Feed baby rabbits wild
Caring For Orphan Baby Rabbits
Wild Baby Bunnies – Orphaned or Not?
Wild baby bunnies are most often not orphaned! Many people mean well when they contact HRS after discovering an “abandoned” nest of wild rabbits. Often they wish to “rehabilitate” them with some advice from others. The reality is fewer than 10% of orphaned rabbits survive a week, and the care that people attempt to provide can be illegal, unnecessary, and potentially harmful.
The best thing you can do is put the bunny right back where you found him, in the general area, as the mom will only come back at night to call and find him. Leave the area. If injured, please contact a wildlife rehabber or rabbit vet immediately! You can search Google for your state/country and wildlife rehabber. Also search your state + wild rabbit rehabbers. You can call your Humane Society for referral and also check here: http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator If you find a baby with eyes open, and he appears healthy, leave him be.
I/My Dog/My Cat Found a Rabbit Nest! What Do I Do?
Rabbits hide their nests in plain view, often putting them in the open, sometimes in the middle of the lawn, as well as in brush piles and long grass. If you find a nest that has been disturbed, do all you can to restore and protect it. Do NOT bring it inside. If a dog has discovered the nest, keep your dog away from the area and reconstruct the nest with grasses. If need be, you can move the nest a few feet away where safer, even up to 5-6 feet away. A moved nest should always be covered with string in a tic tac toe pattern and monitored to be sure the mother found it and came back to the babies. She will scrabble away the surface area to feed her babies beneath her and then scrabble the earth, grass, leaves, back over the nest to hide it again so it’s pretty easy to see if the string has been disturbed and if the babies are warm.
Baby jackrabbits wait like this for momBabies should never be put back into a nest that has been flooded with water, has bugs/ants visibly crawling in and out, or if a baby has been killed and there is blood in the nest.
Use common sense. Baby bunnies who have fleas are compromised and should be immediately taken to a wildlife rehabber or humane society, rabbit vet.
Rabbit mothers nurse their babies for approximately 5 minutes a day. Both wild and domestic mothers will be in the nest early in the morning and then again in the evening. The milk is very rich and the babies “fill up” to capacity within minutes. Mother rabbits do not “sit” on the babies to keep them warm as do some mammals and birds. They build a nest with fur and grasses which helps to keep the babies warm in between feedings. For domestic/pet rabbits, do not force a mother rabbit to sit in the nest box. You can pick up the babies and see if they are feeding by checking the size of their stomachs (should not be sunken in), the pinkness of their skin and activity level (they should not be blue in color or sluggish in movement) and the amount of time that you hear them crying (baby bunnies should be quiet most of the day….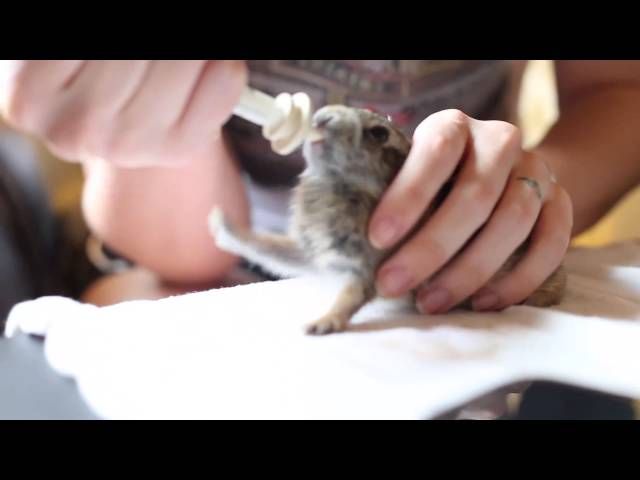 if they are crying constantly then they are not getting fed). If you come across a nest of wild bunnies, and the mother is nowhere to be seen, please DO NOT disturb them.
if they are crying constantly then they are not getting fed). If you come across a nest of wild bunnies, and the mother is nowhere to be seen, please DO NOT disturb them.
If your dog disturbs a nest, or you find a wild bunny with his eyes open, please put him back if not injured. Mom will be coming back at night to call and feed him only once in the middle of the night. Do not take the bunny inside or feed him! IT IS A MATTER OF HIS/HER SURVIVAL AND UP TO US AS HUMANS TO LEAVE NATURE BE AND LET THE MOM CARE FOR HER YOUNG. We often hear of mothers moving their babies and their nests, and have seen moms come back every night for up to a week to look for her missing baby. Do not take the baby from the mom or she will be frantic. Many call or write saying, “… but it is raining, etc., ” but remember, these are wild bunnies and belong out there.
I/My Dog/My Cat Destroyed a Wild Rabbit Nest! What Do I Do?
Remake the nest as best you can with grasses, hay, straw in the same place. Nests can be moved to a safer place up to 10′ away from the original site and can be reconstructed if necessary. To make a new nest, dig a shallow hole about 3″ deep and put into it as much of the original material as you can recover, including the mother’s fur. Add dried grass as needed, and put the young back. Mother rabbits return to the nest to nurse only at night, staying away as much as possible so as not to attract predators. To determine if the mother is returning, create a tic-tac-toe pattern over the nest with straw, grasses or tiny twigs. Wait 24 hours to see if the twigs have been disturbed. She may be able to feed them without moving the twigs much, so double check–If the babies look healthy, are warm, then the mother is coming back. If they are cold, dehydrated, get them to a professional; do not care for them yourself. Please contact a Wildlife Rehabber or rabbit vet or Humane Society immediately. Google your state and wildlife rehabbers.
Nests can be moved to a safer place up to 10′ away from the original site and can be reconstructed if necessary. To make a new nest, dig a shallow hole about 3″ deep and put into it as much of the original material as you can recover, including the mother’s fur. Add dried grass as needed, and put the young back. Mother rabbits return to the nest to nurse only at night, staying away as much as possible so as not to attract predators. To determine if the mother is returning, create a tic-tac-toe pattern over the nest with straw, grasses or tiny twigs. Wait 24 hours to see if the twigs have been disturbed. She may be able to feed them without moving the twigs much, so double check–If the babies look healthy, are warm, then the mother is coming back. If they are cold, dehydrated, get them to a professional; do not care for them yourself. Please contact a Wildlife Rehabber or rabbit vet or Humane Society immediately. Google your state and wildlife rehabbers. Also check http://www.humanesociety.org/animals/resources/tips/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator.html and http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator
Also check http://www.humanesociety.org/animals/resources/tips/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator.html and http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator
How Do I Know If the Wild Baby Bunnies Need Help?
Very young wild baby bunnies with eyes closed and ears back rarely survive in captivity, even given the most expert human care; and so it is very important to determine whether they really need help. Try to assess whether the infants seem warm and healthy or cold, thin, and dehydrated. One test for dehydration is to gently pinch the loose skin at the back of the neck. If it does not spring back in one second, or stays in a “tent,” the bunny is SEVERELY dehydrated and needs rehabilitation IMMEDIATELY by a professional rabbit vet or rehabber. Another test is to stroke the genital area to stimulate elimination if the eyes are closed. If the pee is brown and gritty, the mother rabbit has not been there to help the bunnies urinate.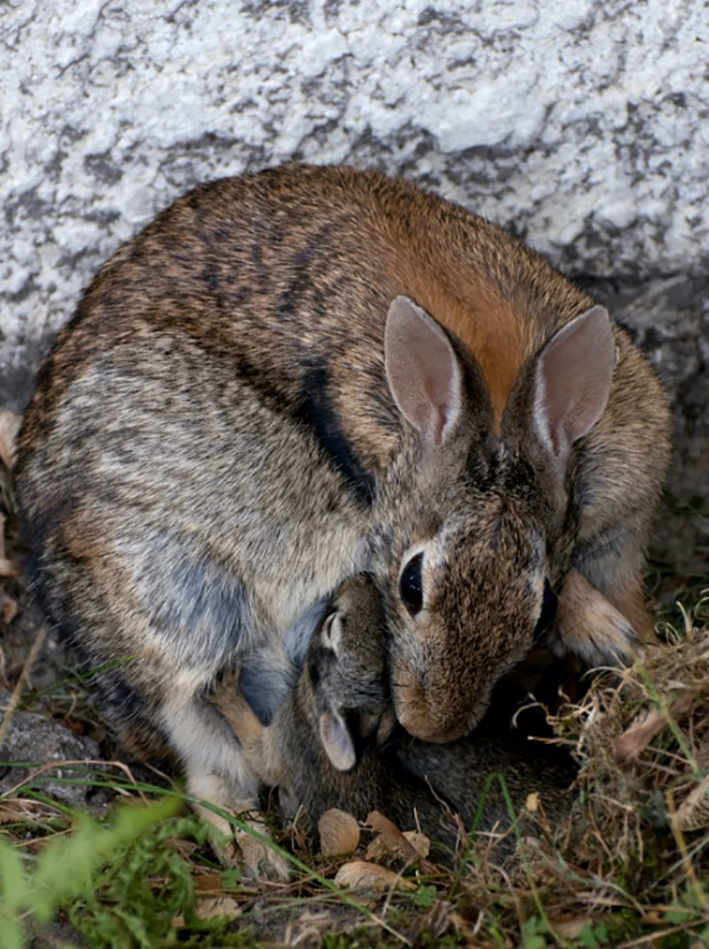 The brown, gritty urine is toxic, and the infant bunny must be cared for by a professional. Please contact a Wildlife Rehabber or rabbit vet immediately. Google your state and wildlife rehabber, call your Humane Society, and also check http://www.humanesociety.org/animals/resources/tips/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator.html and http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator.
The brown, gritty urine is toxic, and the infant bunny must be cared for by a professional. Please contact a Wildlife Rehabber or rabbit vet immediately. Google your state and wildlife rehabber, call your Humane Society, and also check http://www.humanesociety.org/animals/resources/tips/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator.html and http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator.
Older baby bunnies who are found outside of the nest may not be orphaned or in need of assistance. This is most often the case. Baby cottontails are born without fur but develop a full coat in a week. Their eyes open in 10 days, and in three to four weeks they are weaned. At this age, they may explore the world outside of the nest but return there to sleep. They are not ignored by the mother but stay with the family group until four or five weeks of age. To determine whether a bunny of this age needs assistance, first see if the bunny feels cold to the touch; perform the dehydration test. Also look for bleeding, convulsing, fly larvae, broken limbs; if any, get to a rabbit vet or emergency vet immediately. If he is just out and about, leave him be. He is discovering his world, waiting for mom to return at night when we humans are asleep. Don’t assume because he is letting you pick him up, he needs help. They are prey animals, taught to freeze when a predator (or human) approaches. Leave him be!
Also look for bleeding, convulsing, fly larvae, broken limbs; if any, get to a rabbit vet or emergency vet immediately. If he is just out and about, leave him be. He is discovering his world, waiting for mom to return at night when we humans are asleep. Don’t assume because he is letting you pick him up, he needs help. They are prey animals, taught to freeze when a predator (or human) approaches. Leave him be!
What if the Baby Bunny is Injured?
Either call or take him to your local rabbit vet, humane society or animal shelter/animal control. Call first as often they will come pick up the baby. If after hours, contact a local emergency rabbit vet or rabbit vets found here and also here. The best thing you can do for an injured wild baby bunny is to get in touch with a skilled Wildlife Rehabber by searching your state/country and wildlife rehabber, or calling your Humane Society, and or trying this link http://www.humanesociety.org/animals/resources/tips/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator. html and http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator
html and http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator
Is there anything I can do to avoid orphaning wild baby bunnies?
The harsh reality is that many of us who care about wild baby bunnies may be contributing to the suffering and death. House cats who roam outside will kill about every other time they go out. And unlike feral cats who hunt because they are hungry, and kill immediately, house cats maul and torment their prey, sometimes skinning baby bunnies alive. Cat owners need to provide managed outdoor habitats for their cats – such as window boxes or pens. Providing a bell on your cat will help warn the wildlife if you cannot keep him inside. Keep your dogs on a leash with you if you see a rabbit nest.
Lawn chemicals can produce convulsing death in baby rabbits. According to the Poison Control Center for Animals, lawn applications that contain herbicides are not directly toxic to small animals; but they may make toxic plants more palatable to them and may make the animals sick for a few days. Products which contain insecticides, such as Dursban or Diazinion, which are added to many lawn products to control fleas or grubs in the lawn, are toxic.
Products which contain insecticides, such as Dursban or Diazinion, which are added to many lawn products to control fleas or grubs in the lawn, are toxic.
The Bunny is
Wild and Really Orphaned – How do I care for it?Again, make sure you KNOW for sure the mom was killed and the bunnies are abandoned (not warm, etc.). You will not see the mom. The mom will only come back in the middle of the night to feed her babies. If the mom was killed, the best thing you can do for a wild orphaned baby bunny is to get in touch with a skilled rehabilitator. In the meantime, call your local humane society or animal control and one of these vets for a wildlife referral: Rabbit Vets and Pet Bunny Vets. Google your state and wildlife rehabbers, and also try http://www.humanesociety.org/animals/resources/tips/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator.html and http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator
How much formula should I feed a Wild Orphaned Bunny until I get him/her to a rehabber?
The following is a guideline for the daily amount to feed a TRULY orphaned wild bunny (mother was killed, etc. ) Remember with wild bunnies, the mom only comes back at night to call and feed him once or so for 5 mins; please put him back for her if just found and healthy. She leaves them alone between feedings. Don’t assume they are abandoned! Wild rabbits NEED a skilled wildlife rehabber. You should not feed at home or the chances of their surviving is extremely low! Most die from bloat, wrong feedings/stress. These feedings are NOT meant to take place of an actual rehabber, but for someone only who may live too far from a rehabber and is faced with a wild mother, killed, for example. All others need to call your humane society, local rabbit vet, or google your state and wildlife rehabber. You can also check here http://www.humanesociety.org/animals/resources/tips/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator.html and http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator
) Remember with wild bunnies, the mom only comes back at night to call and feed him once or so for 5 mins; please put him back for her if just found and healthy. She leaves them alone between feedings. Don’t assume they are abandoned! Wild rabbits NEED a skilled wildlife rehabber. You should not feed at home or the chances of their surviving is extremely low! Most die from bloat, wrong feedings/stress. These feedings are NOT meant to take place of an actual rehabber, but for someone only who may live too far from a rehabber and is faced with a wild mother, killed, for example. All others need to call your humane society, local rabbit vet, or google your state and wildlife rehabber. You can also check here http://www.humanesociety.org/animals/resources/tips/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator.html and http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator
Age + Amount (This WILL vary SO MUCH depending on type of rabbit. It is impossible over the Internet to see your particular rabbit, so this is only approximate.) Use KMR kitten or KMR kitten plus Goat milk, regular not low fat. Add a pinch of acidophilus (aka Probiotic) to the formula to promote healthy gut flora. Formulas vary depending on region. Avoid Esbilac and any puppy formulas! FEED TWICE A DAY ONLY for healthy babies, three times if low weight. It may be easiest to start with a 3 cc/ml syringe or an eyedropper. Feed only with the bunny sitting UPRIGHT, and point syringe down towards bottom or side of mouth, so if too much comes out, the baby does not aspirate. At first, they may only take a few drops at one feeding until they are not stressed and used to this.
It is impossible over the Internet to see your particular rabbit, so this is only approximate.) Use KMR kitten or KMR kitten plus Goat milk, regular not low fat. Add a pinch of acidophilus (aka Probiotic) to the formula to promote healthy gut flora. Formulas vary depending on region. Avoid Esbilac and any puppy formulas! FEED TWICE A DAY ONLY for healthy babies, three times if low weight. It may be easiest to start with a 3 cc/ml syringe or an eyedropper. Feed only with the bunny sitting UPRIGHT, and point syringe down towards bottom or side of mouth, so if too much comes out, the baby does not aspirate. At first, they may only take a few drops at one feeding until they are not stressed and used to this.
Newborn to One Week: 2- 2+1/2 cc/ml each feeding (two feedings per day).
1-2 weeks: 5-7 cc/ml each feeding (two feedings per day). (depending on bunny..may be much LESS if smaller rabbit!) Newborn babies (if eyes closed) all need to be stimulated to urinate and defecate prior to or following feeding until their eyes open.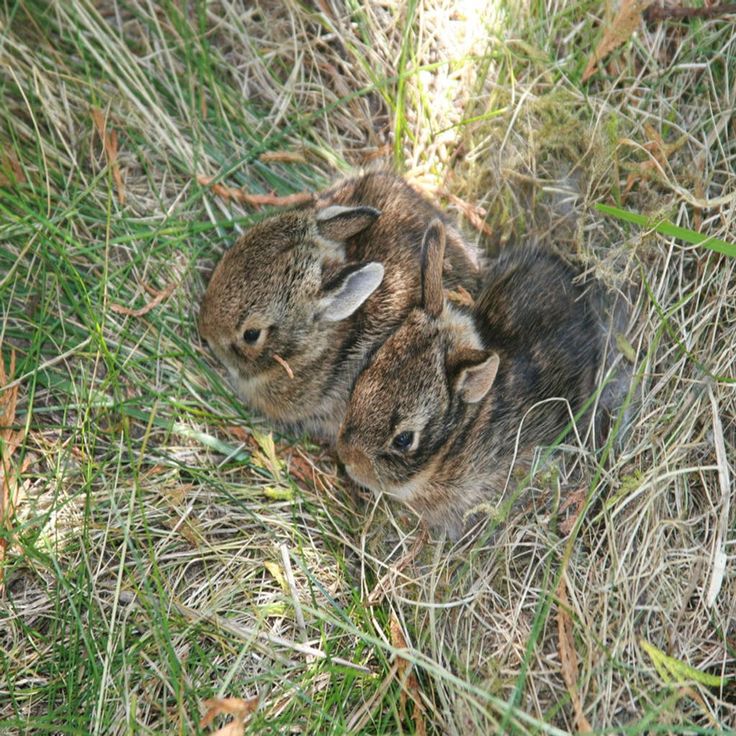 (Except Jackrabbits do not). *See how to below.
(Except Jackrabbits do not). *See how to below.
2-3 weeks: 7-13 cc/ml each feeding (two feedings). Domestic eyes open at about 10 days of age. Start introducing them to timothy and oat hay, pellets and water (always add fresh greens for wild ones).
3-6 weeks: 13-15 cc/ml each feeding (two feedings–again, may be LESS depending on size of rabbit! A cottontail/brush bunny will take so much less!! Half this at most.) Cottontails wean and release about 3-4 weeks and jackrabbits much later (9+ weeks), whereas domestic rabbits are 6 weeks.
6 weeks-9weeks for Jackrabbits only, continue up to 9 weeks with formula, gradually changing to a dish for the warm formula, replacing the formula after 9 weeks slowly, continue adding more of their natural greens and hay (dandelions, oat hay, timothy hay, Italian parsley, carrot tops, small carrots cut up) and a small water bowl. Most markets will sell these greens. They need a rehabber before release!
They need a rehabber before release!
Wild rabbits NEED a skilled wildlife rehabber. These feedings are NOT meant to take place of an actual rehabber, but for someone who may live too far from a rehabber and is faced with a wild mother, killed, for example. Please call your humane society for referrals to rehabbers, or your rabbit vets, or google your state or country and wildlife rehabbers. You can also try here: http://www.humanesociety.org/animals/resources/tips/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator.html and by state here: http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator or http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator
*After each feeding it is important to gently make the bunny defecate and or urinate (brush bunnies/cottontails only..if the eyes are not opened yet) to keep the intestinal and urinary system running smoothly (just UNTIL their eyes open). No need to do this for jackrabbits; they go on their own. Use a cotton ball moistened with warm water after eating, and gently stroke the anal area until the bunny starts producing stool and urine and keep stroking until the bunny stops. You are reproducing the behavior of the mother rabbit who would lick her young to stimulate them to go to the bathroom and to keep the nest clean. Again, ONLY if the eyes are still closed. Handle a wild rabbit only during feedings as excessive handling can be extremely stressful/potentially fatal. Wild rabbits don’t need heat if furred and healthy. Wild rabbits should not be fed at home, but get them to a professional rehabber as it IS CRITICAL for their survival and to be with their own kind. Most die from overfeeding and/or stress.
You are reproducing the behavior of the mother rabbit who would lick her young to stimulate them to go to the bathroom and to keep the nest clean. Again, ONLY if the eyes are still closed. Handle a wild rabbit only during feedings as excessive handling can be extremely stressful/potentially fatal. Wild rabbits don’t need heat if furred and healthy. Wild rabbits should not be fed at home, but get them to a professional rehabber as it IS CRITICAL for their survival and to be with their own kind. Most die from overfeeding and/or stress.
As soon as the wild bunnies’ eyes are open, you may introduce them to plain alfalfa pellets, hay, such as oat hay, timothy, alfalfa and veggies such as carrot tops, Italian parsley, dandelion greens. Dandelion greens and hay (timothy and oat hay) are extremely important for wild rabbits. You can add whole oats from a feed store, and some grated carrots. The greens must be fresh, rinsed, and replaced if not eaten in a few hours. You can place them in a cup of cold water with just the tops sticking out to keep them fresher. (For a domestic rabbit baby, see section under the Domestic heading). Wild cottontail and brush bunny rabbits should be released as soon as they are eating hay and greens and are approximately 5 inches in body length and run from you. This varies with the area, so size is not easy to say. They will be small, but the longer you keep them, the more agitated and difficult to handle they will become and the less likely their chances for survival in the wild. Release ONLY at dusk or dawn. Jackrabbits (hares) are not ready until 9+ weeks.Make sure they get exercise daily. Jackrabbits mature much slower than the brush/cottontails and need to develop strength. If they are ready, earlier, they will let you know.
(For a domestic rabbit baby, see section under the Domestic heading). Wild cottontail and brush bunny rabbits should be released as soon as they are eating hay and greens and are approximately 5 inches in body length and run from you. This varies with the area, so size is not easy to say. They will be small, but the longer you keep them, the more agitated and difficult to handle they will become and the less likely their chances for survival in the wild. Release ONLY at dusk or dawn. Jackrabbits (hares) are not ready until 9+ weeks.Make sure they get exercise daily. Jackrabbits mature much slower than the brush/cottontails and need to develop strength. If they are ready, earlier, they will let you know.
WARNING: Jackrabbits really NEED a skilled wildlife rehabber as they can run from you, throw themselves into walls to get away; many have died or severely injured themselves in captivity as they are so very wild. Please DO NOT raise them if you are not a skilled wildlife rehabber. This is vital. Noises and sounds easily frighten the jackrabbit and they are not able to be handled after 9 weeks. Often, sadly, we get reports of how a well-meaning person who tried to raise a wild rabbit, only to find it literally died of fright or got injured inside the cage. They are wild and belong with their own kind, out in the wild.
This is vital. Noises and sounds easily frighten the jackrabbit and they are not able to be handled after 9 weeks. Often, sadly, we get reports of how a well-meaning person who tried to raise a wild rabbit, only to find it literally died of fright or got injured inside the cage. They are wild and belong with their own kind, out in the wild.
Jackrabbits really enjoy being raised together, whereas cottontails/brush bunnies may fight and do fine alone. Give them a carrier as their place of privacy (line with thick towels) with plenty of fresh hay and greens described above and water bowl. Again, wild rabbits need a skilled wildlife rehabber; it is critical to their survival.
The Bunny is DOMESTIC (i.e., pet rabbit, NOT wild) and Really Orphaned – How do I care for a domestic baby?
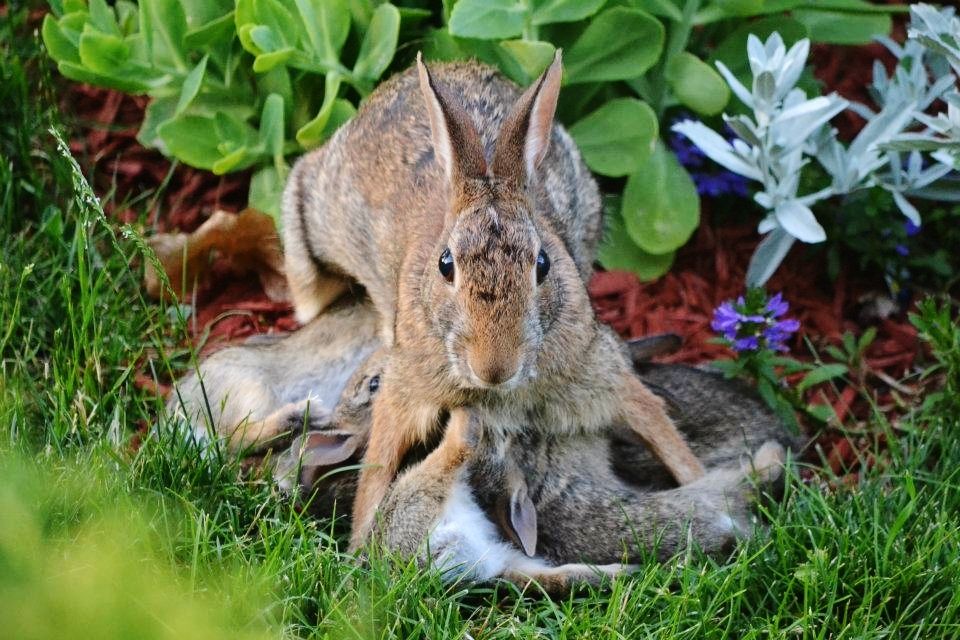
Baby Domestic Agouti Bunny Baby Domestic/Pet Agouti rabbit babyRemember that both the domestic pet rabbit and wild bunny moms only feed their young usually once in the middle of the night. Don’t assume the mom is not caring for them if you don’t see her nurse them. Check their tummies to see if they are round and the babies are warm in the morning–this means she is caring for them. In the rare situation that you have an orphaned domestic bunny, such as when a domestic rabbit mom is sick or refuses to care for her young, you will need to feed the babies. Overfeeding is a leading cause of death in these youngsters which results in fatal intestinal disease.
Don’t assume the mom is not caring for them if you don’t see her nurse them. Check their tummies to see if they are round and the babies are warm in the morning–this means she is caring for them. In the rare situation that you have an orphaned domestic bunny, such as when a domestic rabbit mom is sick or refuses to care for her young, you will need to feed the babies. Overfeeding is a leading cause of death in these youngsters which results in fatal intestinal disease.
If truly orphaned, use KMR KITTEN powder formula (can also use Meyenberg Regular Goat milk found at Safeway in the milk section or Whole Foods until you can find the KMR KITTEN formula), and follow the directions on the can. It may be easiest to start with a 3 cc/ml syringe or an eyedropper. Some use pet nurser nipples on the end of a luer lock syringe, or a teat cannula on the end of a syringe. Feed only with the bunny sitting UPRIGHT, and point syringe down towards bottom or side of mouth, so if too much comes out, the baby does not aspirate! For those who are slow to learn nursing, SC fluids may be necessary to prevent electrolyte imbalance or dehydration (check with a vet on this only!!).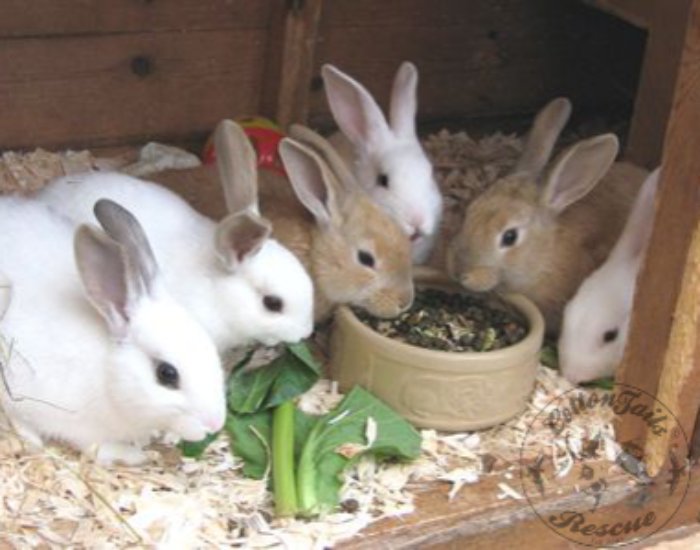 Domestic buns with closed eyes should be fed 2 x a day, and the number of feedings gradually decreased until they are weaned. If their eyes are still closed, you need to stimulate their bottoms with a warm moist towel after feedings to help them to pee. (Domestics are weaned about 6 weeks compared to wild bunnies who are weaned about 3-4 weeks for cottontails and 9+ weeks for jackrabbits). Bloat is commonly associated with too frequent feedings and too much at one time.
Domestic buns with closed eyes should be fed 2 x a day, and the number of feedings gradually decreased until they are weaned. If their eyes are still closed, you need to stimulate their bottoms with a warm moist towel after feedings to help them to pee. (Domestics are weaned about 6 weeks compared to wild bunnies who are weaned about 3-4 weeks for cottontails and 9+ weeks for jackrabbits). Bloat is commonly associated with too frequent feedings and too much at one time.
Feeding Amounts for DOMESTIC/PET Orphaned babies*: Feed twice a day up to these amounts: Newborn– 2.5 cc/ml each feeding. One week old: 6-7 cc/ml each feeding. Two weeks old: 12-13 cc/ml each feeding. Three weeks to six weeks: Up to 15 cc/ml each feeding (a.m. and p.m.). Note this is for DOMESTIC, NOT WILD bunnies. Each bunny varies. If this is a smaller rabbit, he will consume much less. Do NOT overfeed! Contact an HRS contact, rabbit vet, to be sure.
*After each feeding it is important to make the bunny defecate and urinate (if the eyes are not opened yet) to keep the intestinal tract and urinary system running smoothly (only UNTIL their eyes are open). Use a cotton ball moistened with warm water and gently stroke the anal area until the bunny starts producing stool and urine and keep stroking until the bunny stops. You are reproducing the behavior of the mother rabbit who would lick her young to stimulate them to go to the bathroom and to keep the nest clean.
Use a cotton ball moistened with warm water and gently stroke the anal area until the bunny starts producing stool and urine and keep stroking until the bunny stops. You are reproducing the behavior of the mother rabbit who would lick her young to stimulate them to go to the bathroom and to keep the nest clean.
Provide a soft nest area in a box with clean towels, and cover the babies so it is dark until their eyes are open. Do NOT provide extra heat if the room temperature is at least 65 to 70 degrees F because excessive heat can be fatal. If the room is cooler, then you may place a heating pad on a low setting under no more than HALF of the nest so the bunny can move to a cooler area if it gets too warm, and be sure there is no way the mother rabbit can get to or chew the electrical cord!
For domestic rabbits, if you have a healthy adult rabbit at home and you can collect cecotropes (the soft, chain-like droppings that the rabbit usually eats) then these can be mixed with the KMR to give the baby bunny normal bacteria for its intestinal tract. Only one cecotrope per day for 4-5 days is needed. This is particularly important for rabbits under one week of age. Also good is to sprinkle a pinch of acidophilus powder, also called “Probiotic” from human capsules in the milk a little each time for healthy flora for both wild and domestic bunnies.
Only one cecotrope per day for 4-5 days is needed. This is particularly important for rabbits under one week of age. Also good is to sprinkle a pinch of acidophilus powder, also called “Probiotic” from human capsules in the milk a little each time for healthy flora for both wild and domestic bunnies.
As soon as their eyes are open, you may introduce the bunnies to plain alfalfa pellets, hay, such as oat hay, timothy, alfalfa. Please refer to the handout Care of Rabbits for more information on diet for domestic, pet rabbits. You may reach [email protected] for domestic/pet rabbit questions. Below is the email for wild rabbit questions: [email protected] (wild) (If links above did not answer your question).
(See above for wild rabbits). For all rabbits, avoid ANY regular milk, puppy formulas, etc. Use KITTEN formulas like KMR. Avoid Esbilac. Feed only upright. Less is better than more! Overfeeding will cause bloat and pain and possible death. Please get to a rehabber.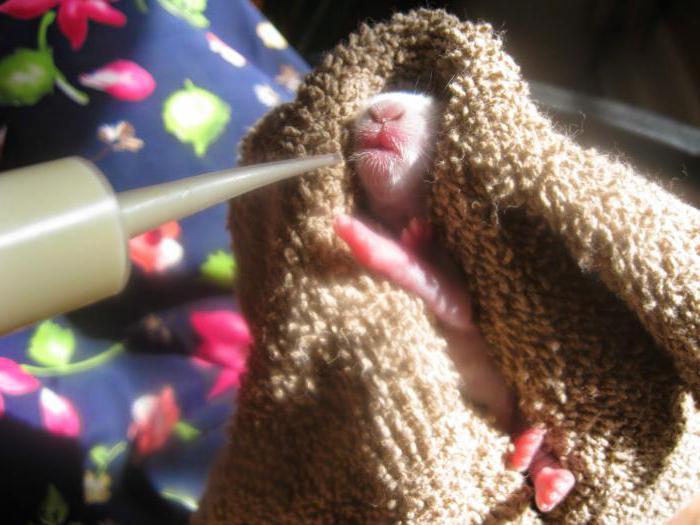
Sources: Caring for Cricket – What Not To Do When You Find a Wild Baby Bunny by Julie Smith and Handout by Midwest Exotic Animal Hospital, and additional wild bunny info by M. Wilson (HRS educator and rehabber). For questions not answered about wild rabbits above, email: wildbunnyrehab at gmail.com
Below content was merged from: /caring-for-orphans/
Rabbit mothers nurse their babies for approximately 5 minutes a day. They will be in the nest or nest box early in the morning and then again in the evening. The milk is very rich and the babies “fill up” to capacity within minutes. Mother rabbits do not “sit” on the babies to keep them warm as do some mammals and birds. They build a nest with fur and grasses which helps to keep the babies warm in between feedings. Do not force a mother rabbit to sit in the nest box. You can pick up the babies and see if they are feeding by checking the size of their stomachs (should not be sunken in), the pinkness of their skin and activity level (they should not be blue in color or sluggish in movement) and the amount of time that you hear them crying (baby bunnies should be quiet most of the day…. if they are crying constantly then they are not getting fed). If they are warm, mom is most likely feeding them, but again, she only comes back in the middle of the night.
if they are crying constantly then they are not getting fed). If they are warm, mom is most likely feeding them, but again, she only comes back in the middle of the night.
If you come across a nest of bunnies in the wild and the mother is no where to be seen, please DO NOT disturb them…this is normal. By removing them from the nest you are greatly reducing their chances of survival.In the rare situation that you have an orphaned bunny, such as when a mother rabbit is killed by another animal or in the road, or when a domestic rabbit refuses to care for her young, you may try feeding with Kitten Milk Replacer (KMR) or Meyenberg Goat Milk (for wild rabbits, but they need a professional reahabber–do not feed at home). Remember though, that both wild/domestic bunny moms only feed in the middle of the night, so don’t assume she is not caring for them! For true orphans, remember to feed ONLY TWICE A DAY. Overfeeding is a leading cause of death in these youngsters which results in fatal intestinal disease. Provide a soft nest area in a box with clean towels, and cover the babies (if eyes are closed) so it is dark.
Provide a soft nest area in a box with clean towels, and cover the babies (if eyes are closed) so it is dark.
DO NOT provide extra heat if the room temperature is at least 65 to 70F because excessive heat can be fatal. If the room is much cooler, then you may place a heating pad on a low setting under no more than HALF of the nest so the bunny can move to a cooler area if it gets too warm.
For a wild bunny, you need to get him to a wildlife rehabilitator if he is TRULY orphaned (mom was killed). Remember with wild bunnies, the mom ONLY comes back at night to call and feed him; please put him back for her if just found and healthy. With domestics, the mom only feeds once or twice a day for only 5 minutes. Leave babies with the mom. For wild orphans, first google your state and wildlife rehabber, and call your humane society, also try http://www.humanesociety.org/animals/resources/tips/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitator.html and http://www.owra.org/find-a-wildlife-rehabilitatoror as it is illegal in most states to keep a wild animal, and they really need a professional as this is critical. Local rabbit veterinarians or humane societies may also know of a rehab facility.
Local rabbit veterinarians or humane societies may also know of a rehab facility.
The following is a guideline for the daily amount to feed a TRULY orphaned bunny (mother was killed, etc.) that will be about 5 lbs as an adult. It is impossible on the internet to be exact. Please find rehabber.
GENERAL FEEDING OF ORPHANS
Age + Amount (This WILL vary depending on type of rabbit.) Use KMR (Kitten Milk Replacer) for domestics and Meyenberg Goat Milk, regular not low fat for wild ones,or KMR. Add a pinch of acidophilus (AKA Probiotic capsules) to all formula to promote healthy gut flora. Other formulas vary depending on the region of the country. Avoid using Esbilac or any puppy formulas or cow’s milk. Do not add Karo syrup. FEED TWICE A DAY ONLY unless baby is low weight, than three times.
Newborn to One Week: 2 – 2+1/2 cc/ml each feeding (two feedings).
1-2 weeks: 5-7 cc/ml each feeding (two feedings).
(depending on bunny.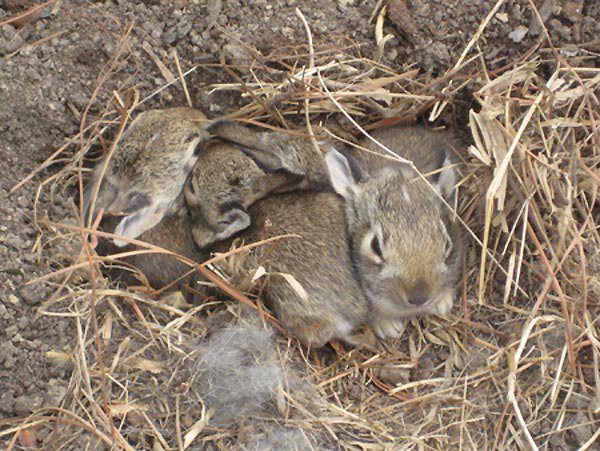 .may be much LESS if smaller rabbit).
.may be much LESS if smaller rabbit).
2-3 weeks: 7-13 cc/ml each feeding (two feedings). Bunnies whose eyes are still CLOSED need to be stimulated to urinate and defecate before or after each feeding. Again, seek a professional on this. Domestic eyes open at about 10 days of age. Then start introducing them to timothy and oat hay, pellets and water (always add fresh greens for wild ones–dandelion greens, parsley, carrot tops, grated carrots, all fresh, watered down). See below for detail.
3-6 weeks: 13-15 cc/ml each feeding (two feedings–again, may be LESS depending on size of rabbit! A cottontail will take so much LESS–about half of this!.)
Domestics are weaned about 6 weeks. Cottontails wean and release about 3-4 weeks and jackrabbits much later (9+ weeks). Feed only twice a day up to these TOTAL amounts. You may find an eyedropper or syringe easiest to use. Feed them upright, and go slowly watching them lick and swallow so they do not aspirate. For domestic rabbits, if you have a healthy adult rabbit at home and you can collect cecotropes (the soft chain-like droppings that the rabbit usually eats) then these can be mixed with the KMR or goat milk to give the baby bunny normal bacteria for its intestinal tract. Only one cecotrope per day for 4-5 days is needed. This is particularly important for rabbits under one week of age. Acidophilus capsules for humans, opened and sprinkled some in formula, works well too.
For domestic rabbits, if you have a healthy adult rabbit at home and you can collect cecotropes (the soft chain-like droppings that the rabbit usually eats) then these can be mixed with the KMR or goat milk to give the baby bunny normal bacteria for its intestinal tract. Only one cecotrope per day for 4-5 days is needed. This is particularly important for rabbits under one week of age. Acidophilus capsules for humans, opened and sprinkled some in formula, works well too.
After each feeding it is important to make the bunny defecate and urinate (until their eyes are open) to keep the intestinal tract and urinary system running smoothly. Use a cotton ball moistened with warm water and gently stroke the anal area until the bunny starts producing stool and urine and keep stroking until the bunny stops. You are reproducing the behavior of the mother rabbit who would lick her young to stimulate them to go to the bathroom and to keep the nest clean. No need to do this for jackrabbits or if bunny’s eyes are open.
As soon as their eyes are open, you may introduce the bunnies to hay, such as oat and timothy hay, some alfalfa, and pellets, and for wild ones, add dark leafy veggies such as dandelion greens, carrot tops, parsley, grated carrots, etc. Keep the greens fresh, moist, and stand them up in a heavy mug of water. Change greens often. If this is a wild rabbit, you do not need to introduce pellets. If this is a domestic rabbit baby, then you may introduce plain alfalfa pellets at 2 weeks of age (please refer to the handout Care of Rabbits for more information on diet). Wild rabbits should be released as soon as they are eating hay and greens and are approximately 5 inches in body length (for cottontails) and are afraid of you (about 3-4 weeks). Jackrabbits are released much later (9 weeks up). They will be small, but the longer you keep them, the more agitated and difficult to handle they will become, and the less likely their chances for survival in the wild. They may be easily injured in your care as they attempt to get free. For wild bunnies, please do not raise them yourself, but take them to a rehabber! Google your state and wildlife rehabber or see links above.
For wild bunnies, please do not raise them yourself, but take them to a rehabber! Google your state and wildlife rehabber or see links above.
Modified from an original document from :
Midwest Bird & Exotic Animal Hospital
Do You Know What to Feed a Wild Baby Rabbit?
Written by The Rabbit Hole Hay Team
Let’s start with the basics about rabbits in general. Baby rabbits are only fed from their mother a few minutes a day. A mother’s milk is packed with the necessary nutrients that feeding once is more than enough for the little bun.
The feeding normally occurs at night to help protect the babies. The mother rabbit can be seen away from the nest during the day which is why it is important to leave babies in nests alone unless you are confident that the mother has either abandoned the nest for good or has died. So needing to take care of a wild baby rabbit is rare, very rare.
Orphaned Baby Bunnies: Wild
So what do wild baby rabbits eat when they don’t have their mother giving them their nutrient packed milk? Rabbit. org provides this information on what to feed an orphaned wild baby rabbit until you are able to take them to a wild rabbit rescue.
org provides this information on what to feed an orphaned wild baby rabbit until you are able to take them to a wild rabbit rescue.
Feeding Of True Orphans
Age + Amount (This WILL vary SO MUCH depending on type of rabbit. It is impossible over the Internet to see your particular rabbit, so this is only approximate.) Use KMR kitten or KMR kitten plus Goat milk, regular not low fat. Add a pinch of acidophilus (aka Probiotic) to the formula to promote healthy gut flora. Formulas vary depending on region. Avoid Esbilac and any puppy formulas! FEED TWICE A DAY ONLY for healthy babies. It may be easiest to start with a 3 cc/ml syringe or an eyedropper. Feed only with the bunny sitting UPRIGHT, and point syringe down towards bottom or side of mouth, so if too much comes out, the baby does not aspirate. At first, they may only take a few drops at one feeding until they are not stressed and used to this.
- Newborn to One Week: 2 – 2+1/2 cc/ml each feeding (two feedings per day).

- 1-2 weeks: 5-7 cc/ml each feeding (two feedings per day). (depending on bunny..may be much LESS if smaller rabbit!) Newborn babies (if eyes closed) all need to be stimulated to urinate and defecate prior to or following feeding until their eyes open. (Except Jackrabbits do not). *See how to below.
- 2-3 weeks: 7-13 cc/ml each feeding (two feedings). Domestic eyes open at about 10 days of age. Start introducing them to timothy and oat hay, pellets and water (always add fresh greens for wild ones).
- 3-6 weeks: 13-15 cc/ml each feeding (two feedings–again, may be LESS depending on size of rabbit! A cottontail/brush bunny will take so much less!! Half this at most.) Cottontails wean and release about 3-4 weeks and jackrabbits much later (9+ weeks), whereas domestic rabbits are 6 weeks.
- 6 weeks-9weeks for Jackrabbits only, continue up to 9 weeks with formula, gradually changing to a dish for the warm formula, replacing the formula after 9 weeks slowly with a a dish of cup-up tiny banana or apple pieces.

To read more on how to take care of an orphaned rabbit, read the full article from here.
A wild rabbit’s diet varies on the temperature they are living in. When the temperature is warmer, their diet consists of: clover, flowers, grasses and other plants that grow in that temperature. When the temperature is cooler, their diet becomes more sparse including: twigs, bark and remaining greens. Sounds very different from the Timothy Hay and Orchard Grass that a domesticated rabbit might eat right?
Not sure if your momma rabbit is feeding your new baby rabbits? Do you need to know how to feed your baby rabbits by yourself? Download our Human's Guide to Feeding Baby Rabbits to learn about what to look for in your baby rabbits, feeding techniques, a feeding schedule and more! We pride ourselves on supporting a community of small pet owners who care deeply about providing happy and healthy lifestyles for their pets.
Wild rabbits - What do they eat and how to feed?
- Treatment, vaccination and chipping of cats
- Treatment, vaccination, chipping of dogs
- Treatment of birds and parrots - tips from the mosquit of
- Treatment of rabbits
- Treatment of ferrets
- Treatment of reptiles
- Treatment of cattle
many They think that wild rabbits are the same in their nature as the domestic rabbit.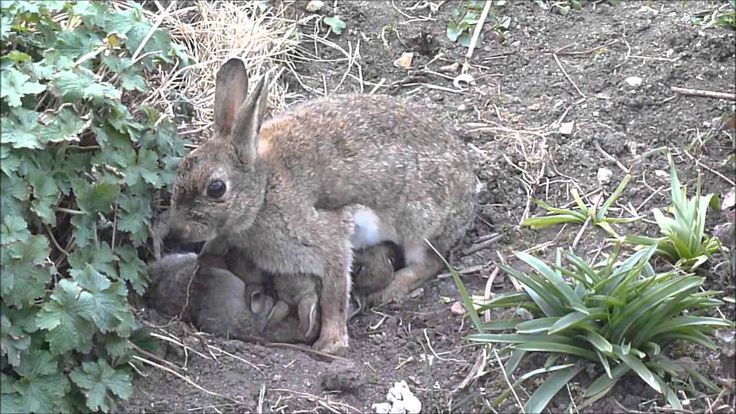 When buying such an animal for home, you need to know its features, because it can die from food for a domestic rabbit. They live in all areas. Avoid dense forests. They love to walk on farm plots and eat up bushes and crops. Some farmers even shoot them.
When buying such an animal for home, you need to know its features, because it can die from food for a domestic rabbit. They live in all areas. Avoid dense forests. They love to walk on farm plots and eat up bushes and crops. Some farmers even shoot them.
Now rabbits are common both in rabbit breeding and as a pet.
Despite their pretty appearance, they can harm the environment. Rabbits compete with sheep and other herbivores by stealing food from them. So in Australia they multiplied so much that they numbered about 20 million rabbits. Then they began to import predators, ferrets, ermine, fox to even out the situation. Then they began to use biological weapons. As a result, 90% died, the remaining 10% developed immunity.
The wild European rabbit is famous for its speed of reproduction, it adapts very quickly to the terrain. The main thing for him is that there is fresh grass, and the land where he will dig minks. They have a light brown color, sometimes change the color of the coat.
Even the wild rabbit was domesticated. The European rabbit has 20 subspecies.
It is worth mentioning the African wild rabbit, it has 13 subspecies.
- Florida is distinguished by whimsical nutrition, has a very soft fluffy tail. Color gray or brown.
- River. The name is due to the agility and ability to swim. As you enter the rabbit hides from danger.
- Pygmy. The ears are of medium size, even smaller than those of its brethren. The wool is softer than the rest.
- Teporingo. Quite a rare sight. It lives most often in Mexico.
Rabbits breed frequently, up to 6 times. Pregnancy takes about a month. The rabbit brings up to 12 rabbits.
If the rabbit lives in the wild, he tries not to move more than 100 meters from the hole. In summer, they eat green plants, if they live near fields, then they eat everything: cabbage, lettuce, cereals and root crops are also included in their diet. In winter, they have a harder time.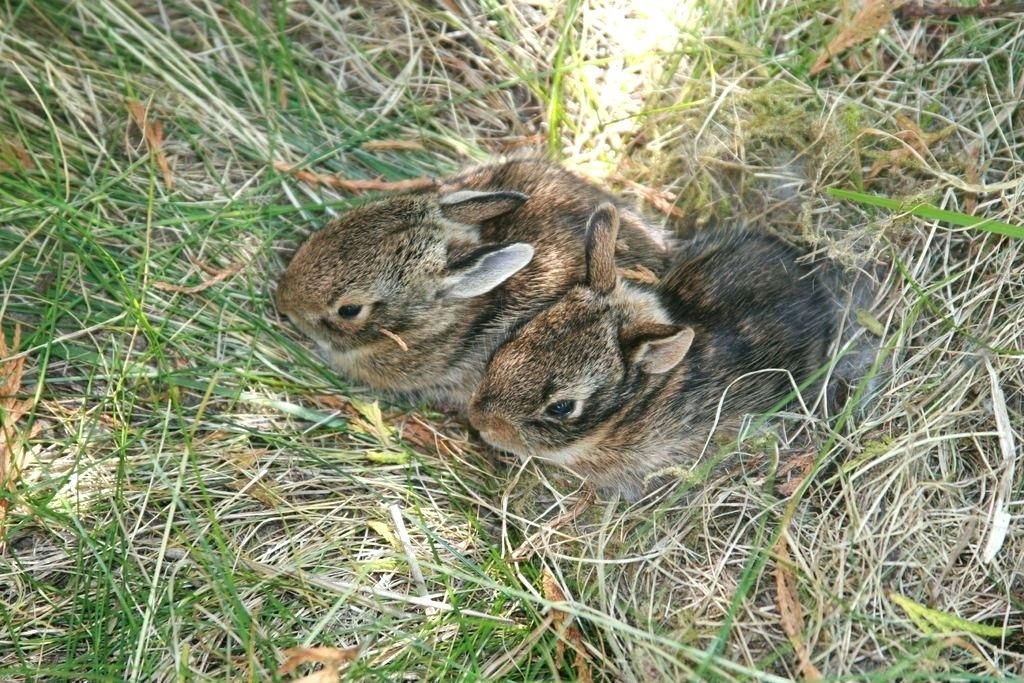 They begin to actively look for the roots of plants. They eat tree bark and some dry branches and leaves. If the wild rabbit fails to find anything, then he starts eating his own feces.
They begin to actively look for the roots of plants. They eat tree bark and some dry branches and leaves. If the wild rabbit fails to find anything, then he starts eating his own feces.
If you have bought a rabbit for yourself and can't figure out what kind of rabbit it is, how it lives and how it is fed, then contact MosVetHelp. Our experts will provide all the necessary information about what wild rabbits eat. We are ready to help you at any time, because we work around the clock. We have only high-quality and proven medicines and effective treatment.
What to feed rabbits? Feeding rabbits for rapid growth
Do you raise rabbits for meat or fur? Take care of a balanced and varied diet, because the rapid growth of animals and their precocity depend on it.
Overfeeding and underfeeding will lead to a decrease in the productivity of rabbits. Due to malnutrition, the quality of rabbit meat and skins is deteriorating. The menu should be made taking into account the general condition of the rabbit, its weight, age and season.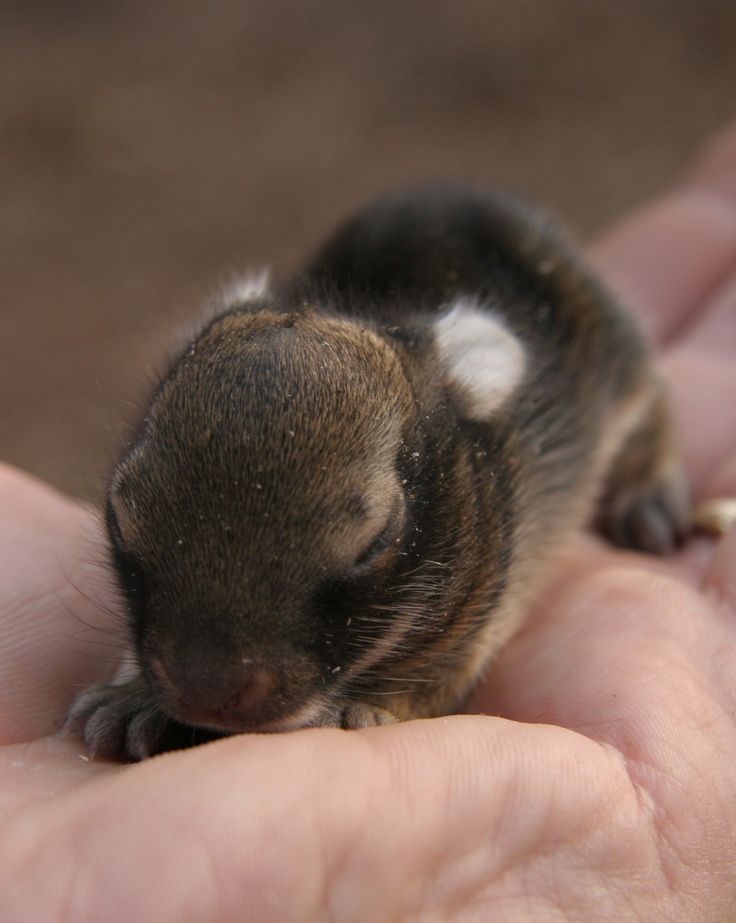
Ears eat a lot. Animals have weak stomach muscles, so food passes into the intestines only when a new portion of food arrives.
What to feed rabbits?
Animals should receive grass, vegetables and cereals, as well as useful elements. You should not feed rabbits with the same type of greenery, as the animals will begin to grow more slowly.
Feed types:
Greens are the main source of nutrients. This includes various herbs and plants (nettle, plantain, dandelion, clover, alfalfa, sage, etc.), as well as vegetable tops (beets, carrots, peas). Rabbits receive such food only in summer and in moderation (10-20% of the daily diet).
Succulent foods are products such as root vegetables, vegetables and fruits. They are especially important in winter and early spring, when there is no green grass, because they contain vitamins, carbohydrates, protein and fiber. Succulent feed is 10% of the daily diet.
Rabbits should be given:
- carrots,
- beets (in moderate doses),
- pumpkin,
- zucchini,
- potatoes (preferably boiled),
- cabbage (white cabbage - in moderation),
- watermelons,
- apples etc.

Roughage is a source of vitamins, protein and fiber. This is hay and tree branches (pine, willow, maple, acacia, linden, etc.). Eating branches, the animals sharpen their teeth. The food is suitable for winter feeding.
Concentrated feeds include: bran, cereals (oats, wheat, rye, barley, corn), legumes, cake and compound feed. This is half the daily ration of rabbits.
Animals must always be provided with water. In cold and frosty water should be poured into the drinkers warm.
Feeding rabbits
The diet of animals in winter and summer is different. Nutrition is also changed, based on the physiological state of the animals.
Feeding rates (g/day):
| Condition of rabbits | Summer | Winter | |||
| Concentrates | Greenery | Concentrates | Vegetables | Dry grass | |
| Rabbits at rest | 40-50 | 400-500 | 50-60 | 150-200 | 120-150 |
| Rabbits in mating | 70-80 | 500-600 | 90-100 | 150-200 | 150-200 |
| Pregnant rabbits | 70-90 | 550-700 | 100-130 | 200-250 | 150-200 |
| Lactating females | 120-150 | 1000-1200 | 140-160 | 300-600 | 200-250 |
What is bad for rabbits?
Not all herbs and foods can be given to rabbits. Some plants cause diarrhea or constipation in animals, lead to respiratory diseases and can cause their death.
Some plants cause diarrhea or constipation in animals, lead to respiratory diseases and can cause their death.
Herbs and products that are prohibited:
poisonous plants (euphorbia, dope, celandine, foxglove, wild radish, etc.) cause poisoning and can lead to death;
sweets provoke the development of diseases of the heart, joints, bones and skin in rabbits;
exotic fruits and vegetables disturb the digestive process in animals (especially if you breed local breeds).
Feeding young animals
The diet of young rabbits generally coincides with that of adults. Animals grow intensively up to 8 or more months (depending on the breed).
Young rabbits should always have clean water in their trough as they need more liquid than adult males and females.
Succulent foods should be introduced into the menu in stages, starting with small proportions (from 4 months of age). At the same time, it is recommended to alternate different types of feed and monitor the condition of the pets.
At the same time, it is recommended to alternate different types of feed and monitor the condition of the pets.
Available
PC 92-1. Grass meal grower, for rabbits 5-14 weeks
Feeding rabbits for accelerated growth
To ensure that individuals grow quickly, they need to be fed grass or hay, vegetables, cereals and compound feed - 3-4 times a day.
Summer:
| Age of rabbits | Green and succulent foods (g/day) | Concentrates (g/day) |
| 1-2 months | 300 | 20 |
| 3-4 months | 500 | 45 |
| 5-7 months | 600 | 55 |
Winter:
| Age of rabbits | Dry grass (g/day) | Root vegetables (g/day) | Concentrates (g/day) |
| 1-2 months | 50 | 150 | 35 |
| 3-4 months | 100 | 300 | 55 |
| 5-7 months | 200 | 400 | 90 |
Rabbit fattening
Beef rabbits are most often fattened in autumn and winter.