of age, they’re less happy to accept a bottle. Bottle resistance is pretty common, but luckily there are some tried-and-true tips for what to do when baby is refusing a bottle.
Bottle resistance is pretty common, but luckily there are some tried-and-true tips for what to do when baby is refusing a bottle.
• Offer often. Even if you’re breastfeeding, O’Day recommends giving baby at least one bottle a week, once breastfeeding has been established. “That way it’s part of their routine, so they’re less likely to resist it,” she says.
• Don’t offer it when baby is starving. If you’re regularly nursing your infant, O’Day suggests offering a bottle in between nursing sessions. “If they’re too hungry, they may be too worked up to take a bottle. If they’re calm and not super hungry, they may take it,” she explains.
• Let others try bottle-feeding. Some moms have success leaving the house and allowing their partner to try feeding baby a bottle. Again, try it at a time that’s not baby’s “must-feed” time.
• Don’t get frustrated. If baby isn’t taking the bottle, O’Day suggests putting it down and trying again later rather than forcing it, which can make both you and baby upset.
• Ask for help. A lactation consultant can suggest some techniques to help get even the most resistant bottle-feeders to accept a bottle. They may check your infant’s mouth and tongue for any latch problems that could contribute to the difficulty, suggest the best bottle for your infant, troubleshoot any behavioral issues or offer alternate nutritive methods, such as cup- or syringe-feeding.
When to Wean Baby Off the Bottle
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends parents stop offering bottles by 18 months due to tooth decay concern, but it’s smart to talk with your pediatrician about exactly when baby should wean from the bottle around the 9-month mark, O’Day says. “How and when to wean depends on how much table food baby is eating, any developmental concerns and your pediatrician’s assessment,” she says. Note, though, that cow’s milk shouldn’t be introduced until baby is 12 months old.
When baby is around 6 months old, offer a sippy cup or straw cup for water, O’Day says, since learning to drink from cups can help make the transition from bottles seamless. Some babies have no problem giving up the bottle, while others may require more time to make the transition, but looping in your pediatrician or lactation consultant can help make sure you’re all on the right track.
Some babies have no problem giving up the bottle, while others may require more time to make the transition, but looping in your pediatrician or lactation consultant can help make sure you’re all on the right track.
Whether you’re breastfeeding and offering the occasional bottle, combo-feeding or exclusively bottle-feeding, you might hit some bumps along your bottle-feeding journey. But there are ways to navigate through any problems that arise. If you’re struggling to find the best baby bottle for your child, need some pointers on how to bottle-feed a baby in an optimal position or encounter a full-on bottle strike, reach out to your pediatrician or lactation consultants for guidance.
Published August 2018
Please note: The Bump and the materials and information it contains are not intended to, and do not constitute, medical or other health advice or diagnosis and should not be used as such. You should always consult with a qualified physician or health professional about your specific circumstances.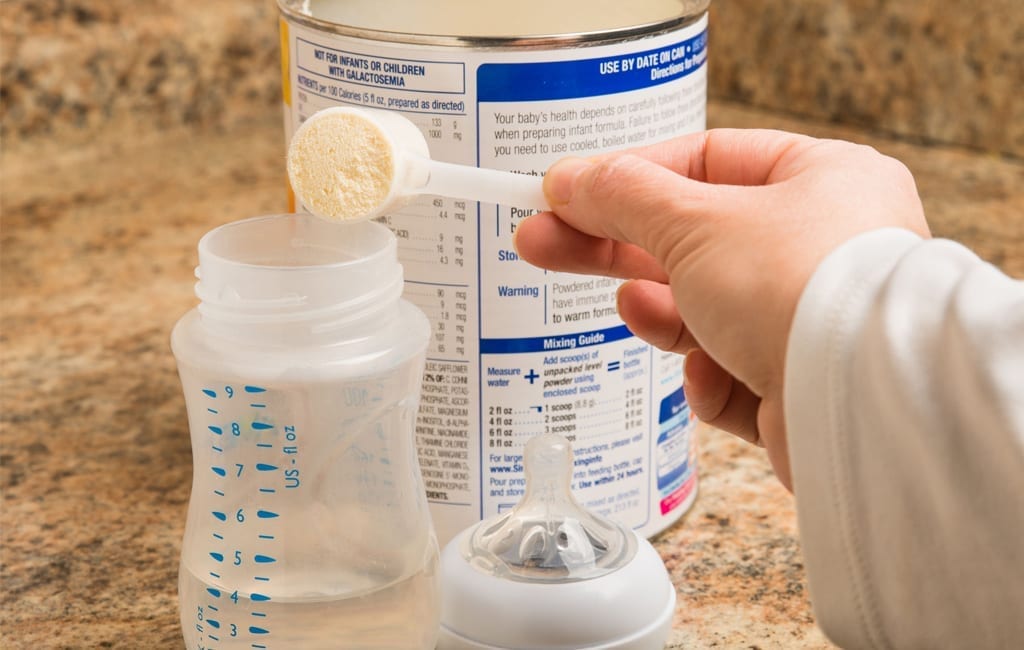
Plus, more from The Bump:
14 Best Bottles for Every Feeding Need
Pumping 101: How to Pump Breast Milk
The Best Baby Formulas for Your Child’s Needs
Best Positions for Bottle Feeding
Bottle feeding is not really a complicated process. However, you must remember a few rules. If you feed your baby incorrectly, he may cry, spill formula, suffer from colic, or slowly gain weight. Therefore, in order to properly bottle feed your baby, you must choose the correct upright feeding position. It should remind the baby of a natural position for feeding. Also remember that your baby's head should rest in the crook of your arm, in line with the spine. The longitudinal part of the nipple that enters the baby's mouth must always be full of milk - otherwise the baby swallows air, which can cause colic. Bubbles inside the bottle mean your baby is suckling properly.
Here are some examples of comfortable bottle feeding positions.
Whatever position you choose, it is best to always sit on the floor, comfortably leaning back against the wall. Try all positions to find the most comfortable one:
Try all positions to find the most comfortable one:
Sitting position
This is the most classic position. The child sits on one of your thighs with his back against your other thigh. You can hold his head in the crook of your arm or straight with your arm.
Side
If your baby spit up frequently, has gastroesophageal reflux disease, or has a runny nose, it is best to feed him when he lies diagonally on his side (preferably on his left side, but from time to time you need to shift to the other side). Your baby lies on its side, on one of your thighs, with its back and head against your other thigh. His ass rests on your stomach. You can change the angle of your child's body by raising or lowering your knees.
Facing each other
Place the baby on your lap with his bottom pressed against your stomach. This position ensures the correct position of the head and torso (the head is in line with the spine). Remember to keep your child's torso straight, don't let him arch his back.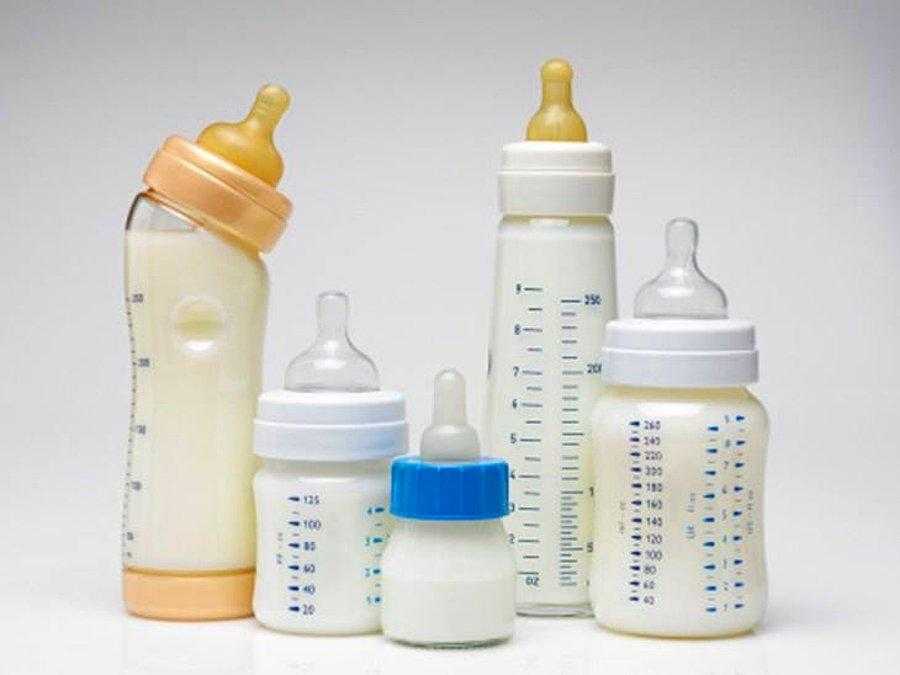
Almost apart from each other
In this position, you must keep the child's torso in line with the head. This will help your baby breathe properly, suck and swallow more effectively, and be less tired during feedings. If your child wants to, let him hold the bottle in his hand, even if he is still very small. At about 7 months, the baby begins to feel independent and wants to hold the bottle on his own. However, you should still support the bottle with your hand and help your baby with feeding until he finishes eating. When your baby grows up (i.e., sits up on his own), you can feed him in a high chair and replace the bottle with a non-spill cup or a regular cup with a straw. Do not leave your child alone with a bottle. This is strictly prohibited! You also shouldn't let your baby sleep with a bottle during mouth. In both cases, it can choke!
Whether you are breastfeeding or bottle feeding, always remember these rules:
- First of all, always feed your baby in your arms.
Do not feed your baby when he is lying, especially on his back. He may choke on milk. Babies often suffer from reflux, which means the mixture flows back from their stomach into their esophagus.
Also remember that your child feels safest in your arms. Try also to change hands from time to time, ie. support the child first with one hand and then with the other. Thanks to this, your child's muscles will develop evenly.
- Second, remember to always keep your child's head higher than his torso (put him on your arm). This is the best position for a baby while breastfeeding. If you are breastfeeding, make sure your baby cuddles and suckles properly. When bottle feeding, make sure that the part of the nipple that is in the baby's mouth is completely filled with milk. This minimizes the risk of swallowing air (i.e., prevents colic). Make sure your baby doesn't tilt their head back or forward too much. This makes sucking very difficult and can even cause food to enter your baby's airways.
- Third, never feed your baby when you are irritable or stressed. Take a moment for yourself first, take a deep breath and try to relax. When you have calmed down, sit in a comfortable chair, place a pillow under your armpit, place your baby on the pillow, and start feeding while speaking gently to your baby. Your child feels your emotions. If you are tense, he will also feel awkward. Also, never feed a baby if he is excited, crying or screaming. When he is in this condition, his airways are not protected and the mixture can enter his larynx instead of his esophagus.
- Fourth, take breaks after and during each feed by holding the baby in an upright or semi-upright position. Lay his head on your shoulder and support his back with your hand. Keep your baby upright until he releases any air he swallows while feeding. It usually only takes a moment, although sometimes it can take a little longer.
Bottle feeding | Canpolbabies.
 com
com Find out how to bottle feed your baby safely, how to help your baby feel safe while feeding, and how to set feeding times based on your baby's needs.
The most important thing is to choose the right position when feeding
When bottle feeding, avoid lying down as the milk flows out of the bottle under the force of gravity (at a constant speed controlled by alternating pressure on the nipple).
An infant may choke on milk if fed in a horizontal position. Therefore, it is very important to choose the right - more upright - position for feeding (the baby's head should always be slightly higher than the rest of the body).
Your baby's head should be in the crook of your arm, in line with his spine. The bottle feeding position should resemble the natural feeding position - especially when you feed him with two different feeding methods.
Remember:
- Never leave your baby alone with a bottle as they may choke
- Never let your baby sleep with a bottle in their mouth
How to give your baby a bottle
Place the bottle in the child's mouth so that it forms a right angle with his face. Your baby should not encircle the entire nipple with his lips, but only its oblong part, while the lips should rest against the rounded part. The oblong part should always be full of milk. Otherwise, the baby will swallow a lot of air during feeding, which can cause colic. Air bubbles in the bottle mean your baby is suckling properly.
Your baby should not encircle the entire nipple with his lips, but only its oblong part, while the lips should rest against the rounded part. The oblong part should always be full of milk. Otherwise, the baby will swallow a lot of air during feeding, which can cause colic. Air bubbles in the bottle mean your baby is suckling properly.
Emotional connection
Little children need parental love and affection. Your closeness helps him feel safe. Therefore, it is very important to talk affectionately with the baby as often as possible, hug and stroke him. Feeding is the best time to build an emotional relationship with your baby.
This is very easy to do when you are breastfeeding because you are already in physical contact with each other. However, bottle feeding also allows you to be closer to your baby as he feels the warmth of your body. Bottle feeding also allows other family members - the father, brothers and sisters to get closer to the child, since not only the mother can feed the baby in this way.
Calm emotional background
Never feed your baby when you are irritated or tense. Take some time for yourself first, take a deep breath and try to relax. When you have calmed down, sit in a comfortable chair, place a pillow under your arm, place your baby on the pillow, and start feeding while speaking gently to your baby. Your child feels your emotions. If you are tense, he will also feel restless. Also, never feed your baby when he is excited, crying or screaming. When he is in this state, his airways are not protected and food can enter his larynx instead of his esophagus.
Feeding by the hour
Formula milk is not as easily digested by the baby's stomach as breast milk, so according to generally accepted rules, it should be given every 3 hours.
Some pediatricians say it's best to give your baby formula on demand, that is, when the baby is hungry. In their opinion, it is better to feed the child than to wait another hour and keep him in suspense because he wants to eat. However, you still need to control the number of feedings and your baby's weight gain.
However, you still need to control the number of feedings and your baby's weight gain.
During the first month of life, the baby should eat > 7-8 times a day, 90-100 ml for each feeding, in the second month of life: 6-7 times a day, 100-120 ml for each feeding. During the first six months, the baby should gain approximately 150-200 g per week.
Feeding breaks
When your baby suckles milk from a bottle, he also swallows air. Therefore, he may feel full even before he drinks half the bottle. When feeding a child, breaks should be taken every few minutes to allow the baby to take in air - after such a break, he should ask for food again. During feeding, hold the baby in an upright or semi-recumbent position for a while (sometimes even for several minutes) to give him the opportunity to release air accumulated during feeding from the digestive tract. Help the child by holding him on your shoulder, putting his hands on your back. Bend and spread his legs a little.