Girls feed baby
Breastfeeding & baby-led attachment | Raising Children Network
Renee Kam (lactation consultant): Baby-led attachment is where a baby uses their own instincts to find the mother’s breast on their own accord. Baby-led attachment really helps to lay down the foundation for breastfeeding. A baby who has had many opportunities, particularly in the early weeks, to do baby-led attachment becomes a lot more orientated towards the breast.
Adele (mother of Charlie, 5 years, Noah, 3 years, and Holly, 4 weeks): I did baby-led attachment because I had a lot of trouble feeding my first baby and getting him to attach and when I saw a video of baby-led attachment it just looked like a natural way to do it, so I thought I would try it to see if that meant that I didn’t have attachment issues with the children I had after my first one.
Miranda (mother of Mattie, 8 years, Tacy, 6 years, Sedna, 7 months): When I had my second baby, when she was born at home and she was lying on me, she all of a sudden attached by herself, which was a wonderful feeling but I never followed-up on it because I didn’t know anything about it. So then when we moved to Australia I so wanted to try it so we tried it with this one. It really started at home, so when we got home we started doing it. You don’t have to do it straight away – baby-led attachment – it’s something that they can do for quite a few weeks after they’re born. It’s imprinted in their being, I guess.
Renee Kam: If a mother wants to do baby-led attachment the tips that I would give her would be the timing of it. So a baby will be able to follow through on their instincts best when they’re calm. So it would be when the baby’s showing early feeding cues such as turning their head from side to side with mouth open, sticking their tongue out, sucking on their hands, or it might be as soon as their baby wakes up from a sleep. So in those situations baby is typically calm and then if the baby is then placed skin-to-skin contact with the mum and the mum, say, is in a semi-reclined position, then that will help a baby to follow through on their instincts to find their mother’s breast.
Narrator: Find a comfortable position. Many mothers find that a semi-reclined position with pillows behind them for support works well. A partially laid-back position allows gravity to assist the baby in moving to the breast. With as much skin-to-skin as possible between you and your baby, place your baby on your chest facing you between your breasts with her head just above your breasts. Start when your baby is calm, such as when she is showing early feeding cues like turning her head from side to side with her mouth open.
As your baby starts to instinctively move towards a breast, she will start to lift her head and bob it around. As she moves towards a breast, you may find it helpful to hug her bottom in close to you and to support her neck and shoulders with your hand and wrist. It is important to avoid putting pressure on her head as she needs her head free to instinctively move it into an extended position to help her attach and feed well.
When her head nears your nipple, she may nuzzle around to find your nipple and bring her tongue toward it.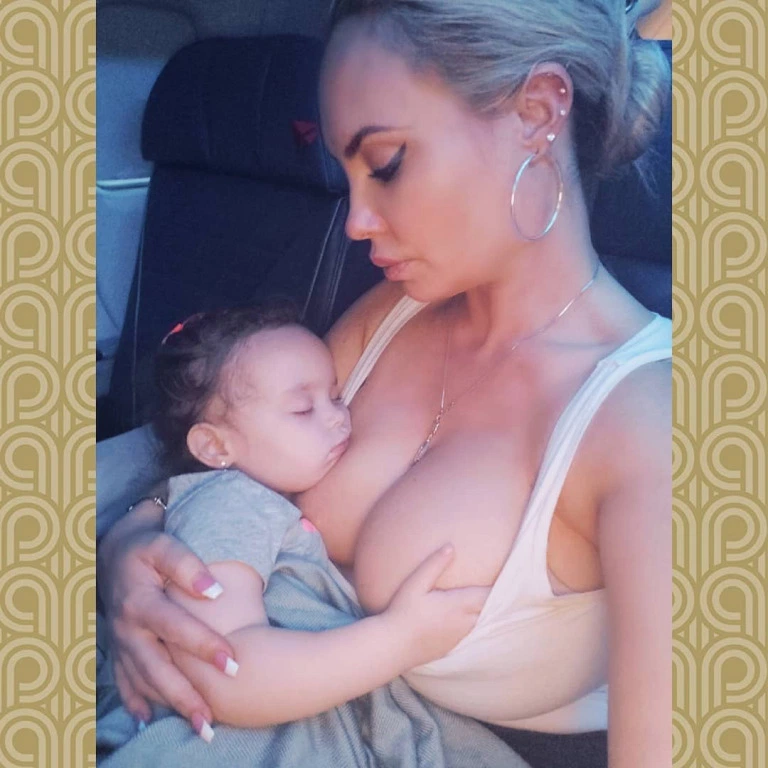 When she finds the right position, she will anchor with her chin, open her mouth wide, attach and begin sucking.
When she finds the right position, she will anchor with her chin, open her mouth wide, attach and begin sucking.
Renee Kam: Straight after a baby is born for the first 1 to 2 hours after they’re born, they’re typically alert and eager and ready to receive their first breastfeed. So when placed into skin-to-skin contact with their mother straight after birth, then that can allow the baby to do baby-led attachment, find the mother’s breasts on their own accord and receive their first breastfeed.
Adele: I did skin-to-skin with all of my children in hospital. So with the baby it probably took a few minutes before like they would kind of just be laying there for a little while and it was a few minutes before they kind of started moving around. But they did the bopping around and choosing a side and finding the nipple and all of that themselves.
Renee Kam: The great news is even if you don’t get to do baby-led attachment straight after a baby is born, babies’ instincts to find a mother’s breasts are easily reproducible for at least the first few months.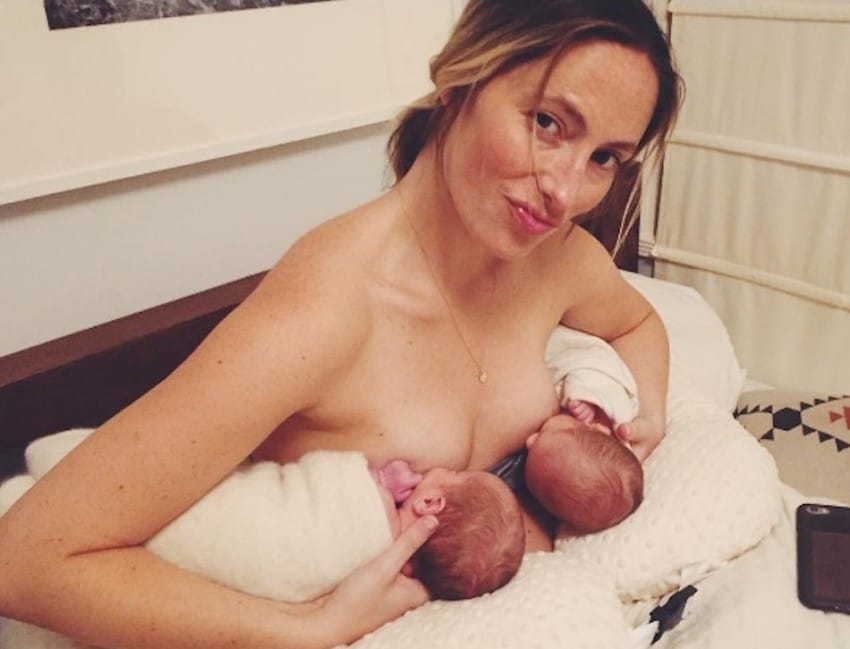 When a mother and baby are in skin-to-skin contact, there are many benefits of it such as the baby’s heart rate and temperature, blood sugar levels, breathing rate are all kept stable and also when a mother and baby are in skin-to-skin contact it also helps a mother to be able to learn her baby’s feeding cues.
When a mother and baby are in skin-to-skin contact, there are many benefits of it such as the baby’s heart rate and temperature, blood sugar levels, breathing rate are all kept stable and also when a mother and baby are in skin-to-skin contact it also helps a mother to be able to learn her baby’s feeding cues.
Miranda: As with the baby-led attachment, I also did try the mother-led attachment, attachment and feeding and it was quite painful. I went to see a lactation consultant a couple of times for her to help as well. Of course, they have told me to use the baby-led attachment, which was great.
Renee Kam: Even if the mother doesn’t have any breastfeeding problems, by using baby-led attachment frequently, particularly in the early weeks, it can help to reduce the risk of developing any breastfeeding problems such as the baby simply not attaching at all or sore nipples.
Miranda: Persevering with the baby-led attachment actually did help to heal the wounds and I think it was around 3 weeks that we had a happy breastfeeding relationship.
Renee Kam: A mother can do baby-led attachment whenever it’s right for her and her baby to do so. By having done baby-led attachment whenever she feels comfortable to do so, then it means that when she is breastfeeding in public, it makes it easier because baby knows what they’re doing and baby attaches easier to the mum’s breast.
Adele: So I think the baby-led attachment improved my confidence by I was able to see them feeding well, when I could look at them and I could see that they were attached really well and I could hear the swallowing and I knew we were having a good feed and so I didn’t have to really think about what I was doing with them.
Miranda: It helps to know about the fact that everyone is different. With baby-led attachment, it doesn’t matter because babies just go for the breast; they know what to look for.
Renee Kam: Baby-led attachment – it helps a mum and baby get breastfeeding off to a really good start.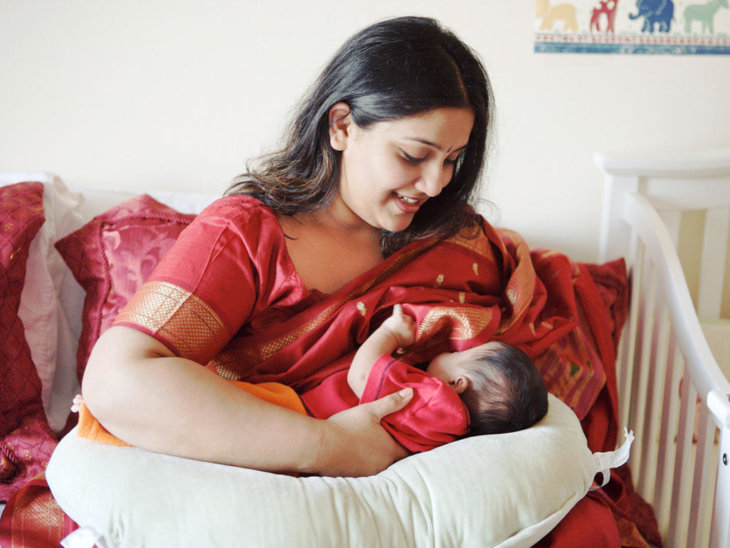 Then, it may help a mum to be able to breastfeed for as long as she wanted to and reach her own breastfeeding goals.
Then, it may help a mum to be able to breastfeed for as long as she wanted to and reach her own breastfeeding goals.
Feeding Your 1- to 3-Month-Old (for Parents)
During your baby's first 3 months, breast milk or formula will provide all the nutrition needed. Doctors recommend waiting until your baby is about 6 months old to start solid foods. Some babies may be ready for solids sooner than 6 months, but wait until your baby is at least 4 months old.
What Changes Should I Expect?
As your infant grows, feeding will change. Babies will start drinking more milk during each feeding, so they won't need to feed as often and will sleep longer at night.
Your baby's appetite will increase during growth spurts. Continue to feed on demand and increase the number of feedings as needed.
Your infant also will become more alert as the weeks go by, cooing and smiling. So there will be more interaction between you and your baby during feedings.
The following are general guidelines, and your baby may be hungrier more or less often than this.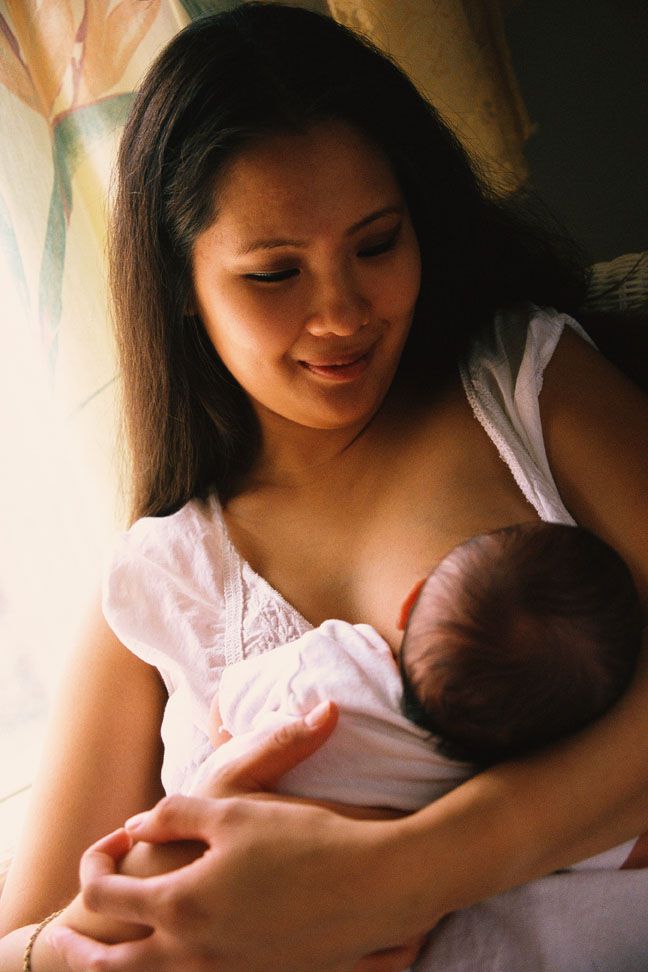 That's why it's important to pay attention to your baby's signals of being hungry or full. A baby who is getting enough might slow down, stop, or turn away from the breast or bottle.
That's why it's important to pay attention to your baby's signals of being hungry or full. A baby who is getting enough might slow down, stop, or turn away from the breast or bottle.
Breastfeeding: How Much and How Often?
As babies get older, they will start to breastfeed less often and sleep for longer periods at night. Your infant probably is eating enough if he or she:
- seems alert, content, and active
- is steadily gaining weight and growing
- feeds six to eight times per day
- is wetting and soiling diapers on a regular basis
Babies might not be eating enough if they:
- don't appear satisfied
- cry constantly
- are irritable, even after feeding
- are not making wet diapers
Call your doctor if you're concerned your baby isn't eating enough.
A few weeks after birth, breastfed babies tend to have fewer bowel movements (BMs, or poop) than they did before. At around 2 months of age, your baby may not poop after each feeding, or even every day. During growth spurts, you may notice that your little one wants to feed more often. This frequent nursing sends a signal to make more milk. Within a couple of days, supply and demand will get into balance.
During growth spurts, you may notice that your little one wants to feed more often. This frequent nursing sends a signal to make more milk. Within a couple of days, supply and demand will get into balance.
Babies who get breast milk only should get vitamin D supplements within the first few days of life. Other supplements, water, juice, and solid foods aren't usually needed.
Formula Feeding: How Much and How Often?
Babies digest formula more slowly than breast milk, so if you're bottle-feeding, your baby may have fewer feedings than a breastfed infant.
As babies grow, they can eat more at each feeding and may go for longer stretches between feedings. You'll also notice that your baby is starting to sleep longer at night.
During the second month, infants may take about 4 or 5 ounces at each feeding. By the end of 3 months, your baby may need an additional ounce at each feeding.
It's easy to overfeed a baby when using a bottle because it easier to drink from a bottle than from a breast. Make sure that the hole on the bottle's nipple is the right size. The liquid should drip slowly from the hole and not pour out. Also, resist the urge to finish the bottle when your baby shows signs of being full.
Make sure that the hole on the bottle's nipple is the right size. The liquid should drip slowly from the hole and not pour out. Also, resist the urge to finish the bottle when your baby shows signs of being full.
Never prop a bottle. Propping a bottle might cause choking and it increases the chances of getting ear infections and tooth decay.
Should I Worry About Spitting Up?
It's normal for infants to "spit up" after eating or during burping. Spitting up a small amount — usually less than 1 ounce (30 ml) — shouldn't be a concern as long as it happens within an hour of feeding and doesn't bother your baby.
You can reduce spitting up in these early months by:
- feeding before your baby gets very hungry
- keeping your baby in a semi-upright position during the feeding and for an hour after
- burping your baby regularly
- avoiding overfeeding
- not jostling or playing vigorously with your baby right after a feeding
If your baby seems to be spitting up large amounts, is spitting up forcefully, is irritable during or after feedings, or seems to be losing weight or is not gaining weight as expected, call your doctor. And if your child has a fever or shows any signs of dehydration (such as not wetting diapers), call the doctor right away.
And if your child has a fever or shows any signs of dehydration (such as not wetting diapers), call the doctor right away.
Call your doctor if you have any questions or concerns about feeding your infant.
Until what age is breastfeeding recommended?
How long can I breastfeed?
Currently, the World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF* place great emphasis on continued breastfeeding in children older than 1 year of age, recommending that this process be continued up to two years of age or beyond. After 2.5 years, the child goes through the process of natural extinction of the sucking reflex. Gradually, he nullifies all feedings, simply ceasing to need the sucking process as such.
WHO is known to recommend breastfeeding up to 2 years of age and beyond if the mother wishes. Domestic pediatricians, based on practical experience and scientific research, voice the figure - up to 1.5 years. In any case, the choice remains with the mother and will depend primarily on the readiness of both the mother and the child to stop this process. It is not recommended to stop breastfeeding during the illness of the child, during the period of his vaccination, during other stressful conditions, as well as in the summer season. It is possible to successfully save HB even after a year, but under a number of conditions.
It is not recommended to stop breastfeeding during the illness of the child, during the period of his vaccination, during other stressful conditions, as well as in the summer season. It is possible to successfully save HB even after a year, but under a number of conditions.
Is it good to breastfeed after a year?
After a year, breast milk changes its composition, but not for the worse. The main reason for these changes is that milk is no longer the main food for the baby, and other functions come to the fore. The older the child becomes, the more the concentration of immunoglobulins in milk increases, which protect the child from diseases. Studies have shown that in the second year of lactation, the content of total protein in milk increases, as well as such an important protein as lactoferrin. Breast milk contains leukocytes and a number of anti-infectious factors, as well as antibodies against infectious agents previously transferred by the mother.
- Breastfeeding after a year should not "interfere" with the organization of rational nutrition of the child, providing for the introduction of basic products, dishes, the formation of a diet and a certain ritual of eating. GW during this period should not be a "snack". The child must learn in a timely manner to eat from a spoon, chew, observe certain rules of behavior at the table.
- Breastfeeding after one year should not "prevent" the child from growing up. Such child's emotions as resentment, pain, boredom, irritation, anger, feeling of loneliness, selfishness should not be “jammed” with breast milk. It is during this period of growing up that many mothers make a big mistake, without realizing it themselves, offering the breast not as a source of food, but as a source of emotional satisfaction. This can lead to a painful attachment of the child to the mother, later development of independence skills , which will burden both the mother and the baby himself.
 Instead of breast milk in these cases, the child may be offered such signs of attention as tactile caress, playing, reading a book, playing with plasticine, paints, etc.
Instead of breast milk in these cases, the child may be offered such signs of attention as tactile caress, playing, reading a book, playing with plasticine, paints, etc.
If, for various reasons, mother and child do not see each other during the day (mother at work, baby in kindergarten, etc.), then it is reasonable to keep evening and one night breastfeeding (if the child wishes).
Author: d.m.s. Lukoyanova Olga Leonidovna
What is normal breastfeeding? | Interview with Dr. Jacqueline Kent
It can be difficult for new mothers to understand if breastfeeding is going well, so we decided to ask the expert if it is possible to talk about the norms when it comes to breastfeeding.
Share this information
Dr Jacqueline Kent , Research Fellow , Hartmann Human Lactation Research Group:
Jacqueline joined the University of Western Australia research group in 1986 and received her PhD in 1999. She is currently researching the biochemical and physiological aspects of breast milk synthesis and release in search of scientific information to help mothers breastfeed longer.
She is currently researching the biochemical and physiological aspects of breast milk synthesis and release in search of scientific information to help mothers breastfeed longer.
Dr. Jacqueline Kent and her colleagues have been studying breastfeeding for many years. As it turned out, for all mothers and babies, this process occurs in its own way.
What were the most unexpected results of your research for you?
Variety. It turns out that the limits of the norm are extremely wide.
We are used to textbooks that say that an infant should eat 8-12 times a day and gain 150 grams per week. But babies don't read textbooks and do things their own way! Some gain weight more slowly, others very quickly.
We looked at infants aged one to six months who were exclusively breastfed. As our studies have shown, on average, a child is breastfed 4 to 13 times a day, and the duration of one feeding varies from 12 minutes to 1 hour. 1
How much milk do breastfed babies usually consume?
According to our research, the amount of milk consumed by baby
ranges from 54 to 234 ml per feeding. 1
1
Sometimes it seems to the mother that the baby has eaten well, but when weighed, it turns out that he ate very little milk. And it happens the other way around: the child is distracted, breastfeeds for only a few minutes and still eats 100 ml of milk. Even if the baby is restless, this does not mean at all that he is malnourished.
All babies are different, but they all get as much milk as they need in one way or another. One needs 500 ml of milk per day, while others eat up to 1356 ml!
By the way, boys on average eat 76 ml more milk per day than girls. The main thing is that you have enough milk, and the baby will decide when and how much he will eat.
Should I offer my baby a second breast?
I advise offering the second breast to the baby after the first has been completely emptied. If he accepts it, then he hasn't finished eating. If not, don't worry. Let the baby decide for himself - only he knows when he is full. According to our research, 30% of babies get enough milk from one breast, 13% eat from two breasts at each feed, and 57% from time to time.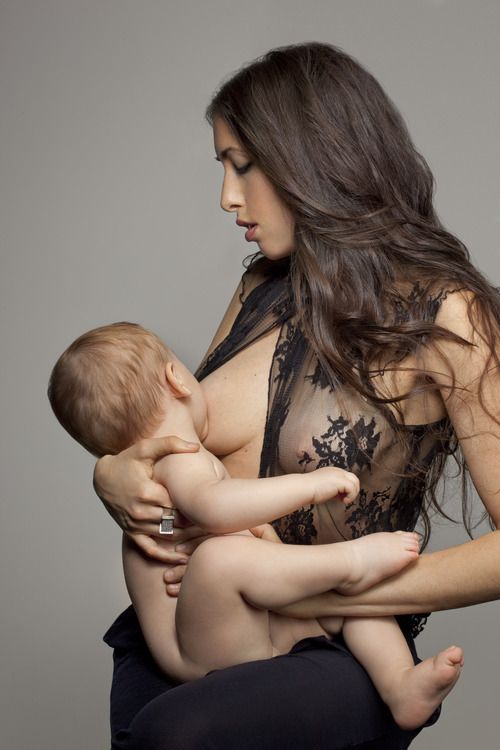 1
1
How do you know if a baby is getting enough milk?
In my experience, mothers often blame themselves for not producing enough milk. Ask yourself: Is my child growing? Is he putting on weight? Is he cheerful? Is his skin healthy? How often does he get diapers dirty? If the answer is “yes”, then the baby is getting enough milk, no matter if he eats a lot or a little.
What is the most common misconception about breastfeeding?
Mothers usually think that the older the child gets, the
more often you need to feed him and the more milk he will eat. They are often surprised to learn that between the 4th and 26th weeks, total milk production normally does not change. 2
In the first few months, the baby grows very quickly and his metabolism is accelerated. The milk that the child consumes during this period is almost completely used for growth and maintenance of metabolism.
Between the ages of three and six months, metabolism slows down and growth slows, so the same amount of milk is sufficient for the baby. In other words, the baby does not have to consume more and more milk as they grow older. On the contrary, feedings become shorter and less frequent, but at the same time the child receives the same amount of milk, because he suckles better.
In other words, the baby does not have to consume more and more milk as they grow older. On the contrary, feedings become shorter and less frequent, but at the same time the child receives the same amount of milk, because he suckles better.
Do studies say anything about the age at which breastfed babies start sleeping through the night?
Most babies need to be fed at night.
A baby's stomach is not large enough to go all night without a feed, and breast milk is digested very quickly. Therefore, it is natural for the baby to wake up at night - and this usually continues for at least the first six months. Feeding at night is normal. When you feed your baby at night, do not even hesitate - all over the world at this moment other mothers of babies of the same age are doing the same. Be patient - it usually only lasts a few months. 1
What worries new mothers the most during the first few weeks of breastfeeding?
The most common concern is whether the baby latch on properly, sucks well, and is full during feeding.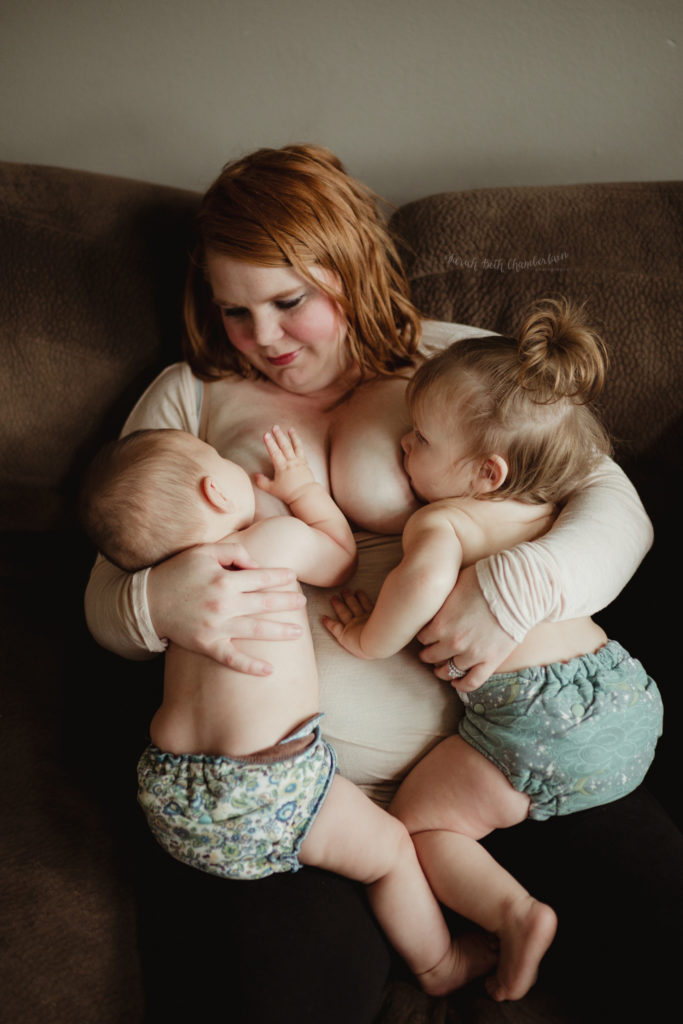 Often mothers also worry about sore nipples. The main thing is to find the right position for feeding from the very beginning and ensure that the baby is latching on correctly. Practice shows that this significantly affects the flow of milk and the convenience of feeding.
Often mothers also worry about sore nipples. The main thing is to find the right position for feeding from the very beginning and ensure that the baby is latching on correctly. Practice shows that this significantly affects the flow of milk and the convenience of feeding.
What breastfeeding symptoms should be of concern?
Milk production usually returns to normal levels two weeks after birth. If the child does not begin to gain weight on the fifth or sixth day of life, it's time to sound the alarm. You should contact your doctor to make sure that milk is being produced and that its composition is changing from colostrum to mature breast milk.
What advice would you give to a new breastfeeding mother?
Try to have skin-to-skin contact with your baby as soon as possible after delivery. If possible, feed your baby within the first hour of life, or at least breastfeed. As soon as possible, contact a specialist to correct the position and grip of the breast during feeding and thus avoid damage to the nipples.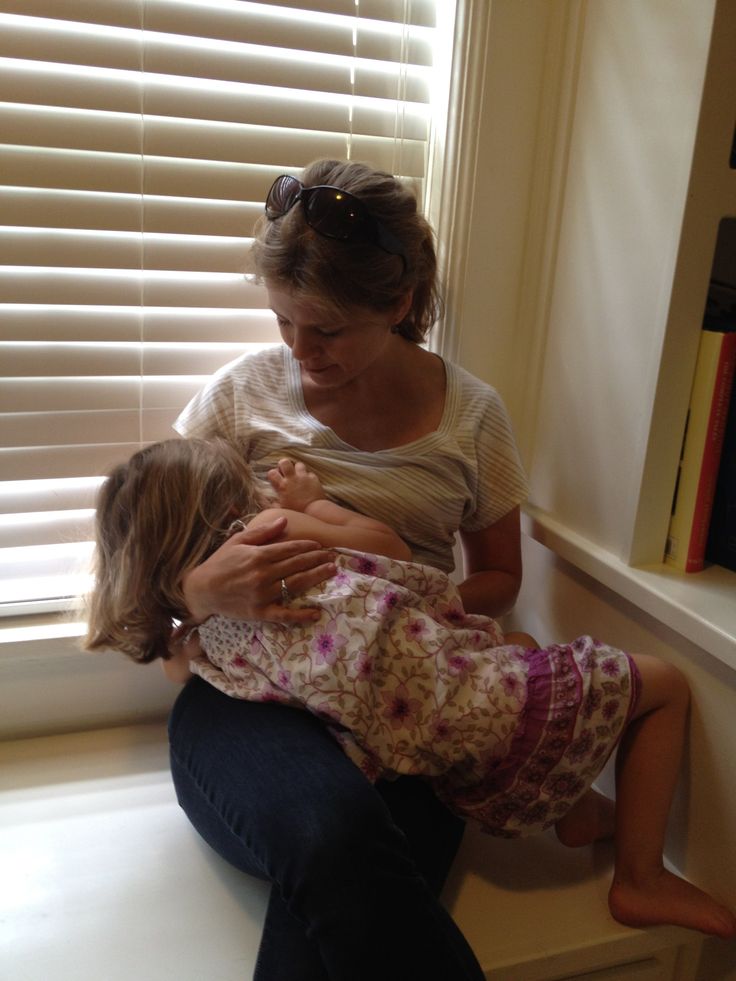
Feed frequently. Young mothers do not immediately succeed in correctly recognizing the signals that the child gives. Be sure to feed your baby on demand, and not at set intervals. Offer the breast as soon as you notice any signs of hunger - as a rule, the baby suckles better when he is calm. If he cries, it is more difficult for him to take the breast. If you are not sure what the child wants, offer him the breast. He decides whether he wants to eat or not.
To learn more about Dr. Kent's research, download infographic "How to determine the limits of normal when it comes to breastfeeding" or see it below.
Literature
1 Kent JC et al. Volume and frequency of breastfeedings and fat content of breast milk throughout the day. Pediatrics . 2006;117(3): e 387-395. - Kent J.S. et al., "Amount and frequency of breastfeeding and fat content of breast milk during the day." Pediatrix (Pediatrics).
Learn more