Wind baby after every feed
Winding and burping your baby
Wind is air that your baby has swallowed when they were feeding, crying or yawning.
Wind is common from the newborn stage to about 3 months, as a baby's digestive system matures.
Common signs of trapped wind include squirming or crying during a feed, or looking uncomfortable and in pain if laid down after feeds.
Some babies need a little more help than others to release wind. To wind your baby, hold them in an upright position against your shoulder. Massage their back.
How to wind your babyHow to wind your baby
Please accept Youtube cookies to view this content.
Read our cookies policy to find out more about our cookies and how we use them.
When your baby gets windEvery baby is different and over time you will grow to know your baby's cues.
Sometimes the wind builds up from the day's feeds. This is especially true if an unsettled feeding period happens in the late afternoon or evening period.
The period of being unsettled is sometimes called 'the witching hour'. Most babies will experience this period of being unsettled. Some suffer worse than others. It usually begins around 2 to 4 weeks old and may last for 6 weeks.
Tips for windingGeneral tips
- skin-to-skin contact may relax your baby and wind may break more easily
- hold your baby up against your shoulder after a feed and massage their back
- after feeding, keep your baby in an upright position
- walk with your baby in your arms or in a baby sling - the upright position gently helps to relax them
- put a gentle little bump or bounce in your walk
- try the 'magic baby hold' - hold your baby's back against your tummy.
 Their tummy should rest on your crossed arms. Their legs and arms should gently fall either side of your arms
Their tummy should rest on your crossed arms. Their legs and arms should gently fall either side of your arms - respond as quickly as possible to your baby crying. Provide comfort by feeding, holding, rocking, singing or other method. Leaving a baby to cry will cause more air to be swallowed and will worsen wind
Breastfeeding tips
- make sure your baby is positioned and attached well to the breast. Ask your public health nurse or lactation consultant to observe a breastfeed if you need help
- hand expressing a small amount of milk before feeding can help to slow down the flow of milk
Information:
Breastfeeding
Formula feeding tips
- wind your baby often during and after each feed, this may help ease the build-up of wind
- reduce flow of feed from bottle or try different teat size
- tilt the bottle so the teat and bottle neck are constantly full of milk
- don't let your baby suck on the bottle when the feed is finished or when only milk bubbles are left
- let your baby's bottle stand until all the air bubbles produced by shaking have settled
- hold your baby a little more upright, rather than lying them flat while you are feeding them their bottle
- if you are considering changing your baby's infant formula milk, discuss it with your public health nurse first
Avoid chopping and changing between brands or types of formula. Frequently changing can cause your baby to become more unsettled.
Frequently changing can cause your baby to become more unsettled.
Page last reviewed: 25 March 2018
Next review due: 25 March 2021
How and When to Burp Your Baby
A key part of your baby's feeding routine is burping him. Your baby may swallow lots of air while feeding, and burping can help remove some of that gassiness and ease his fussiness. It may also help prevent him from spitting up.
Find out how to burp your baby, and pick up some tips on making burping more effective.
How to Burp Your Baby: Positions to Try
Here are three burping techniques that have stood the test of time. After trying each of them out, you’ll probably settle on one that works best for you and your baby:
Hold your baby upright against your chest with his chin on your shoulder, all the while supporting him with one hand as you gently pat his back with your other hand.

Place your baby on your lap with him sitting up, all the while supporting his head and chest with one hand while you softly pat his back with your other hand.
Lay your baby on your lap with his belly faced down, all the while supporting his head so it’s higher than his chest, and pat his back.
Tips for Burping Your Baby
Try these tips the next time you need to burp your baby:
Use repeated, gentle pats on her back.
Cup your hand slightly as you pat her, as this is gentler than using a flattened palm.
Drape a towel or bib over your lap or shoulder to protect your clothing as you burp your baby, in case your baby spits up (sometimes called “wet burps”).
Now that you know how to burp your baby, and these tips help you do so effectively, here’s a helpful visual guide:
How Long Should You Burp Your Baby?
There is no specific length of time needed for burping your baby. The more important factor is how often you burp him. With that in mind, burp your baby frequently throughout feeds, even when it looks like he doesn’t need to be burped.
The more important factor is how often you burp him. With that in mind, burp your baby frequently throughout feeds, even when it looks like he doesn’t need to be burped.
Waiting until after a feeding to burp your baby may mean your little one has swallowed too much air and may be fussier, so it’s better to stop feeding every so often and try to burp your little one. You could also try paced bottle feeding, which slows the flow of breast milk or formula from the bottle, which could help prevent gas.
Here are some tips for burping your baby during a feeding:
If you’re bottle feeding (which can include formula feeding or offering expressed breast milk), you’ll want to burp him after every two to three ounces of milk.
If you’re breastfeeding, burp your baby each time he switches breasts. Some breastfed babies may not need to burp as often, as they may not swallow as much air.
If your baby hasn’t burped after some time, go back to feeding.
 Not every baby burps every time you want him to burp.
Not every baby burps every time you want him to burp.
If your baby shows any of the following signs, you may want to burp him more regularly — for example, after every ounce of milk during bottle feeding or every five minutes during breastfeeding:
He is gassy
He spits up frequently
He has Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
He seems very fussy.
After a feeding is over, keep your baby in an upright position for 10 to 15 minutes. This can help prevent him from spitting up. You may need to burp him longer if he does spit up or has been diagnosed with GERD.
Other Instances When Burping Your Baby Might Be Beneficial
If your sleeping baby wakes suddenly and you suspect it may be because of gas, burping her might help relieve the pressure and help her fall back asleep.
A colicky baby, who may cry for three or more hours per day, might have gas from all the air she’s swallowed during one of these crying spells. You may consider burping her to see if it helps comfort her.
You may consider burping her to see if it helps comfort her.
We hope these tips can help you burp your baby during feeding time to ensure she’s more comfortable.
Don’t forget to stock up on plenty of diapers, which you will surely need after all these feedings and burpings. Get rewarded for your Pampers purchases by using the Pampers Club app to earn rewards like coupons, gifts, and gift cards.
How to help the baby when regulating
Support icon ofKeywords for searching
Home ›!! How to help a child in sprinkling
Home Home ›!! How to help a child in regurgitation
↑ Verki
Breastal feeding - completely special time for mom and her newborn baby. Together with the feeling of closeness and affection that feeding brings, understanding its nuances cannot but raise many questions, including the question of how to help an infant spit up. Regurgitation in a newborn is by no means always the result of a simple pat on his back.
In this article, we'll talk about the basics of helping a newborn spit up, as well as other questions you may have about spitting up.
Why do babies spit up?
Let's get it straight: why do newborns need to burp in the first place? During feeding, children usually swallow extra air - this is called aerophagy. Spitting up helps prevent this air from entering the intestines, as well as vomiting, gas, and crankiness in the baby. To avoid the return of milk after feeding, you should give the baby the opportunity to burp more often.
How to help a newborn spit up?
During the first six months, the baby should be kept upright in a column for 10-15 minutes after each feed. This will help keep the milk in his stomach, but if the baby occasionally burps anyway, parents need not worry. While carrying your baby in an upright position, you can put a baby diaper or wipes on your shoulder to keep your clothes clean.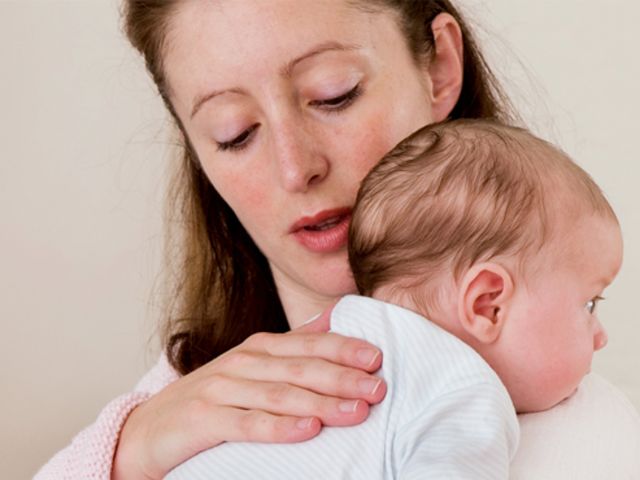
We've already seen why spitting up is important, now let's find out how to help your baby spit up. Parents should gently pat the baby on the back with a hand folded in a handful until he burps. Folding your hand into a handful is important because clapping with a flat palm may be too strong for an infant.
Every baby is different and there is no one right position for spitting up. To get started, you can try the following options:
- Sitting position with the baby on the chest. In this position, the parent puts the baby's head with his chin on his shoulder and with one hand supports the baby under the back. With the other hand, you can gently pat the baby on the back. This method is most effective in a rocking chair or when the baby is gently rocking.
- Holding the child upright on your legs. With one hand, parents can hold the baby by the back and head, supporting his chin and placing his palm on the baby’s chest, with the other hand, you can gently pat him on the back.
 At the same time, it is important to be careful: do not press the child on the throat, but only gently support his chin.
At the same time, it is important to be careful: do not press the child on the throat, but only gently support his chin. - Holding a baby on your lap while lying on your tummy. Make sure his head is above his chest and gently pat your baby on the back until he burps.
Here are some tips on how best to help your newborn spit up:
- Let your baby spit up during feeding. If the baby is restless or has swallowed air, it is worth giving him the opportunity to burp during feeding, and not just after.
- When bottle feeding, let the newborn burp after every 50-60 ml.
- When breastfeeding, let the baby burp at every breast change.
It is important to let your baby spit up after eating, even if he spit up during feeding!
If your baby is gassy, spit up more often. Also, if he vomits frequently or suffers from gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), have him spit up after every 30 ml bottle-feeding or every five minutes while breastfeeding.
How long should a baby be held for it to burp? It's different for everyone, but generally keeping a newborn upright for 15 to 20 minutes after a feed helps the milk stay in the baby's stomach.
Minimize the amount of air you swallow. Gas production and regurgitation result from aerophagia during feeding. The baby will inevitably swallow air, but there are ways to prevent it from swallowing too much. Whether you bottle feed your baby or combine breastfeeding with bottle feeding, the Philips Avent anti-colic bottle with AirFree valve is designed so that the nipple is always filled with milk without excess air, even in a horizontal position, thus preventing the baby from swallowing excess air during feeding.
Reducing the amount of air your baby swallows can help reduce your baby's risk of colic, gas, and spitting up.
Breastfeeding is a wonderful time to strengthen the bond between parent and baby. Every mom and every baby is different, so learning to help your newborn burp properly can take time and practice.
Articles and tips from Philips Avent
Baby+ app
Download the app and track your child's development and growth with trackers, and keep those special moments forever.
Download app:
You are leaving the Philips Healthcare (“Philips”) official website. Any links to third party websites that may be included on this site are provided solely as a convenience to you. Philips makes no warranties regarding any third party websites or the information they contain.
I understand
You are about to visit a Philips global content page
You are about to visit the Philips USA website.
Is regurgitation in a child normal?!
31.Mar.2021
Regurgitation is the reflux of small amounts of gastric contents or gastric juice mixed with saliva up the esophagus. Regurgitation often occurs in infants and in the vast majority of cases is a variant of the physiological norm.
The younger the child, the more often regurgitation can be observed. As the child grows, they gradually disappear until they disappear completely. In the first month, regurgitation occurs in 85% of children, this indicator does not depend on the type of feeding (formula or breast milk) and on the method of administration (bottle or natural feeding). After 3 months, regurgitation is much less common, and by one year it disappears completely.
As the child grows, they gradually disappear until they disappear completely. In the first month, regurgitation occurs in 85% of children, this indicator does not depend on the type of feeding (formula or breast milk) and on the method of administration (bottle or natural feeding). After 3 months, regurgitation is much less common, and by one year it disappears completely.
In the new issue of " Advice of the day from a doctor" , the local pediatrician of the DPO No. 3 Shayakhmetova Yazgul Fayzrakhmanovna will give parents practical advice on topical and frequent questions about the features of feeding the baby and due to what factors the involuntary process of regurgitation occurs.
Causes and mechanism of regurgitation
• Filling the stomach with air that the child can swallow while eating. This is the most common cause, which practically does not require special correction.
• Muscular weakness of the valve between the esophagus and stomach. It develops with the growth of the child and begins to function normally by the first year of life. Therefore, food can pass from the stomach into the esophagus without hindrance, which happens during regurgitation.
It develops with the growth of the child and begins to function normally by the first year of life. Therefore, food can pass from the stomach into the esophagus without hindrance, which happens during regurgitation.
• Food allergy (or food intolerance). Most often, it is manifested by skin reactions, but in rare cases, regurgitation can be a symptom.
• Congenital defects of the gastrointestinal tract. The digestive system is quite complex, some violations in its structure can lead to digestive problems that will begin to appear immediately after birth. Thus, narrowing in the area of the gastrointestinal junction can lead to frequent atypical regurgitation.
Regurgitation and vomiting
Regurgitation is in most cases a physiological phenomenon that does not require special treatment and observation. But it can be similar to vomiting, being a sign of dangerous diseases, in which case a doctor's consultation is necessary. Regurgitation and vomiting are similar in their mechanism of occurrence, namely, the release of gastric contents into the oral cavity.
It is important to distinguish between them, as vomiting in newborns is very dangerous and can lead to aspiration of the contents into the respiratory tract and respiratory arrest.
There are differences between regurgitation and vomiting:
• Regurgitation most often occurs after eating. Usually this is a single, non-recurring episode. The child spits up the food that he just ate, there are no foreign impurities in it.
• Vomiting usually recurs repeatedly. It may not be related to eating.
• Regurgitation does not affect the well-being and mood of the child - he is active, does not show signs of anxiety, smiles, plays.
• Vomiting is accompanied by a deterioration in general well-being. The child is lethargic or restless.
• Regurgitation usually occurs suddenly, vomiting is preceded by a decrease in activity and mood.
• Vomiting is rarely the only symptom - there are also other problems with the functioning of the digestive tract or fever. Vomiting in a child is a reason to see a doctor!
Vomiting in a child is a reason to see a doctor!
Tips for parents!
Let's figure out how to avoid the possible dangers associated with regurgitation. The main thing that responsible parents need to know is that most often children spit up in a prone position. This position is dangerous by aspiration (inhalation) of gastric contents.
Preventing aspiration is as simple as bringing the baby upright or turning it over on its side or stomach immediately after spitting up. Then the baby himself will be able to push the food out of his mouth.
It is worth remembering that it is unacceptable to leave a child with regurgitation syndrome without adult supervision, especially in the supine position.
Feeding rules
Frequent regurgitation can be prevented by following a few feeding rules.
• Keep your baby upright after feeding. Even if the baby is tired or wants to sleep, do not immediately put him down. Babies are very comfortable to hold on the shoulder. After waiting for the belching of air, the child can be given any position.
After waiting for the belching of air, the child can be given any position.
• The same should be done before feeding. The thing is that in an upright position, the child can release excess air from the stomach. If this is not done before eating, belching is guaranteed.
• There is a specific position recommended for breastfeeding. One of the main goals of the correct position of a nursing mother and baby is the prevention of regurgitation. The semi-upright position of the baby with the head raised above the level of the body must be maintained during each feeding.
• Feeding should be frequent but small. Overfeeding is fraught not only with regurgitation, but also with other digestive problems.
• It is important not to feed the baby when he is crying or laughing, otherwise he will swallow extra air.
• When feeding with a teat bottle, make sure that the opening of the teat is not too large and that the position of the bottle is such that the teat is always filled with formula and not with air.
• From active games you need to refrain from the first half hour after feeding.
Following these simple rules will help reduce the frequency of regurgitation.
Proper diet
If the above recommendations do not bring results, it is worth changing the diet. For a formula-fed baby, you can thicken each serving.
Breastfed babies may require additional treatment formulas.
There are also special mixtures against regurgitation. But they belong to therapeutic mixtures, which means that only a doctor can prescribe them.
Warning signs
Responsible parents should be aware of danger symptoms that require medical advice:
• The baby is very restless and often rolls over and arches its back when spitting up or feeding. Such a symptom may indicate chronic irritation of the esophagus.
• Regurgitation is frequent, plentiful, observed after each feeding.
• The child has signs of dehydration.
• Regurgitation, which first appeared after the first half of the year.
• Prolonged spitting up without improvement (same frequency and same amount of spitting up in a child aged 1 year and older).
• Regurgitation is accompanied by fever.
• The child is not gaining or even losing weight.
• You can't tell for yourself if the baby is spitting up or vomiting.
There are even more dangerous symptoms that require an ambulance call:
• The child stopped breathing after spitting up.
• A bluish tint appears on the lips and face.
• After spitting up, the child lost consciousness.
• Green or brown reflux (gastric contents) - this may be a sign of intestinal obstruction or stomach bleeding.
Aspiration is extremely dangerous in infants who are unable to get rid of food in the airways on their own. The only thing parents can do is call an ambulance. It is not recommended to try to help the child on your own.
Should I supplement my baby after spitting up?
• If the baby has eaten for a long time, the milk/mixture is almost digested, if the position of the body changes, the baby may still burp.