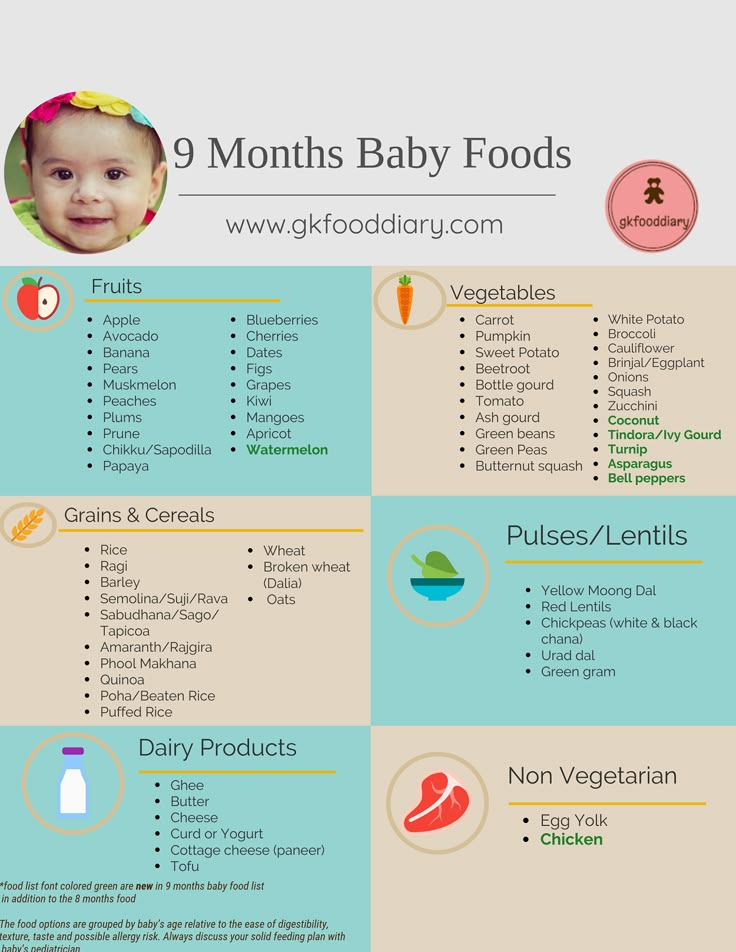
Kiwi baby food 6 months
Kiwi for Babies - Can Babies Eat Kiwi? First Foods for Baby
When can babies eat kiwi?
Kiwi may be introduced as soon as baby is ready to start solids, which is generally around 6 months of age.
Where do kiwis come from?
Kiwi originated in East Asia, where it is called kei ji gwo and míhóutáo, among other names. The latter name means “macaque fruit,” a nod to monkeys who discovered the fruit long before humans did. Kiwis are now grown commercially across the globe, including in New Zealand, where the crop has been successful and widespread. In fact, the fruit was known as gooseberry until entrepreneurial New Zealanders rebranded it with the name of the fuzzy, brown-skinned kiwi bird living all over their islands.
Is kiwi healthy for babies?
Yes. Kiwis offer a remarkable number of nutrients that are important for early growth.1 Kiwi is rich in both soluble and insoluble fibers to support digestion and baby’s developing gut microbiome.2 The fruit also offers a good amount of vitamins C and E, which support immunity, power organ functions, and aid cell growth and repair. Lastly, kiwi is loaded with phytonutrients and enzymes that are anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, anti-cancerous, and that support heart, skin, and digestive health.3 4 5
★Tip: Kiwi lasts up to a week in the fridge and is best stored away from other fruit. The natural ripening compounds in other fruits, such as bananas, can speed up kiwi’s ripening, shortening its shelf life.6
Can babies have kiwi juice?
No. Juice generally should not be given to babies under 12 months of age, unless directed to do so by a pediatric health provider. After the first birthday, small amounts of juice (less than 4 ounces a day, ideally diluted with water to reduce sweetness) may be offered on occasion as desired. 7 That said, it is good practice to wait to serve juice until a child is two years old and even then, aim to reduce the amount offered to minimize sugar in a child’s diet. Excessive consumption of sweet beverages may reduce the diversity of foods and nutrients consumed and increase the risk of diabetes, heart disease, and dental caries.8
7 That said, it is good practice to wait to serve juice until a child is two years old and even then, aim to reduce the amount offered to minimize sugar in a child’s diet. Excessive consumption of sweet beverages may reduce the diversity of foods and nutrients consumed and increase the risk of diabetes, heart disease, and dental caries.8
Is kiwi skin edible?
Yes, all varieties of kiwi skin are edible and are high in a number of beneficial nutrients (fiber, various antioxidants, and more). Kiwi skin may have some pesticide residue, although this can be reduced by washing in water.9
Can kiwi help babies poop?
Yes. Kiwi is an excellent source of fibers, polyphenols, non-starch polysaccharides, and actinidin – together, they contribute to overall digestive health and bowel regularity.10 11 In fact, daily kiwi consumption has been shown to improve stool frequency and decrease abdominal pain in otherwise healthy adults. 12 It is important to remember that pooping patterns can vary significantly from baby to baby. Be sure to talk to your pediatric healthcare provider if you have concerns about baby’s pooping and digestive function.
12 It is important to remember that pooping patterns can vary significantly from baby to baby. Be sure to talk to your pediatric healthcare provider if you have concerns about baby’s pooping and digestive function.
Is kiwi a common choking hazard for babies?
Yes. The flesh of kiwis can be firm and slippery—two qualities that increase the risk of choking. To reduce the risk, serve ripe, soft kiwi (it should be sweetly fragrant and give slightly when pressed) and cut the fruit in age-appropriate ways. As always, make sure to create a safe eating environment and stay within an arm’s reach of a baby during mealtime. For more information, visit our section on gagging and choking and familiarize yourself with common choking hazards.
Is kiwi a common allergen?
No. While kiwi is not considered to be a common food allergen, allergies to kiwi are being increasingly reported, with reactions ranging from mild to severe.13 Additionally, some individuals may be sensitive to actinidin, an enzyme that is naturally present in kiwi, and can also be used as a meat tenderizer in other foods. 14 15
14 15
Individuals with latex-fruit syndrome (including avocado, banana, and chestnut) may be allergic to kiwi as well.16 17 18 Kiwi has multiple protein allergens that have been identified, many of which cross-react with other food allergens, such as peanut, tree nuts, and stone fruits. However, it is rare for an individual to be sensitized to all the possible kiwi allergens, and most people with kiwi allergies can safely consume these other foods. Individuals with Oral Allergy Syndrome due to birch or beech pollen allergy (also known as pollen food allergy) may also be sensitive to kiwi.19 Oral Allergy Syndrome typically results in short-lived itching, burning, or tingling in the mouth and is unlikely to result in a dangerous reaction. Peeling or cooking kiwi can help minimize the reaction.20 21
Acidic foods like kiwi are often mistaken for allergens as they can cause a harmless rash around the mouth as baby eats and can cause or worsen diaper rashes. 22 23 Barrier ointments can be applied to the face before mealtime to help protect the skin from acidic foods.
22 23 Barrier ointments can be applied to the face before mealtime to help protect the skin from acidic foods.
Kiwi does contain enzymes called proteases which can break down proteins in the mouth and cause irritation or bleeding if the kiwi is consumed when not fully ripe, or in excess. To limit these reactions, ensure that you only serve kiwi that is fully ripe, serve modest quantities at a time, and serve kiwi alongside other foods.
As you would when introducing any new food, start by serving a small quantity of kiwi on its own. If there is no adverse reaction, gradually increase the quantity over future servings.
How do you prepare kiwi for babies with baby-led weaning?
Every baby develops on their own timeline, and the suggestions on how to cut or prepare particular foods are generalizations for a broad audience. Your child is an individual and may have needs or considerations beyond generally accepted practices. In determining the recommendations for size and shape of foods, we use the best available scientific information regarding gross, fine, and oral motor development to minimize choking risk.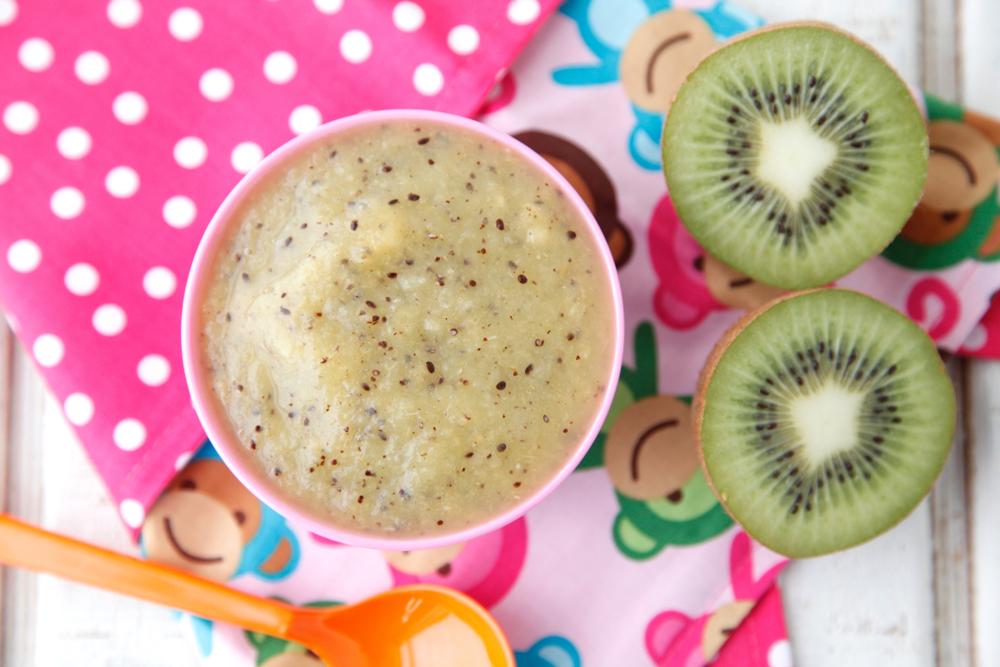 The preparation suggestions we offer are for informational purposes only and are not a substitute for child-specific, one-on-one advice from your pediatric medical or health professional or provider. It is impossible to fully eliminate all risk of a baby or child choking on any liquid, puree, or food. We advise you to follow all safety protocols we suggest to create a safe eating environment and to make educated choices for your child regarding their specific needs. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read or seen here.
The preparation suggestions we offer are for informational purposes only and are not a substitute for child-specific, one-on-one advice from your pediatric medical or health professional or provider. It is impossible to fully eliminate all risk of a baby or child choking on any liquid, puree, or food. We advise you to follow all safety protocols we suggest to create a safe eating environment and to make educated choices for your child regarding their specific needs. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read or seen here.
6 to 8 months old: Serve peeled or unpeeled ripe whole kiwis for baby to munch from. Offering a whole kiwi with half of the skin left on works well as baby can more easily hold the part with the skin and munch at the fruit that does not have the skin. The skin is edible though it may contain pesticides. You can also serve a ripe kiwi half, as long as the child is not overstuffing their mouth with an entire half.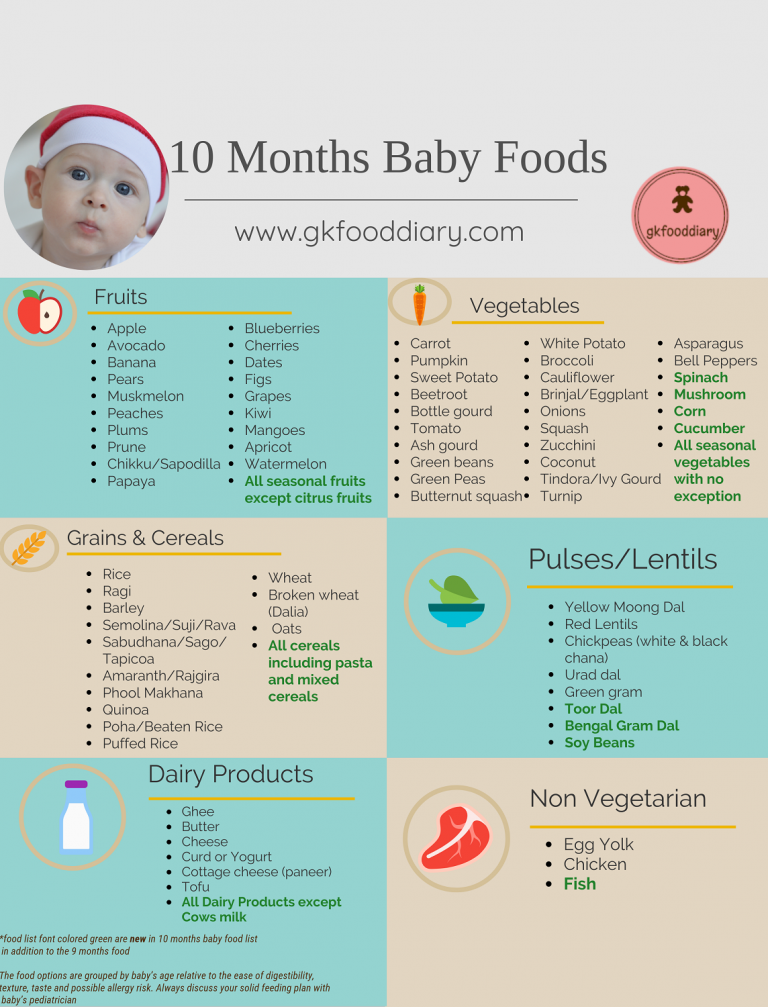 Either way, make sure the kiwi is ripe, soft, and smashes easily with light pressure. You can also mash the kiwi and mix it with unsweetened coconut cream, yogurt, or ricotta cheese.
Either way, make sure the kiwi is ripe, soft, and smashes easily with light pressure. You can also mash the kiwi and mix it with unsweetened coconut cream, yogurt, or ricotta cheese.
9 to 11 months old: Try offering kiwi, with skin on or off, chopped into large bite-sized pieces (since kiwi is slippery, small bite-sized pieces may be too tricky for this age) or thin slices. If the kiwi pieces are too slippery and baby gets frustrated, roll them in a finely ground food like shredded coconut flakes, breadcrumbs, crushed cereal, hemp seed, or finely ground nut. If baby isn’t able to pick up small pieces of food yet, keep serving ripe kiwi whole or cut in half or continue to mash the fruit into other scoopable foods.
12 to 24 months old: Offer bite-sized pieces of ripe, peeled or unpeeled kiwi as finger food or serve with a fork to encourage utensil practice. At this age, the pieces can be a bit smaller as a child’s pincer grasp has more fully developed. Kiwi can be added as a sweet topping to foods like oatmeal, quinoa, rice, yogurt, and even fish and chicken dishes.
Kiwi can be added as a sweet topping to foods like oatmeal, quinoa, rice, yogurt, and even fish and chicken dishes.
Mix up your mornings with ideas from our guide, 50 Breakfasts for Babies & Toddlers.
Recipe: Kiwi Two Ways
Yield: 1 kiwi half + ½ c (120 ml) yogurt
Cook Time: 5 minutes
Age: 6 months+
Ingredients
- 1 kiwi
- ½ c (120 ml) plain yogurt
- 1 tsp (3 g) hulled hemp seeds (optional)
This recipe contains a common allergen: dairy (yogurt). Only serve to a child after this allergen has been safely introduced. Always check for potential allergens in ingredients listed on the labels of store-bought processed foods, such as yogurt. Added ingredients may include honey, which should not be given to babies younger than 12 months.
Directions
- Make sure the kiwi is ripe enough that it mashes easily. Wash and cut the kiwi in half crosswise.
- Set aside one half to serve whole and keep the skin on. Its texture helps baby grip the slippery fruit. If the skin makes you nervous, peel it and roll the kiwi half in hemp seeds to add grip.
- Scoop the flesh from one half and mash until smooth. Swirl the mashed kiwi into the yogurt, then sprinkle hemp seeds on top.
How to Serve
Offer the kiwi two ways and let baby self-feed. If help is needed, pass the kiwi half or a pre-loaded spoon of yogurt in the air for baby to grab from you. As baby munches on the kiwi half, don’t worry if baby swallows some of the skin. It’s full of fiber.
To Store: Cut kiwi keeps in an air-tight container in the refrigerator for 3 days.
Flavor Pairings
Kiwi pairs well with all sorts of fruits, from blueberries and raspberries, to bananas and papayas, plus its acidity and brightness balance heart-healthy fats like cashews, coconut, and yogurt. Or try adding kiwi to some of your marinades for a little kick.
Or try adding kiwi to some of your marinades for a little kick.
Reviewed by
V. Kalami, MNSP, RD, CSP. Board-Certified Pediatric Dietitian and Nutritionist
K. Tatiana Maldonado, MS, CCC-SLP, CBIS, CLEC. Pediatric Feeding Therapist
K. Grenawitzke, OTD, OTR/L, SCFES, IBCLC, CNT. Pediatric Feeding Therapist
Dr. S. Bajowala, MD, FAAAAI. Board-Certified Allergist & Immunologist (allergy section)
Dr. R. Ruiz, MD, FAAP. Board-Certified General Pediatrician & Pediatric Gastroenterologist
- Richardson, D. P., Ansell, J., & Drummond, L. N. (2018). The nutritional and health attributes of kiwifruit: a review. European journal of nutrition, 57(8), 2659–2676. DOI: 10.1007/s00394-018-1627-z. Retrieved July 22, 2022
- Richardson, D. P., Ansell, J., & Drummond, L. N. (2018). The nutritional and health attributes of kiwifruit: a review. European journal of nutrition, 57(8), 2659–2676. DOI: 10.
 1007/s00394-018-1627-z. Retrieved July 22, 2022
1007/s00394-018-1627-z. Retrieved July 22, 2022 - Kim, Y. M., Abas, F., Park, Y. S., Park, Y. K., Ham, K. S., Kang, S. G., Lubinska-Szczygeł, M., Ezra, A., & Gorinstein, S. (2021). Bioactivities of Phenolic Compounds from Kiwifruit and Persimmon. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 26(15), 4405. DOI: 10.3390/molecules26154405. Retrieved July 22, 2022
- Recio-Rodriguez, J. I., Gomez-Marcos, M. A., Patino-Alonso, M. C., Puigdomenech, E., Notario-Pacheco, B., Mendizabal-Gallastegui, N., de la Fuente, A., Otegui-Ilarduya, L., Maderuelo-Fernandez, J. A., de Cabo Laso, A., Agudo-Conde, C., Garcia-Ortiz, L., & EVIDENT Group (2015). Effects of kiwi consumption on plasma lipids, fibrinogen and insulin resistance in the context of a normal diet. Nutrition journal, 14, 97. DOI: 10.1186/s12937-015-0086-0. Retrieved July 22, 2022
- Richardson, D. P., Ansell, J., & Drummond, L. N. (2018). The nutritional and health attributes of kiwifruit: a review. European journal of nutrition, 57(8), 2659–2676.
 DOI: 10.1007/s00394-018-1627-z. Retrieved July 22, 2022
DOI: 10.1007/s00394-018-1627-z. Retrieved July 22, 2022 - Mitalo OW, Tokiwa S, Kondo Y, Otsuki T, Galis I, Suezawa K, Kataoka I, Doan AT, Nakano R, Ushijima K and Kubo Y (2019) Low Temperature Storage Stimulates Fruit Softening and Sugar Accumulation Without Ethylene and Aroma Volatile Production in Kiwifruit. Front. Plant Sci. 10:888. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00888. Retrieved July 22, 2022
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Where we stand: Fruit juice. Retrieved July 22, 2022
- Fidler Mis N, Braegger C, Bronsky J, Campoy C, Domellöf M, Embleton ND, Hojsak I, Hulst J, Indrio F, Lapillonne A, Mihatsch W, Molgaard C, Vora R, Fewtrell M; ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition. (2017). Sugar in Infants, Children and Adolescents: A Position Paper of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Committee on Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 65(6):681-696. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001733. Retrieved July 22, 2022
- Wang S, Qiu Y, Zhu F.
 (2021). Kiwifruit (Actinidia spp.): A review of chemical diversity and biological activities. Food Chem. 350:128469. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128469. Retrieved July 22, 2022
(2021). Kiwifruit (Actinidia spp.): A review of chemical diversity and biological activities. Food Chem. 350:128469. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128469. Retrieved July 22, 2022 - Alim A, Li T, Nisar T, Ren D, Liu Y, Yang X. Consumption of two whole kiwifruit (Actinide chinensis) per day improves lipid homeostasis, fatty acid metabolism and gut microbiota in healthy rats. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;156:186-195. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.028. Retrieved July 22, 2022
- Richardson, D. P., Ansell, J., & Drummond, L. N. (2018). The nutritional and health attributes of kiwifruit: a review. European journal of nutrition, 57(8), 2659–2676. DOI: 10.1007/s00394-018-1627-z. Retrieved July 22, 2022
- Richardson, D. P., Ansell, J., & Drummond, L. N. (2018). The nutritional and health attributes of kiwifruit: a review. European journal of nutrition, 57(8), 2659–2676. DOI: 10.1007/s00394-018-1627-z. Retrieved July 22, 2022
- Lucas, J. S., Grimshaw, K. E., Collins, K.
 , Warner, J. O., & Hourihane, J. O. (2004). Kiwi fruit is a significant allergen and is associated with differing patterns of reactivity in children and adults. Clinical and experimental allergy : journal of the British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 34(7), 1115–1121. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2004.01982.x. Retrieved July 22, 2022
, Warner, J. O., & Hourihane, J. O. (2004). Kiwi fruit is a significant allergen and is associated with differing patterns of reactivity in children and adults. Clinical and experimental allergy : journal of the British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 34(7), 1115–1121. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2004.01982.x. Retrieved July 22, 2022 - Giangrieco, I., Proietti, S., Moscatello, S., Tuppo, L., Battistelli, A., La Cara, F., Tamburrini, M., Famiani, F., & Ciardiello, M. A. (2016). Influence of Geographical Location of Orchards on Green Kiwifruit Bioactive Components. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 64(48), 9172–9179. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b03930. Retrieved July 22, 2022
- Palacin, A., Rodriguez, J., Blanco, C., Lopez-Torrejon, G., Sánchez-Monge, R., Varela, J., Jiménez, M. A., Cumplido, J., Carrillo, T., Crespo, J. F., & Salcedo, G. (2008). Immunoglobulin E recognition patterns to purified Kiwifruit (Actinidinia deliciosa) allergens in patients sensitized to Kiwi with different clinical symptoms.
 Clinical and experimental allergy : journal of the British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 38(7), 1220–1228. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2007.02927.x. Retrieved July 22, 2022
Clinical and experimental allergy : journal of the British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 38(7), 1220–1228. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2007.02927.x. Retrieved July 22, 2022 - Díez-Gómez, M. L., Quirce, S., Aragoneses, E., & Cuevas, M. (1998). Asthma caused by Ficus benjamina latex: evidence of cross-reactivity with fig fruit and papain. Annals of allergy, asthma & immunology : official publication of the American College of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology, 80(1), 24–30. DOI: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)62934-1. Retrieved July 22, 2022
- van Odijk, J., Sjölander, S., Brostedt, P., Borres, M. P., & Englund, H. (2017). High frequency of IgE sensitization towards kiwi seed storage proteins among peanut allergic individuals also reporting allergy to kiwi. Clinical and molecular allergy : CMA, 15, 18. DOI: 10.1186/s12948-017-0073-4. Retrieved July 22, 2022
- Lucas, J. S., Grimshaw, K. E., Collins, K., Warner, J. O., & Hourihane, J. O. (2004). Kiwi fruit is a significant allergen and is associated with differing patterns of reactivity in children and adults.
 Clinical and experimental allergy : journal of the British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 34(7), 1115–1121. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2004.01982.x. Retrieved July 22, 2022
Clinical and experimental allergy : journal of the British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 34(7), 1115–1121. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2004.01982.x. Retrieved July 22, 2022 - Wagner, S., Breiteneder, H. (2002). The Latex-Fruit Syndrome. Biochemical Society Transactions, 30(6), 935-940. DOI: 10.1042/bst0300935. Retrieved July 22, 2022
- American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology. Oral allergy syndrome (OAS). Retrieved July 22, 2022
- Kashyap, R. R., & Kashyap, R. S. (2015). Oral Allergy Syndrome: An Update for Stomatologists. Journal of allergy, 2015, 543928. DOI: 10.1155/2015/543928. Retrieved July 22, 2022
- Cleveland Clinic. Contact dermatitis. Retrieved July 22, 2022
- Katta, R., & Schlichte, M. (2014). Diet and dermatitis: food triggers. The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology, 7(3), 30–36. Retrieved July 22, 2022
Easy 5-Minute Kiwi Puree for Babies and Toddlers
byAmy Palanjian
Updated
Jump to RecipeThis post may contain affiliate links. If you shop from one of our links, we may earn a commission.
If you shop from one of our links, we may earn a commission.
Transform fresh kiwi into a simple Kiwi Puree for babies and toddlers. This easy baby food recipe is full of Vitamin C and fiber and is easy to freeze!
Kiwi Puree
I love blending up fresh fruit into homemade baby food purees and this one is a great option to introduce kiwi to babies. We love this as is, or mixed with Mango Puree or Banana Puree.
How to Buy Kiwi
You’ll want to choose kiwi that’s slightly soft to the touch, but isn’t too squishy. That should have the best flavor and texture for making this recipe.
TIP: Find more tips on how to cut kiwi for baby led weaning and kids.
Ingredients You Need
To make this recipe, you just need fresh kiwi. You may need a little liquid, such as water, breastmilk, or formula, depending on the moisture in the fruit.
TIP: You can also try using full-fat coconut milk to add nutrients and flavor to this puree.
Step-by-Step Instructions
Here’s a look at this super simple baby food recipe. Scroll down for the full recipe.
- Peel the brown skin from the kiwi and discard..
- Add the fruit to a blender.
- Blend until very smooth, adding a little liquid if needed.
- Serve or store in the fridge or freezer for later.
TIP: If the fruit has a hard time blending smooth, you can double the amount to make it easier for the blender to work.
How to Freeze Kiwi Puree
To freeze, portion puree into an ice cube tray and freeze for 4-6 hours or until frozen. Transfer to a freezer storage bag for up to 3 months. To thaw from frozen, place a cube into an airtight container and allow to thaw overnight in the fridge. Freezing some of your batch is a great way to keep it fresh and have easy meals or meal components ready and waiting.
TIP: Find my best tips for baby food storage here.
My Kiwi Puree is tart—what should I do?
Depending on the flavor of the fresh fruit, it may taste a little tart when pureed.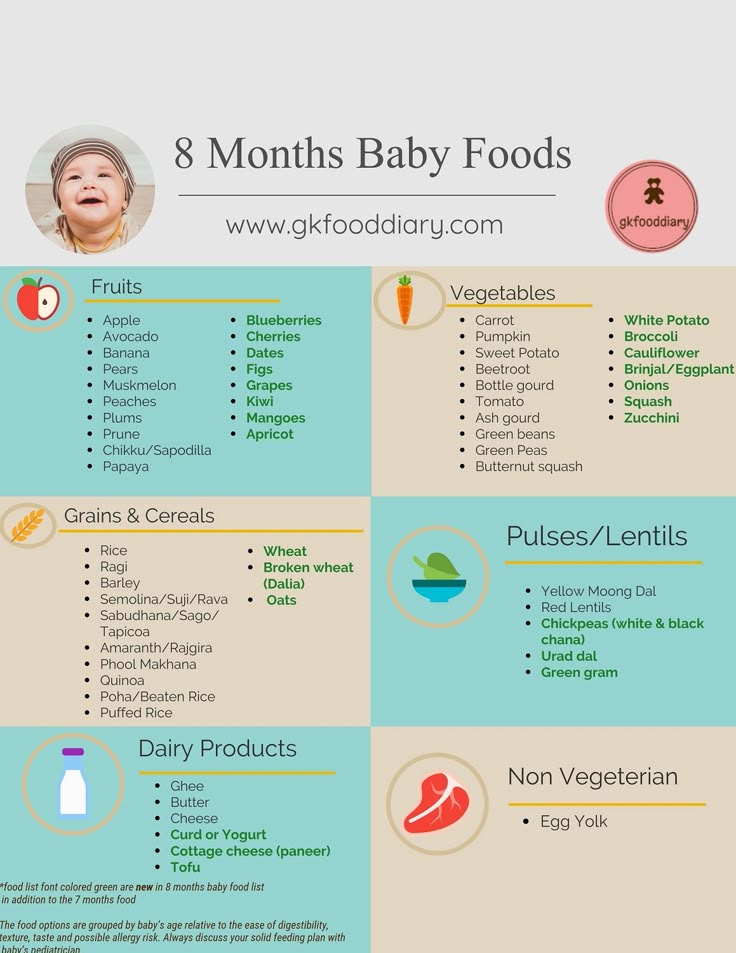 If tastes too tart to you, you can mix it with plain whole milk yogurt, applesauce, Banana Puree, or Avocado Puree to mellow the flavor.
If tastes too tart to you, you can mix it with plain whole milk yogurt, applesauce, Banana Puree, or Avocado Puree to mellow the flavor.
Stage 2 Baby Food Recipe
Kiwi can be a little acidic, so offer this to a baby once they’ve eaten other solids around 7 or 8 months. Sometimes acidic foods can cause a minor skin reaction in babies.
Tips for Making the Best Kiwi Puree
- If the blender has a hard time blending the fruit totally smooth, increase the amount of kiwi to 2 cups.
- To freeze, portion puree into an ice cube tray and freeze for 4-6 hours or until frozen. Transfer to a freezer storage bag for up to 3 months.
- To thaw from frozen, place a cube into an airtight container and allow to thaw overnight in the fridge.
- Serve as is or mix into yogurt, oatmeal, or a smoothie.
- Mix it with another puree as desired, such as applesauce, Banana Puree, or Mango Puree.
- See more of my favorite baby food combinations here.

- Learn how to cut kiwi for babies and kids.
I’d love to hear what you think of this recipe, so please comment below to share feedback!
Prep Time 5 minutes
Cook Time 0 minutes
Total Time 5 minutes
Author Amy Palanjian
Cuisine American
Course Baby Food
Calories 28kcal
Servings 4
- ▢ 2-3 fresh kiwi fruit
- ▢ water, formula, breastmilk, or full-fat coconut milk as needed
Peel the brown skin from the kiwi and discard, keeping just the green fruit.
Add the fruit to a blender.
Blend until very smooth, adding a little liquid if needed.
Serve or store in the fridge or freezer for later.
Vitamix Blender
Storage Containers
Reusable Pouch
- If the blender has a hard time blending the fruit totally smooth, increase the amount of kiwi to 2 cups.
- To freeze, portion puree into an ice cube tray and freeze for 4-6 hours or until frozen.
 Transfer to a freezer storage bag for up to 3 months.
Transfer to a freezer storage bag for up to 3 months. - To thaw from frozen, place a cube into an airtight container and allow to thaw overnight in the fridge.
- Serve as is or mix into yogurt, oatmeal, or a smoothie.
- Mix it with another puree as desired, such as Apple Puree, Banana Puree, or Mango Puree.
Calories: 28kcal, Carbohydrates: 7g, Protein: 1g, Fat: 1g, Saturated Fat: 1g, Polyunsaturated Fat: 1g, Monounsaturated Fat: 1g, Sodium: 1mg, Potassium: 142mg, Fiber: 1g, Sugar: 4g, Vitamin A: 40IU, Vitamin C: 42mg, Calcium: 15mg, Iron: 1mg
Tried this recipe?Rate in the comments and tag @yummytoddlerfood on IG!
Related Posts
Related Products
Happy Family Meals (Meal Plans)
Buy Now
Happy Family Meals (Vol 2)
Buy Now
Yummy Toddler Snacks
Buy Now
Yummy Baby Food
Buy Now
Share it with the world
FacebookTweetPinFiled Under
90,000 from what age can children (benefit and harm)?Child’s birthday » Baby food » Age restrictions on the use of kiwi for children
06/24/2016
Contents tasty fruit
When a newborn child appears in the house, the parents have much more trouble and responsibilities.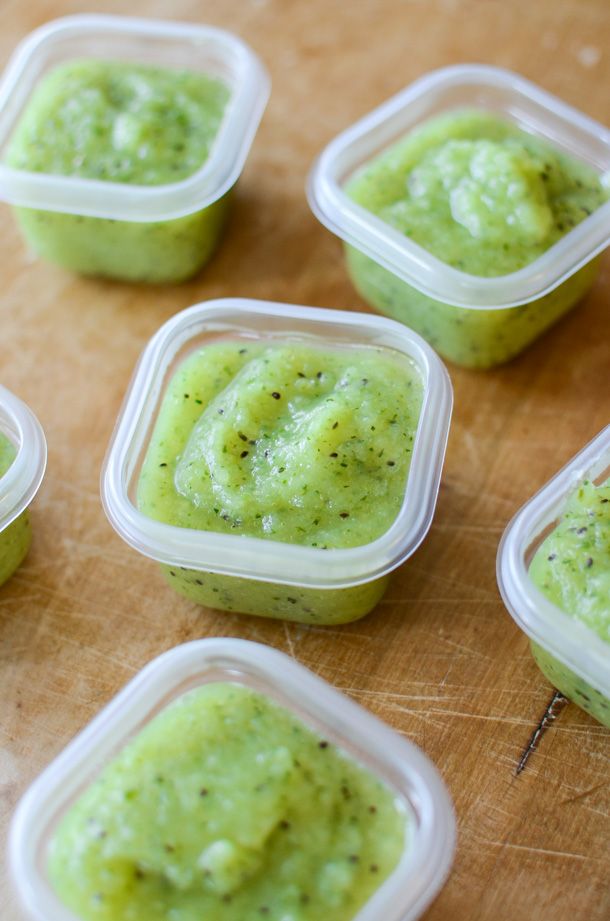 Along with this, there is a desire to feed the baby in the early months with maximum benefit for the body. You can replenish the supply of vitamins with the help of vegetables and fruits. But not all adults know when and from what age to introduce additional products into the menu, from how many months you can feed your baby with vegetables, which properties of fruits will be harmful, and which ones will be beneficial.
Along with this, there is a desire to feed the baby in the early months with maximum benefit for the body. You can replenish the supply of vitamins with the help of vegetables and fruits. But not all adults know when and from what age to introduce additional products into the menu, from how many months you can feed your baby with vegetables, which properties of fruits will be harmful, and which ones will be beneficial.
Many mothers and fathers try to start giving their offspring kiwi fruit as early as possible. This plant is native to China and has been bred in New Zealand to form the kiwi fruit known today. Useful properties of the plant are undeniable:
- high content of potassium, vitamin C and B; Nutritional value of kiwi
- the presence of vitamins A, D, E, nicotinic acid, calcium, magnesium, sodium, magnesium, phosphorus, zinc in the composition of kiwi;
- low calorie and active fat burning;
- reducing the risk of developing cancer;
- improvement of the cardiovascular system;
- strengthening the protective and regenerative abilities of the body;
- regulation of metabolic processes.

As a prophylactic, kiwi prevents rheumatic diseases and urolithiasis, and improves the functioning of the respiratory system. In babies who receive the required amount of fruit, the body is more resistant to viral and infectious diseases, there are less problems with the functioning of the heart muscle, problems with bowel movements disappear, and hematomas are less likely to form with bruises. And if the child suffers from diabetes, then kiwi will brighten up the boring diet of the patient.
Acceptable age for eating exotic fruit
Interesting facts about kiwiLet's start with the fact that pediatricians forbid giving kiwi to small children under five years old. From this age, it is allowed to eat one fruit per week.
But caring mothers can't wait to buy an exotic treat for their child from an early age, the benefits of which are very obvious. Then they introduce kiwi into the daily diet of children much earlier. From the third year, ½ fetus is allowed 1 time per week.
Then they introduce kiwi into the daily diet of children much earlier. From the third year, ½ fetus is allowed 1 time per week.
If parents decide to give an interesting fruit to a child of the first year of life, then you should remember that up to six months the use of kiwi is strictly prohibited! But from six months to one year, kiwifruit can be given to an infant 1 teaspoon in the form of juice or puree, again - no more than once a week.
Calorie content of kiwi in 100gA seven-month-old child can already take 2 teaspoons of overseas berries, and from nine to eleven months, children who start getting kiwi early are given ¼ share per week. Thus, in a year the baby is ready to eat fruit in the amount allowed for a three-year-old child.
It should be remembered that the introduction of a new fruit into the menu of young children should be gradual, carefully observing skin reactions and the functioning of the digestive system. Any unusual abnormal manifestations will indicate the development of an allergy.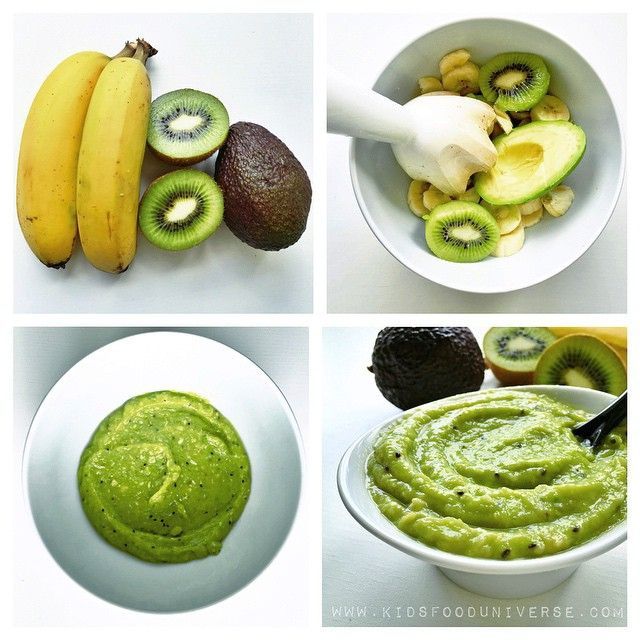 In such cases, it is necessary to stop giving the product to the child, otherwise the expected benefit will turn into an obvious harm to health.
In such cases, it is necessary to stop giving the product to the child, otherwise the expected benefit will turn into an obvious harm to health.
Contraindications and negative effects
The benefits of vitamin CIt is important to remember that an exotic fruit not only has beneficial properties, but can also be harmful to the body.
- The high content of vitamin C makes it impossible for children who are allergic to citrus fruits to take kiwi.
- Risk of developing hypervitaminosis due to frequent fruit consumption.
- The fruit is rich in various acids, so excessive consumption can cause irritation of the oral mucosa. Feeding kiwifruit to children with hyperacid gastritis is also excluded.
- Absolute contraindications for children of any age: disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, frequent diarrhea, allergic reactions.
At what age and at what age to start giving kiwi fruit to children, it is up to each parent to decide.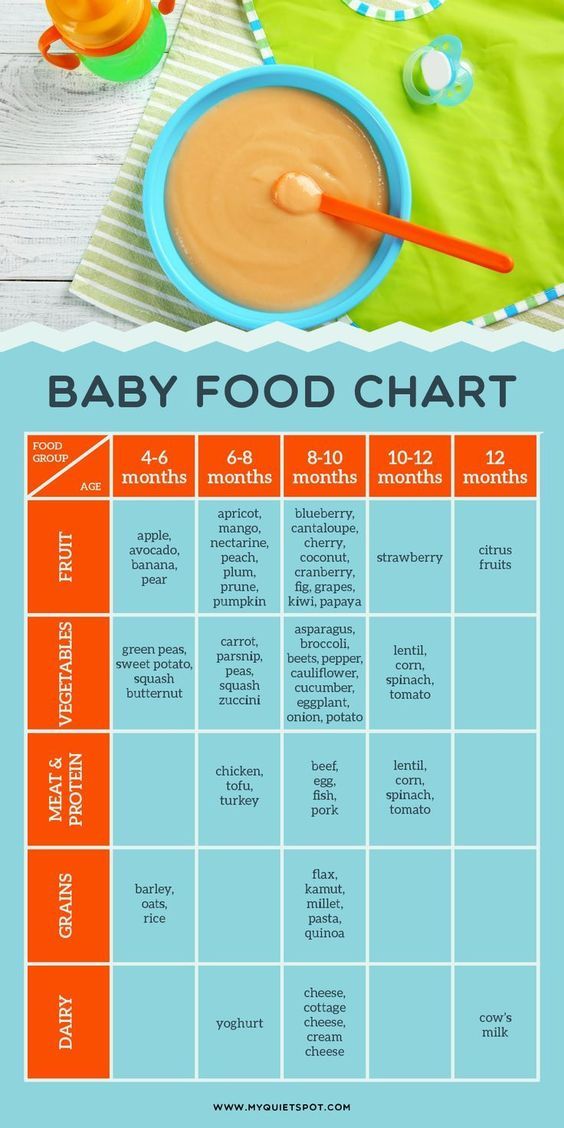 It doesn’t matter if the baby is 11 months old or 3 years old, you should carefully weigh the pros and cons and only then decide whether the fruit will be useful or harm the child.
It doesn’t matter if the baby is 11 months old or 3 years old, you should carefully weigh the pros and cons and only then decide whether the fruit will be useful or harm the child.
Choosing and storing ripe and tasty fruit
It is very important to be able to choose ripe natural fruits and subsequently store the fruits correctly. Especially if the purchase is intended for a six-month-old baby or children of the first years of life.
Do not buy fruits that have spots, cuts or rot.So, the fruit should be moderately soft, so that you can slightly push the structure with light pressure. Too hard or too soft fruit indicates violations of the rules of cultivation or collection. You can't give it to children. The benefits of such a kiwi will be minimal, or even there will be no positive actions at all.
The aroma emanating from the fruit should not be too tart or harsh. A spoiled fruit is considered when a "wine" smell is felt. It speaks of fermentation. So kiwi can be poisoned.
An important factor in the choice of fruit is hard hairs that easily peel off from the surface. By the way, about the surface. The presence of spots, cracks, weeping and other violations of the integrity of the fruit is not allowed.
Kiwifruit should be stored in refrigerators at positive temperaturesKiwifruit can be stored for one and a half months in the refrigerator, but at a temperature not lower than 0º. But if an unripe fruit is purchased, then it should be in room conditions. Over time, it will ripen and will not only be useful, but also tasty.
Be that as it may, it is more expedient to wait until the age at which it is officially allowed to eat kiwi, and already without fear for the health of the child, feed the baby sweet and sour fruit. The benefits and positive properties of the fetus are obvious, but when there is a risk of adverse reactions, it is better to wait a year or two.
Start giving fruit to children from as many months as the local pediatrician allows.

Fashion or the desire to diversify the diet as much as possible?
It is often not helpful to give babies as many different foods as possible. First, pediatricians around the world unanimously argue that the most useful food for humans is the one that comes from the same places where we live. Secondly, exotic products from distant lands are rarely fresh and are most often processed with harmful substances in order to increase their shelf life.
Despite the variety of exotic fruits, it is better for a child to give more familiar to the region where he was born Of course, eyes widen at the sight of many exotic fruits on supermarket shelves, and I want to give my child the opportunity to try them all, but common sense tells me that most often this is not necessary. It is better to replace overseas fruit delicacies with cheaper, fresh and high-quality locally produced counterparts.
Video: Well, Very tasty - Fruit Ice Kiwi Ice Cream!
Didn't find your organization?
Add now!
2016-06-24
Previous When and in what quantities can figs be given to children?
Next Expediency of using ketchup and mayonnaise in a child's diet
See also
About the benefits of chamomile tea for children
Contents1 What is it?2 Useful properties3 Instructions for use3.1 How to brew?4 Age restrictions and ...
From what age can a child be given kiwi fruit: From how many months, from what age, when is it possible - answers to questions from parents
Parents, as a rule, have a lot of temporary questions - from how many months this or that action is possible, from what age the child is allowed to do this or that product, when it is possible to do this and that. Of course, each child is individual, and only the doctor observing him can give an accurate answer. But, the most common answers of pediatricians to popular questions of parents, too, we hope will be useful.
But, the most common answers of pediatricians to popular questions of parents, too, we hope will be useful.
In this section, we have collected the most frequent answers from children's doctors to parents' questions. At the same time, it should be remembered that even well-known pediatricians do not have a unanimous opinion on certain temporary issues. Before using the answers below, we recommend that you seek advice from your pediatrician.
At what age can a child sleep on a pillow?
Today, specialists (orthopedists and physical therapy doctors) consider it possible to use a pillow during a child's sleep not earlier than from the age of two. This is explained by the fact that during the first 2 years of life there is an active formation of physiological curves of the spine, and the early use of pillows can affect their formation. The appearance in recent years of the so-called "orthopedic" pillows, which can be used in child care, starting from the neonatal period, is quite justified.
At what age can a baby be sent to the nursery?
Pediatricians agree that when the skeletal and muscular system is ready for sitting, the child begins to sit up by himself. Some kids have been trying to sit down since the age of four or five months, especially not on a flat surface, but on a curved one: in a sun lounger, car seat, on their parents' laps. The child begins to sit confidently at the age of about six months. Therefore, the question of planting is formulated incorrectly. It is worth planting the child when he begins to sit down on his own.
At what age can a child be given kiwi fruit?
Doctors recommend not earlier than a year. So far, very few allergic reactions to kiwifruit have been reported. But the number of people with similar manifestations is increasing, and in some of the cases already noted, especially in children, the allergy has become severe. This may be due to the general increase in the incidence of allergies and the growing popularity of this exotic fruit, especially among children.
Kiwifruit is a good source of vitamin C, potassium and fibre. If your child is allergic to any other foods, or if you have a family member with allergies, do not give your child kiwifruit before the age of six months. (Ideally, before six months of age, you should not introduce complementary foods at all, unless your doctor has advised otherwise.)
At what age can you have pea soup?
Pediatricians do not recommend giving a child pea soup before two years of age. At the same time, you should start with small portions and cook soup without smoked meats.
At what age can a child be given bread? And which is better white or black?
From 7 months. It is best to accustom a child to bread by giving him crackers: 5-10 grams (a quarter of a piece of white bread). If the baby is not gaining weight well, he has a plentiful stool, consult with the pediatrician whether it is worth including bread in the child's diet or if it is worth waiting.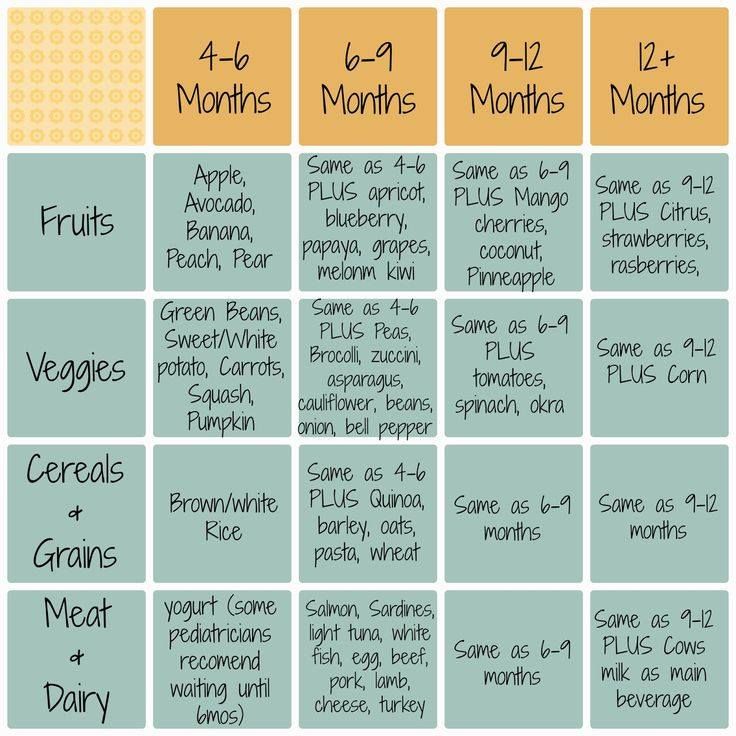 Up to 3 years it is better to give white bread , because the child's digestive system is still maturing, and rye bread requires more enzymes.
Up to 3 years it is better to give white bread , because the child's digestive system is still maturing, and rye bread requires more enzymes.
The most useful is gray bread, with bran, from wholemeal flour. It is rich in B vitamins, minerals: K, Ca, Mg, Fe and dietary fiber. And fluffy white bread is less valuable in terms of a healthy diet.
Do not give children fresh white bread, it contains a lot of gluten, and this is an unnecessary burden on the pancreas.
Until what age should vitamin D be given?
Healthy children are given vitamin D up to a year old one drop per day in the autumn-winter period. For children with a lack of vitamin D, the pediatrician prescribes the dosage. After a year, also consult a pediatrician about the appropriateness of the appointment.
At what age can eggs be given to a child?
Boiled eggs (yolk) can be given to a baby when he is six months old. You should avoid raw eggs in your child's diet, as they sometimes contain salmonella bacteria. These bacteria can cause poisoning, so boil your eggs hard. For the same reason, try not to give your child anything that might contain a raw egg. For example, raw pie dough, homemade ice cream, or desserts and mousses that include a raw egg.
These bacteria can cause poisoning, so boil your eggs hard. For the same reason, try not to give your child anything that might contain a raw egg. For example, raw pie dough, homemade ice cream, or desserts and mousses that include a raw egg.
When can a baby eat nuts?
Whole nuts should not be given to children under the age of five. They can choke and suffocate. However, nut butter and ground nuts can be given to a child older than one year, provided that no one in the family suffers from allergies. Serious allergies to nuts and nut products and some seeds occur in less than one percent of the population. Your child may be at greater risk if you, the child's father, or siblings have allergic conditions such as hay fever (hay fever), asthma, and/or atopic dermatitis (eczema).
At what age can fish be given?
Children under six months of age should not be given any fish, shellfish or crustaceans because there is a small risk of an allergic reaction.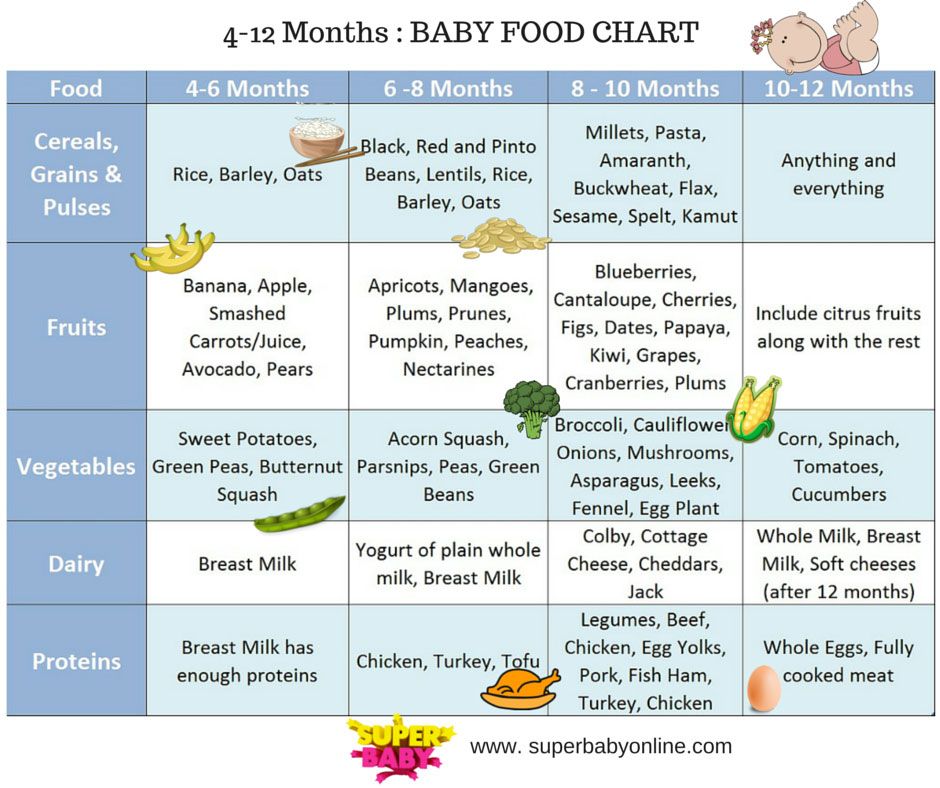 After six months, fish should be given as complementary foods in jars of baby food, see the age recommendations on the packages. Self-preparation of fish for a child should be subject to the strictest safety measures when deboning and processing during cooking.
After six months, fish should be given as complementary foods in jars of baby food, see the age recommendations on the packages. Self-preparation of fish for a child should be subject to the strictest safety measures when deboning and processing during cooking.
When can a baby eat honey?
Honey is sugar, and giving sugar to a child can develop a sweet tooth and/or provoke tooth decay. It is not recommended to give honey to a child under one year old, because sometimes honey can contain bacteria that release dangerous toxins. Once in the intestines of a child, these bacteria can cause infant botulism. When a child is over a year old, their intestines are already sufficiently developed to prevent these bacteria from multiplying and growing.
In addition, honey can cause allergies. You should start giving honey from very small volumes, carefully monitoring the result.
At what age can a child eat citrus fruits?
Citrus fruits such as oranges, grapefruits, lemons and limes are high in vitamin C. However, fruit juices and citrus fruits should not be given to a child under six months of age. If you buy ready-made baby food, check to see if it contains lemon juice. It is often added to puree, such as apple or banana. If you give your child fruit juice, do so only at mealtimes and keep it well diluted (one part juice to 10 parts water).
However, fruit juices and citrus fruits should not be given to a child under six months of age. If you buy ready-made baby food, check to see if it contains lemon juice. It is often added to puree, such as apple or banana. If you give your child fruit juice, do so only at mealtimes and keep it well diluted (one part juice to 10 parts water).
Encourage your child to drink juice from a cup or drinker (never from a bottle). When a child drinks juice from a sippy cup, they are less likely to develop tooth decay because they drink the juice faster. With prolonged contact with sugars and acids naturally found in juice, the risk of developing caries increases.
When can a baby goat's and sheep's milk?
Do not give goat's or sheep's milk to a child under one year of age. If you are offering this milk to an older child, make sure it is pasteurized.
At what age can a baby be given cheese?
Cheese is an excellent source of calcium and energy. From the age of six months, you can introduce a small amount of cheese into your baby's diet. Soft blue cheeses such as brie and camembert are not suitable for a baby. This is due to the small risk of containing bacteria that cause listeriosis.
From the age of six months, you can introduce a small amount of cheese into your baby's diet. Soft blue cheeses such as brie and camembert are not suitable for a baby. This is due to the small risk of containing bacteria that cause listeriosis.
At what age can a baby be put in a walker?
The condition for putting a baby in a walker is when he/she sits independently and stands at the support, that is, not earlier than 6-7 months. It is not worth using for more than 15-20 minutes in a row, as pathological foot settings are formed. Do not use a walker as a means of keeping the child busy all the time; the load on the spine is not properly distributed in the walker. In general, if you can do without walkers, it is better to do without them.
At what age can a baby be carried upright in a kangaroo?
It depends on the design of the "kangaroo" (usually manufacturers write relevant information on the product) and on the state of the child's musculoskeletal system. If you do gymnastics with your baby, and the “kangaroo” supports your head, then you can wear it from 1-2 months (not for long). From about 4 months, all restrictions are removed.
If you do gymnastics with your baby, and the “kangaroo” supports your head, then you can wear it from 1-2 months (not for long). From about 4 months, all restrictions are removed.
At what age can kefir be given to a baby?
From eight months. According to modern ideas, kefir can be given to a child no earlier than seven to eight months of age. And in the first months of life, this product is not at all suitable for babies - it is painfully different from mother's milk and adapted milk formulas. Firstly, kefir contains a lot of "coarse" casein protein, which is not only difficult for the body of a newborn to assimilate, but is also unbalanced in terms of amino acid composition. Secondly, the fat composition of kefir is not diverse enough, moreover, the ratio of fatty acids in this product is not physiological for the baby's body. Thirdly, kefir carbohydrates are not at all similar to those present in breast milk or its artificial substitutes. Finally, if we take into account that kefir contains significantly more mineral salts than human milk, then the load on the digestive and excretory system of the baby turns out to be disproportionately higher than when breastfeeding.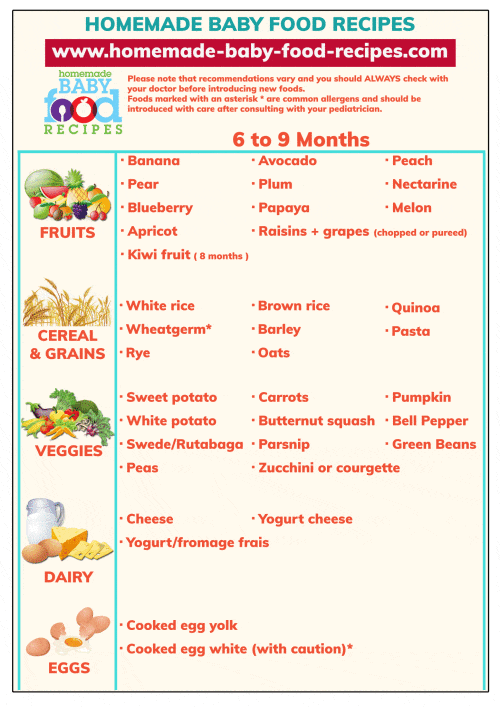
At what age can a child be given chocolate?
The later the better - preferably not before two or three years. Chocolate, or rather cocoa, which it contains, often provokes an allergic reaction.
The smaller the piece of chocolate, the lower the risk of allergies.
The older the child, the lower the risk of allergies.
The lower the cocoa content in chocolate, the lower the risk of allergies.
Conclusion: if possible, do not give chocolate until 3 years, after milk chocolate should be given, no more than 1-2 times a week and no more than 1-2 pieces.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JRBR5JxshoM
Category Vegetables and fruits for newborns
174 112662088Previous article
How to travel with a baby? How to avoid problems on vacation?
Next article
How old is the TV?
Other articles on this topic
- How much water can you give
- Children do not sit up by themselves at 10 months
- How many eggs can eat at 2 years
- from how many months you can wear a child in a kangaroo
- bone age
Actual posts
20 weeks of pregnancy are low -up
to which week toxicosis
Learn and participate
Clubs clubs Baby.